Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Apr 19, 2025; 15(4): 103092
Published online Apr 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.103092
Published online Apr 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.103092
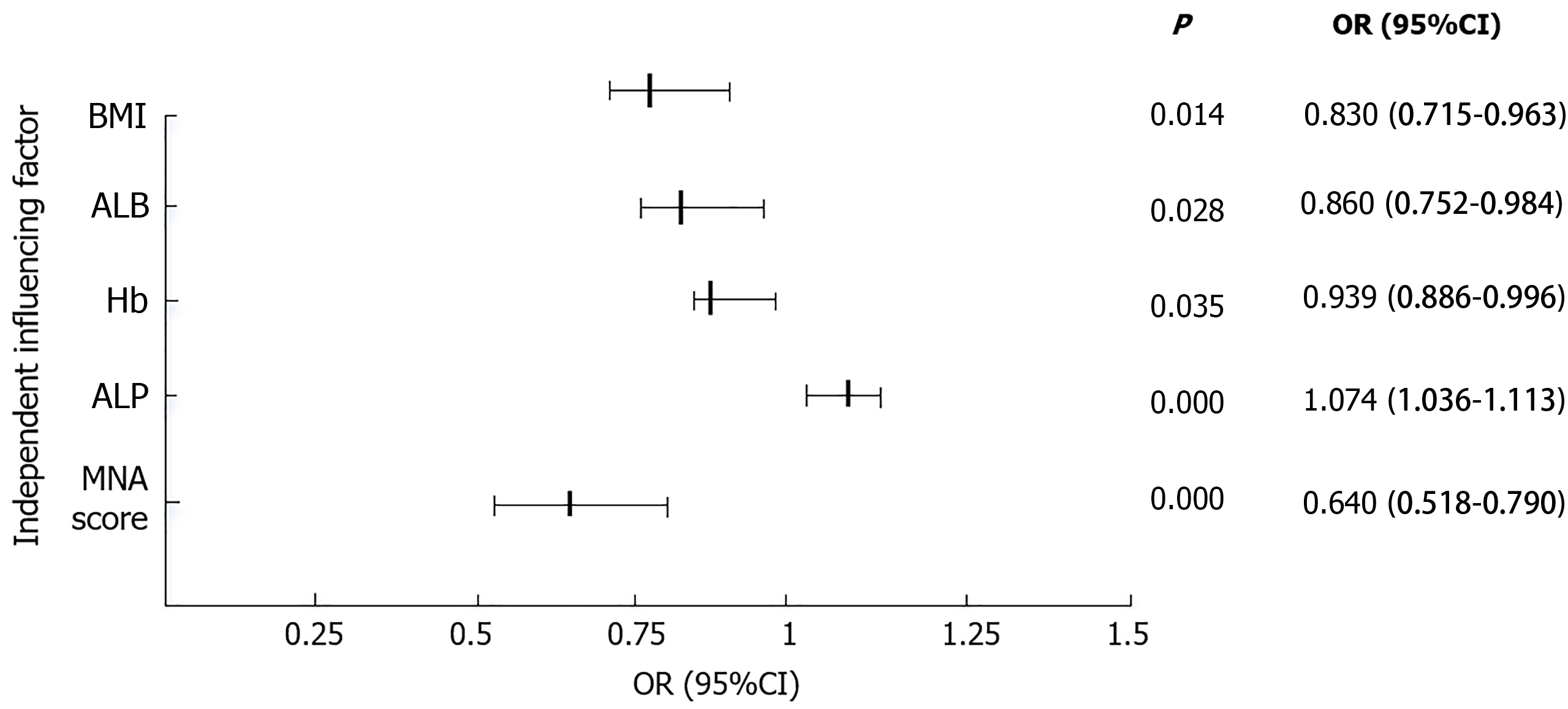
Figure 1 Multi-factor forest diagram.
Multivariate logistic analysis was used to analyze the influencing factors of cognitive impairment in 140 elderly patients with hypertension in the modeling cohort. body mass index, albumin, hemoglobin and Mini-Nutritional Assessment Scale scores were independent protective factors for patients without cognitive impairment, while alkaline phosphatase was independent risk factor for patients with cognitive impairment. BMI: Body mass index; ALB: Albumin; Hb: Hemoglobin; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; MNA: Mini-Nutritional Assessment Scale; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence intervals.
