Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2023; 14(12): 620-627
Published online Dec 24, 2023. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i12.620
Published online Dec 24, 2023. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i12.620
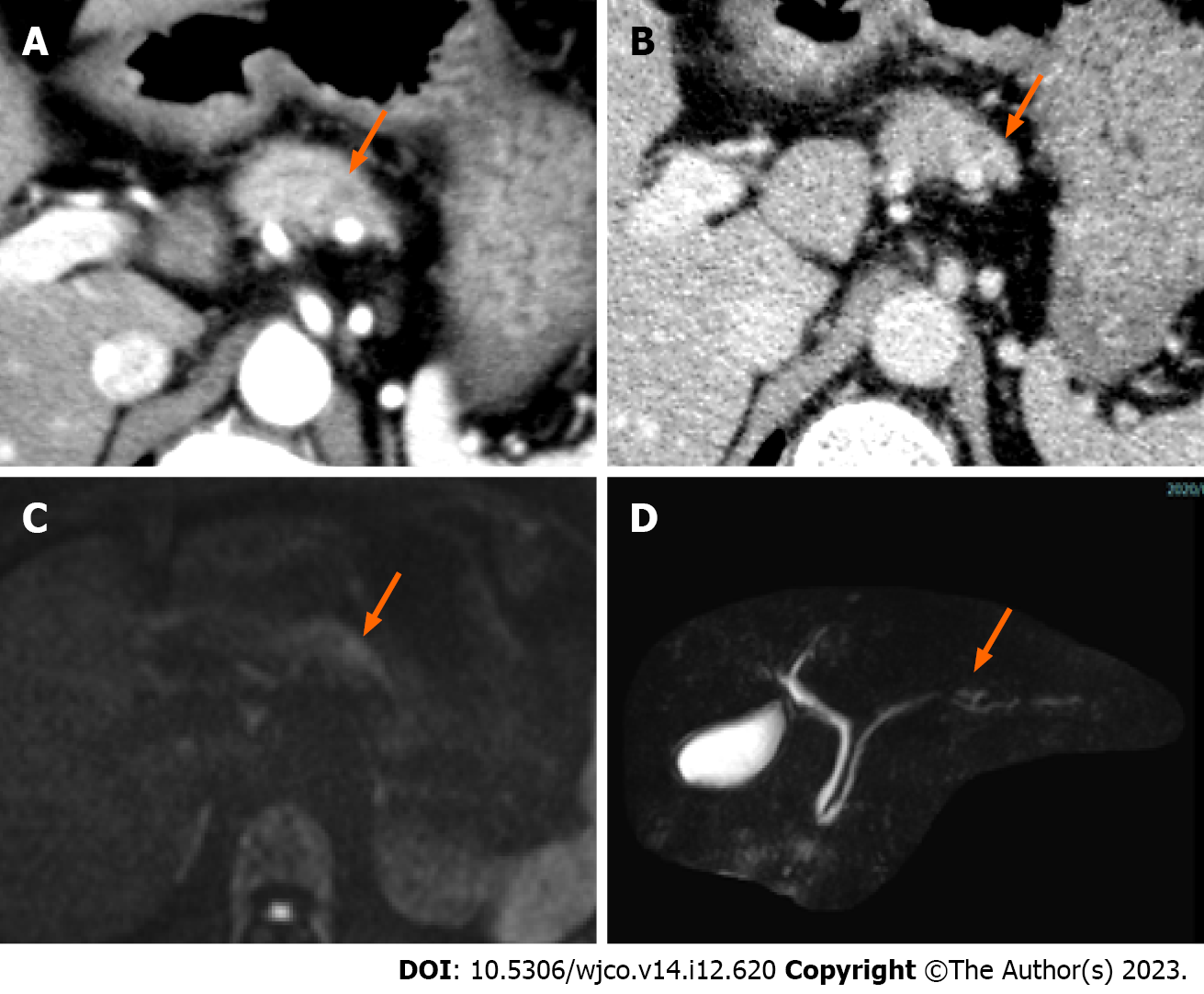
Figure 1 Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
A and B: A 5-mm nodule-like mass was observed in the pancreatic body; the nodule was not contrasted in the arterial phase, arrow (A) and was faintly contrasted in the late phase, arrow (B); C: Diffusion-weighted imaging showed a mild signal increase in the pancreatic body nodule noted on computed tomography, arrow; D: Magnetic resonance pancreatography showed no obvious dilatation or stenosis of the main pancreatic duct, arrow.
