Published online Mar 9, 2023. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v12.i2.45
Peer-review started: December 4, 2022
First decision: January 9, 2023
Revised: January 25, 2023
Accepted: February 13, 2023
Article in press: February 13, 2023
Published online: March 9, 2023
Processing time: 91 Days and 19.2 Hours
Patients with immune-mediated diseases, such as juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are at increased risk of developing infections, due to disease-related immune dysfunction and applying of immu
To evaluate vaccine coverage in patients with IBD and JIA, and compare it with healthy children.
In the cross-sectional study we included the data from a questionnaire survey of 190 Legal representatives of children with JIA (n = 81), IBD (n = 51), and healthy children (HC, n = 58). An electronic online questionnaire was created for the survey.
There were female predominance in JIA patients and younger onset age. Parents of JIA had higher education levels. Employment level and family status were similar in the three studied groups. Patients with JIA and IBD had lower vaccine coverage, without parental rejection of vaccinations in IBD, compare to JIA and healthy controls. The main reason for incomplete vaccination was medical conditions in IBD and JIA. IBD patients had a lower rate of normal vaccine-associated reactions compared to JIA and HC. The encouraging role of physicians for vaccinations was the lowest in JIA patients. IBD patients had more possibilities to check antibodies before immune-suppressive therapy and had more supplementary vaccinations compared to JIA and HC.
JIA and IBD patients had lower vaccine coverage compared to HC. Physicians' encouragement of vaccination and the impossibility of discus about future vaccinations and their outcomes seemed the main factors for patients with immune-mediated diseases, influencing vaccine coverage. Further investigations are required to understand the reasons for incomplete vaccinations and improve vaccine coverage in both groups, especially in rheumatic disease patients. The approaches that stimulate vaccination in healthy children are not always optimal in children with immune-mediated diseases. It is necessary to provide personalized vaccine-encouraging strategies for parents of chronically ill children with the following validation of these technics.
Core Tip: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease patients had lower vaccine coverage compared to healthy children. Physician’s encouraging to vaccination and impossibility to discus about future vaccinations and their outcomes seemed the main factors for patients with immune-mediated diseases, influenced the vaccine coverage. Further investigations required to understand the reasons for incomplete vaccinations and improve the vaccine coverage in both groups, especially in rheumatic disease patients. The approaches that stimulate vaccination in healthy children are not always optimal in children with immune-mediated diseases. It is necessary to provide personalized vaccine-encouraging strategies for parents of chronically ill children with following validation of these technics.
- Citation: Makarova E, Khabirova A, Volkova N, Gabrusskaya T, Ulanova N, Sakhno L, Revnova M, Kostik M. Vaccination coverage in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and healthy peers: Cross-sectional electronic survey data. World J Clin Pediatr 2023; 12(2): 45-56
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v12/i2/45.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v12.i2.45
Patients with immune-mediated diseases, such as juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), are at increased risk of developing infections, due to disease-related immune dysfunction and applying of immunosuppressive drugs[1,2]. Additional factors of increased infection risk include disease activity, malnutrition, surgical interventions, and concomitant chronic diseases, such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, atopic dermatitis, asthma, and others[3-5].
Biologic therapy with and without immune suppressors can reliably control inflammatory activity in many patients with immune-mediated diseases, including JIA and IBD. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors - adalimumab and infliximab, with or without azathioprine, methotrexate, and sulfasalazine uses in IBD[6]. Etanercept, adalimumab, tocilizumab, abatacept, and tofacitinib with and without methotrexate applied in JIA[7]. Infections are the most common complications associated with biological treatment and immune suppressors. The main infectious, associated with immune-mediated diseases are pneumococcus, influenza, varicella-zoster virus, and measles[8-10]. Immune-compromised patients may have a more severe course of infections, requiring hospital admissions, using intravenous antibiotics and intravenous immunoglobulin lead to withdrawal of current therapy with following disease flare and non-achievement of the remission[11,12]. These above-mentioned factors may influence a child's overall health and long-term therapy outcomes[13].
Vaccination is a well-known and effective tool, which allows for reducing the frequency and severity of infectious episodes, and indirectly might reduce the risks of disease flare and failure to achieve remission, and significantly improve disease course and outcomes[14].
Several studies assessed reasons for low vaccine coverage from a medical point of view, but studies from a parental point of view are limited.
Our study aimed to assess the parental-related reasons for incomplete vaccination.
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Saint-Petersburg State Pediatric Medical University (Protocol №3 from 01/03/2021). There were no violations of patients' rights according to the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was completely anonymous.
In the cross-sectional study, we included the data from questionnaire surveys of 190 Legal representatives of children, with JIA (n = 81), IBD (n = 51), and healthy children HC (n = 58). The electronic survey was disseminated through the parental social network for IBD and JIA in Saint-Petersburg and the North-West part of the Russian Federation from January 2022 to March 2022. The group of HC was collected with portable electronic devices in one of the city's schools and kindergartens with the exclusion of children with chronic diseases if it was reported in the survey. All parents of patients with IBD and JIA who were invited to participate responded to the survey. Initially, 58 out of 152 guardians of HC who had been asked to participate in the survey answered.
An electronic online questionnaire was created for the survey, containing 62 questions for parents of children with IBD, 55 questions for parents of children with JIA, and 37 questions for parents of healthy children. The majority of questions were identical for all three groups, some questions were equal for IBD and JIA and the remaining questions were disease-specific. The survey is in the Supplementary material.
We collected the following information: (1) Patient’s demography: gender, type of disease, disease onset, age of inclusion; (2) Parental demography: gender of respondent, education, family status, and employment status; and (3) Information about vaccines: the coverage with obligatory and additional vaccines, reasons for incomplete vaccinations.
The sample size did not initially calculate. Descriptive statistics are reported in terms of medians and interquartile ranges for continuous variables and absolute frequencies and percentages for categorical variables. Missing data were not included in the analyses. We used a non-parametric statistic because all variables had non-normal distribution. To check whether the distribution was normal or not, we used the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and distribution graphs. Pearson's χ2 test or Fisher's exact test in the expected frequencies < 5 was used to compare the categorical variables. A comparison of two quantitative variables was carried out using the Mann-Whitney test. Bonferroni’s correction test was applied to avoid multiple comparisons. The software Statistica (release 10.0, StatSoft Corporation, Tulsa, OK, United States) was used for data analysis, P value < 0.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference.
