Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Urol. Mar 18, 2025; 14(1): 104791
Published online Mar 18, 2025. doi: 10.5410/wjcu.v14.i1.104791
Published online Mar 18, 2025. doi: 10.5410/wjcu.v14.i1.104791
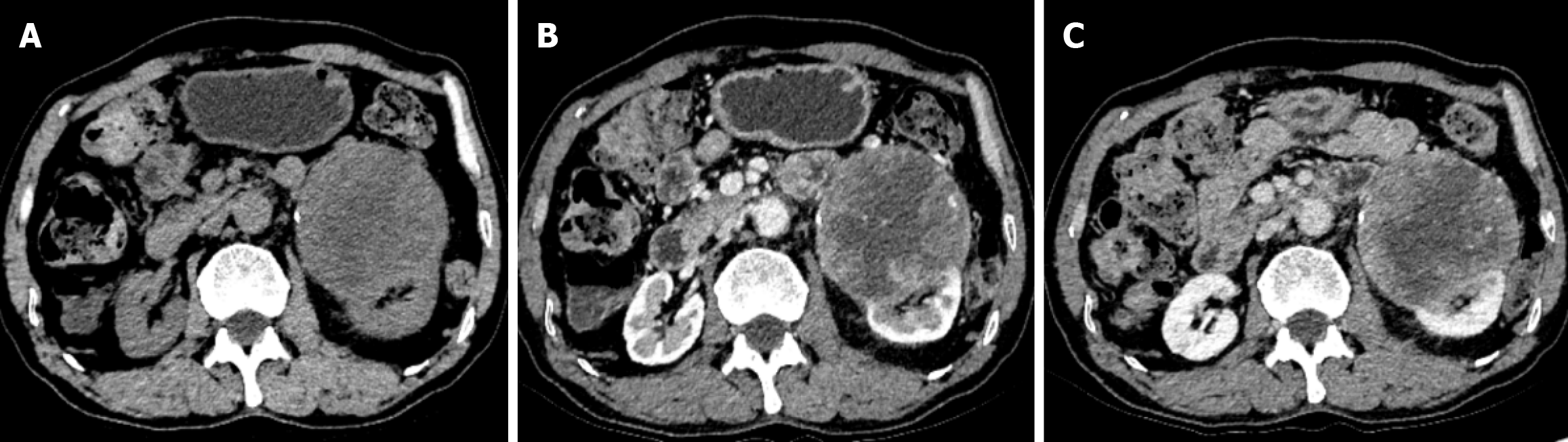
Figure 1 The preoperative computed tomography images of the patient.
A: The plain scan of computed tomography examination shows a cystic- solid mass shadow with uneven density; B: After enhanced scanning, it shows heterogeneous enhancement; C: The solid part in the venous phase shows a "fast in and slow out" performance.
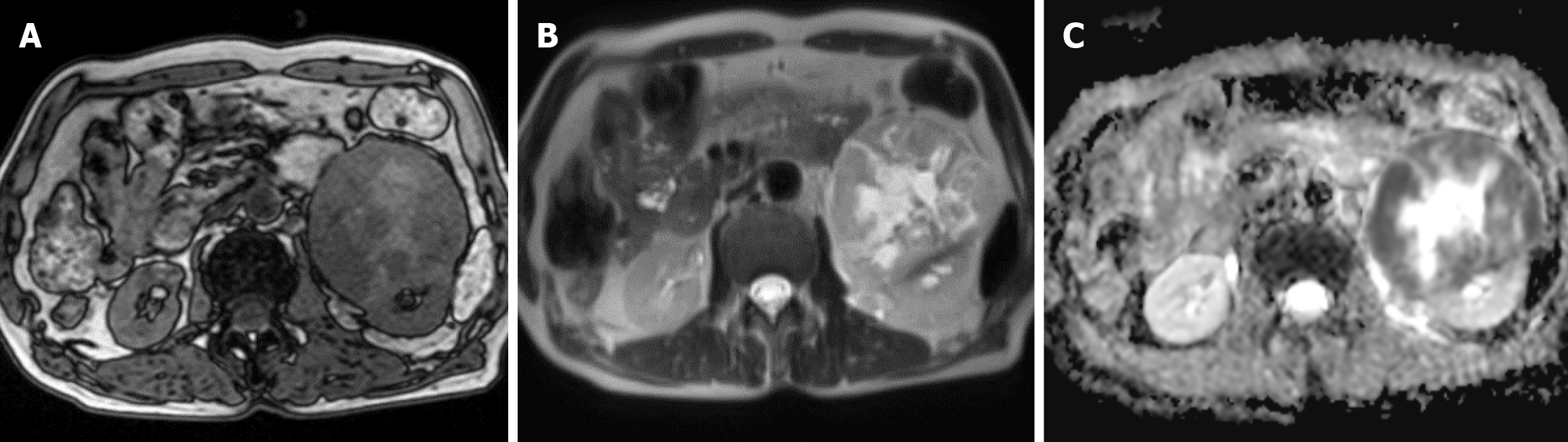
Figure 2 The preoperative computed tomography images of the patient.
A: There is a mass-like iso/long T1 and iso/long T2 signal shadow in the left kidney; B: On diffusion-weighted imaging, the lesion shows a high/low heterogeneous signal; C: The signal of the lesion is heterogeneous, the boundary is relatively clear, and the boundary between the lesion and the left renal cortex is unclear.
