Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Orthop. Jun 18, 2022; 13(6): 564-573
Published online Jun 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i6.564
Published online Jun 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i6.564
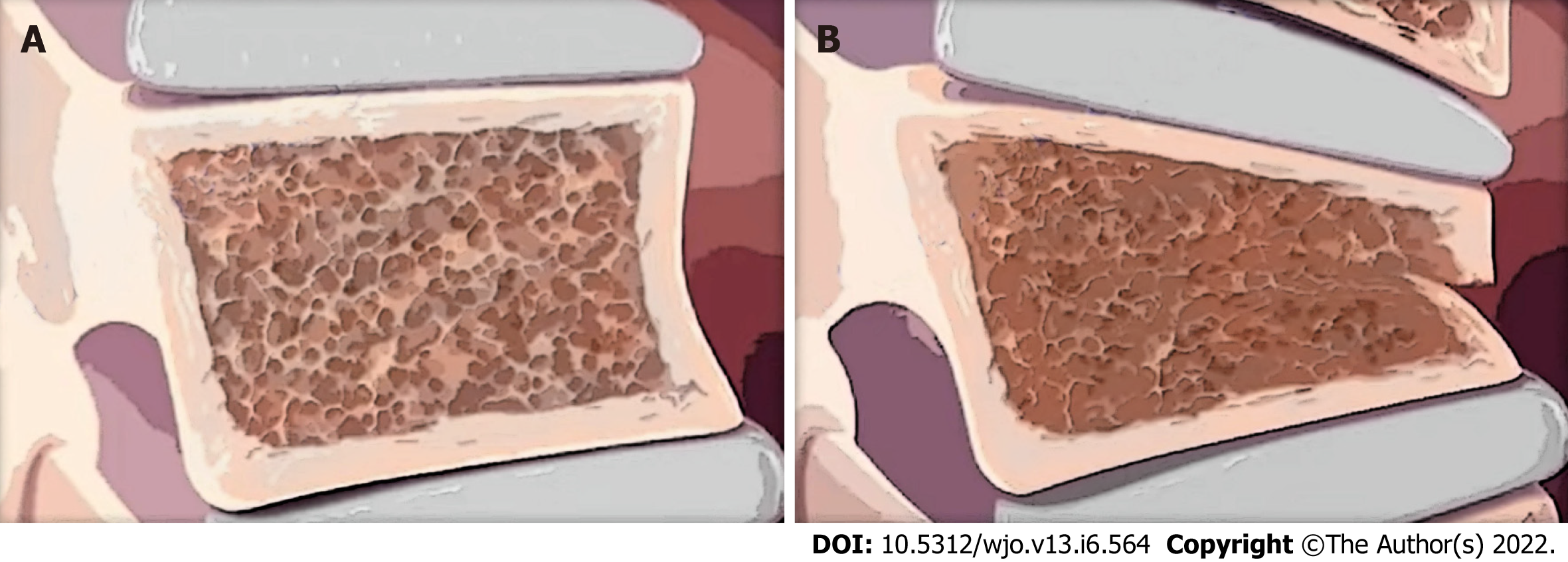
Figure 1 Osteoporotic vertebra.
A: Osteoporotic vertebra before a compression fracture; B: Osteoporotic vertebra after a compression fracture. Note the wedge shape of the vertebral body, which can cause kyphotic deformity.