A total of 190 individuals participated in the survey. The IBD group consisted of 51 patients, 39 (76%) with Crohn's disease and 12 (24%) with ulcerative colitis. The JIA group represented 81 parents, including systemic JIA (n = 10; 12.3%), RF positive or negative polyarthritis (n = 23; 28.4%), persistent or extended oligoarthritis (n = 38; 46.9%), enthesitis-related arthritis (n = 3; 3.7%), psoriatic (n = 4; 4.9%) and undifferentiated arthritis (n = 3; 3.7%). There was a female predominance in JIA patients (n = 43; 54% vs n = 24; 47% and n = 28; 49% for IBD and HC, respectively) and younger onset [4.7 (0.8; 16.0) vs 10.9 (1.0; 17.0) years for IBD] age and age of inclusion [7.8 (2.0; 18.0) years vs 13.6 (2.7; 17.0) and 11.3 (3.0; 17.0) for IBD and HC, respectively] in the present study. Mothers were the main survey respondents, with a lower part in JIA (88.2%) compared to IBD (96.1%) and HC (98.3%). Parents of JIA had higher education levels - 81.5% compared to 64% (IBD) and 77.6% (HC). Employment level and family status were similar in the three studied groups. Data are presented in Table 1.
| Parameters | Parents of IBD patients (n = 51) | Parents of JIA patients (n = 81) | Parents of HC (n = 58) | P value |
| Patients characteristics | ||||
| Age of inclusion in the study, years, Me (25%; 75%) | 13.6 (2.7; 17.0) | 7.8 (2.0; 18.0) | 11.3 (3.0; 17.0) | 0.00006 |
| Gender, females, n (%) | 24 (47) | 43 (54) | 28 (49) | 0.0000001 |
| The onset of the disease, years, Me (25%; 75%) | 10.9 (1.0; 17.0) | 4.7 (0.8; 16.0) | NA | 0.0000001 |
| Parental status | ||||
| Gender of representative, females, n (%) | 49 (96.1) | 71 (88.2) | 57 (98.3) | 0.022 |
| Education level, n (%) -secondary school -higher education -academic degree | 18 (36) 33 (64) 0 (0) | 11 (13.6) 66 (81.5) 3 (4.9) | 13 (22.4) 45 (77.6) 0 (0) | 0.019 |
| Level of employment, n (%) -working -self-employed -unemployed -receiving welfare support | 32 (62.7) 5 (9.8) 8 (15.7) 6 (11.8) | 48 (59) 8 (9.9) 12 (14.8) 13 (16,3) | 37 (65) 11(18.5) 9 (16.5) 0 (0) | > 0.050 |
| Family status, n (%) - Married - Divorced - Widow/widower - Single parent | 43 (85.2) 4 (8.6) 1 (1.2) 2 (5) | 66 (80.4) 9 (11.8) 3 (3.9) 3 (3.9) | 46 (79.3) 11 (19.0) 1 (1.7) 0 (0) | 0.327 |
