Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Transplant. Jun 18, 2025; 15(2): 100065
Published online Jun 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i2.100065
Published online Jun 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i2.100065
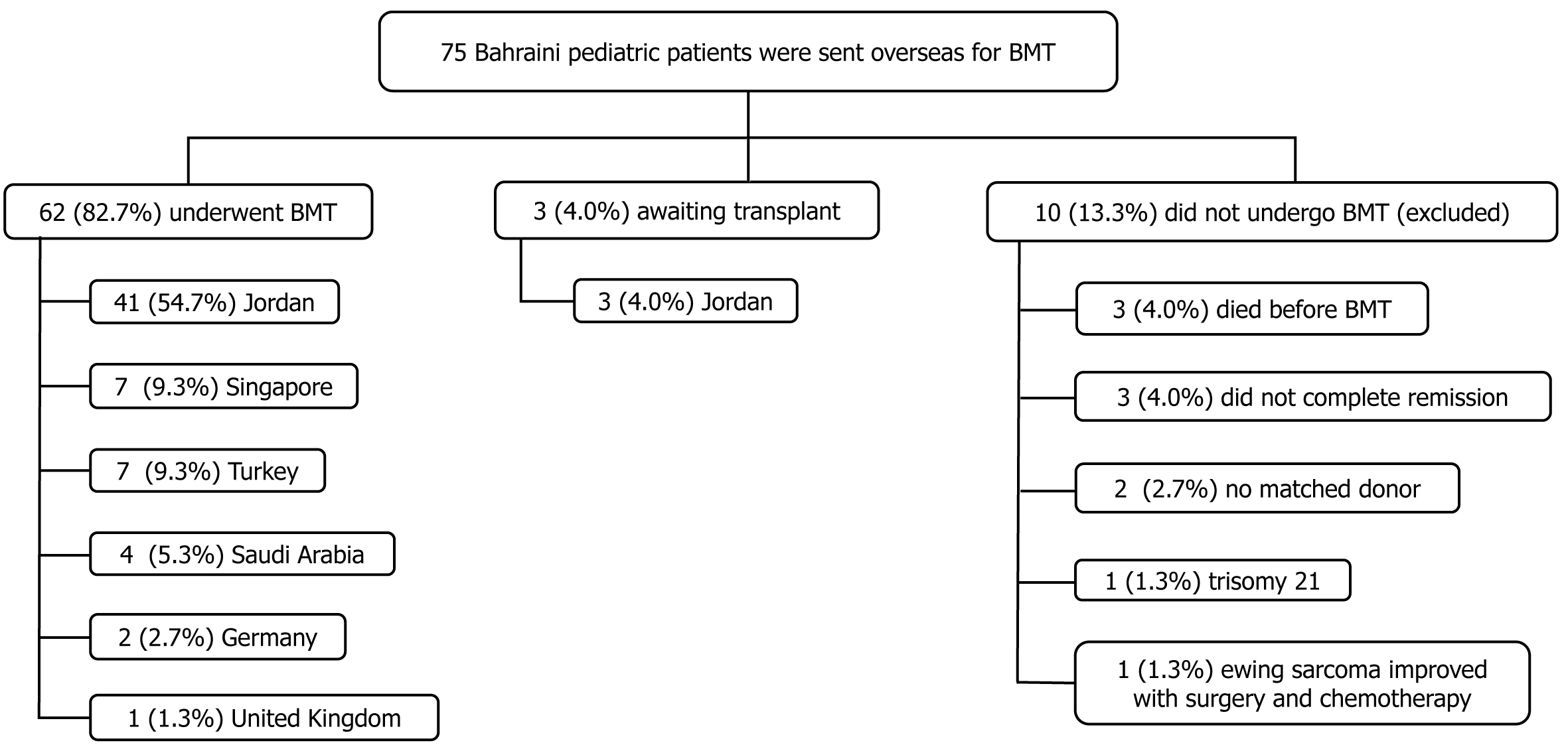
Figure 1 Flow charts of pediatric patients who underwent an overseas bone marrow transplantation, Kingdom of Bahrain, 2013-2024.
BMT: Bone marrow transplantation.
