Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Psychiatry. May 19, 2023; 13(5): 191-202
Published online May 19, 2023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i5.191
Published online May 19, 2023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i5.191
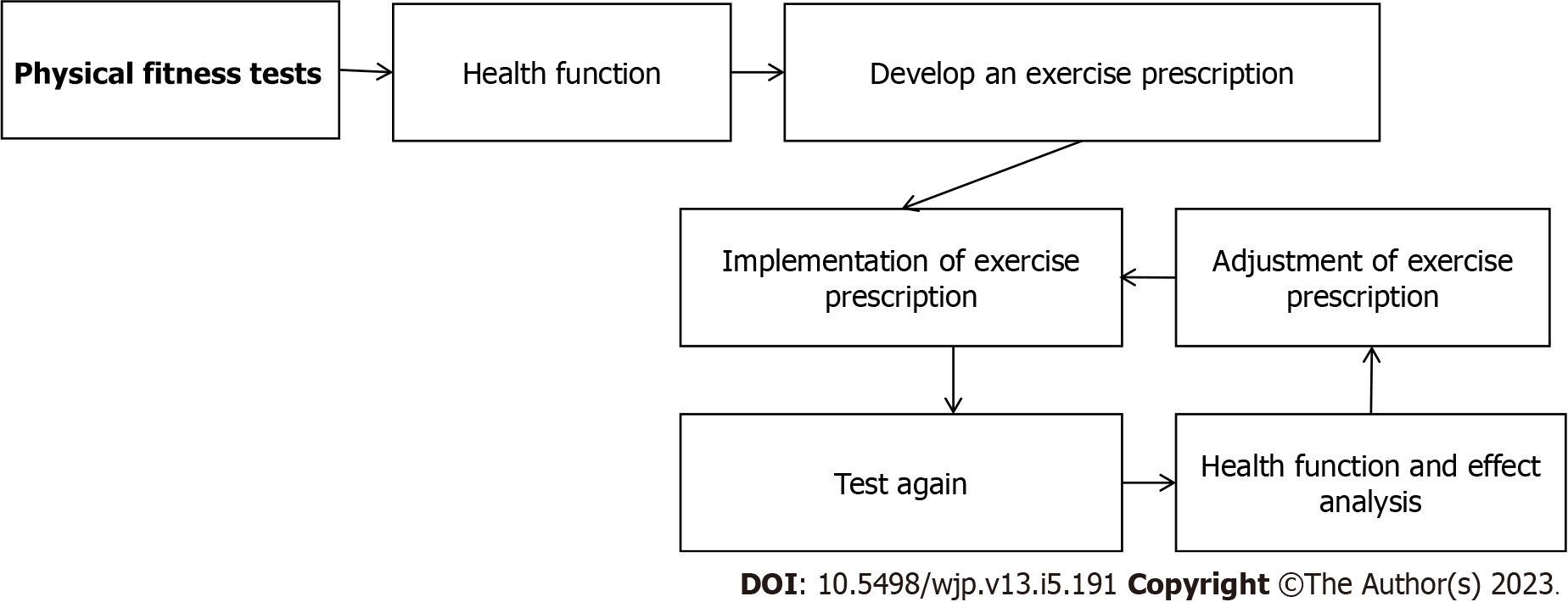
Figure 1 Diagram of the implementation process of exercise prescription in the experimental group.
