Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Feb 19, 2025; 15(2): 99008
Published online Feb 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.99008
Published online Feb 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.99008
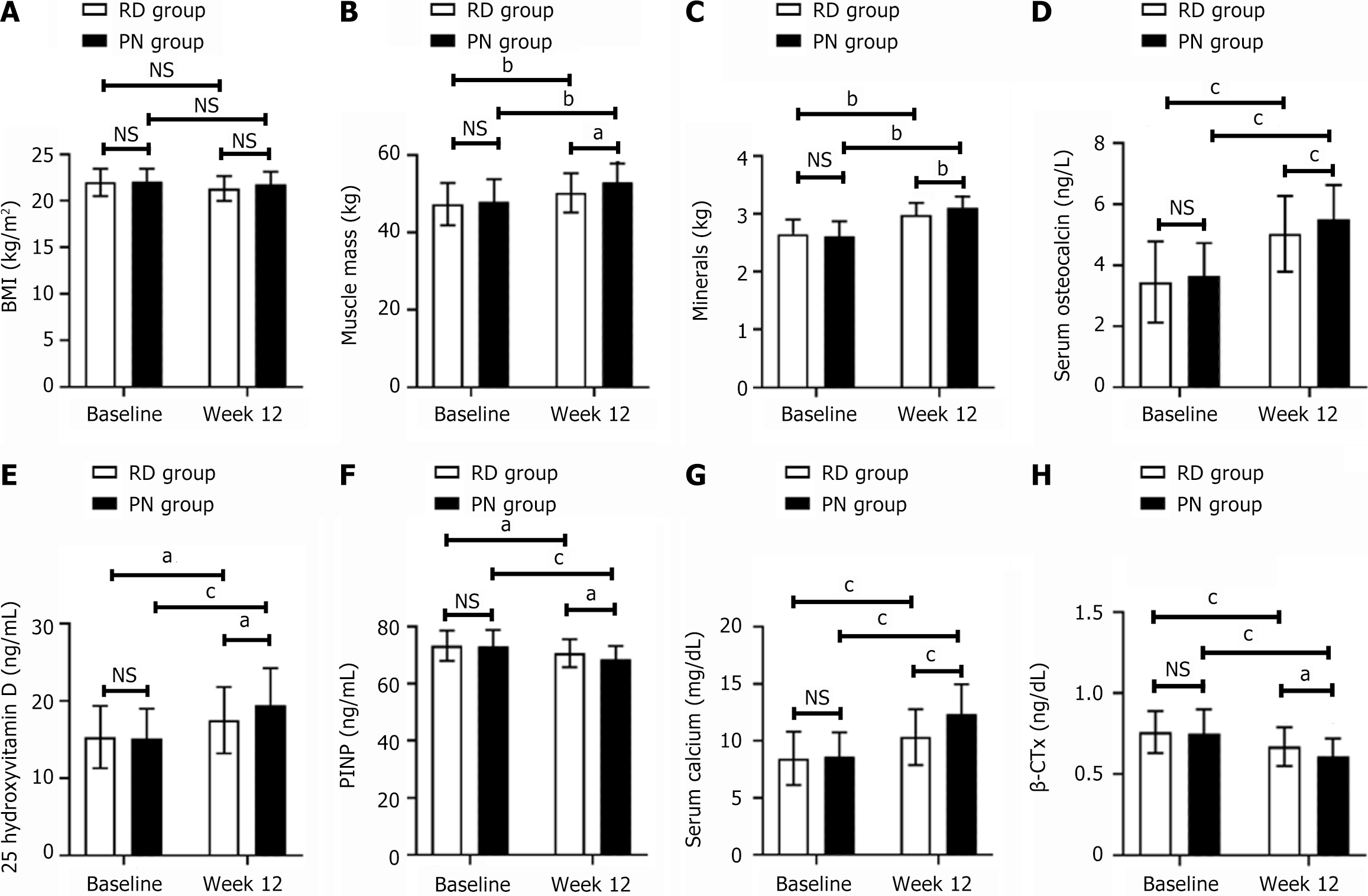
Figure 1 Comparison of body composition, osteocalcin, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide, serum calcium, and beta C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen before and after intervention for 12 weeks.
A: Body mass index; B: Muscle mass; C: Minerals; D: Serum osteocalcin; E: 25-hydroxyvitamin D; F: Procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide; G: Serum calcium; H: Beta C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. ns indicted P > 0.05. RD: Routine diet; PN: Personalized nutrition; BMI: Body mass index; PINP: Procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide; β-CTX: Beta C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen.
- Citation: Wang XL, Zhao YR, Yu Y, Mao ZF, Tan SX, Yu SS. Impact of dietary nutrition regimens based on body composition analysis on bone metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease patients. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(2): 99008
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i2/99008.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.99008