Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Aug 24, 2024; 15(8): 1002-1020
Published online Aug 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i8.1002
Published online Aug 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i8.1002
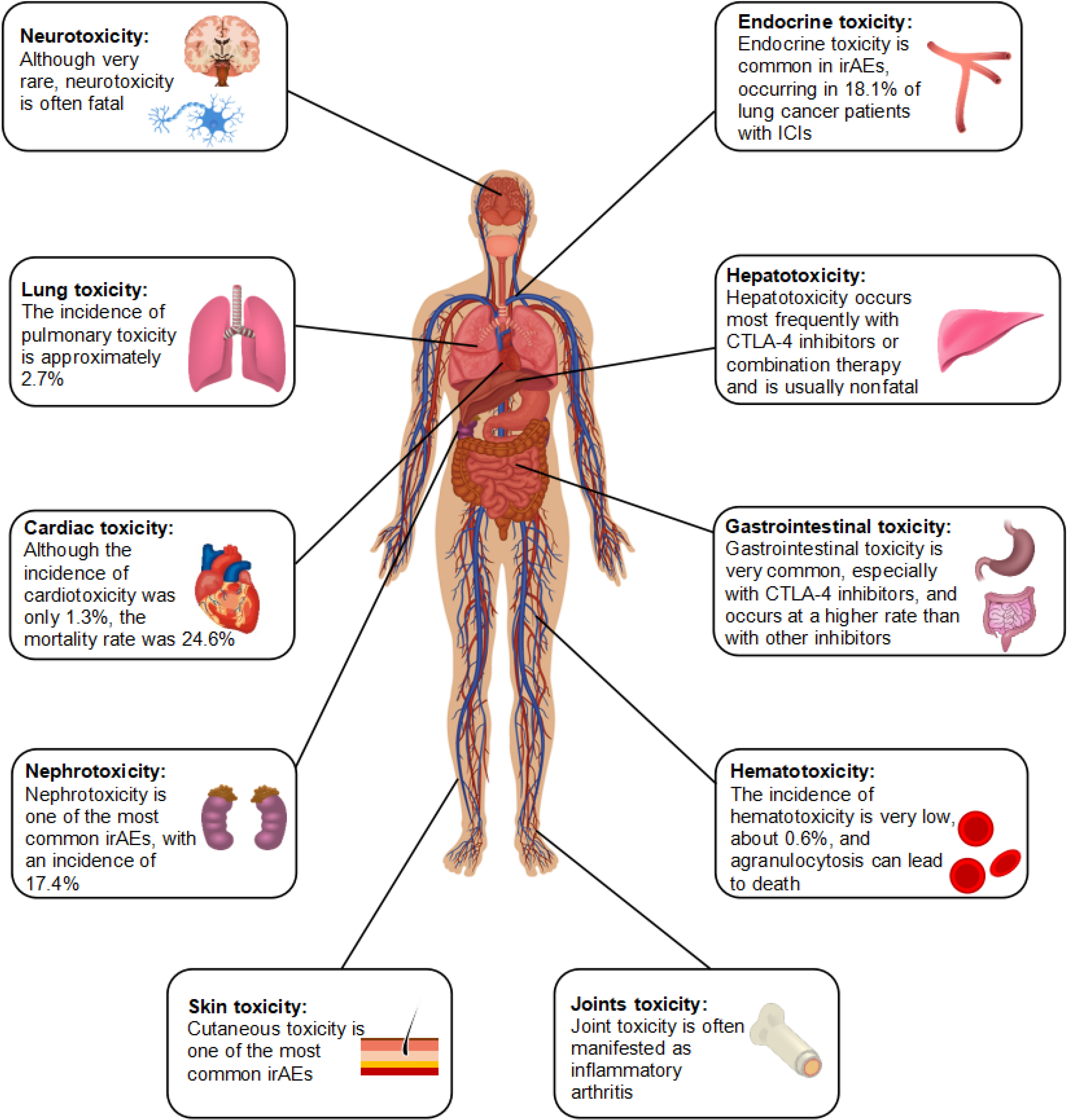
Figure 1 Immune-related adverse events in different organs.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors therapy causes immune-related adverse events primarily in the brain, lungs, heart, kidneys, skin, joints, endocrine system, liver, intestines, and blood. irAEs: Immune-related adverse events.