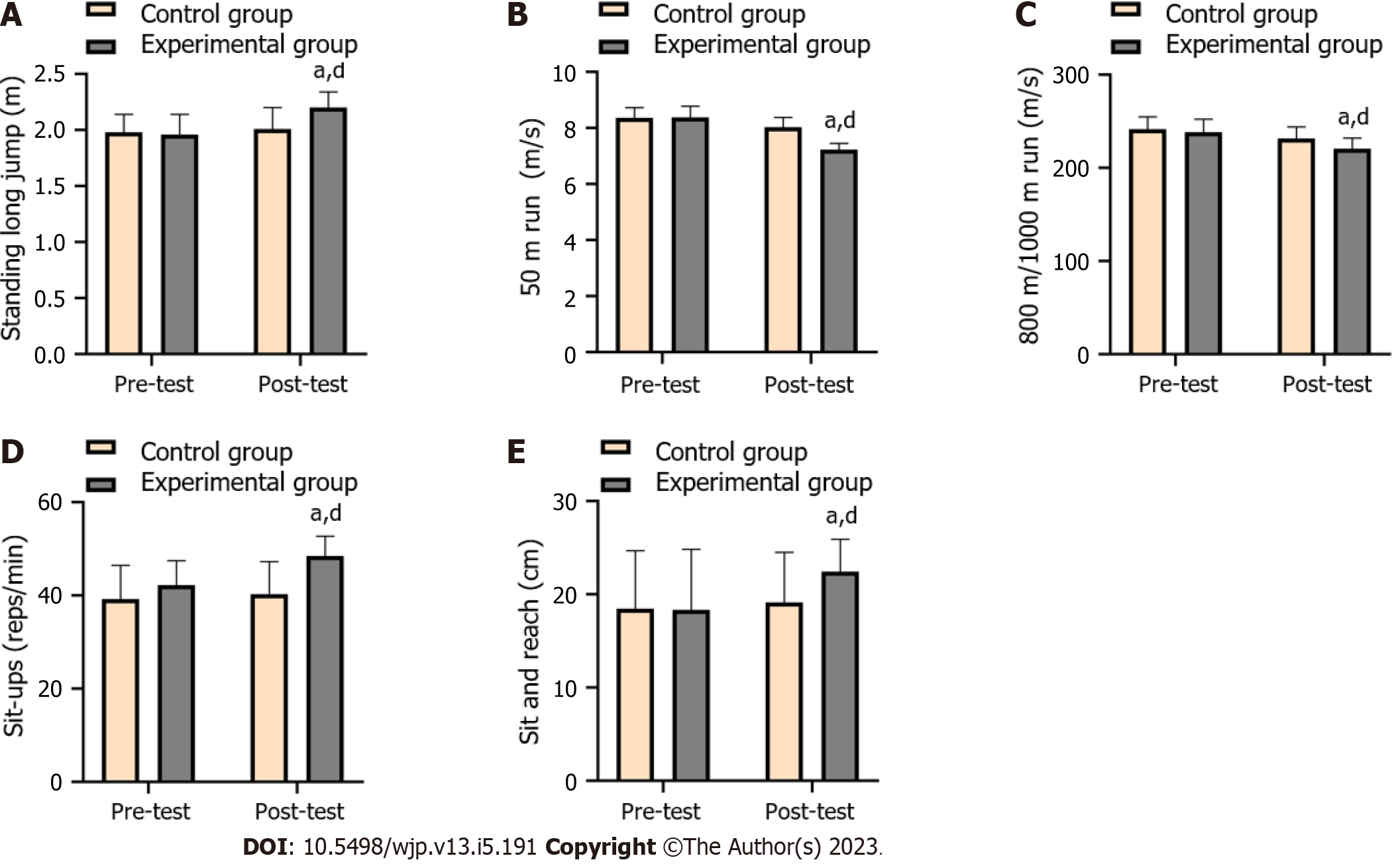
Figure 2 Comparison of exercise quality between the two groups before and after the experiment.
A: Standing long jump test (m); B: 50 m run test (m/s); C: 800 m/1000 m run test (m/s); D: Sit-up test (reps/min); E: Sit and reach test (cm). aP < 0.05 vs the same group before test. dP < 0.05 vs the control group after test.