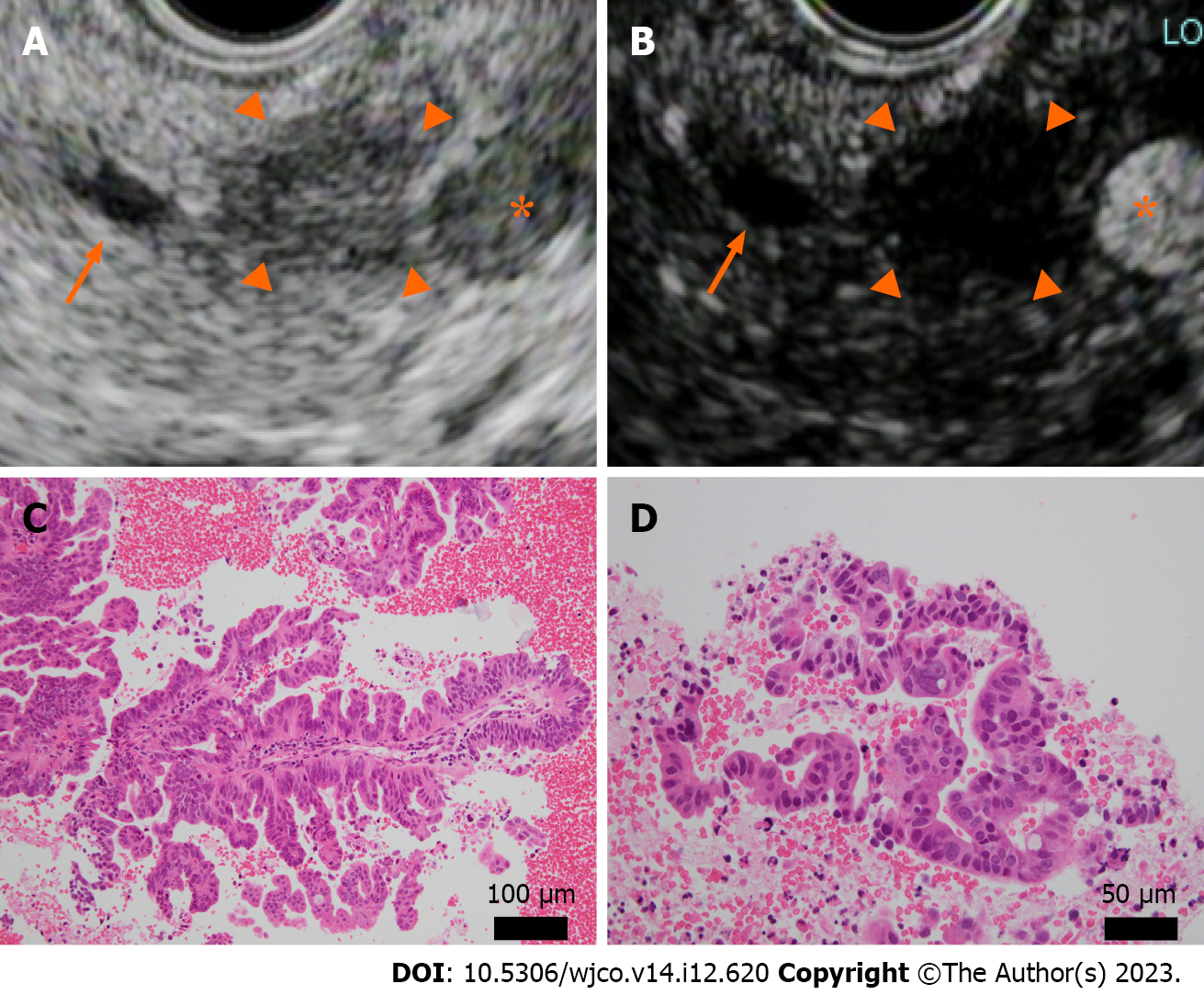
Figure 2 Endoscopic ultrasound and histopathology (hematoxylin-eosin staining) at the time of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration.
A and B: A well-defined hypoechoic mass 10 mm in size was observed in the pancreatic body (A), arrowhead. The main pancreatic duct, arrow; splenic artery, asterisk. The mass was recognized as an oligo-hypoechoic mass with Sonazoid® contrast agent (B), arrowhead; C and D: Atypical epithelium with ductal papillary growth was seen. No intraductal papillary mucinous tumor-like mucus component was present. Original magnification was × 20 (C) and × 40 (D).