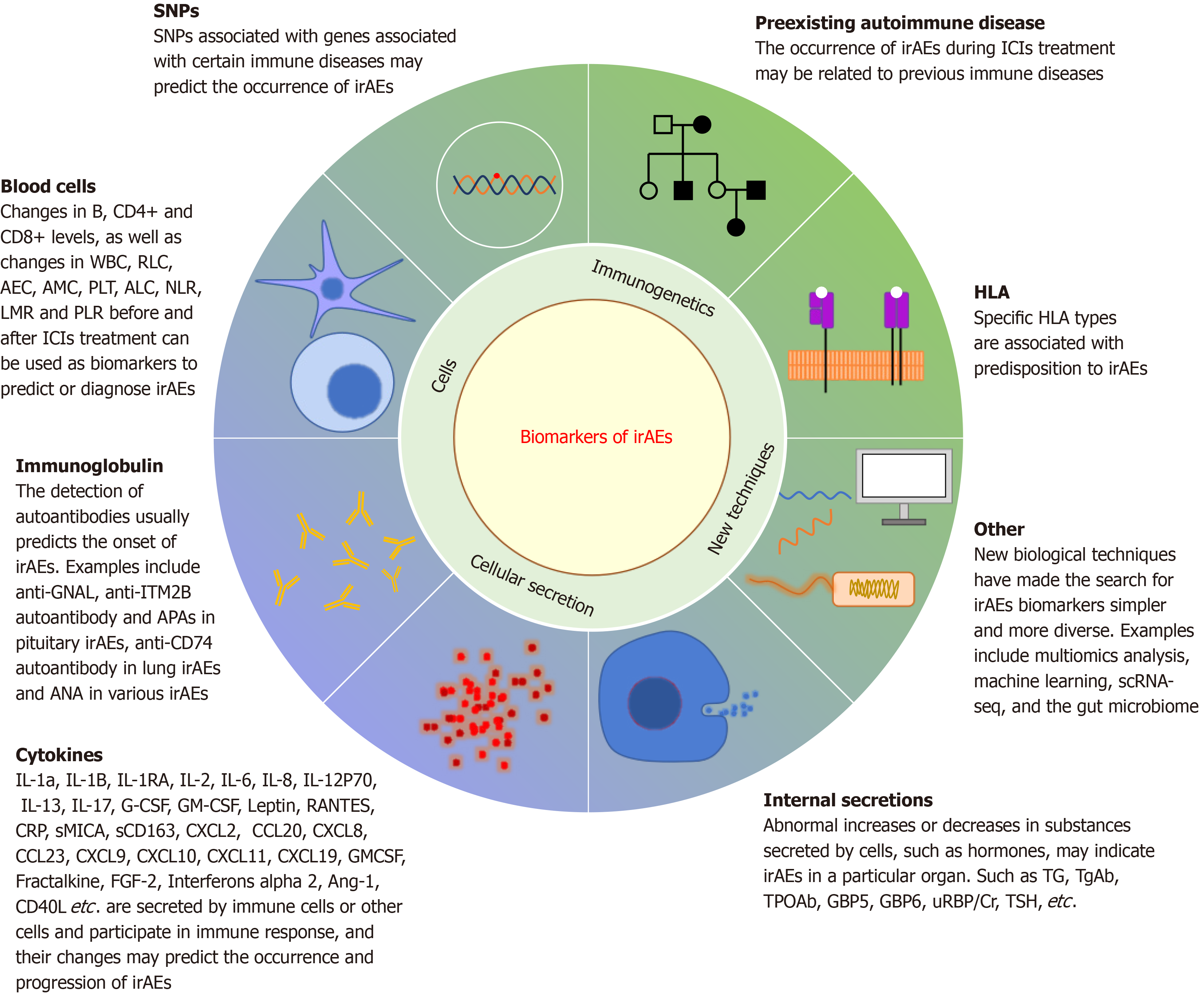
Figure 2 The biomarkers of immune-related adverse events.
Biomarkers encompass cellular components, secretions, and immunogenetics, with emerging technologies poised to unveil novel biomarkers. Cellular biomarkers primarily entail variations in blood cell counts and ratios, while cellular secretions comprise cytokines, hormones, and antibodies. Immunogenetics focuses on identifying genetic predispositions to immune-related adverse events (irAE) from a genetic perspective. These categories collectively offer insights into potential biomarkers and genetic factors associated with irAE susceptibility. WBC: White blood cell count; RLC: Relative lymphocyte count; AEC: Absolute eosinophil count; AMC: Absolute monocyte count; PLT: Platelet count; ALC: Absolute lymphocyte count; NLR: Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio; LMR: Lymphocyte/monocyte ratio; PLR: Platelet/lymphocyte ratio; CRP: C-reactive protein; sMICA: Soluble major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related protein A; TG: Thyroglobulin; GBP5: Guanylate binding protein 5; GBP6: Guanylate binding protein 6; uRBP/Cr: Urine retinol binding protein/urine creatinine; APAs: Anti-pituitary antibodies; TSH: Thyroid stimulating hormone; ANA: Antinuclear antibody; scRNA-seq: Single-cell RNA sequencing; irAEs: Immune-related adverse events; ICI: Immune checkpoint inhibitors; IL: Interleukin; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; RANTES: Regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted; sCD: Soluble CD; CXCL: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; CCL: C motif chemokine ligand; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; TgAb: Anti-thyroglobulin antibodies; TPOAb: Thyroid peroxidase antibodies; HLA: Human leukocyte antigen; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphisms.