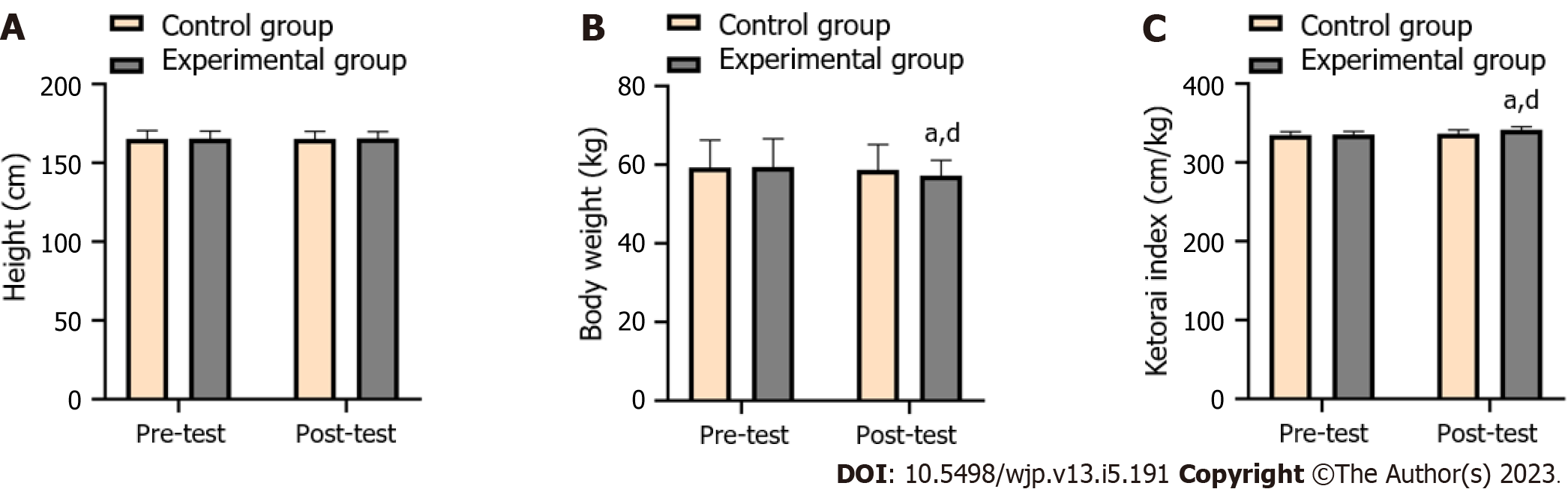
Figure 3 Comparison of body morphology between the two groups before and after the experiment.
A: Height (cm); B: Weight (kg); C: Ketorai index (cm/kg). aP < 0.05 vs the same group before teaching. dP < 0.05 vs the control group after teaching.
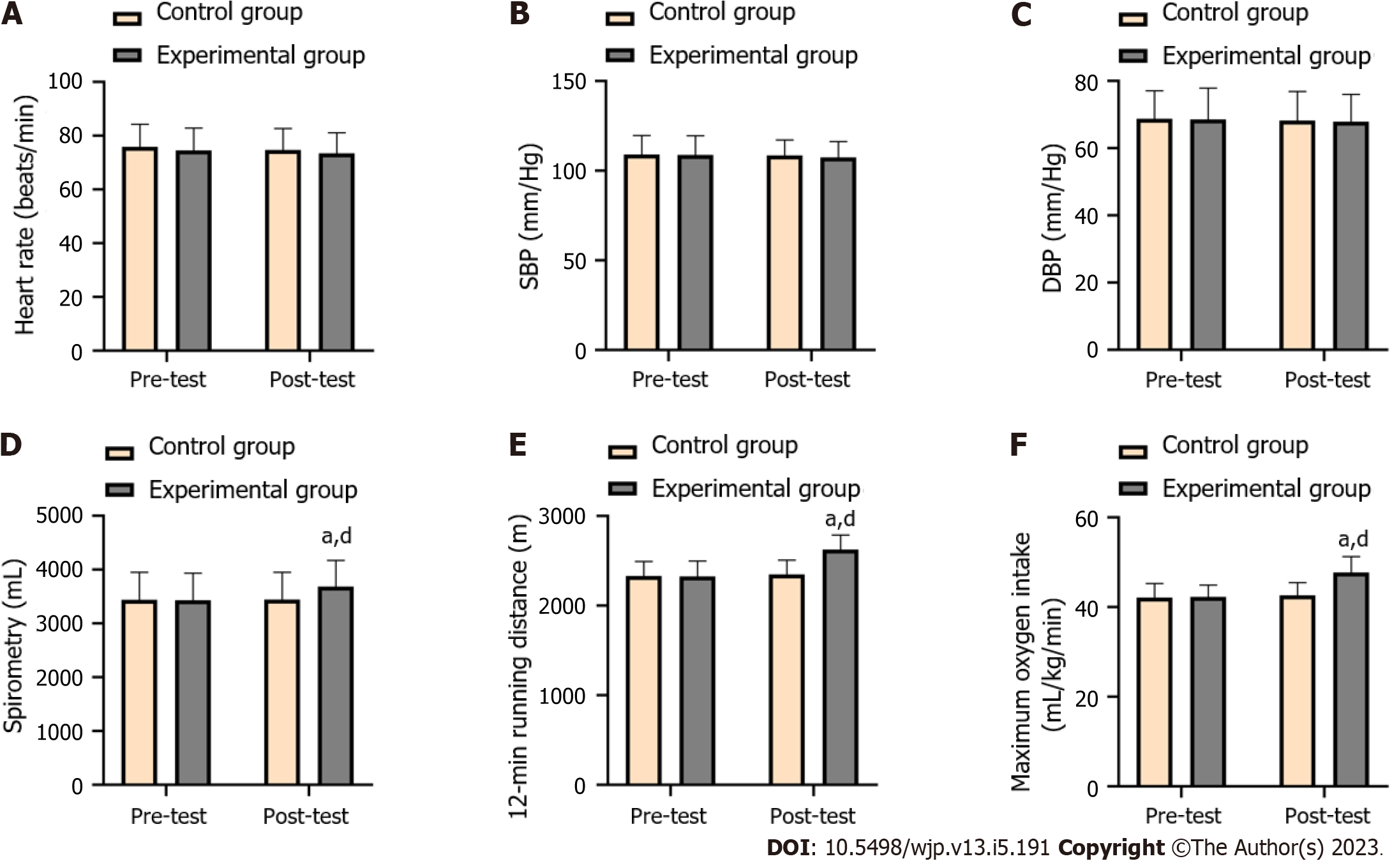
Figure 4 Comparison of cardiopulmonary function between the two groups before and after the experiment.
A: Heart rate (beats/min); B: Systolic blood pressure (mm/Hg); C: Diastolic blood pressure (mm/Hg); D: Spirometry (mL); E: 12-min running distance (m); F: Maximum oxygen intake (mL/kg/min). aP < 0.05 vs the same group before teaching. dP < 0.05 vs the control group after teaching. SBP: Systolic blood pressure; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure.
