Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Pediatr. Jun 9, 2025; 14(2): 101080
Published online Jun 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i2.101080
Published online Jun 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i2.101080
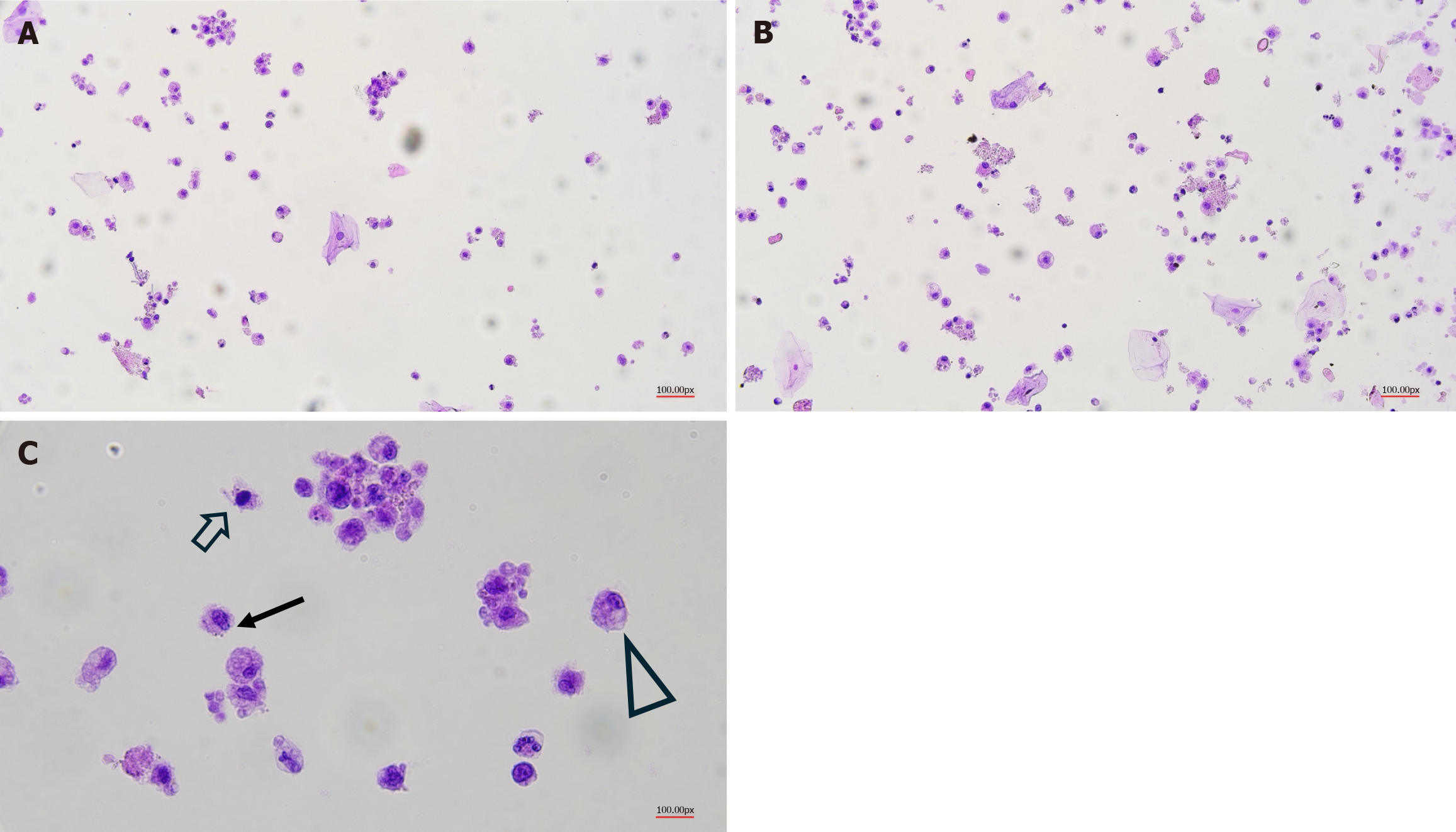
Figure 1 Different example of cells isolated with from fresh human milk.
A-C: These cells, fixed and stained using our cytological methods routinely used in our laboratories, are characterized by different morphological aspects, underling the presence of a heterogeneous cell population. Briefly, breast milk samples were recruited from six healthy volunteers. The experimental analysis were authorized by the Comitato Etico Indipendente Ospedaliero (Università di Cagliari; Prot. PG/2022/795). Breast milk cells were isolated from fresh milk, diluted with an equal volume of Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4; Gibco) and centrifugated at 810 g for 20 minutes at 20 °C. The fat layer and liquid were removed, while the cell pellet was washed twice with Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline. The pellet was fixed with ThinPrep solution (Hologic, Inc. www.hologic.com) and the cell samples were processed for immunocytochemistry analysis with a ThinPrep 5000 Processor. Different arrows highlight possible different cell types. Solid arrow: Stem cells; Hollow arrow: Immune cells; Triangle: Milk-secretory cells.