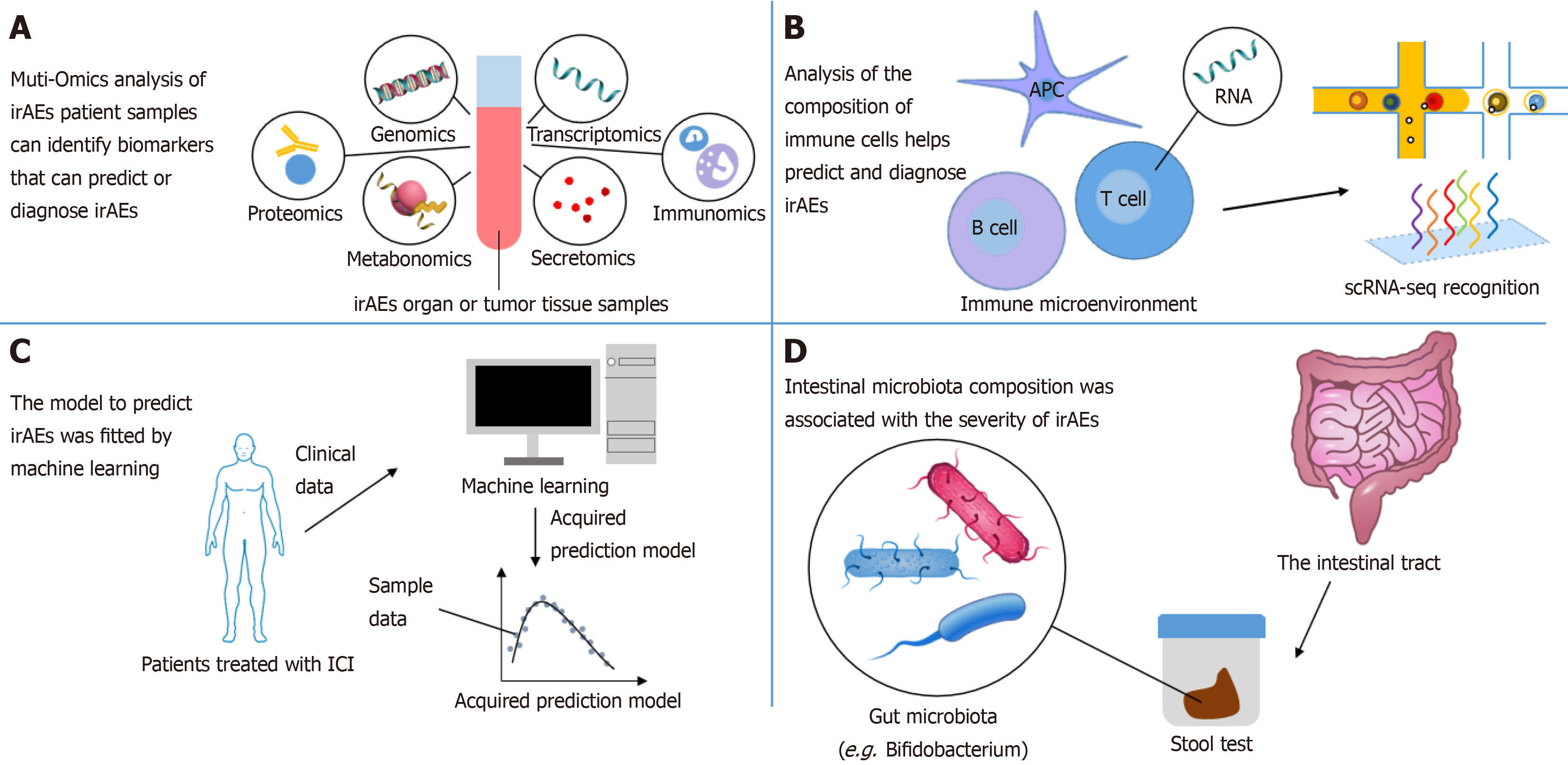
Figure 3 Methods that enable the discovery of new biomarkers.
This includes multiomics analysis, single-cell RNA sequencing, machine learning, and gut microflora analysis. A: Integrated analysis of mutiomics; B: Single-cell RNA sequencing; C: Machine learning; D: Gut microbiota. scRNA-seq: Single-cell RNA sequencing; irAEs: Immune-related adverse events; ICI: Immune checkpoint inhibitors; APC: Antigen-presenting cells.
- Citation: Guo AJ, Deng QY, Dong P, Zhou L, Shi L. Biomarkers associated with immune-related adverse events induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(8): 1002-1020
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i8/1002.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i8.1002