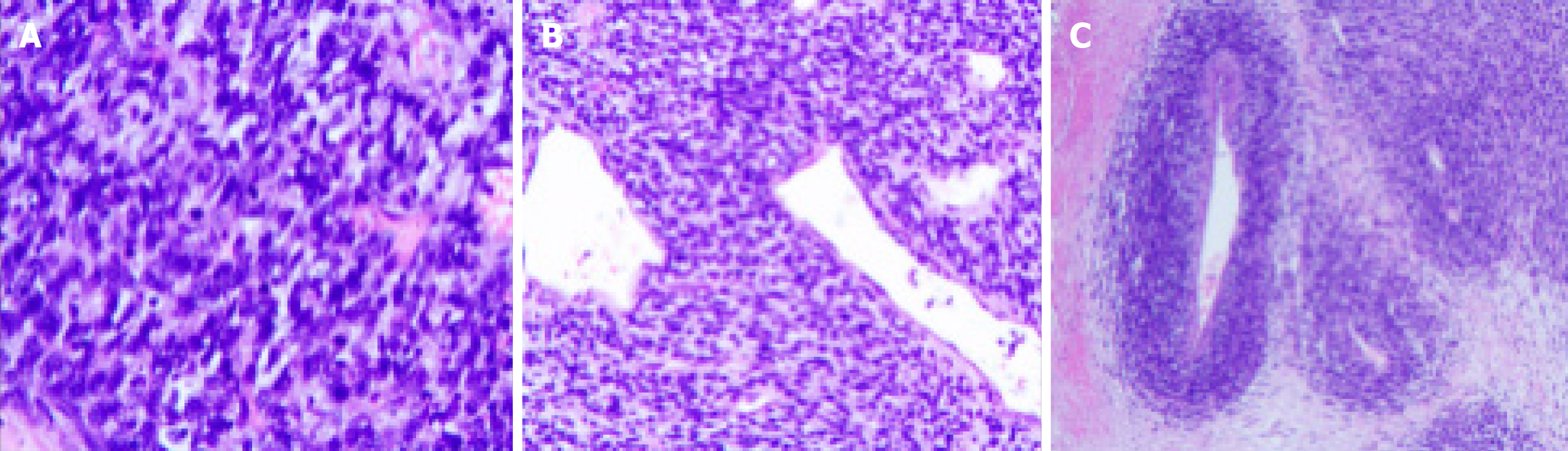
Figure 3 The pathological images of the patient after surgery.
A: Microscopic observation reveals that the tumor cells are spindle - shaped cells distributed in a sheet - like or fascicular pattern; B: The tumor cells with a tight arrangement; C: Small amount of cytoplasm, a large nuclear - cytoplasmic ratio, and obvious nuclear atypia.
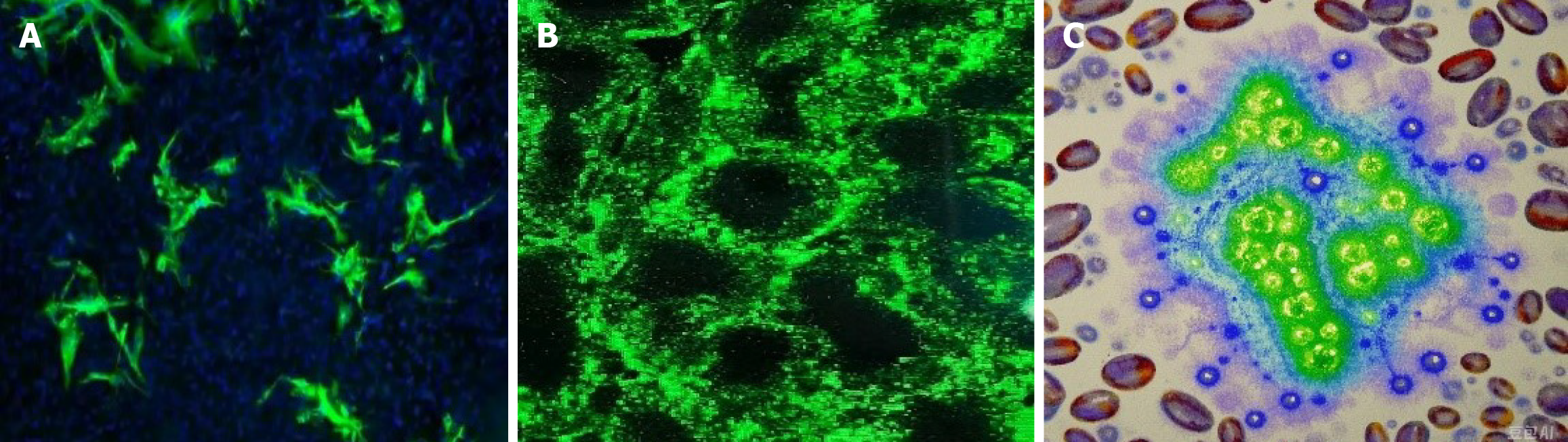
Figure 4 The immunohistochemistry images of the patient after surgery.
A: Immunohistochemistry showed that the MDM2 protein was mainly located in the cell nucleus; B: Distinct staining signals could be observed in the cell nuclei, forming a sharp contrast with the nuclei of surrounding non-amplified cells. In the tumor tissue sections, strong positive staining for MDM2 could be detected in almost the entire tumor area; C: Schematic diagram of MDM2 gene amplification.
- Citation: Deng CH, Zhou Y, Chen J, He GF, Fu QS, Li JM, Wang G, Hu XD. Diagnostic and therapeutic considerations for primary penal synovial sarcoma with specific MDM2 gene amplification: A case report. World J Clin Urol 2025; 14(1): 104791
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2816/full/v14/i1/104791.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5410/wjcu.v14.i1.104791