The 2021 Russian national vaccination schedule included vaccinations against hepatitis B virus (HBV), tuberculosis, pneumococcus infection, poliomyelitis, diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, and measles - mumps - rubella (MMR)[21]. In addition, Haemophilus influenzae type B is recommended for all children from 3 mo (before 2021 it was voluntary and just for the risk group). Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) vaccination can be performed voluntarily, recommended for children after 1 year with negative VZV history. Influenza vaccination should be performed annually in children after 1 year. Vaccination against meningococcal, hepatitis A and tick-borne encephalitis are not recommended routinely for healthy children but can be performed voluntarily. Vaccinations against influenza (annually), pneumococcal, Haemophilus influenzae, Meningococcal, and hepatitis B infections are strongly recommended for IBD and JIA patients.
Patients with JIA (n = 65; 79.9%) and IBD (n = 42; 82.3%) had lower vaccine coverage compared to HC (n = 52; 91.4%, P = 0.320). At least one episode of vaccine-associated reaction (low-grade fever, injection site reactions) was meant with a similar rate by parents in 40 (49.3%) JIA patients and 27 (46.6%) HC, and two times rarely in IBD (n = 13; 26.1, P = 0.02) patients. Fever after vaccination was reported by parents of JIA patients more frequently (33.3%) than by parents of IBD patients (21.6%) and HC (24.1%). Injections site reactions rate was the lowest in IBD children (3.9%) compare to JIA (16.1%) and HC (22.4%).
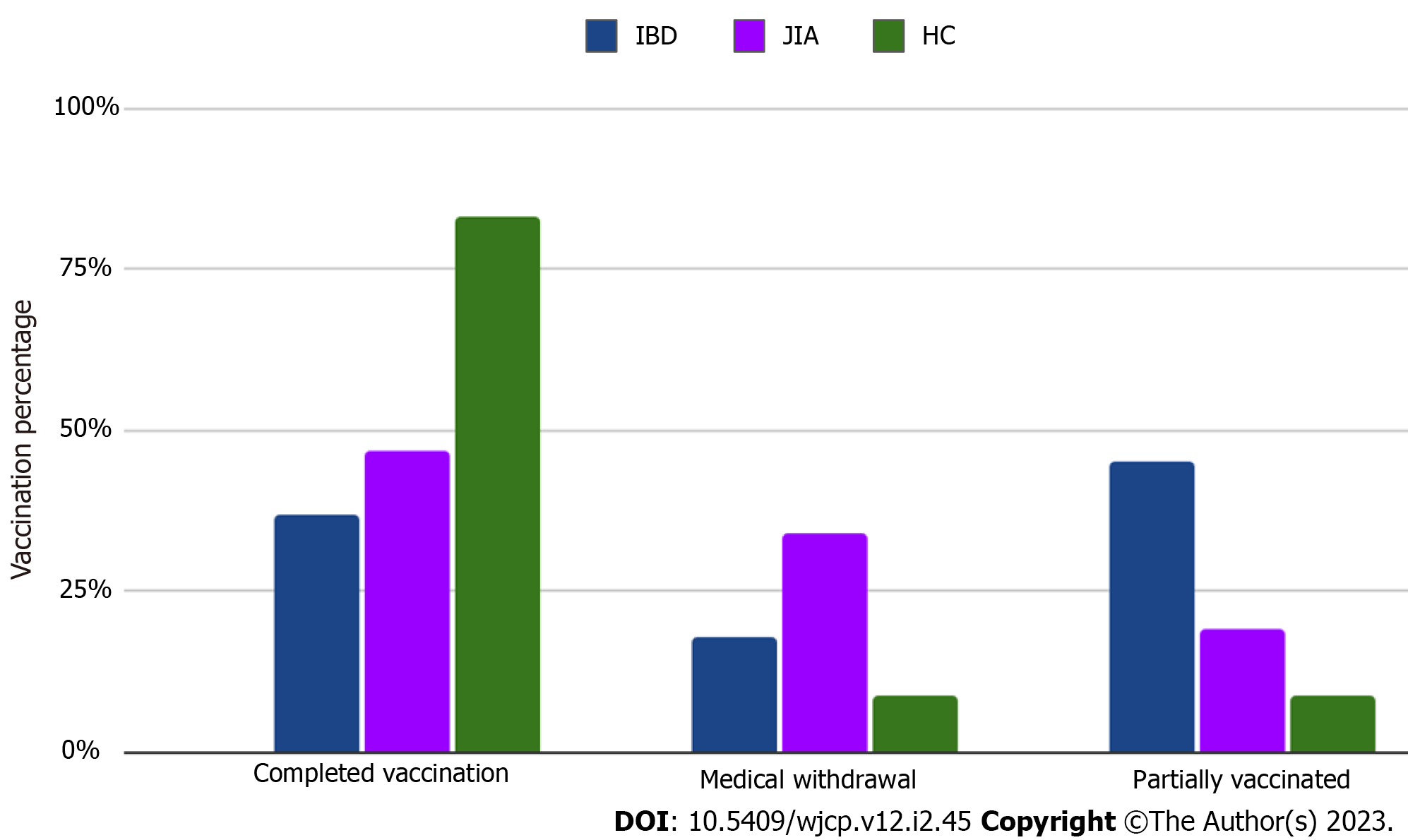
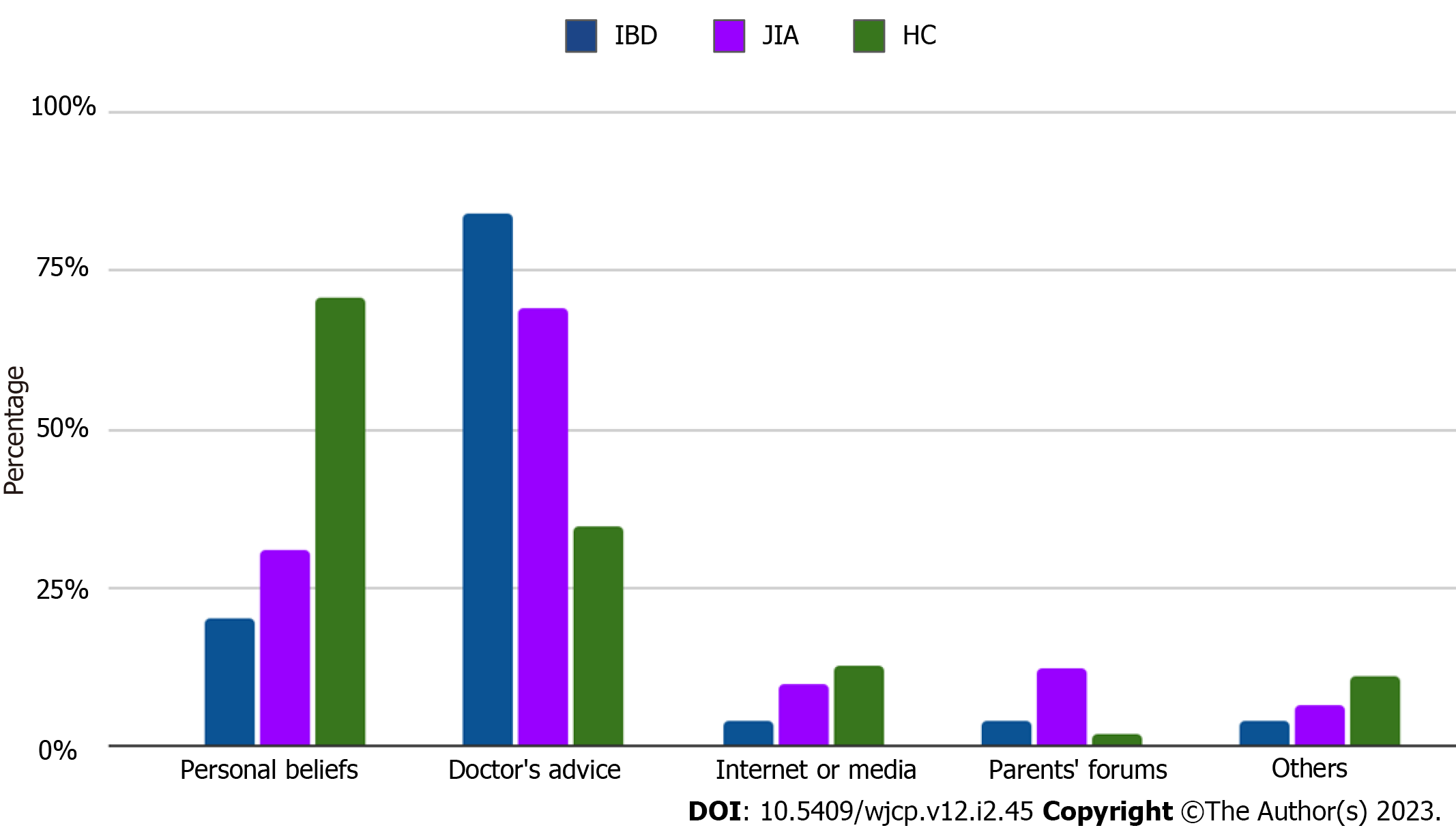
Temporary medical conditions (active stage of diseases, acute respiratory infections, high dose corticosteroids, and biologic therapy for live vaccines) were noted as the main reason for missing or delayed vaccinations in IBD (n = 9; 17.6%) and JIA patients (n = 14; 17.3%) with the same rate (Figure 1). No cases of parental rejection of vaccinations in IBD compared to JIA (n = 2; 2.5%) and HC (n = 3; 5.2%) were reported by respondents. A small proportion of JIA (n = 6; 7.4%) and IBD (n = 5; 10.9%) patients continue vaccinations after disease onset. Only a third part of immune-compromised patients: 23 (28.4%) of JIA and 16 (32%) of IBD patients' parents had the opportunity to discuss perspectives related to following vaccination with their attending physician. IBD patients (n = 22; 43.2%) had more frequent opportunities to measure levels of anti-vaccine antibodies before immune-suppressive therapy than JIA patients (n = 24; 29.6%). Among encouraging vaccination factors the role of attending physicians was the leading in IBD patients (n = 42; 84%), compared to JIA patients (n = 56; 69.1%) (Figure 2).