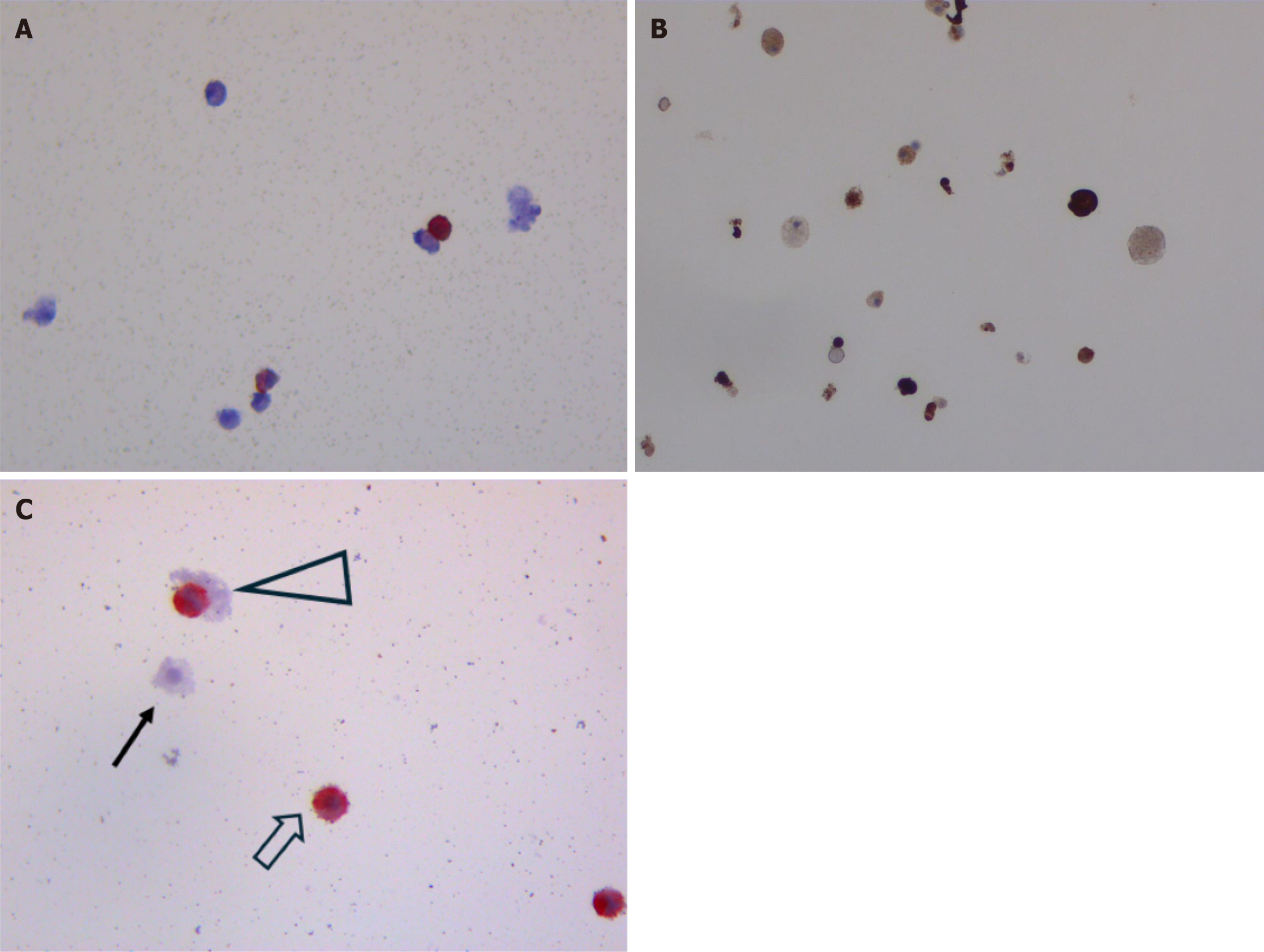
Figure 2 Immunocytochemistry staining.
Different arrows highlight possible different cell types. Different arrows highlight possible different cell types. Antibodies for CD44 (SP37, Ventana 790-4537), CD133 (polyclonal, biorbyt, orb99113, 1:100), CD45 (LCA, 2B11 and PD7/26, Ventana 760-4279), Ki-67 (30-9, Ventana 790-4286), Wt1 (6F-H2, Cell Marque 760-4397), nestin (10C2, Sigma-Aldrich), Nanog (polyclonal, Abcam, ab80892, 1:100), OCT4 (MRQ-10, Cell Marque 760-4621), SOX2 (SP76, Cell Marque 760-4621), CK5 (SP27, Cell Marque 760-4935), CD34 (QBEnd/10, Ventana 790-2927), P63 (4A4, Ventana 790-4509), Thymosin β4 (Tβ4; polyclonal, abcam, ab14334, 1: 1000) and CK14 (SP23, Cell Marque 760-4805) were used for immunocytochemistry. Sample preparation was performed using standard validated cytologic protocols (ThinPrep Preserv Cyt solution, ThinPrep 5000 system, https://www.hologic.com). The Ventana automated stains system (http://diagnostics.roche.com) was used for immunocytochemistry staining and a qualitative analysis was performed by three different pathologists comparing the reactivity of different markers in slides of the same sample using an individual scoring system (morphological parameters, % of number of stained cells, area, and intensity of the stain). A: Immunocytochemistry staining for CD45; B: Immunocytochemistry staining for CD133; C: Immunocytochemistry staining for CD44. Solid arrow: Negative stem cell; Hollow arrow and triangle: Positive stem cell.