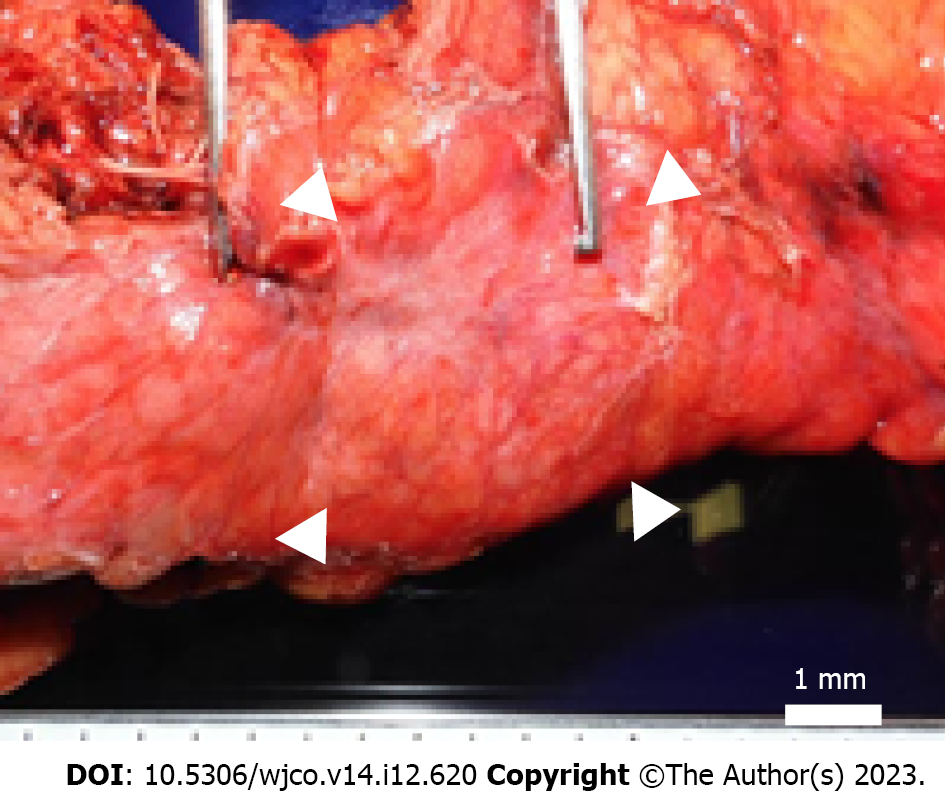
Figure 3 Macroscopic findings.
A well-defined brownish nodule measuring 4 mm × 4 mm bordering the pancreatic body; fibrosis extending to 8 mm × 12 mm in the periphery, arrowheads.
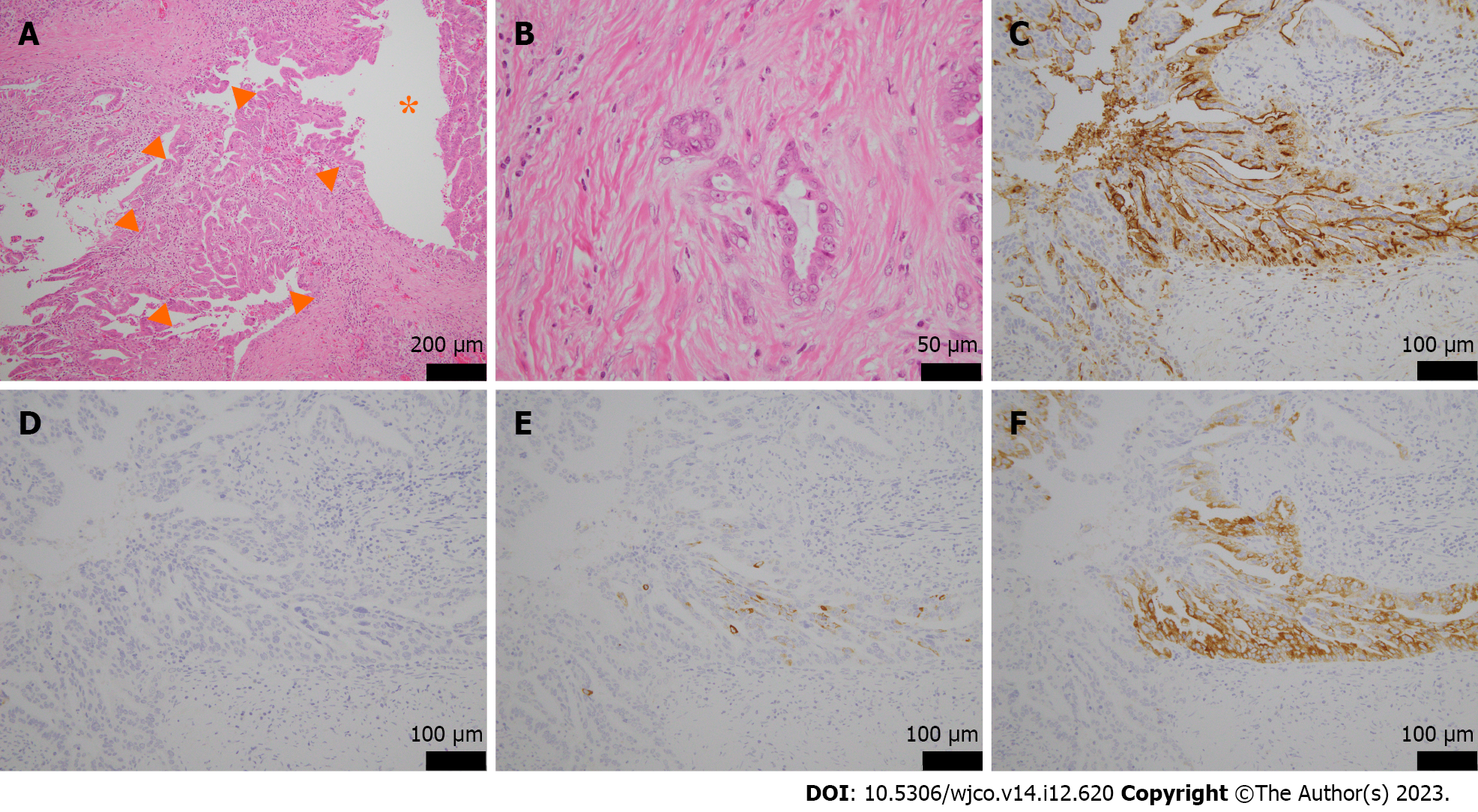
Figure 4 Microscopic and immunohistological findings.
