Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Transplant. Jun 24, 2016; 6(2): 336-346
Published online Jun 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.336
Published online Jun 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.336
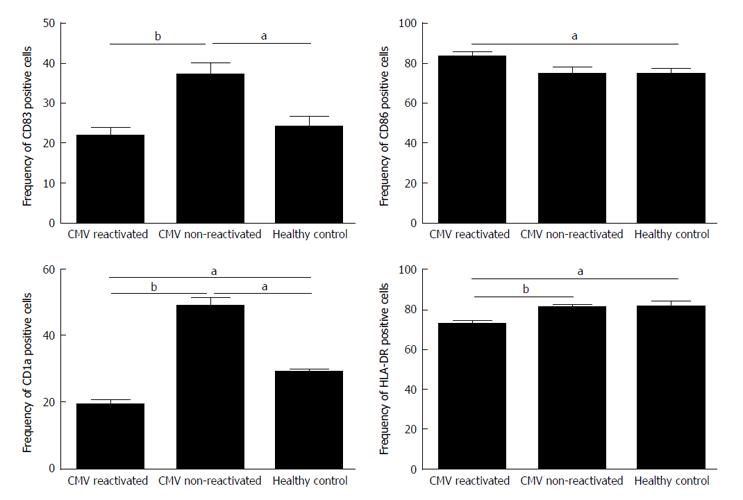
Figure 1 The expression rates for surface monocyte derived dendritic cell markers of CD83, CD86, CD1a and human leukocyte antigen DR in cytomegalovirus reactivated patients, cytomegalovirus non-reactivated recipients, and healthy control.
The expression rates of CD83, CD1a and HLA-DR were significantly decreased in CMV reactivated patients vs non-reactivated recipients. Any significance is indicated aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. The data are the means ± SE. HLA-DR: Human leukocyte antigen DR; CMV: Cytomegalovirus.
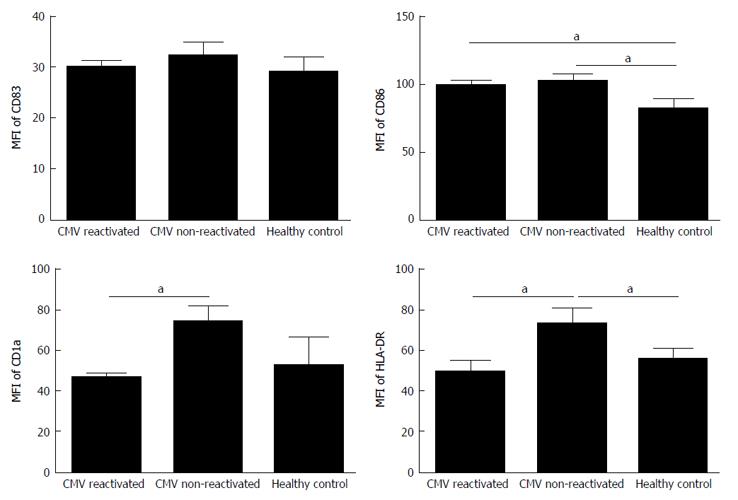
Figure 2 Mean fluorescence intensity for surface monocyte derived dendritic cell markers of CD83, CD86, CD1a and human leukocyte antigen DR in cytomegalovirus reactivated patients, cytomegalovirus non-reactivated recipients, and healthy control.
The MFI of CD1a and HLA-DR were significantly decreased in CMV reactivated patients vs non-reactivated recipients. Any significance is indicated aP < 0.05. The data are the means ± SE. MFI: Mean fluorescence intensity; HLA-DR: Human leukocyte antigen DR; CMV: Cytomegalovirus.
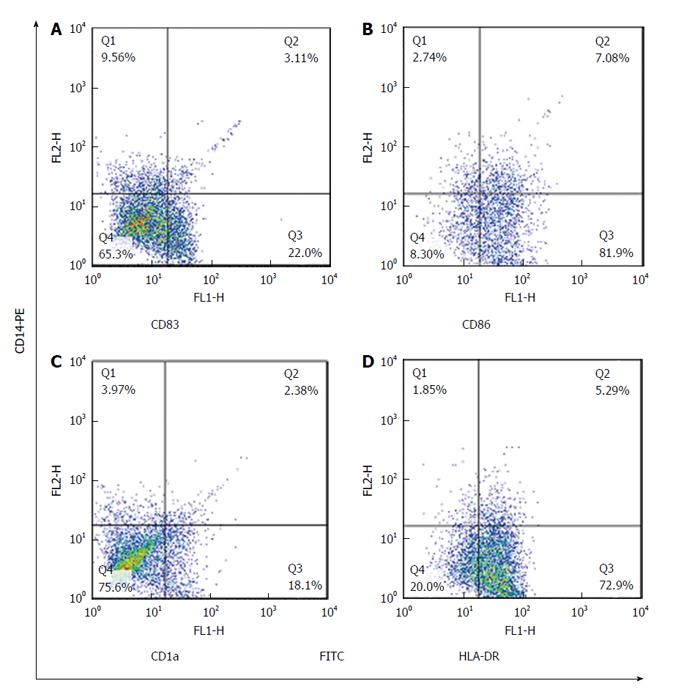
Figure 3 The expression rate of monocyte derived dendritic cell markers in cytomegalovirus reactivated patients was examined by dual-color cytometry.