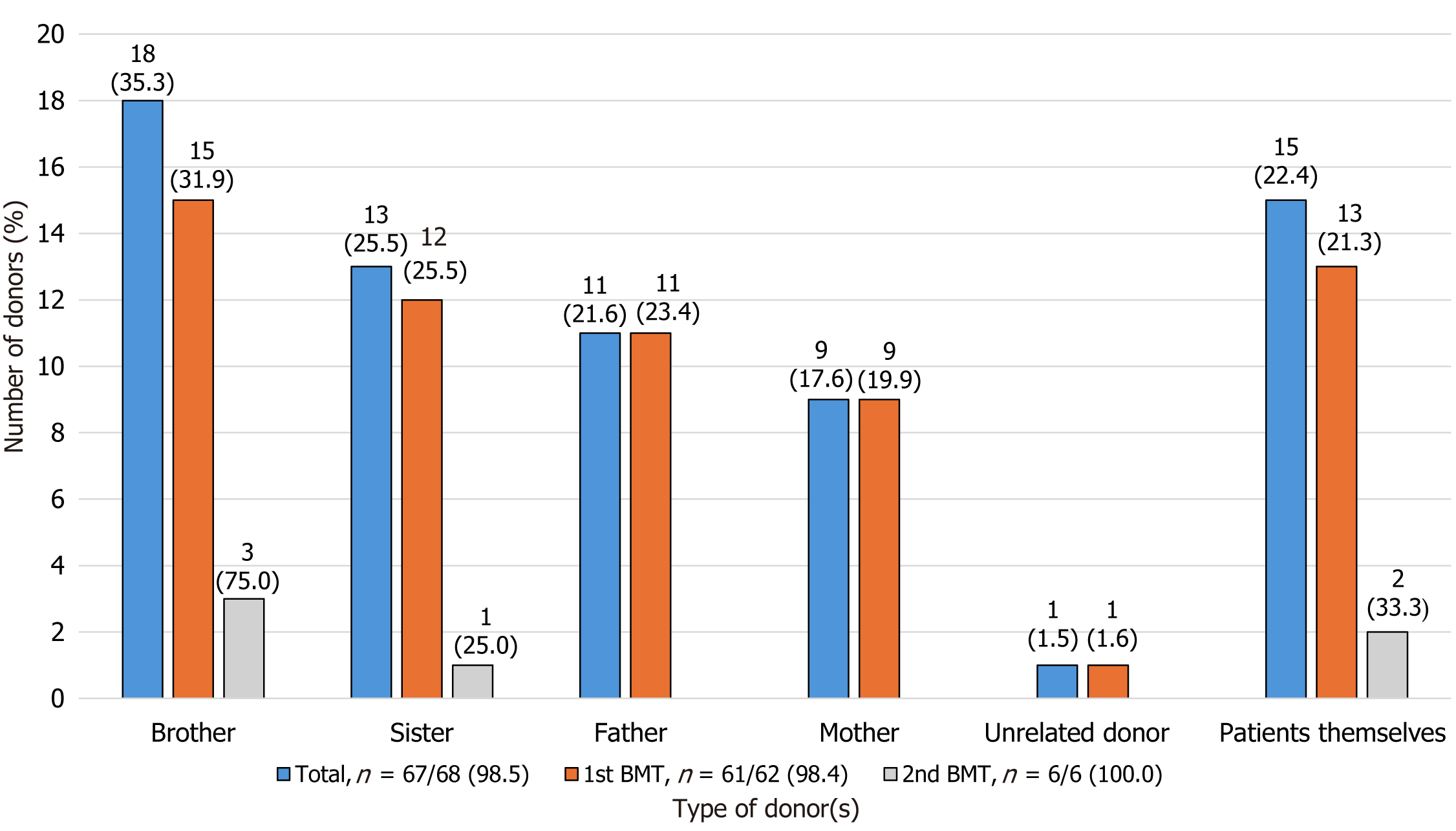
Figure 2 Donor-recipient relationship of patients who underwent bone marrow transplantation (n = 67/68, 98.
5%). BMT: Bone marrow transplantation.