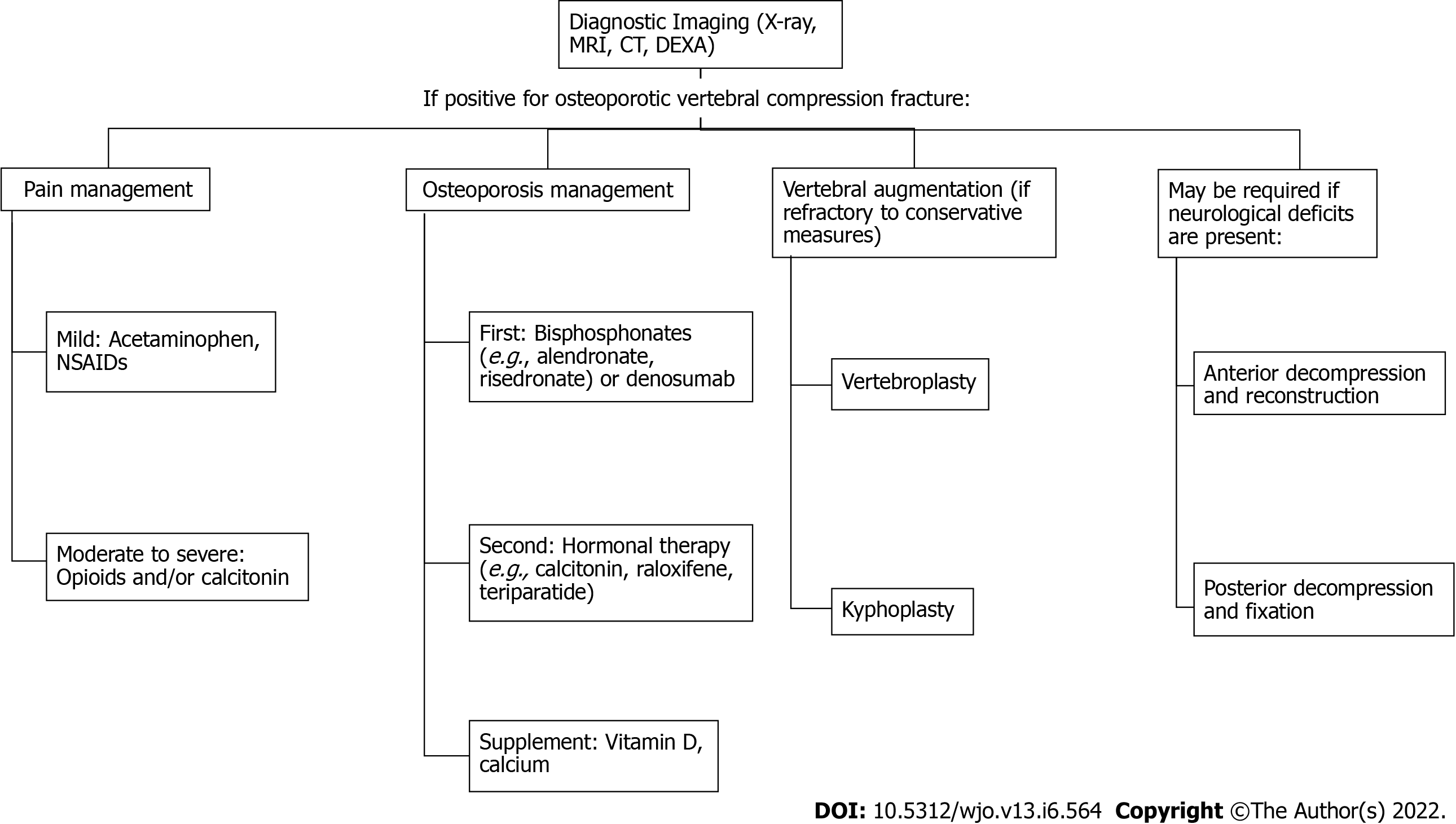
Figure 2 Treatment steps for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.
NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; CT: Computed tomography; DEXA: Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry.