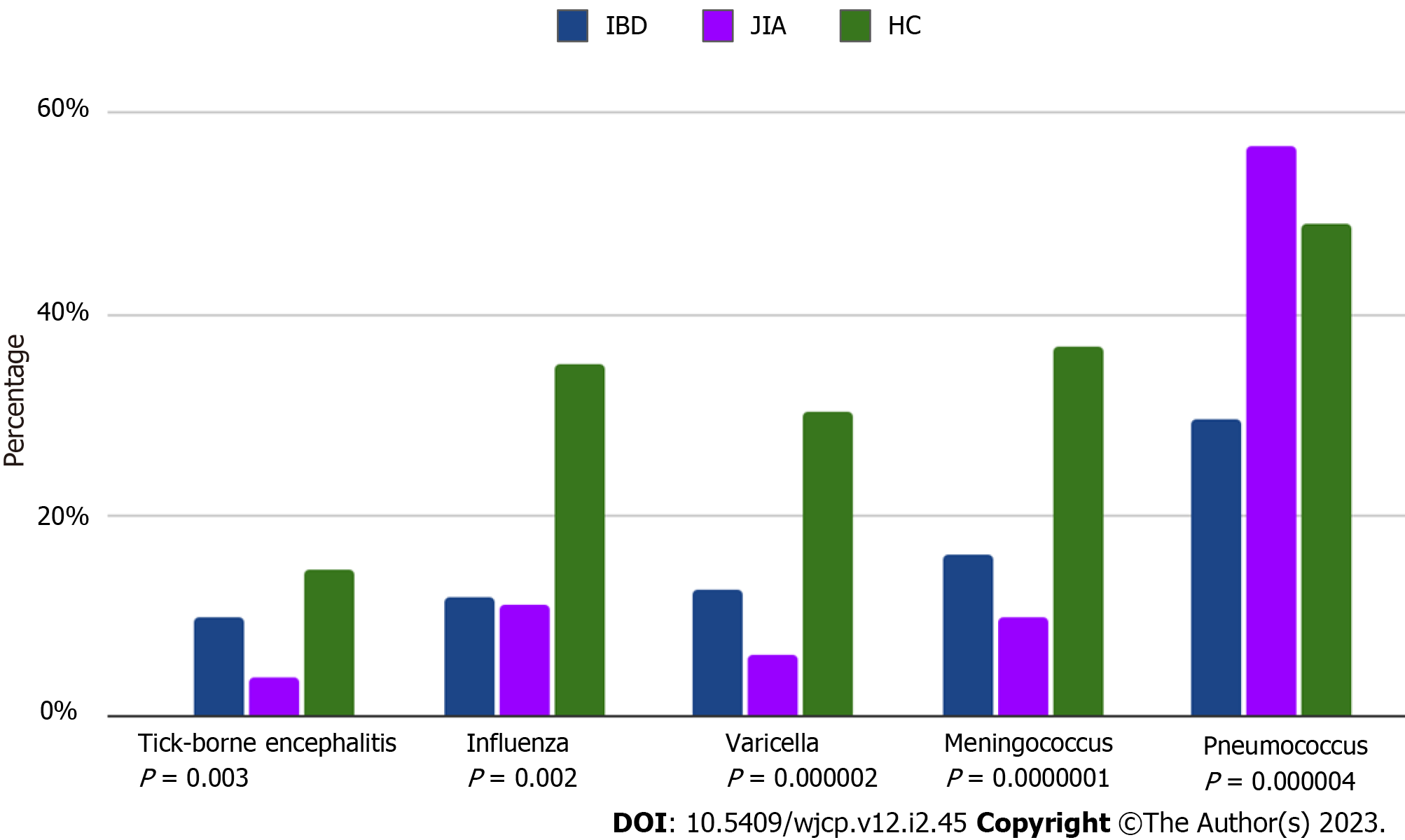
Patients with both immune-mediated diseases had a lower rate of supplementary vaccines, compared to HC, with an exception for the pneumococcal vaccine, which was more frequently used in IBD patients (data are in Table 2 and Figure 3).
| Parameters | Parents of IBD patients (n = 51) | Parents of JIA patients (n = 81) | Parents of HC (n = 58) | P value |
| Vaccine status | ||||
| Completed vaccination according to the national calendar, n (%) | 42 (82.3) | 65 (79.9) | 52 (91.4) | 0.320 |
| Temporary medical contraindications for vaccination (postponed vaccination), n (%) | 9 (17.6) | 14 (17.3) | 2 (3.4) | 0.000001 |
| Refused to be vaccinated, n (%) | 0 (0) | 2 (2.5) | 3 (5.2) | 0.00001 |
| Vaccine-associated reactions: No reaction Fever Injection site reactions | 38 (74.5) 11 (21.6) 2 (3.9) | 41 (50.6) 27 (33.3) 13 (16.1) | 31 (53.5) 14 (24.1) 13 (22.4) | 0.020 |
| Continued vaccination after diagnosis, n (%) | 5 (10.9) | 6 (7.4) | NA | 0.505 |
| Had an opportunity to discuss vaccinations with the attending physician, n (%) | 16 (32) | 23 (28.4) | NA | 0.716 |
| Control of anti-vaccine antibodies before immunosuppressive treatment, n (%) | 22 (43.2) | 24 (29.6) | NA | 0.147 |
| Factors encouraged vaccination, n (%) - Personal beliefs - Doctor's advice - Internet / Media - Parents' forums - Others | 10 (20) 42 (84) 2 (4) 2 (4) 2 (4) | 25 (30.8) 56 (69.1) 8 (9.9) 9.9 (12.3) 5 (6.4) | 40 (70.9) 19 (34.5) 7 (12.7) 1 (1.8) 6 (10.9) | 0.010 |
| Additional vaccines, n (%), against - tick-borne encephalitis - influenza - meningococcus - pneumococcus - varicella | 8 (9.8) 6 (11.7) 8 (16.0) 29 (56.8) 6 (12.7) | 3 (3.7) 9 (11.1) 8 (9.8) 23 (29.4) 7 (6,2) | 8 (14.5) 20 (35.1) 21 (36.8) 27 (48.9) 17 (30.2) | 0.003 0.002 0.0000001 0.000004 0.000002 |
According to parental opinion, lack of discussion about the safety of vaccines and future disease-related perspectives was the main factor, in the restraining of active vaccination. Vice versa, encouraging manner of attending physicians to vaccinate was meant by parents as a factor, that stimulated vaccination.
In this study vaccine coverage and parental point of view on vaccination in patients with immune-mediated disease, (IBD and JIA) and HC were demonstrated.