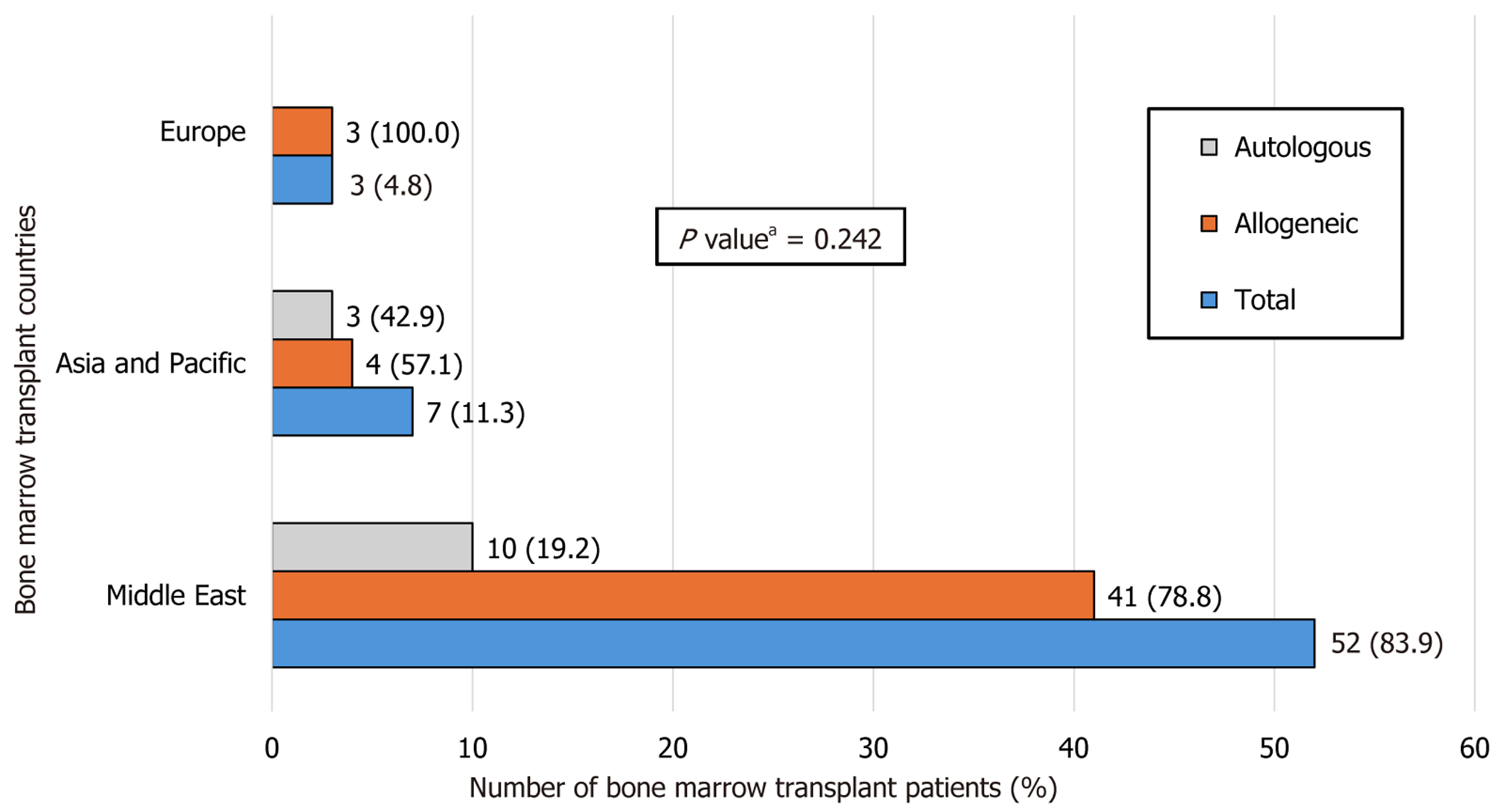
Figure 3 The main countries where the Kingdom of Bahrain sent pediatric patients overseas to undergo bone marrow transplantation.
Middle East countries included Jordan (n = 41, 66.2%), Turkey (n = 7, 11.3%), and Saudi Arabia (n = 4, 6.5%); Asia and Pacific countries included Singapore (n = 7, 11.3%); European countries included Germany (n = 2, 3.2%) and United Kingdom (n = 1, 1.6%). aPearson’s χ2 test.