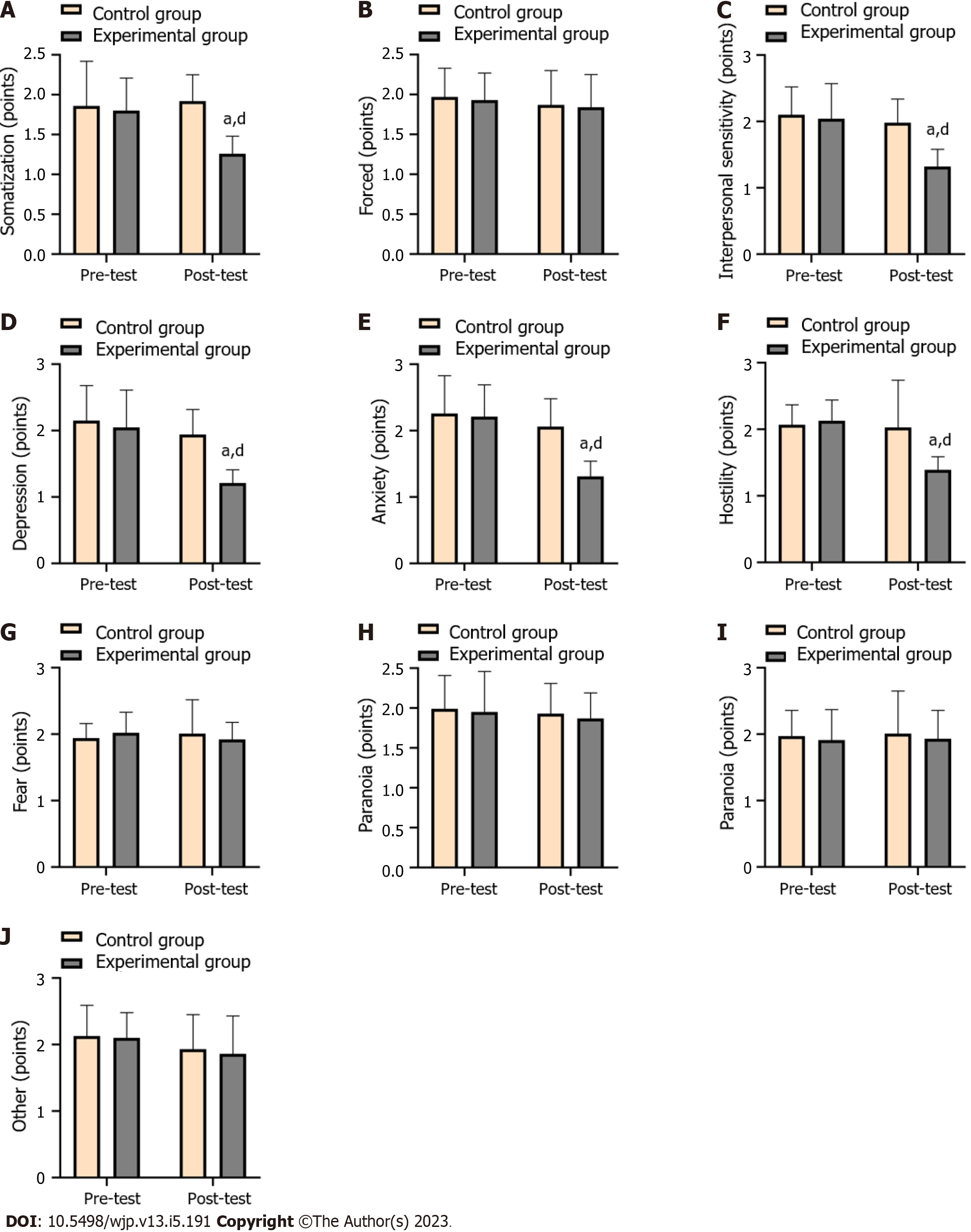
Figure 5 Comparison of the mental health status of the two groups before and after the experiment.
A: Scores of somatization (points); B: Scores of forced (points); C: Scores of interpersonal sensitivity (points); D: Scores of depression (points); E: Scores of anxiety (points); F: Scores of hostility (points); G: Scores of fear (points); H: Scores of paranoia (points); I: Scores of psychotic (points); J: Scores of other (points). aP < 0.05 vs the same group before teaching. dP < 0.05 vs the control group after teaching.
- Citation: Zhong XL, Sheng DL, Cheng TZ, Zhang ZW. Effect of exercise prescription teaching on exercise quality and mental health status of college students. World J Psychiatry 2023; 13(5): 191-202
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v13/i5/191.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v13.i5.191