Vaccine prophylaxis recommendations have been around for years, but the problem of low vaccination rates among these patients is still relevant. For children with rheumatic diseases, the major national and international medical societies, including the American College of Rheumatology and the European League of Associations for Rheumatology, as well as for children with IBD, including ECCO Guidelines, have recommended expanded vaccinations including pneumococcal, varicella-zoster, influenza and human papillomavirus (HPV) in addition to the common vaccines (hepatitis B, pertussis, diphtheria, tetanus, measles, rubella) [4,5,15]. Despite the existing international recommendations and consensus of the European communities of pediatric gastroenterologists and rheumatologists according to vaccination, current studies note a low level of awareness of the necessity and safety of vaccination among both types of physicians and parents, which translates into lower vaccine coverage in patients with both inflammatory bowel disease and juvenile idiopathic arthritis[16-19]. At the same time, it has been proven that maintaining appropriate vaccination status in these patients is critical for optimizing treatment outcomes. Vaccination recommendations for IBD and JIA patients are available, however, the implementation rate remains suboptimal[20,21]. In real practice, only 82.9% of gastroenterologists reported as "very important" to perform the vaccinations recommended by the guidelines in patients with IBD according to A Survey of the Italian Group for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease[22].
The main previously published reasons for incomplete vaccination were the fear of physicians, as primary care or specialists in the efficacy and safety of vaccinations, and fears of parents about disease flares after vaccinations[18,19,25,26]. The fear and concerns of the physicians about the role of vaccines in the flares of pediatric rheumatic diseases might lead to vaccine delays or schedule interruption or neglect of some "non-important vaccinations, according to their opinion”[25-27]. Due to the relevant issue of the effect of vaccination on the outcome of immune-mediated diseases, several large-scale cohort studies have been conducted, with no convincing evidence that the activity of immune-mediated diseases can be increased by vaccination[28,29]. The risk of infections, missing treatment, disease flare, and non-achievement of the remission usually are not mentioned as factors, associated with incomplete vaccination. Incomplete vaccination in JIA and pediatric rheumatic disease patients were reported in several previous studies[18,19,30,31,32]. From the medical point of view, the main predictors of incomplete vaccination were polyarticular and systemic JIA categories and immunosuppressive medications[30,31,33]. In our previous study, the younger JIA onset age was associated with a higher proportion of omitted vaccines similar to the study of Minden et al[18], but some authors reported that preschool children had a similar rate of vaccine coverage as healthy peers[30,32,33].
Usually, decreased vaccine coverage correlated with patients’ age and teens had more omitted vaccines than preschools[18,30,32,33]. In our study, the proportion of patients, who received vaccination against pneumococcus was the highest in the IBD subgroup. Professional GI medical associations recommended using this vaccine to prevent respiratory infections, ensuring the treatment was uninterrupted and maintained remission. Many GI physicians follow this recommendation and encourage this vaccination. We hope that this can become a bridge to other vaccinations in patients with immune-mediated diseases.
The diphtheria vaccination coverage was lower in JIA and IBD patients[31,34]. The lower seroprotection was associated with an increased level of immunosuppression both in JIA and IBD children[31,35]. Booster revaccinations against diphtheria increased the proportions of subjects with seroprotection and were safe for JIA patients[31,34,36]. Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Clinical recommends vaccination against diphtheria for IBD patients[37].
Patients with JIA and IBD may have lower vaccine coverage (40%-75.8%) and seroprotection against hepatitis B (50%-60.7%) according to the data of several studies[35,38,39]. The vaccine against hepatitis B (HB) is recombinant and may be recommended for vaccination to all immune-compromised children because of its safety and efficacy[40,41,42]. The Japanese College of Rheumatology and the Japanese College of Hepatology considered anti-HB vaccination for unimmunized patients with JIA as soon as JIA has been under control for 3 mo[41,42].
Vaccines are considered to be effective and safe. There is no evidence that vaccines increase the risk of developing immune-mediated conditions or exacerbating the existing IBD or rheumatic diseases in children[43-45]. There are no contraindications for the administration of inactive or live vaccines in patients who are not receiving immunosuppressive treatment[15,16]. Despite the higher risk of live vaccines in immune-mediated diseases patients there was no strong correlation between the type of omitted vaccines (live or non-live) and disease activity[30,33]. Sometimes patients with pediatric rheumatic diseases might have omitted non-live vaccines[30,33]. Contemporary EULAR recommendations for children (2021) and adults (2019) with rheumatic diseases allow using live-attenuated vaccines, especially booster doses of MMR and varicella zoster virus in patients with low-grade immune suppression[5,15]. The protective role of vaccines in immune-compromised children was successfully demonstrated in several studies. Compared to healthy children, morbidity and mortality from influenza and streptococcus pneumonia-associated pneumonia are higher among patients with immune-mediated diseases. According to Tinsley A. 2013, patients with IBD who got influenza are more likely to be hospitalized and develop viral pneumonia, although this disease can be prevented by vaccination[46]. Vaccine coverage against pneumococcus was 5% in the Australian pediatric IBD cohort, 18.6% in 430 pediatric IBD patients, from a multicentre study, and 50.3% in JIA patients from Switzerland without differences irrespective of immune-suppressive therapy[33,47,48]. In the study of pneumococcal and anti-Hib vaccination of non-systemic and systemic JIA patients was shown the decreasing number of episodes of acute respiratory infections different etiology[49]. No differences in response related to treatment and disease activity stage were observed. The vaccination against both infections was safe and not associated with following short-term flares[49,50].
There are a lot of barriers between primary care physicians and specialists (rheumatologists, gastroenterologists) in the immunization process of patients with immune-mediated diseases. In a survey of 178 pediatric gastroenterologists conducted by Lester R, 2015, a different view on immunization of IBD patients among gastroenterologists was reported[15]. The main problem was the inability to coordinate patient follow-up for dispensary and immunoprophylaxis between gastroenterologists and pediatricians. Only 28% of GI physicians believed that only primary care physicians were responsible for immunizations. In contrast, in a survey of general pediatricians, only 29% were ready to prescribe vaccination to their patients with IBD[17]. General pediatricians avoid vaccinating patients with a pediatric rheumatic disease without specialists' confirmation. In a recent Greece study, it was shown that 50% of primary care physicians required rheumatologist approval for vaccination[25].
Similar to our data, patients themselves identified a lack of information and fear of side effects as the main reasons for low vaccination rates[51,52].
Practicing gastroenterologists checked the immunization status in 63.5% of cases at the time of diagnosis and in 44.4% before initiating immunosuppressive therapy, according to the survey of 657 gastroenterologists from North America, and only 9% checked serology to assess the protection of IBD children from vaccine-preventable diseases[17]. A relatively small number of our respondents had an opportunity to discuss vaccines and diseases course perspectives and check the serology against vaccines to vaccine-preventable diseases. This point should be improved.