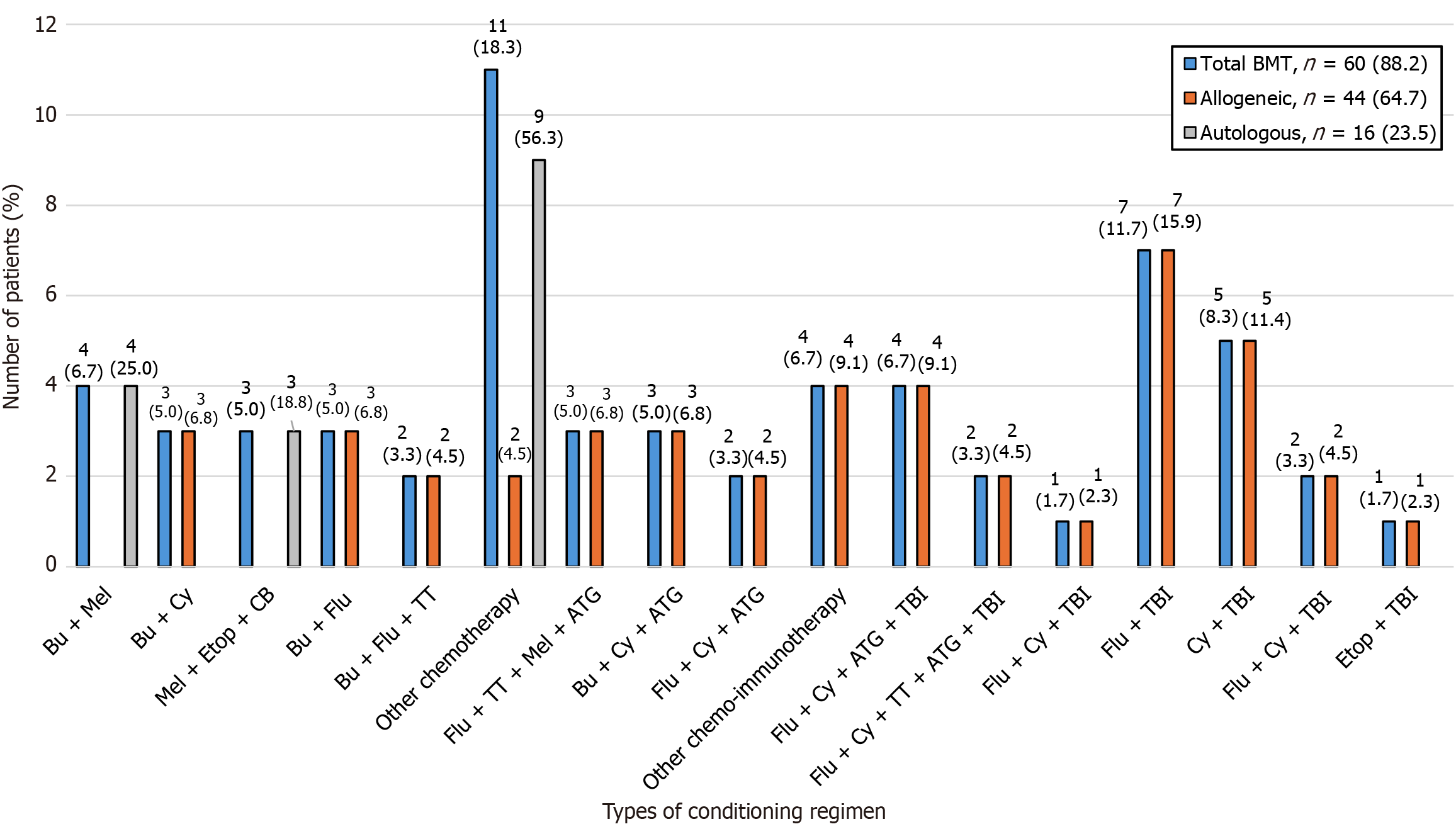
Figure 4 Conditioning regimens of patients who underwent bone marrow transplantation (n = 60/68 bone marrow transplantations).
Other conditioning regimens are shown in Supplementary Table 2. BMT: Bone marrow transplantation; Bu: Busulfan; Mel: Melphalan; Cy: Cyclophosphamide; Etop: Etoposide; CB: Carboplatin; Flu: Fludarabine; TT: Thiotepa; ATG: Antithymocyte globulin; TBI: Total body irradiation.
