Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Orthop. May 18, 2022; 13(5): 503-514
Published online May 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i5.503
Published online May 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i5.503
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the study.
PJI: Prosthetic joint infection.
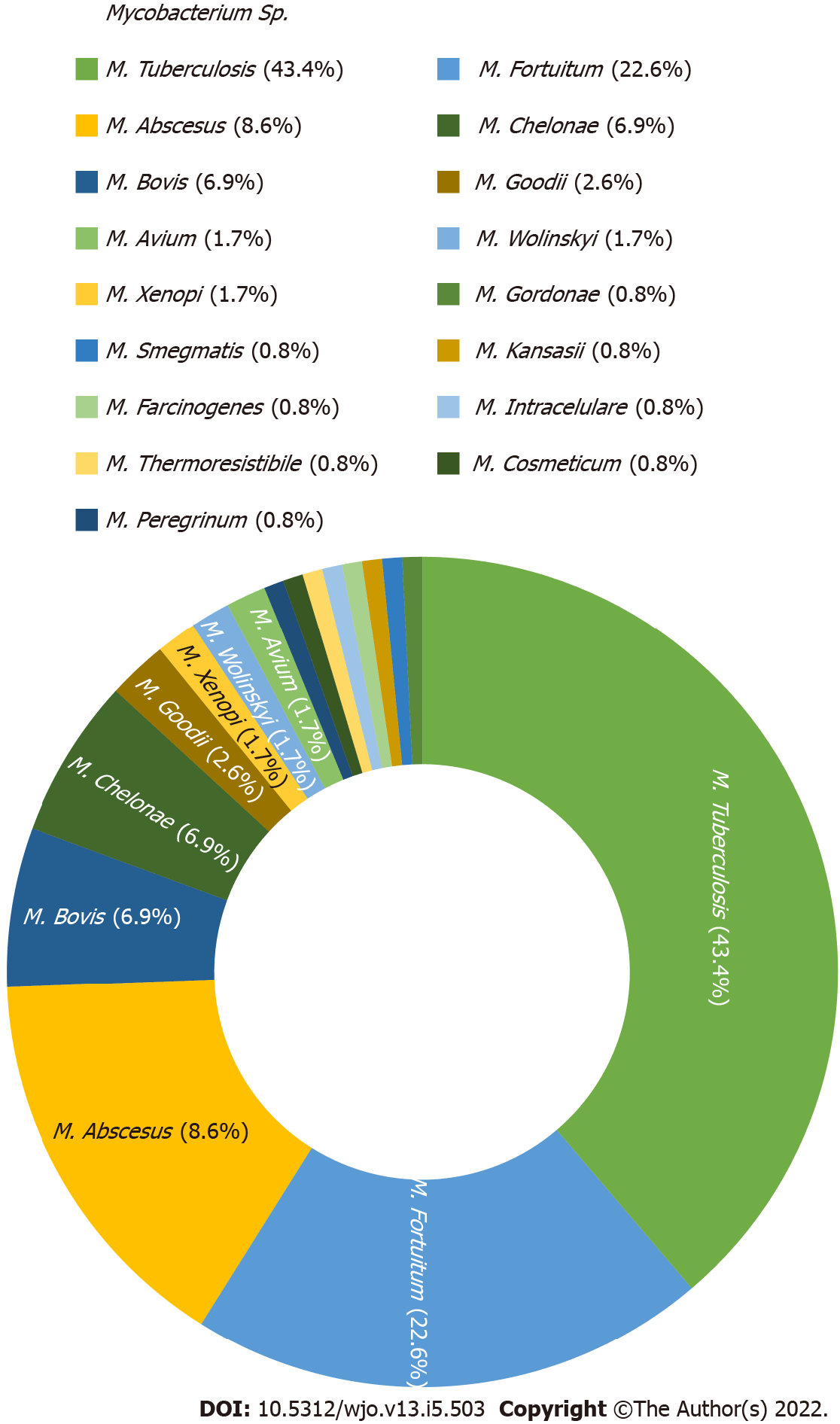
Figure 2 Distribution of Mycobacterium strains as the cause of hip/knee prosthetic joint infection (n = 115).
M.: Mycobacteria.