The discrepancy of factors, encouraging vaccination, between IBD and JIA patients was observed. The urging role of attending physicians was lower in JIA patients compared to IBD, but the role of the parent's forum was higher. The sum of the role of internet/media and parental forums in vaccination coverage JIA patients was higher 22.2% compare to IBD - 8% (P = 0.01). It might explain the fact that a survey for JIA patients was disseminated through the parental forum where one of the manuscript co-authors (Mikhail K) delivered several lectures about the efficacy and safety of vaccinations in the last two years. This educational effort was very effective: the vaccine coverage for MMR and diphtheria in JIA patients was 42% and 50% respectively in 2018 and now vaccine coverage (complete vaccination) has raised to 79.9% in 2022[31].
The international guidelines on the management of opportunistic infections and vaccine prophylaxis in patients with IBD were updated in 2021[14]. Regular surveys of vaccine status in patients with inflammatory bowel disease have been recommended, as well as mandatory vaccination against common vaccines: tetanus, diphtheria, and poliomyelitis. In addition, each patient with inflammatory bowel disease should be considered for additional vaccination with the following five vaccines: Varicella-zoster vaccine, HPV, annual influenza (trivalent inactivated vaccine), pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, and hepatitis B vaccine for all HBV seronegative patients[4,5,16].
Professional communities should provide more information about the safety and efficacy of vaccination in immune-compromised children and encourage applying modern recommendations in their practical work and discussions with families. Education and vaccine access in clinics lead to the growth of influenza vaccine coverage from 47% to 75% (education) and 89.5% (plus vaccine access)[53]. It was shown that even a single specialized infectious disease consultation with patients can improve patients' knowledge of vaccination and influence their decision to vaccinate from initial coverage of 16.1% for pneumococcus to 85.7% after intervention[51]. Educational programs for IBD children and their parents increased the coverage for vaccines against diphtheria-tetanus-poliomyelitis (92% vs 100%) and Haemophilus influenzae (88% vs 98%), hepatitis B (52% vs 71%), pneumococcus (36% vs 57%), and meningococcus C (17% vs 41%) (P < 0.05)[38].
Physicians' encouragement of vaccination and the impossibility to discuss future vaccinations and their outcomes seemed the main positive and negative factors that influenced vaccine coverage in immune-mediated diseases patients. Individual vaccine schedules based on the evaluation of vaccine status and serial anti-vaccine antibody assessment should be a reliable tool for increasing trust in vaccines and persuading parents to continue vaccinations, especially omitted ones. It is strongly recommended to implement educational algorithms and programs for parents and children, provided by the attending physicians or other care-given providers about the safety and efficacy of vaccines in children with immune-mediated diseases.
The main limitation of this study related to the self-reported nature of results, assessment of parental outcomes, and inability to compare parental data with official medical records related to vaccination. We cannot be sure of the proper meaning of complete vaccination and parental knowledge of the national vaccine schedule, which makes some bias in the study results. The small sample size and lack of validated surveys make some bias.
JIA and IBD patients had lower vaccine coverage compared to HC. Physicians' encouragement of vaccination and the impossibility of discus about future vaccinations and their outcomes seemed the main factors for patients with immune-mediated diseases, influencing vaccine coverage. Further investigations are required to understand the reasons for incomplete vaccinations and improve vaccine coverage in both groups, especially in rheumatic disease patients. The approaches that stimulate vaccination in healthy children are not always optimal in children with immune-mediated diseases. It is necessary to provide personalized vaccine-encouraging strategies for parents of chronically ill children by following the validation of these techniques. Increasing immunization coverage and implementing advocacy events among special groups are required.
Patients with immune-mediated diseases have incomplete vaccination.
There are no previous studies about parental view of the reasons of incomplete vaccination.
To evaluate the parental view about possible reasons of incomplete vaccination.
An electronic survey for parents of immune-mediated disease patients and healthy controls was created and disseminated. The analysis of response was done.
Lower vaccine coverage in immune mediated patients was detected, compared to healthy controls. Medical conditions were the main medical reasons for incomplete vaccination in juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Less rate of vaccine-associated reactions was reported in IBD. Pediatric rheumatologists rarely explain the safety and benefits of vaccinations. Pediatric gastroenterology physicians frequently checked anti-vaccine antibodies and recommend more supplementary vaccines.
Children with immune-mediated disease (IBD and JIA) have incomplete vaccination. The encouraging role of physicians and lack of discussion about the vaccines from physicians are factors, influencing completeness of the vaccination.
Future studies on the effectiveness of educational programs supporting vaccinations may be planned.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Pediatrics
Country/Territory of origin: Russia
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B, B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Chen K, China; Poddighe D, Kazakhstan S-Editor: Wang LL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Wang LL
| 1. | Groot N, Heijstek MW, Wulffraat NM. Vaccinations in paediatric rheumatology: an update on current developments. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015;17:46. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Nuti F, Civitelli F, Cucchiara S. Long-term safety of immunomodulators in pediatric inflammatory diseases. Paediatr Drugs. 2014;16:343-352. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Rahier JF, Magro F, Abreu C, Armuzzi A, Ben-Horin S, Chowers Y, Cottone M, de Ridder L, Doherty G, Ehehalt R, Esteve M, Katsanos K, Lees CW, Macmahon E, Moreels T, Reinisch W, Tilg H, Tremblay L, Veereman-Wauters G, Viget N, Yazdanpanah Y, Eliakim R, Colombel JF; European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO). Second European evidence-based consensus on the prevention, diagnosis and management of opportunistic infections in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2014;8:443-468. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 694] [Cited by in RCA: 746] [Article Influence: 67.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Kucharzik T, Ellul P, Greuter T, Rahier JF, Verstockt B, Abreu C, Albuquerque A, Allocca M, Esteve M, Farraye FA, Gordon H, Karmiris K, Kopylov U, Kirchgesner J, MacMahon E, Magro F, Maaser C, de Ridder L, Taxonera C, Toruner M, Tremblay L, Scharl M, Viget N, Zabana Y, Vavricka S. ECCO Guidelines on the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Infections in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2021;15:879-913. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 275] [Cited by in RCA: 263] [Article Influence: 65.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (32)] |