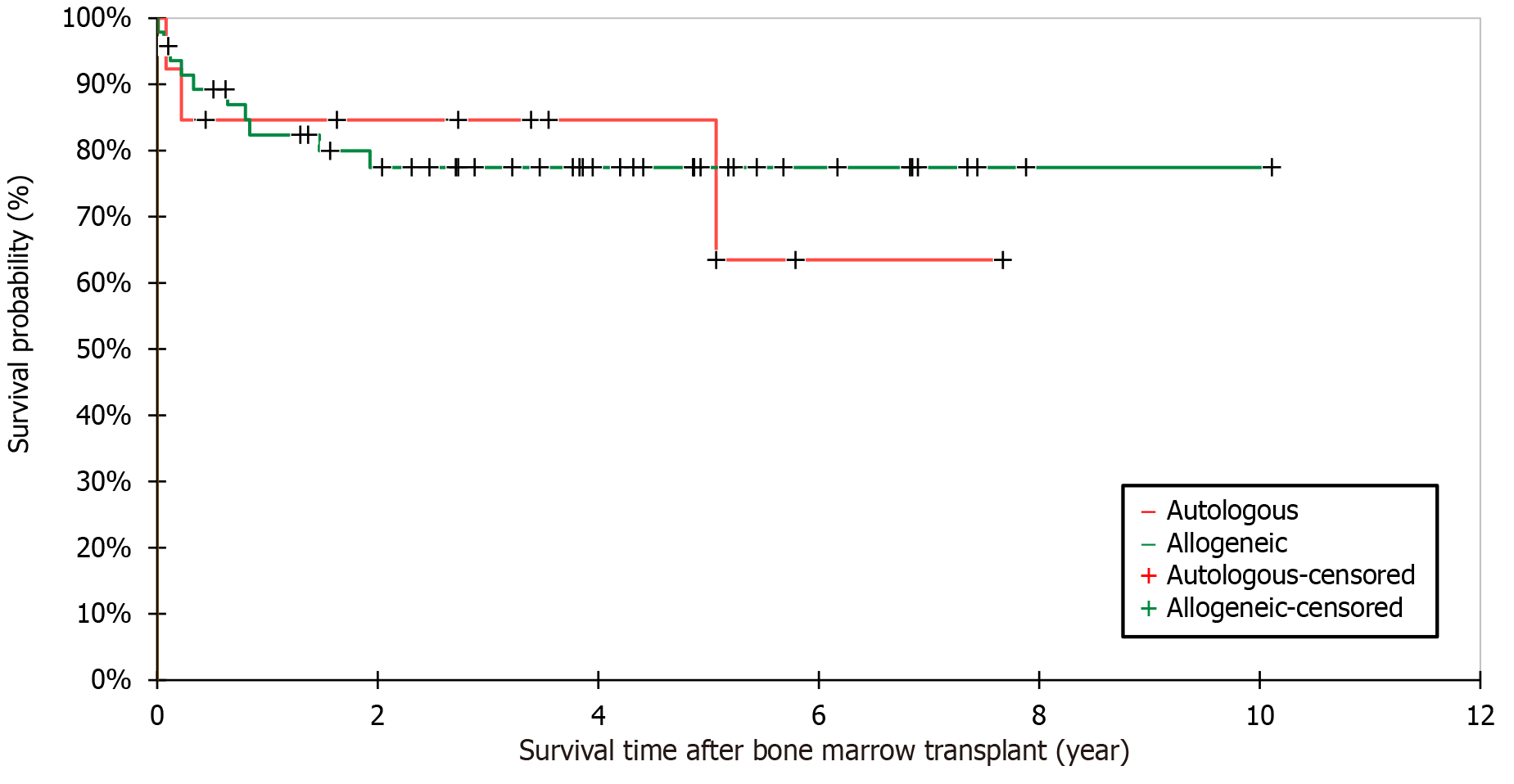
Figure 5 Survival analysis based on type of transplant in pediatric patients post bone marrow transplantation using the Kaplan-Meier method.
- Citation: Isa HM, Bucheeri ST, Aldoseri JY, Redha AA, Mubarak AF, Altamimi SA, AlOraibi AA, Alshaikh MI. Characteristics and outcomes of Bahraini pediatric patients sent abroad for bone marrow transplantation: A ten-year retrospective cohort study. World J Transplant 2025; 15(2): 100065
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v15/i2/100065.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v15.i2.100065