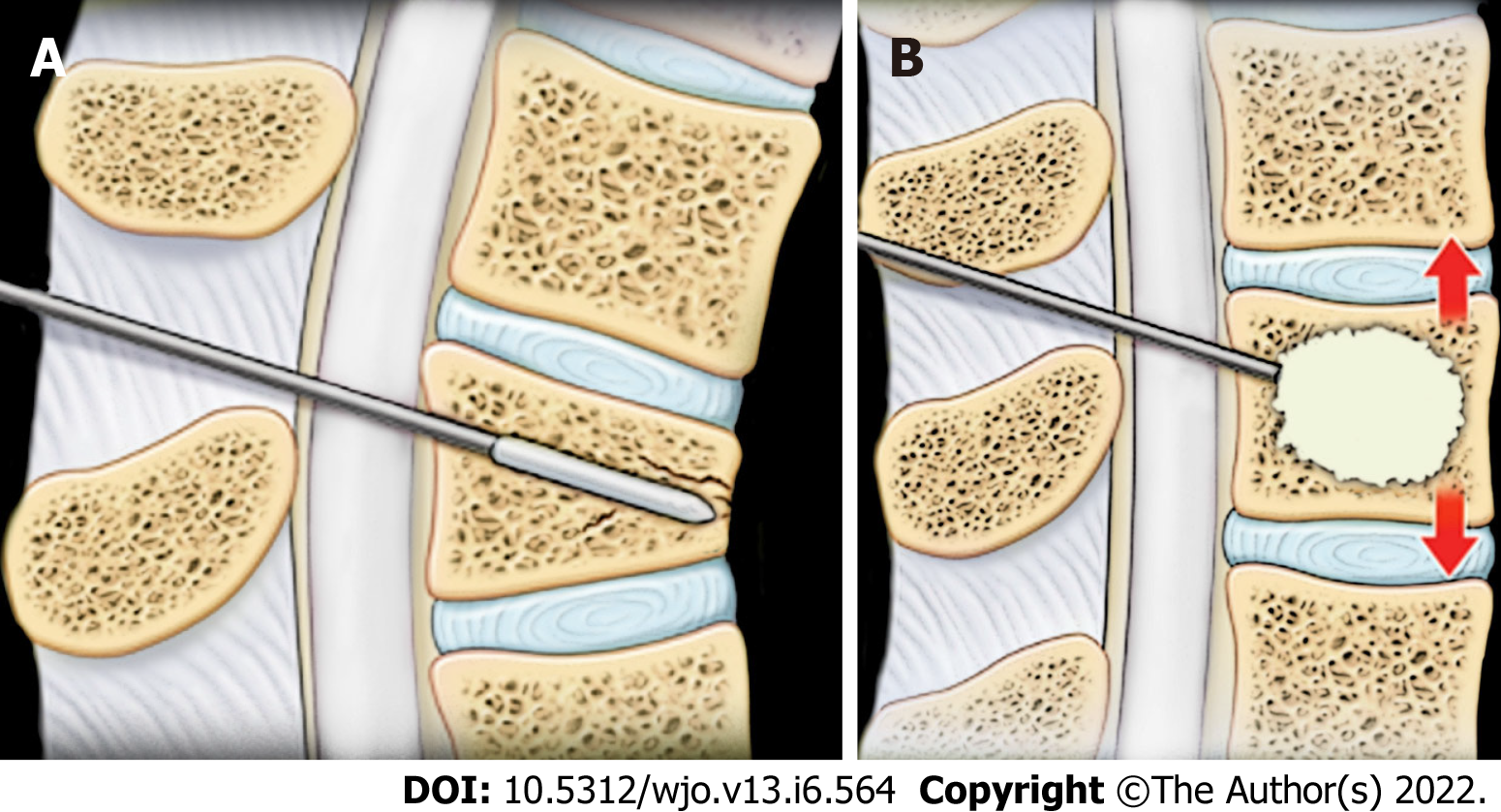
Figure 3 Kyphoplasty.
A: Kyphoplasty involves inserting a balloon into the vertebral body with compression fractures; B: Kyphoplasty involves inflating a balloon to reduce the fractures and injecting cement into the cavity to fix the fractures.
- Citation: Patel D, Liu J, Ebraheim NA. Managements of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A narrative review. World J Orthop 2022; 13(6): 564-573
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v13/i6/564.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v13.i6.564