Expression of surface markers: CD83 (22%) (A), CD86 (82%) (B), CD1a (18%) (C) and HLA-DR (72.9%) (D) on MoDCs in CMV reactivated patients. CD14-PE, phycoerythrin-conjugated CD14, CD83-FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated CD83, CD86-FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated CD86, CD1a-FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated CD1a, HLADR-FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated HLA-DR. HLA-DR: Human leukocyte antigen DR; CMV: Cytomegalovirus; MoDC: Monocyte derived dendritic cell.
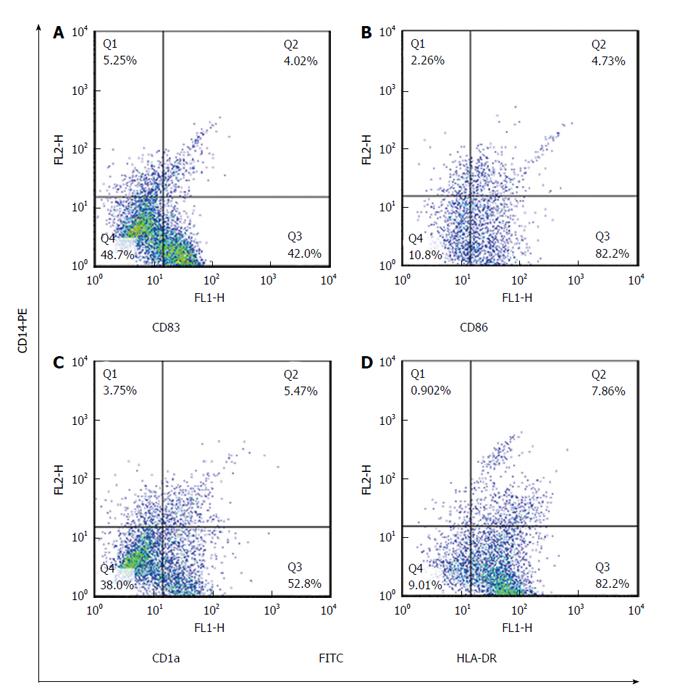
Figure 4 The expression rate of monocyte derived dendritic cells markers in cytomegalovirus non-reactivated patients was examined by dual-color cytometry.
Expression of surface markers: CD83 (42%) (A), CD86 (82%) (B), CD1a (52.8%) (C) and HLA-DR (82%) (D) on MoDCs in CMV non-reactivated patients. HLA-DR: Human leukocyte antigen DR; CMV: Cytomegalovirus; MoDC: Monocyte derived dendritic cell.
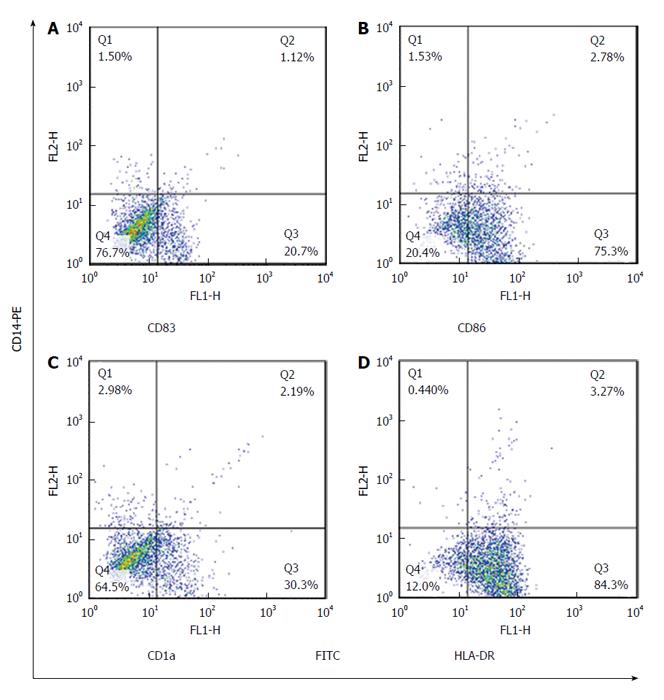
Figure 5 The expression rate of monocyte derived dendritic cell markers in healthy control was examined by dual-color cytometry.
Expression of surface markers: CD83 (20.7%) (A), CD86 (75.3%) (B), CD1a (30%) (C) and HLA-DR (84%) (D) on MoDCs in healthy control. HLA-DR: Human leukocyte antigen DR; MoDC: Monocyte derived dendritic cell.