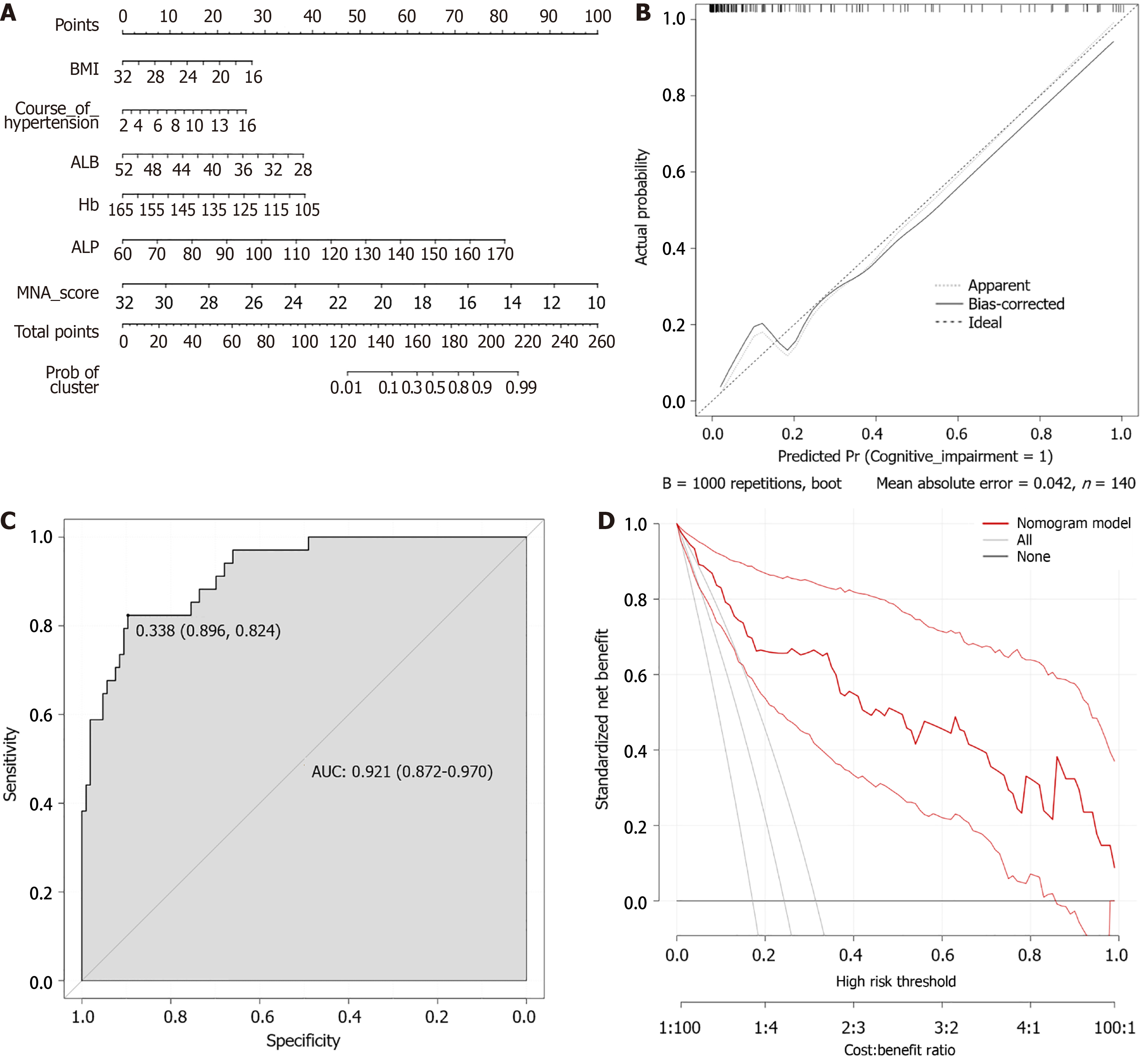
Figure 2 Development of a column-line diagram model for predicting cognitive impairment in elderly hypertensive patients.
A: Column line diagram. R software quantified modeling cohort of 140 elderly hypertensive patients with cognitive impairment risk coefficient; B: Modeling queue calibration curves. R software was used to perform curve correction on the cognitive impairment model of 140 elderly hypertensive patients in the modeling cohort (mean absolute error = 0.042); C: Modeling queue receiver operating characteristic curve. R software was used to analyze the receiver operating characteristic curve of the model of cognitive impairment in 140 elderly hypertensive patients in the modeling cohort, and the area under the curve was 0.921; D: Modeling queue decision analysis curve. R software decision curve analysis was used to evaluate the discriminant ability of the model of cognitive impairment in 140 elderly hypertensive patients in the modeling cohort. BMI: Body mass index; ALB: Albumin; Hb: Hemoglobin; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; MNA: Mini-Nutritional Assessment Scale; AUC: Area under the curve.
