Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Transplant. Jun 18, 2025; 15(2): 99287
Published online Jun 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i2.99287
Published online Jun 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i2.99287
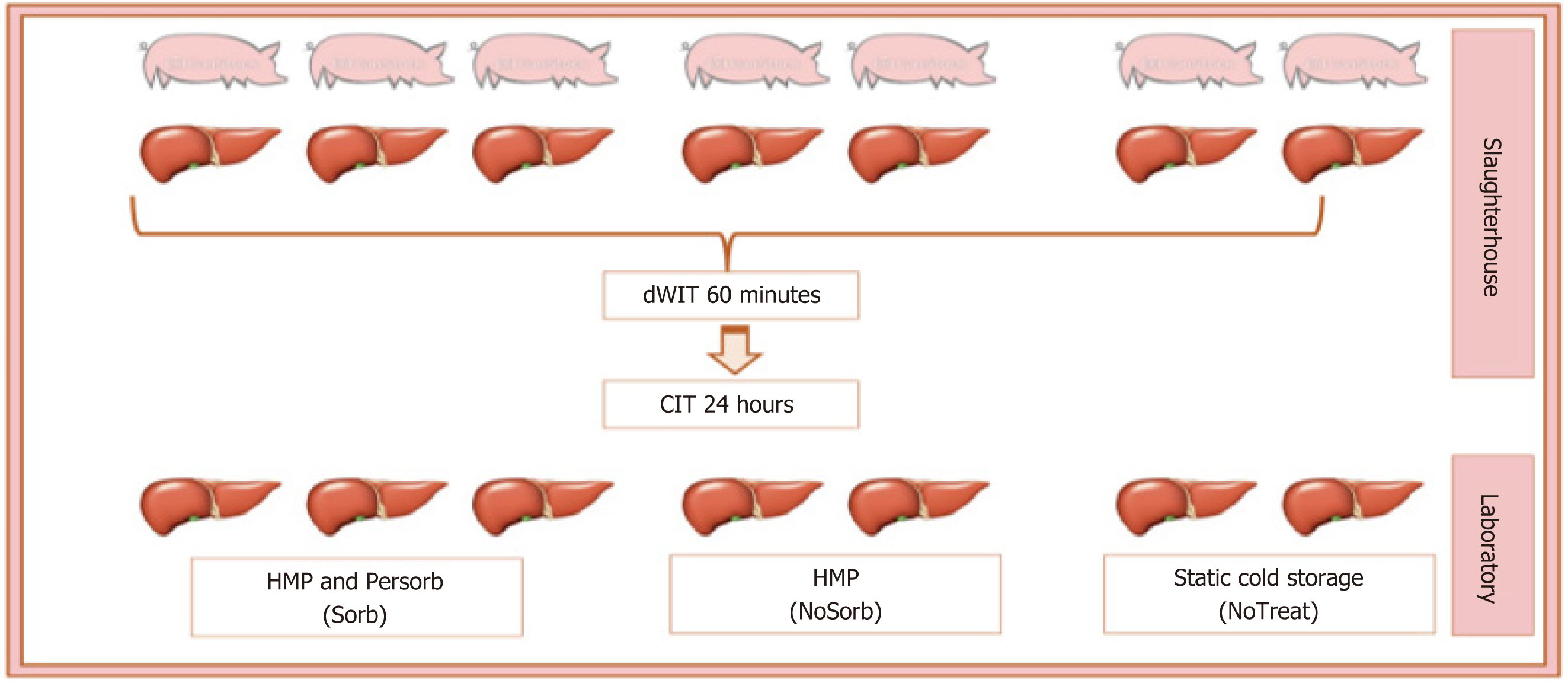
Figure 1 Study design.
After the slaughter of 7 pigs, the livers were made very marginal with long donor warm ischemia time and cold ischemia time and 4 of them were perfused in a hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP); 3 of them with HMP connected to the filter of the cytokines, Persorb (Sorb) and 2 underwent a standard cycle of HMP (NoSorb). Two livers were stored in the ice box without any preservation treatment (NoTreat). CIT: Cold ischemia time; DWIT: Donor warm ischemia time; HMP: Hypothermic machine perfusion; NoSorb: Hypothermic machine perfusion without the cartridge; NoTreat: No treatment; Sorb: Hypothermic machine perfusion with PerSorb.
