Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Clin Oncol. Aug 10, 2013; 4(3): 75-81
Published online Aug 10, 2013. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v4.i3.75
Published online Aug 10, 2013. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v4.i3.75
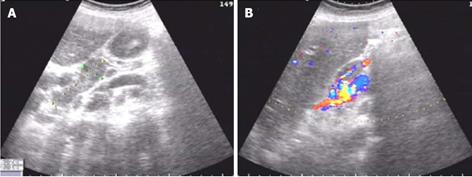
Figure 1 Ultrasound endoscopy showed cholecystitis and several enlarged abdominal lymph nodes.
A: The enlarged lymph nodes were found in the porta; the lymph nodes showed a syncretic image with a clear boundary and uniform echo; B: A rich blood flow signal was observed in the lymph nodes.
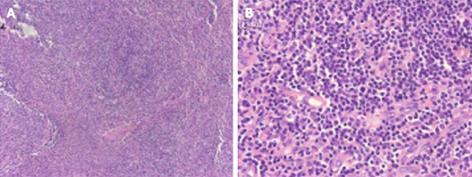
Figure 2 Photomicrograph of biopsy specimens of peripheral lymph nodes.
Significant inflammatory cell infiltration was observed; however, tumor cells, such as lymphoma cells, were not found in the specimens. A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, × 100; B: HE staining, × 400.
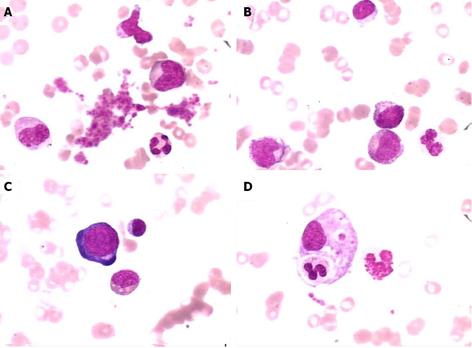
Figure 3 Representative images of bone marrow examination.
The images showed anemia with marked red cell aplasia and the remarkable proliferation of granulocytes and megakaryocytes (Wright and Giemsa stain, × 1000). A: platelet; B: phagocyte; C: pronormoblast; D: megakaryocyte.
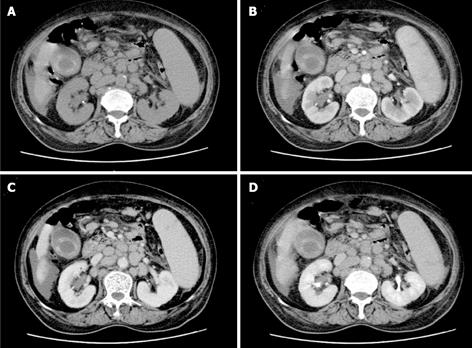
Figure 4 Abdominal computed tomography scan revealed a fuzzy peritoneal cavity and multiple enlarged portal peripheric lymph nodes with cholecystitis.
A: Plain computed tomography (CT) scan image; B: CT image in the arterial phase of contrast enhancement; C: CT image in the portal venous phase of contrast enhancement; D: CT image in the parenchymal phase of contrast enhancement.
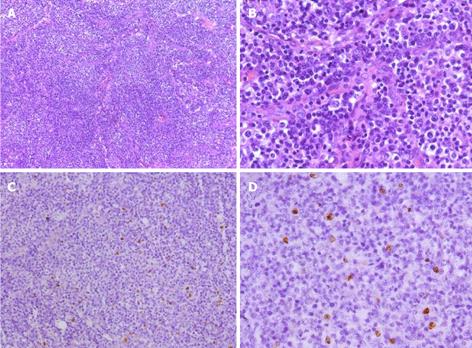
Figure 5 Photomicrograph of biopsy specimens in the celiac lymph nodes.
The normal architecture was lost, except for the presence of occasional depleted follicles with concentrically arranged follicular dendritic cells, and the architecture was effaced by polymorphic infiltrate with marked vascular proliferation. A weakly positive nuclear labeling of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small nuclear RNA was observed in the celiac lymph nodes by in situ hybridization. A: Hematoxylin and eosin (H and E) staining, × 100; B: H and E staining, × 400. C: In situ hybridization staining for Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small nuclear RNA, × 100; D: In situ hybridization staining, × 400.
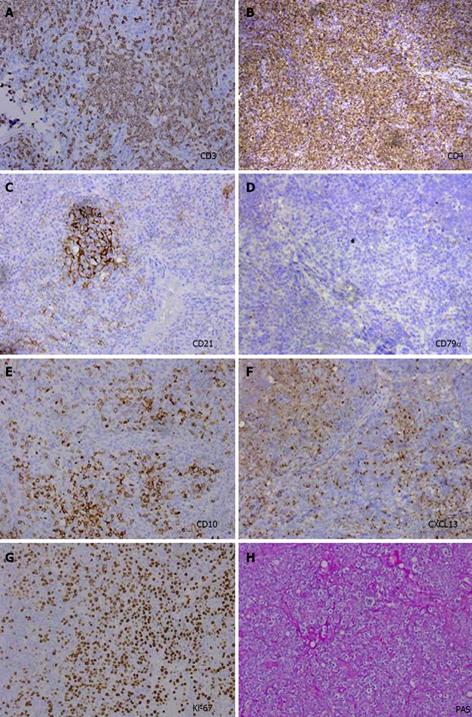
Figure 6 Immunohistochemical characteristics of the celiac lymph nodes.
A: Neoplastic cells showed strong staining for cytoplasmic CD3; B: Strong staining for CD4; C: Strong vascular endothelial cell staining for CD21; D: Negative staining for CD79α; E: Strong staining for CD10; F: Moderate positive staining for CXCL13; G: Strong staining for Ki-67 over 70%; H: Strong staining for PAS.
- Citation: Tao J, Zheng FP, Tian H, Lin Y, Li JZ, Chen XL, Chen JN, Shao CK, Wu B. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma-associated pure red cell aplasia with abdominal pain. World J Clin Oncol 2013; 4(3): 75-81
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v4/i3/75.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v4.i3.75