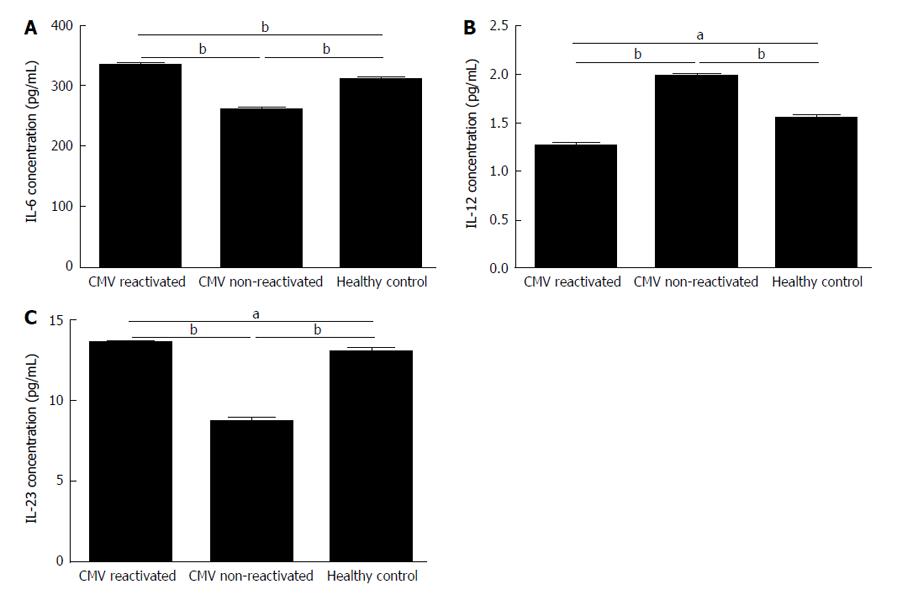
Figure 6 Levels of cytokines secreted by monocyte derived dendritic cells in cytomegalovirus reactivated patients, non-reactivated recipients, and healthy controls.
The IL-6, IL-12 and IL-23 concentrations in the supernatants were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. IL-6 and IL-23 secretions were significantly increased in CMV reactivated patients compared to non-reactivated recipients and healthy controls (A and C). IL-12 secretion was significantly decreased in CMV reactivated patients compared to non-reactivated ones and healthy controls (B). Any significance is indicated aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. The data are the means ± SE. CMV: Cytomegalovirus; IL: Interleukin.
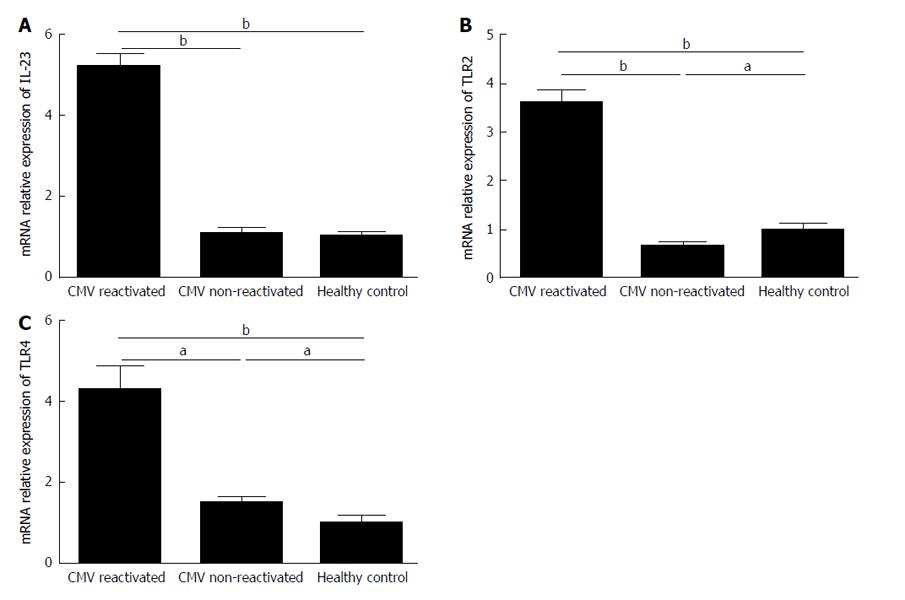
Figure 7 In cytomegalovirus reactivated patients, non-reactivated recipients, and healthy controls, mRNA relative expressions of interleukin-23 (A), toll-like receptor 2 (B) and toll-like receptor 4 (C) were determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction protocols.
The gene expression levels of IL-23, TLR2 and TLR4 were significantly increased in CMV reactivated patients in comparing with non-reactivated ones and healthy controls. Any significance is indicated aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. The data are the means ± SE. CMV: Cytomegalovirus; IL: Interleukin; TLR: Toll-like receptor.
- Citation: Karimi MH, Shariat A, Yaghobi R, Mokhtariazad T, Moazzeni SM. Role of cytomegalovirus on the maturation and function of monocyte derived dendritic cells of liver transplant patients. World J Transplant 2016; 6(2): 336-346
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v6/i2/336.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.336