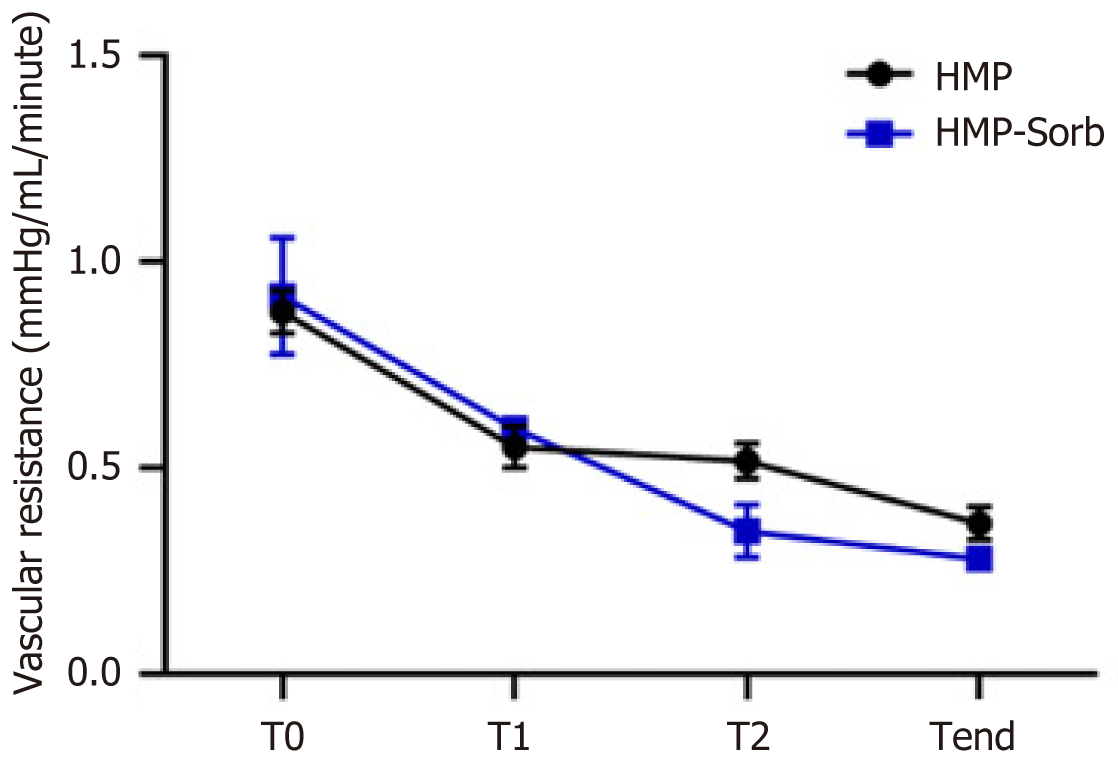
Figure 2 Vascular resistance parameters collected during machine perfusion treatment.
HMP: Hypothermic machine perfusion; Sorb: Hypothermic machine perfusion with PerSorb.
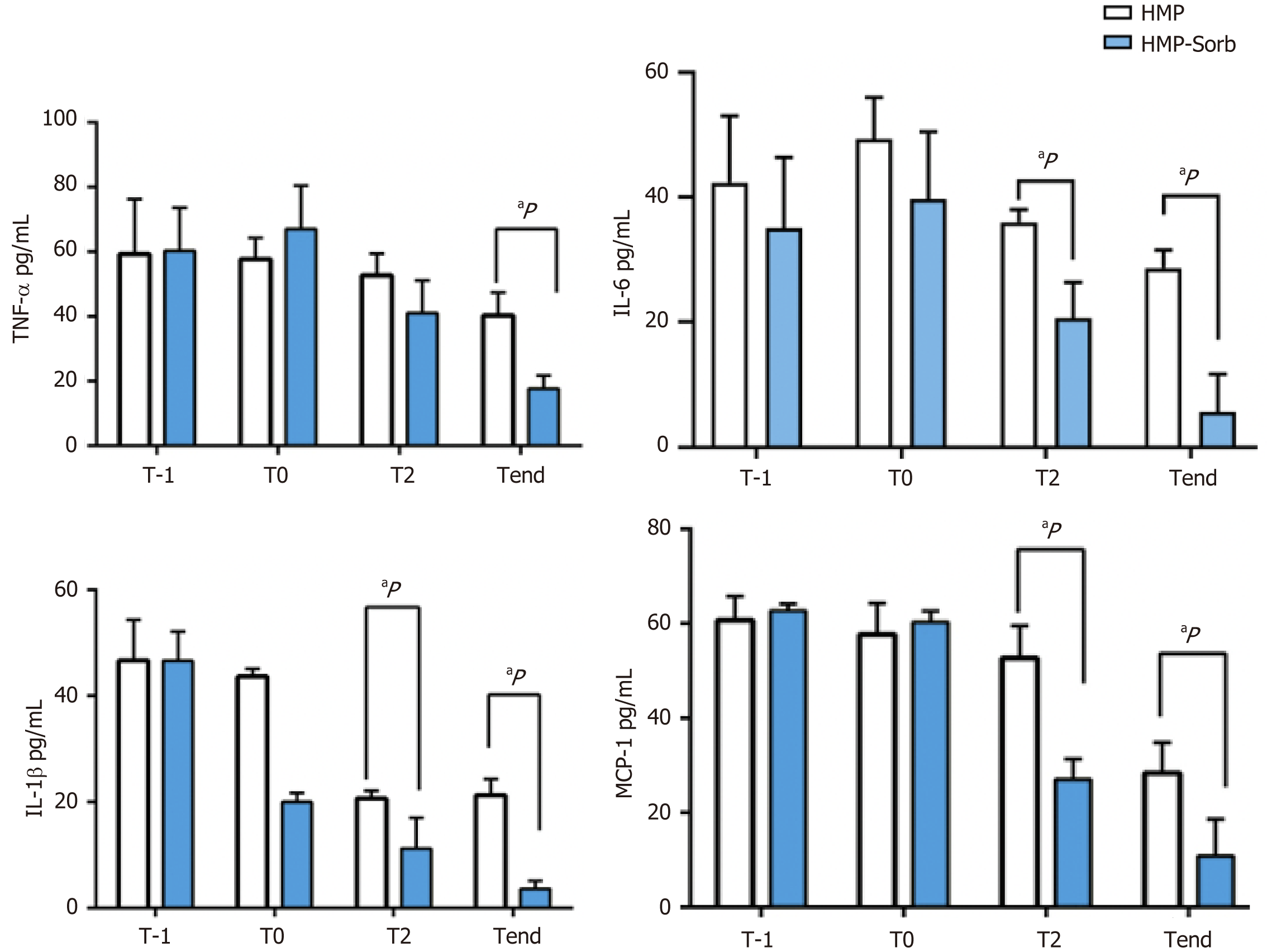
Figure 3 Cytokines measurements from perfusates of the livers during hypothermic machine perfusion and hypothermic machine perfusion-Persorb treatments.
Baseline levels of cytokines were similar between groups at liver biopsies were analyzed, thereby retrieved at the slaughterhouse immediately after the donor warm ischemia time. Significantly changes were observed for interleukin (IL)-1β at start. Levels of monocyte chemotactic protein-1, IL-6 and IL-1β and IL-8 remained significantly higher in the hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP) group compared to HMP-Sorb group (aP < 0.05). The following cytokines were presented in abbreviations in the graphs: (1) IL-β; (2) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; and (3) Monocyte chemotactic protein-1. Data are presented as mean ± SD. IL: Interleukin; MCP-1: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1; Sorb: Hypothermic machine perfusion with PerSorb; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; T-1: Liver biopsies were analyzed, thereby retrieved at the slaughterhouse immediately after the donor warm ischemia time; Tend: At the end; T0: Start; T2: After two hours.