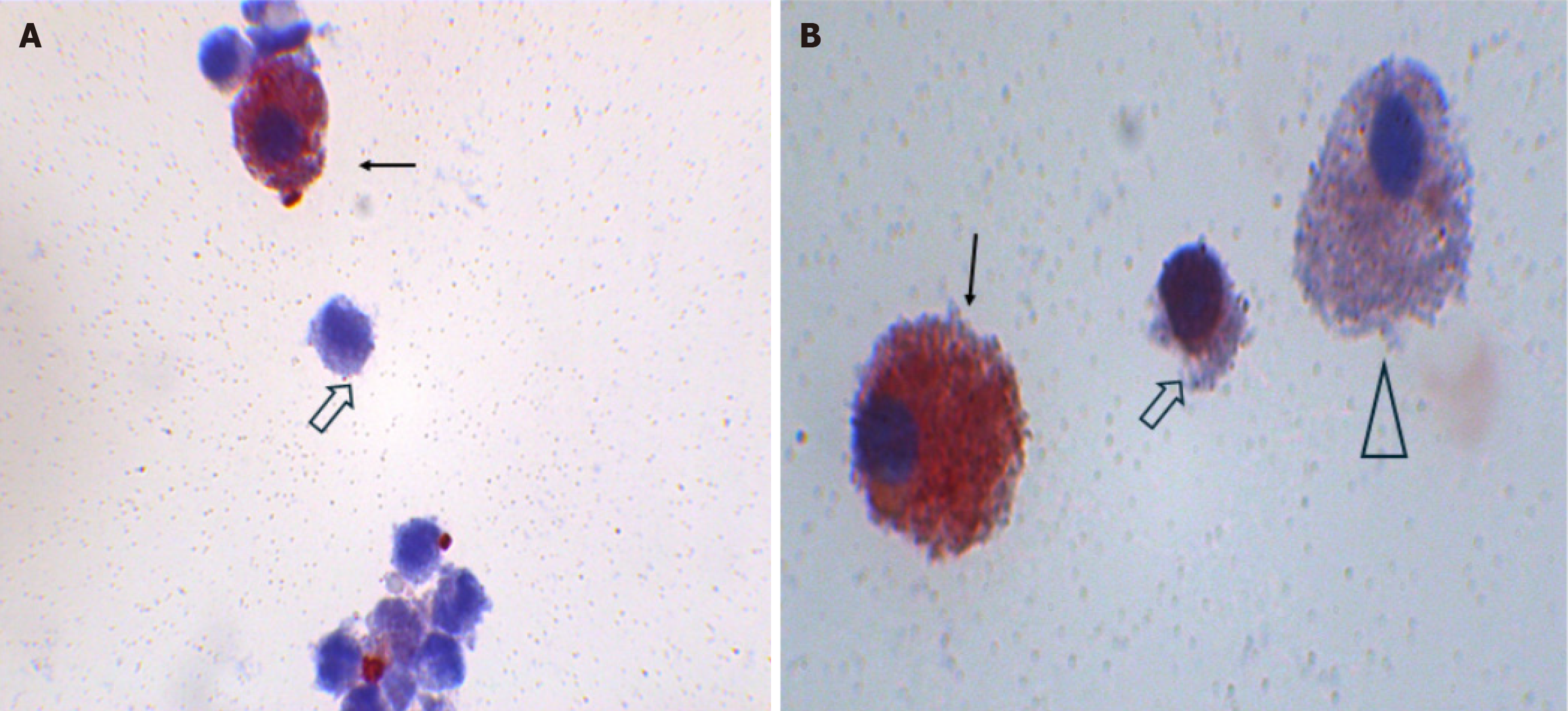
Figure 3 A and B: ISL1 immunocytochemistry staining of some fresh human breast milk cells isolated using a ThinPrep™ CytoLyt™ solution and stained as described previously.
Solid arrow: Positive stem cells; Hollow arrow and triangle: Negative stem cell.
- Citation: Faa G, Pichiri G, Coni P, Dessì A, Fraschini M, Fanos V. They will be famous: Multipotent stem cells in breast milk. World J Clin Pediatr 2025; 14(2): 101080
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v14/i2/101080.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v14.i2.101080