| 5. | Furer V, Rondaan C, Heijstek MW, Agmon-Levin N, van Assen S, Bijl M, Breedveld FC, D'Amelio R, Dougados M, Kapetanovic MC, van Laar JM, de Thurah A, Landewé RB, Molto A, Müller-Ladner U, Schreiber K, Smolar L, Walker J, Warnatz K, Wulffraat NM, Elkayam O. 2019 update of EULAR recommendations for vaccination in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:39-52. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 547] [Cited by in RCA: 497] [Article Influence: 99.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Hemperly A, Sandborn WJ, Vande Casteele N. Clinical Pharmacology in Adult and Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018;24:2527-2542. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Poddighe D, Romano M, Gattinara M, Gerloni V. Biologics for the Treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Curr Med Chem. 2018;25:5860-5893. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Toussi SS, Pan N, Walters HM, Walsh TJ. Infections in children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease treated with tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors: systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:1318-1330. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Becker I, Horneff G. Risk of Serious Infection in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients Associated With Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors and Disease Activity in the German Biologics in Pediatric Rheumatology Registry. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017;69:552-560. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Nagy A, Mátrai P, Hegyi P, Alizadeh H, Bajor J, Czopf L, Gyöngyi Z, Kiss Z, Márta K, Simon M, Szilágyi ÁL, Veres G, Mosdósi B. The effects of TNF-alpha inhibitor therapy on the incidence of infection in JIA children: a meta-analysis. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2019;17:4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Wakabayashi A, Ishiguro T, Takaku Y, Miyahara Y, Kagiyama N, Takayanagi N. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of pneumonia in patients with and without rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0201799. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Ardura MI, Toussi SS, Siegel JD, Lu Y, Bousvaros A, Crandall W. NASPGHAN Clinical Report: Surveillance, Diagnosis, and Prevention of Infectious Diseases in Pediatric Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease Receiving Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibitors. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016;63:130-155. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Rosen MJ, Dhawan A, Saeed SA. Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children and Adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169:1053-1060. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 335] [Cited by in RCA: 520] [Article Influence: 52.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Papp KA, Haraoui B, Kumar D, Marshall JK, Bissonnette R, Bitton A, Bressler B, Gooderham M, Ho V, Jamal S, Pope JE, Steinhart AH, Vinh DC, Wade J. Vaccination Guidelines for Patients with Immune-mediated Disorders Taking Immunosuppressive Therapies: Executive Summary. J Rheumatol. 2019;46:751-754. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Jansen MHA, Rondaan C, Legger GE, Minden K, Uziel Y, Toplak N, Maritsi D, van den Berg L, Berbers GAM, Bruijning P, Egert Y, Normand C, Bijl M, Foster HE, Koné-Paut I, Wouters C, Ravelli A, Elkayam O, Wulffraat NM, Heijstek MW. EULAR/PRES recommendations for vaccination of paediatric patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases: update 2021. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82:35-47. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 21.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 16. | Esposito S, Antoniol G, Labate M, Passadore L, Alvisi P, Daccò V, Ghizzi C, Colombo C, Principi N. Vaccines in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Brief Review. Vaccines (Basel). 2021;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Lester R, Lu Y, Tung J. Survey of Immunization Practices in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease Among Pediatric Gastroenterologists. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015;61:47-51. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Minden K, Niewerth M, Borte M, Singendonk W, Haas JP. [Immunization in children and adolescents with rheumatic diseases]. Z Rheumatol. 2007;66:111-112, 114. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Morin MP, Quach C, Fortin E, Chédeville G. Vaccination coverage in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis followed at a paediatric tertiary care centre. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51:2046-2050. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Rollet-Cohen V, Mirete J, Dingulu G, Hofer F, Hofer M, Woerner A, Dommergues MA, Hentgen V. Suboptimal vaccination coverage of recommended vaccines among French children with recurrent autoinflammatory fever syndromes: a study from the Juvenile Inflammatory Rheumatism cohort. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40:2855-2864. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Benchimol EI, Tse F, Carroll MW, deBruyn JC, McNeil SA, Pham-Huy A, Seow CH, Barrett LL, Bessissow T, Carman N, Melmed GY, Vanderkooi OG, Marshall JK, Jones JL. Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Clinical Practice Guideline for Immunizations in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)-Part 1: Live Vaccines. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2021;4:e59-e71. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Macaluso FS, Mazzola G, Ventimiglia M, Alvisi P, Renna S, Adamoli L, Galli M, Armuzzi A, Ardizzone S, Cascio A, Cottone M, Orlando A; on behalf of IG-IBD (Italian Group for the study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease). Physicians' Knowledge and Application of Immunization Strategies in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Survey of the Italian Group for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Digestion. 2020;101:433-440. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | The Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation from 06.12.2021 № 1122n "On approval of the national calendar of preventive vaccinations, calendar of preventive vaccinations for epidemic indications and the order of preventive vaccinations" (Registered 20.12.2021 № 66435). |
| 24. | Soon IS, deBruyn JC, Wrobel I. Immunization history of children with inflammatory bowel disease. Can J Gastroenterol. 2013;27:213-216. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Crawford NW, Buttery JP. Adverse events following immunizations: fact and fiction. Paediatr Child Health. 2013;23:121-124. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Papailiou S, Markade A, Eleftheriou I, Tsolia MN, Garoufi A, Maritsi DN. A National Survey Across Primary Care Pediatricians Regarding Immunization Views and Practices in Children With Rheumatic Diseases. J Clin Rheumatol. 2021;27:e588-e590. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Hussain A, Ali S, Ahmed M, Hussain S. The Anti-vaccination Movement: A Regression in Modern Medicine. Cureus. 2018;10:e2919. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 123] [Cited by in RCA: 138] [Article Influence: 19.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Rahier JF, Papay P, Salleron J, Sebastian S, Marzo M, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Garcia-Sanchez V, Fries W, van Asseldonk DP, Farkas K, de Boer NK, Sipponen T, Ellul P, Louis E, Peake ST, Kopylov U, Maul J, Makhoul B, Fiorino G, Yazdanpanah Y, Chaparro M; European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO). H1N1 vaccines in a large observational cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with immunomodulators and biological therapy. Gut. 2011;60:456-462. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Subesinghe S, Rutherford AI, Ibrahim F, Harris H, Galloway J. A large two-centre study in to rates of influenza and pneumococcal vaccination and infection burden in rheumatoid arthritis in the UK. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:322. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Balažiová B, Kuková Z, Mišíková D, Novosedlíková K, Dallos T. Real-life vaccination coverage in Slovak children with rheumatic diseases. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:956136. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Kostik MM, Lubimova NA, Fridman IV, Goleva OV, Kharit SM. The vaccine coverage and vaccine immunity status and risk factors of non-protective levels of antibodies against vaccines in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: cross-sectional Russian tertiary Centre study. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021;19:108. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Bizjak M, Blazina Š, Zajc Avramovič M, Markelj G, Avčin T, Toplak N. Vaccination coverage in children with rheumatic diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020;38:164-170. [PubMed] |