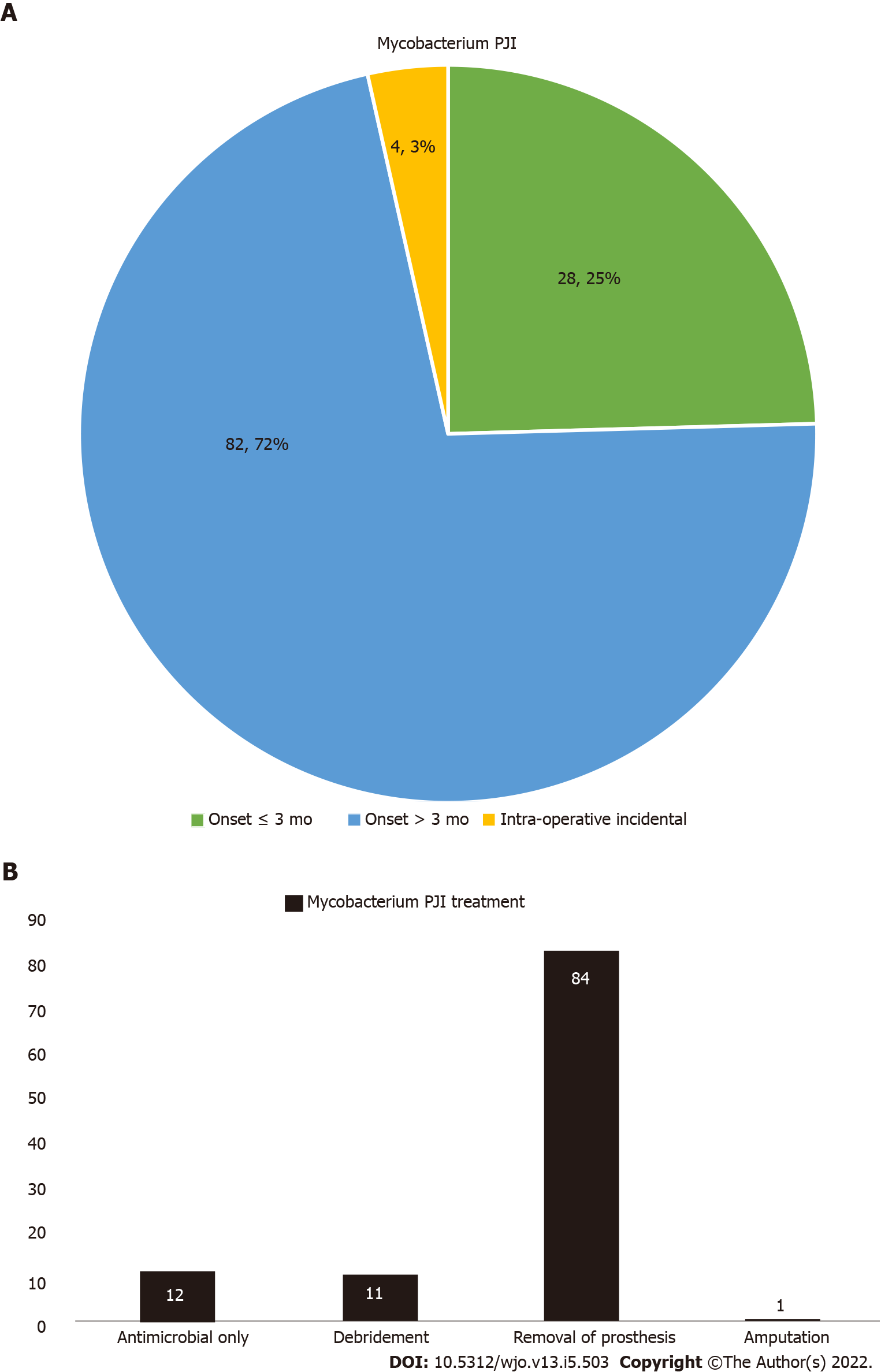
Figure 3 Distribution of overall Mycobacterium prosthetic joint infection cases.
A: By onset of infection after index surgery (n = 114); B: By treatment (n = 108). PJI: Prosthetic joint infection.