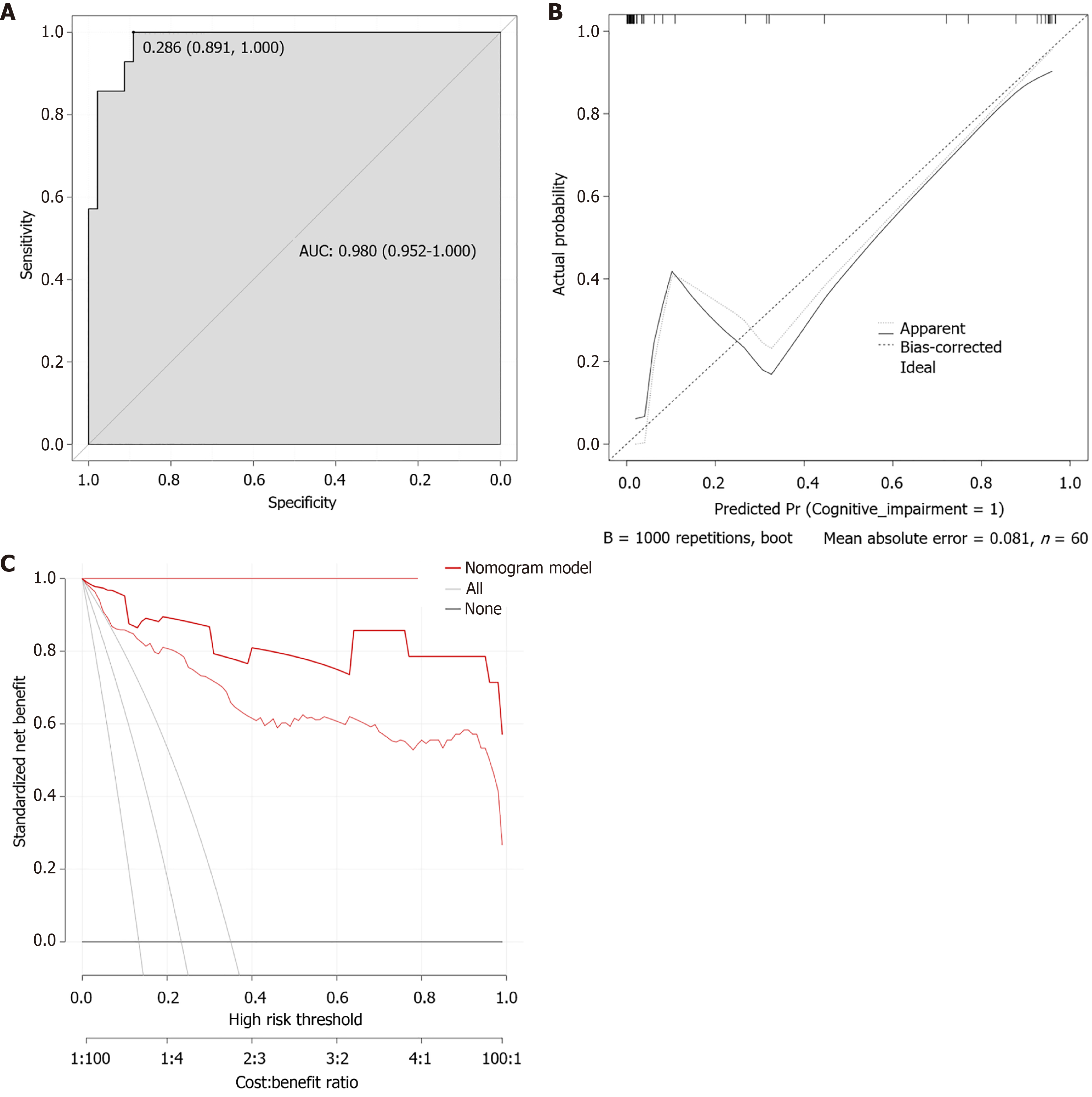
Figure 3 Validation of the column-line diagram model.
A: Verification queue receiver operating characteristic curve. The nomogram of the risk of cognitive impairment constructed by R software for 140 patients in the modeling cohort was externally verified by receiver operating characteristic curve in 60 patients in the validation cohort, with an area under the curve of 0.980; B: Verification queue calibration curve. R software was used to make curve correction for the occurrence model of cognitive impairment in 140 elderly hypertensive patients in the modeling cohort and 60 patients in the verification cohort (mean absolute error = 0.081); C: Verification queue decision analysis curve. R software decision curve analysis was used to evaluate the ability of the model to distinguish the occurrence of cognitive impairment in 140 elderly hypertensive patients in the modeling cohort from 60 patients in the verification cohort. AUC: Area under the curve.
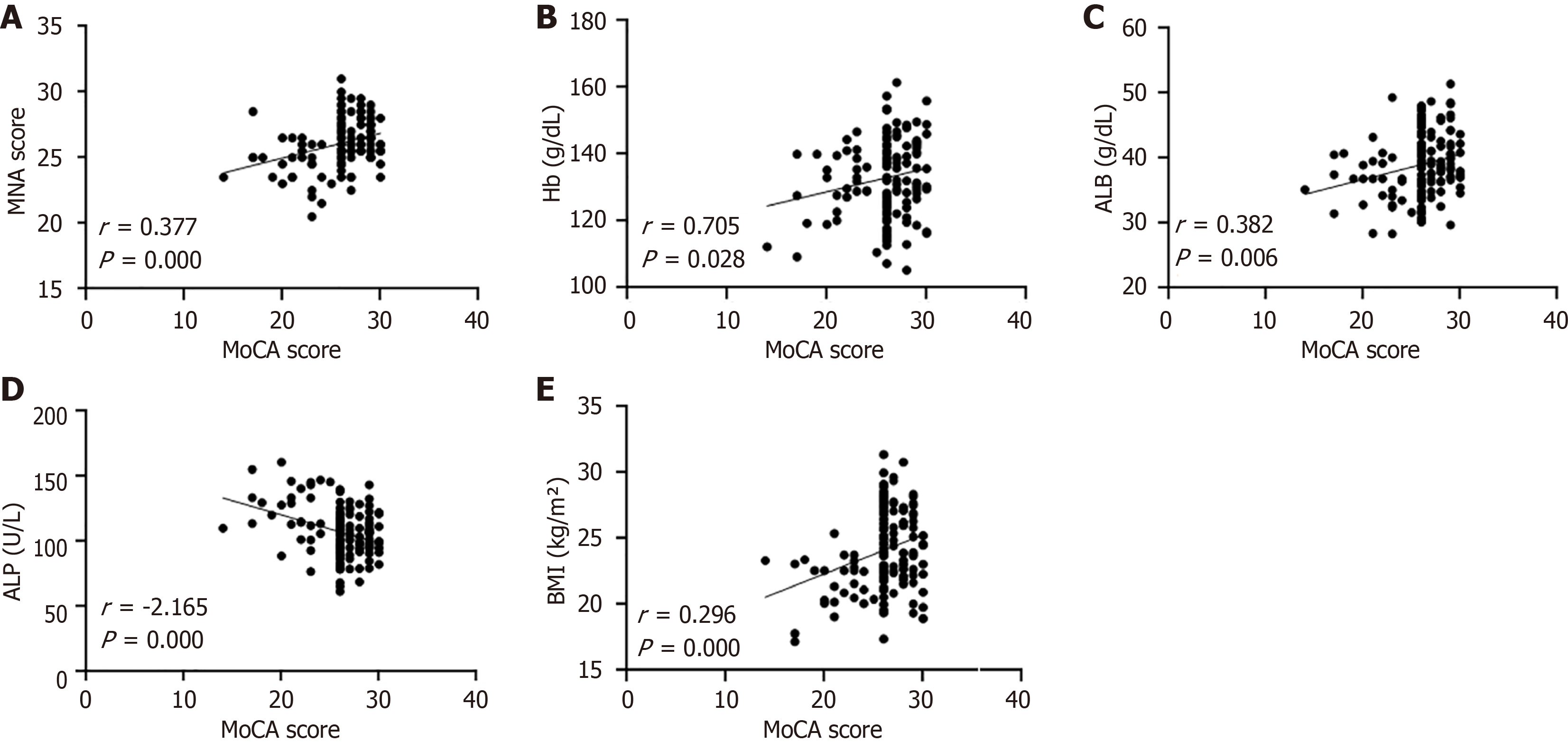
Figure 4 Relationship between nutrition-related indicators and Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale scores.
Linear correlation analysis of nutrition-related indexes and Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MoCA) scores in 200 elderly patients with hypertension was performed by GraphPad Prism8.0 software. A: Relationship between Mini-Nutritional Assessment Scale score and MoCA score; B: Relationship between hemoglobin and MoCA score; C: Relationship between albumin and MoCA score; D: Relationship between alkaline phosphatase and MoCA score; E: Relationship between BMI and MoCA score. MoCA: Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale; MNA: Mini-Nutritional Assessment Scale; Hb: Hemoglobin; ALB: Albumin; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; BMI: Body mass index.
- Citation: Xu Q, Lu SR, Shi ZH, Yang Y, Yu J, Wang Z, Zhang BS, Hong K. Nutritional status of elderly hypertensive patients and its relation to the occurrence of cognitive impairment. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(4): 103092
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i4/103092.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.103092