| 33. | Welzel T, Kuemmerle-Deschner J, Sluka C, Carlomagno R, Cannizzaro Schneider E, Kaiser D, Hofer M, Hentgen V, Woerner A. Vaccination completeness in children with rheumatic diseases: A longitudinal, observational multicenter cohort study in Switzerland. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:993811. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Heijstek MW, van Gageldonk PG, Berbers GA, Wulffraat NM. Differences in persistence of measles, mumps, rubella, diphtheria and tetanus antibodies between children with rheumatic disease and healthy controls: a retrospective cross-sectional study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:948-954. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 70] [Cited by in RCA: 56] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | deBruyn JCC, Soon IS, Fonseca K, Feng S, Purtzki M, Goedhart C, Kuhn S, Vanderkooi OG, Wrobel I. Serologic Status of Routine Childhood Vaccines, Cytomegalovirus, and Epstein-Barr Virus in Children With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019;25:1218-1226. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Wanlapakorn N, Maertens K, Thongmee T, Srimuan D, Thatsanathorn T, Van Damme P, Leuridan E, Poovorawan Y. Levels of antibodies specific to diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, and Haemophilus influenzae type b in healthy children born to Tdap-vaccinated mothers. Vaccine. 2020;38:6914-6921. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Jones JL, Tse F, Carroll MW, deBruyn JC, McNeil SA, Pham-Huy A, Seow CH, Barrett LL, Bessissow T, Carman N, Melmed GY, Vanderkooi OG, Marshall JK, Benchimol EI. Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Clinical Practice Guideline for Immunizations in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)-Part 2: Inactivated Vaccines. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2021;4:e72-e91. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Fleurier A, Pelatan C, Willot S, Ginies JL, Breton E, Bridoux L, Segura JF, Chaillou E, Jobert A, Darviot E, Cagnard B, Delaperriere N, Grimal I, Carre E, Wagner AC, Sylvestre E, Dabadie A. Vaccination coverage of children with inflammatory bowel disease after an awareness campaign on the risk of infection. Dig Liver Dis. 2015;47:460-464. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Szczygielska I, Hernik E, Kwiatkowska M, Rutkowska-Sak L, Kołodziejczyk B, Gazda A. Assessment of the level of vaccine-induced anti-HBs antibodies in children with inflammatory systemic connective tissue diseases treated with immunosuppression. Reumatologia. 2015;53:56-60. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Kasapçopur O, Cullu F, Kamburoğlu-Goksel A, Cam H, Akdenizli E, Calýkan S, Sever L, Arýsoy N. Hepatitis B vaccination in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:1128-1130. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Nerome Y, Akaike H, Nonaka Y, Takezaki T, Kubota T, Yamato T, Yamasaki Y, Imanaka H, Kawano Y, Takei S. The safety and effectiveness of HBV vaccination in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis controlled by treatment. Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26:368-371. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 42. | Kobayashi I, Mori M, Yamaguchi K, Ito S, Iwata N, Masunaga K, Shimojo N, Ariga T, Okada K, Takei S. Pediatric Rheumatology Association of Japan recommendation for vaccination in pediatric rheumatic diseases. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25:335-343. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Uziel Y, Moshe V, Onozo B, Kulcsár A, Tróbert-Sipos D, Akikusa JD, Salviato Pileggi G, Maritsi D, Kasapcopur O, Rodrigues M, Smerla R, Rigante D, Makay B, Atsali E, Wulffraat N, Toplak N; PReS working party of Vaccination Study Group. Live attenuated MMR/V booster vaccines in children with rheumatic diseases on immunosuppressive therapy are safe: Multicenter, retrospective data collection. Vaccine. 2020;38:2198-2201. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 8.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Heijstek MW, Kamphuis S, Armbrust W, Swart J, Gorter S, de Vries LD, Smits GP, van Gageldonk PG, Berbers GA, Wulffraat NM. Effects of the live attenuated measles-mumps-rubella booster vaccination on disease activity in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;309:2449-2456. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Alfayadh NM, Gowdie PJ, Akikusa JD, Easton ML, Buttery JP. Vaccinations Do Not Increase Arthritis Flares in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Study of the Relationship between Routine Childhood Vaccinations on the Australian Immunisation Schedule and Arthritis Activity in Children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Int J Rheumatol. 2020;2020:1078914. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Tinsley A, Navabi S, Williams ED, Liu G, Kong L, Coates MD, Clarke K. Increased Risk of Influenza and Influenza-Related Complications Among 140,480 Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019;25:369-376. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 95] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 19.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Martinelli M, Giugliano FP, Strisciuglio C, Urbonas V, Serban DE, Banaszkiewicz A, Assa A, Hojsak I, Lerchova T, Navas-López VM, Romano C, Sladek M, Veres G, Aloi M, Kucinskiene R, Miele E. Vaccinations and Immunization Status in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Multicenter Study From the Pediatric IBD Porto Group of the ESPGHAN. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020;26:1407-1414. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Crawford NW, Catto-Smith AG, Oliver MR, Cameron DJ, Buttery JP. An Australian audit of vaccination status in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011;11:87. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Alexeeva EI, Soloshenko MA, Dvoryakovskaya TM, Lomakina OL, Denisova RV, Isaeva KB, Karasyova AV. Efficacy and Safety of Immunization With Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine in Children With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Preliminary Results of a Prospective Open-Label Study. Current Pediatrics. 2017;16:142-147. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 50. | Alexeeva EI, Vankova DD, Dvoryakovskaya TM, Isaeva KB, Denisova RV, Mamutova AV, Chomakhidze AM, Radygina TV, Zubkova IV, Tkachenko NE, Fetisova AN, Lomakina OL, Orlova YO, Kurdup MK, Gautier MS, Krekhova EA, Shingarova MS, Galkina OP. Efficacy of Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine (13-valent, Adsorbed) in Patients with Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Treated with Genetically Engineered Biologic Drugs (Tocilizumab or Canakinumab): Prospective Cohort Study. Current Pediatrics. 2020;19:190-199. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 51. | Sitte J, Frentiu E, Baumann C, Rousseau H, May T, Bronowicki JP, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Lopez A. Vaccination for influenza and pneumococcus in patients with gastrointestinal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease: A prospective cohort study of methods for improving coverage. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49:84-90. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 52. | Melmed GY, Ippoliti AF, Papadakis KA, Tran TT, Birt JL, Lee SK, Frenck RW, Targan SR, Vasiliauskas EA. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease are at risk for vaccine-preventable illnesses. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1834-1840. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 235] [Cited by in RCA: 245] [Article Influence: 12.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Huth K, Benchimol EI, Aglipay M, Mack DR. Strategies to Improve Influenza Vaccination in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Through Education and Access. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21:1761-1768. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |