Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stomatol. Feb 20, 2015; 4(1): 22-28
Published online Feb 20, 2015. doi: 10.5321/wjs.v4.i1.22
Published online Feb 20, 2015. doi: 10.5321/wjs.v4.i1.22
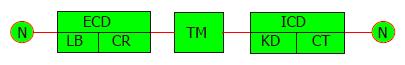
Figure 1 Epidermal growth factor receptor structure: Extracellular domain, transmembrane pass, intracellular domain, ligand binding, cysteine-rich domains.
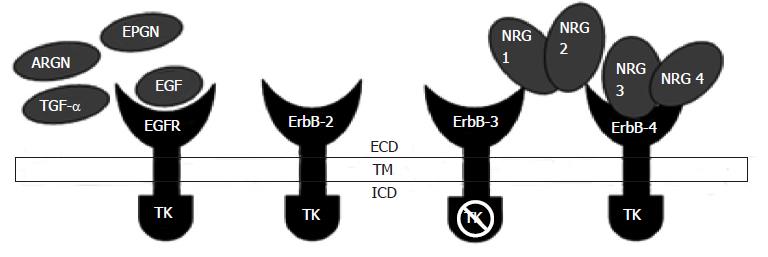
Intracellular domain includes the kinase domain and cytoplasmic tail. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ECD: Extracellular domain; TM: Transmembrane pass; ICD: Intracellular domain; ARGN: Amphiregulin; EPGN: Epiregulin; TGF-α: Transforming growth factor alpha; TK: Tyrosine kinase; NRG: Neuregulin.
Figure 2 Epidermal growth factor receptor and its major ligands epidermal growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha, neuregulin, amphiregulin and epiregulin.
ECD: Extracellular domain; TM: Transmembrane pass; ICD: Intracellular domain; LB: Ligand binding; CR: Cysteine-rich; KD: Kinase domain; CT: Cytoplasmic tail.
- Citation: Mohan BC, Angadi PV. Unraveling the role of epidermal growth factor receptor in oral lesions: Key to non surgical treatment modes. World J Stomatol 2015; 4(1): 22-28
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6263/full/v4/i1/22.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5321/wjs.v4.i1.22