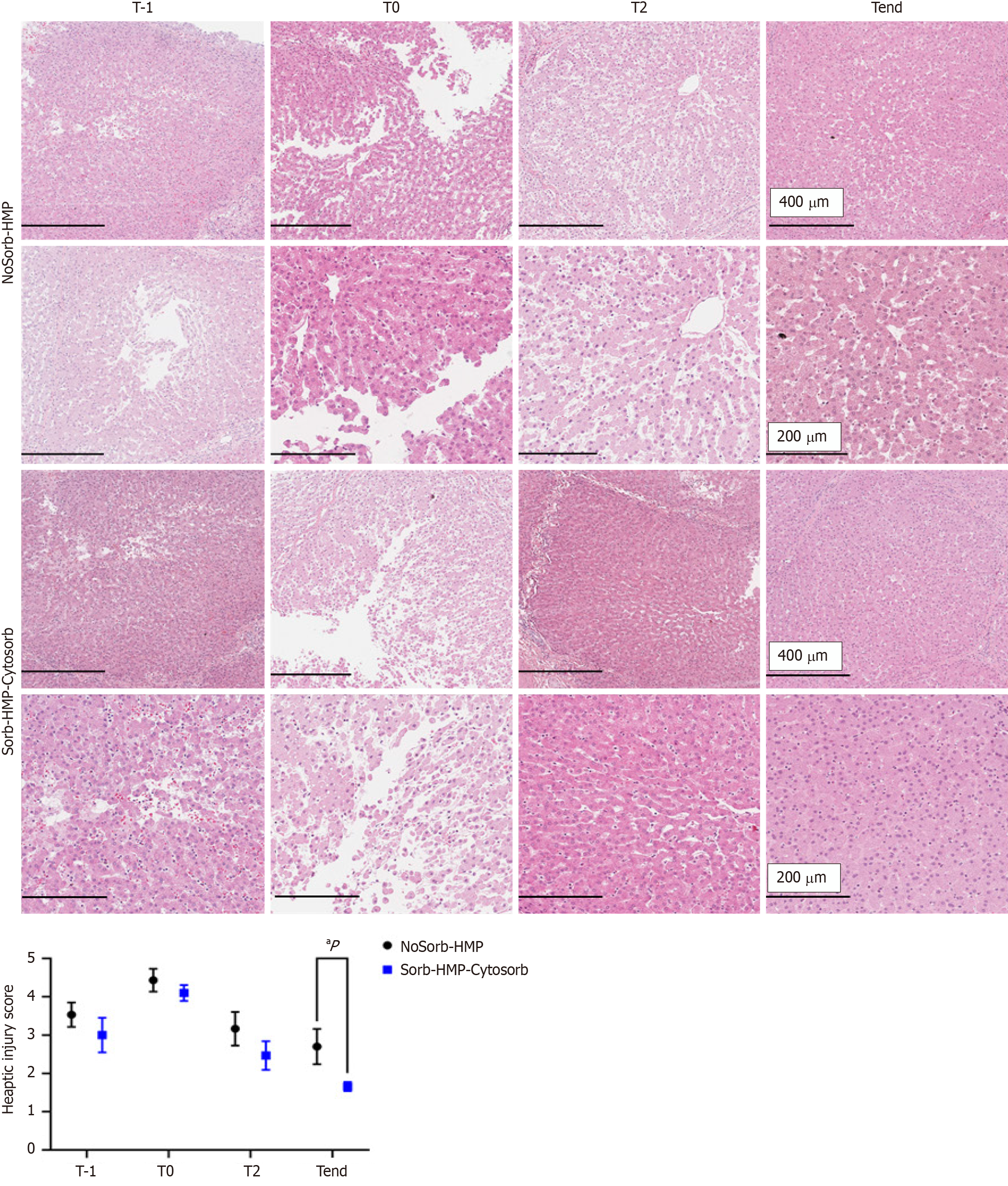
Figure 4 Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining histology of liver tissue at the hepatic injury score at different time points during machine perfusion treatment with or without Persorb device.
Liver biopsies were analyzed, thereby retrieved at the slaughterhouse immediately after the donor warm ischemia time: Liver biopsies retrieved at the slaughterhouse showed low/absent liver damage. At start of liver biopsies, collected after long-time of cold static storage in ice showed diminished liver architecture, with sinusoid dilation, congestion, portal inflammation, microvacuolization and infiltrating inflammatory cells. The hepatocytes appeared swollen and the hepatic cords were disorganized, furthermore exhibited patchy subcapsular hepatocyte necrosis (black arrows). After hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP) treatments, repaired interlobular septa of pig livers and improved tissue architecture were detected. Significant histological alteration were detected at the end in HMP and HMP-Sorb group. All these results were graphically summarized with the trend of the hepatic injury score. aP < 0.05. HMP: Hypothermic machine perfusion; NoSorb: Hypothermic machine perfusion without the cartridge; Sorb: Hypothermic machine perfusion with PerSorb; Tend: At the end; T-1: Liver biopsies were analyzed, thereby retrieved at the slaughterhouse immediately after the donor warm ischemia time; T0: Start; T2: After two hours.
- Citation: Scalera I, Franzin R, Stasi A, Castellaneta A, Fischetti E, Morelli G, Raele M, Panetta E, Kurevija A, Pulga W, Atti M, Gesualdo L. Haemoadsorption cartridge connected to the machine perfusion for donation after circulatory death porcine liver marginal grafts. World J Transplant 2025; 15(2): 99287
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v15/i2/99287.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v15.i2.99287