Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Apr 19, 2025; 15(4): 103827
Published online Apr 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.103827
Published online Apr 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.103827
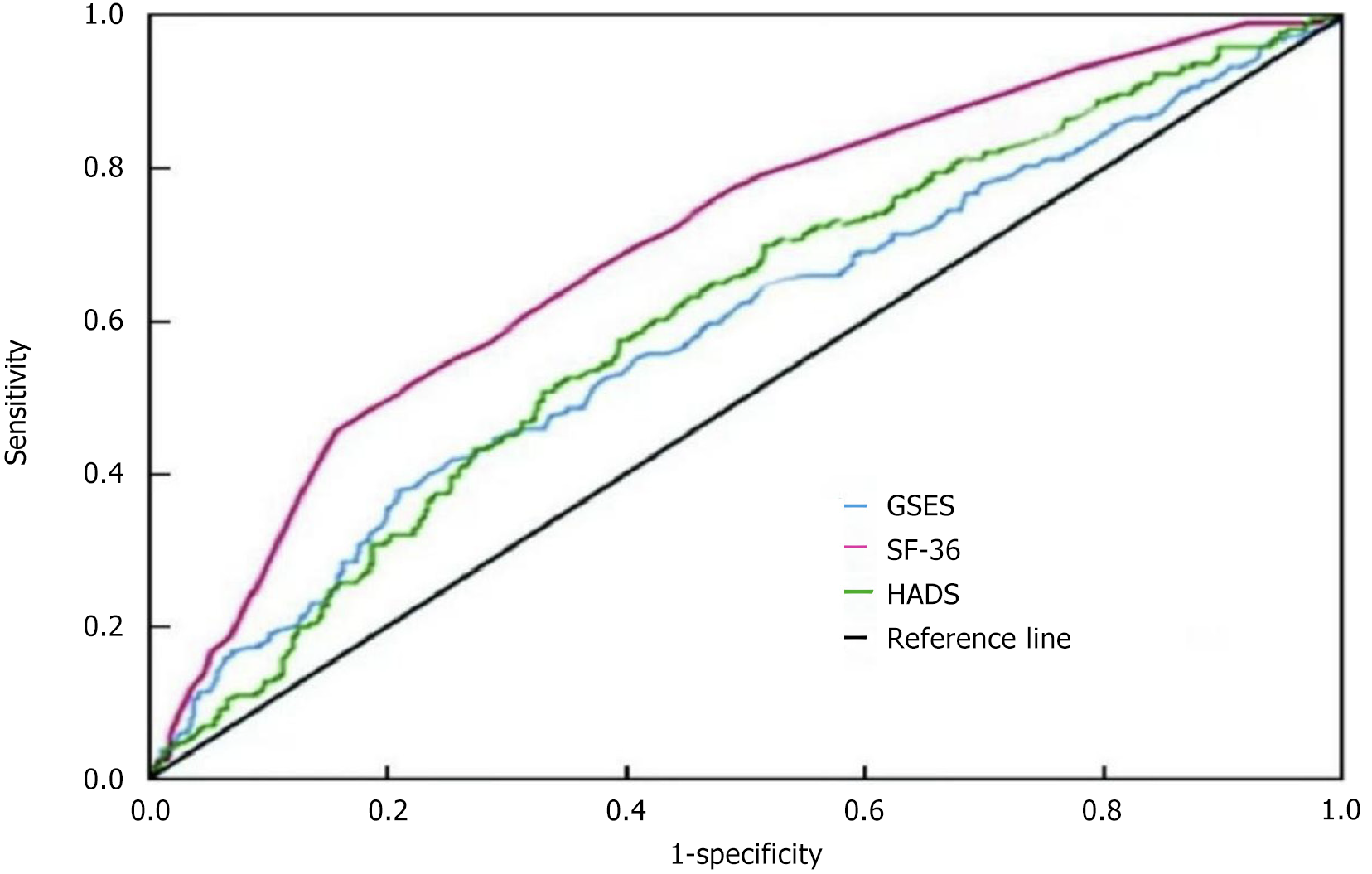
Figure 1 Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of general self-efficacy scale, Hamilton depression scale, and 36-item short form survey for predicting frailty in elderly patients.
GSES: General self-efficacy scale; SF-36: 36-item short form survey; HADS: Hamilton depression scale.