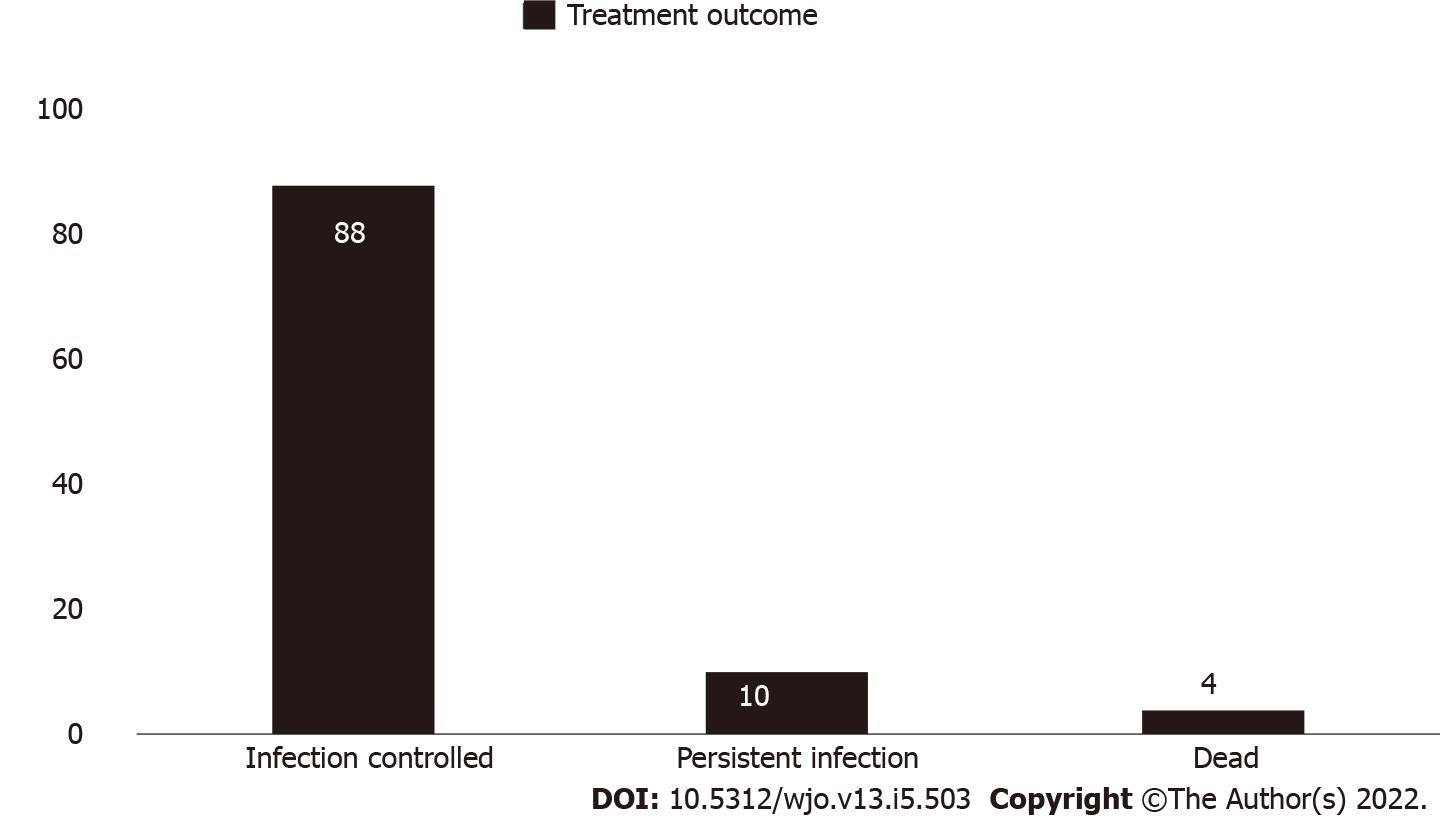
Figure 4 Distribution of overall final outcome of Mycobacterium prosthetic joint infection treatments (n = 102).
- Citation: Santoso A, Phatama KY, Rhatomy S, Budhiparama NC. Prosthetic joint infection of the hip and knee due to Mycobacterium species: A systematic review. World J Orthop 2022; 13(5): 503-514
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v13/i5/503.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v13.i5.503