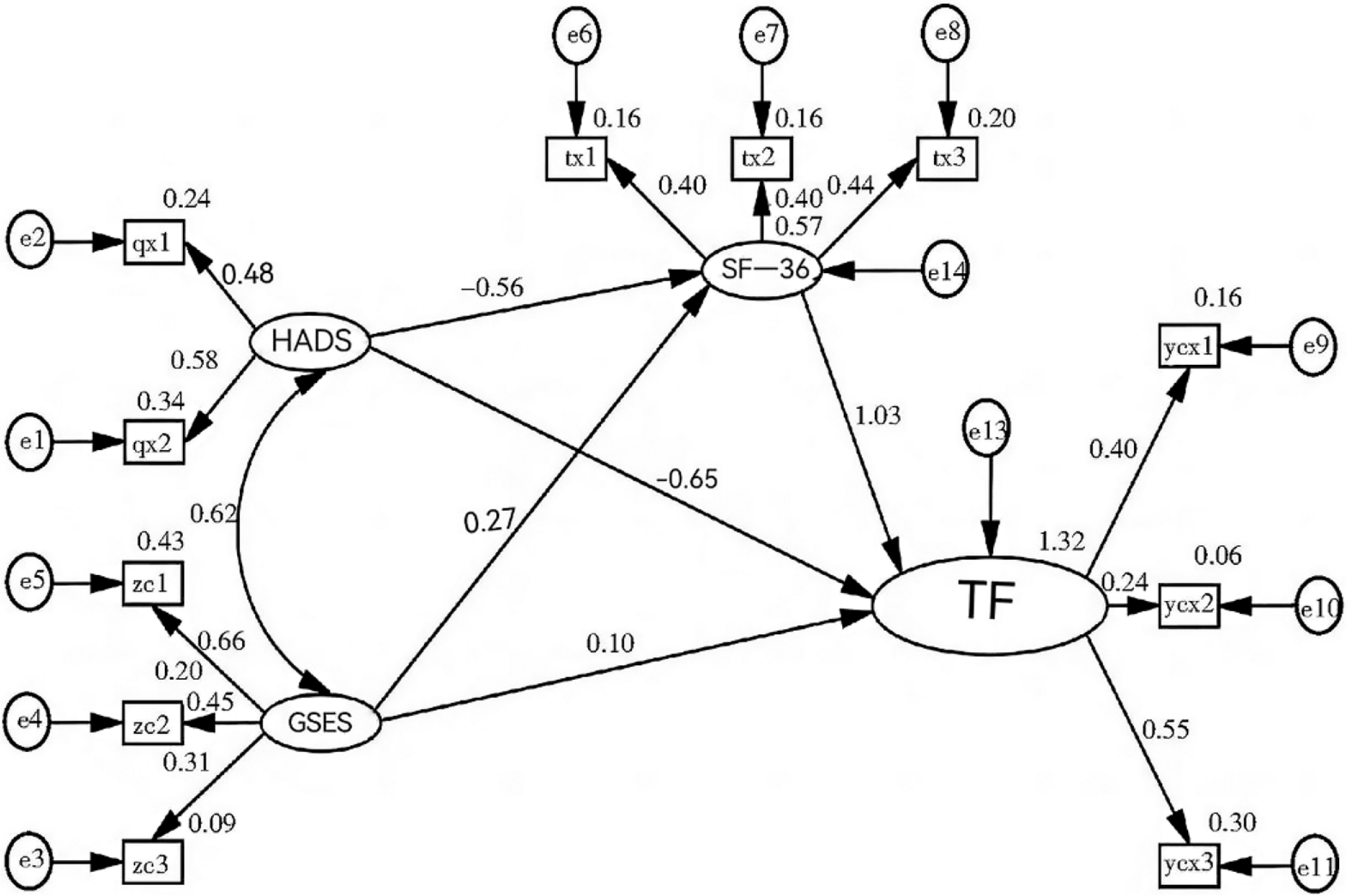
Figure 2 Structural equation model of factors influencing frailty.
Yex1-3 represent cognitive frailty, balance and gait function, and physical frailty; tx1-3 represent physical, emotional, and social dimensions; qx1-2 represent anxiety and depression; zc1-3 represent emotional dimension, motivational dimension, and cognitive dimension. GSES: General self-efficacy scale; SF-36: 36-item short form survey; HADS: Hamilton depression scale; TF: Tilburg frailty indicator.
- Citation: Zhou Y, Miao XM, Zhou KL, Yu CJ, Lu P, Lu Y, Zhao J. Effects of exercise-cognitive dual-task training on elderly patients with cognitive frailty and depression. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(4): 103827
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i4/103827.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.103827