A and B: Original magnification, (× 20, A), and (× 40, B). Tumors with papillary growth with adenoductal structures in the branching pancreatic ducts (asterisk) and some invasive, well-differentiated adenocarcinomas were present, arrowheads. There was no mucus production or cyst formation; C: Mucin 1 was positive; D: Mucin 2 was negative; E: Mucin 5AC was partially positive; F: Mucin 6 was positive. Original magnification was × 40.
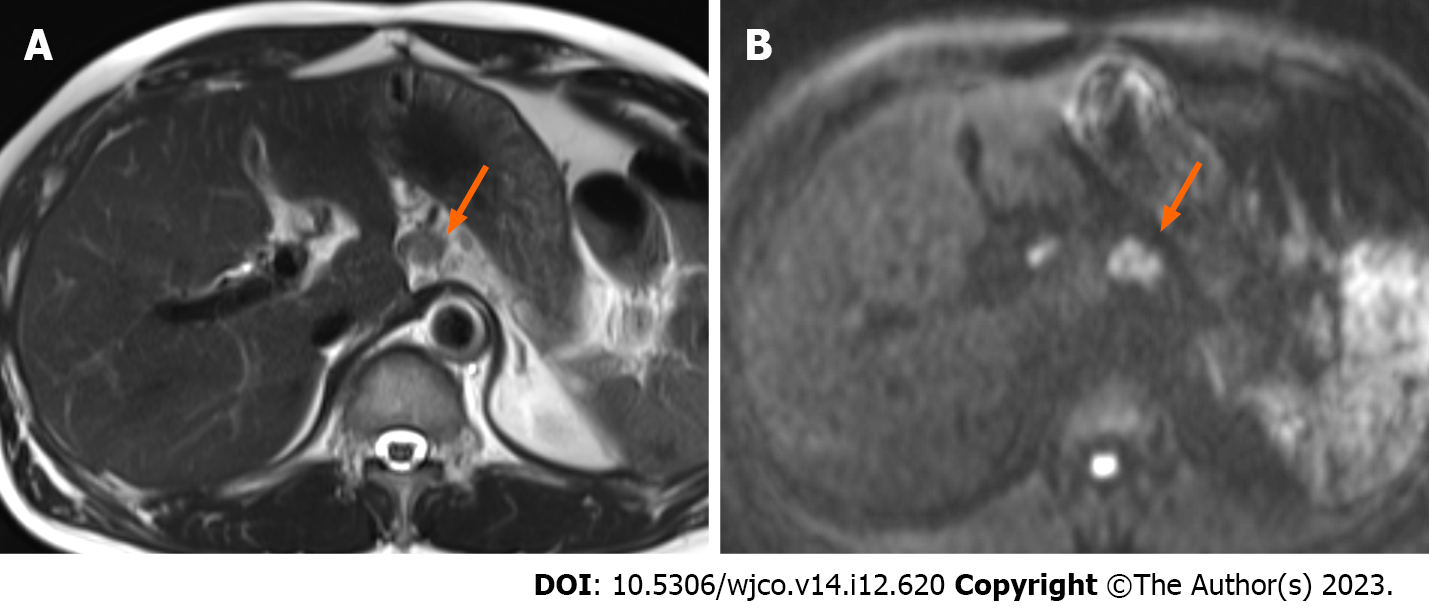
Figure 5 Magnetic resonance imaging 1 year and 10 mo postoperatively.
A: T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging showed a small nodule in the postoperative area; B: Diffusion-weighted imaging showed a high signal in the same area, indicating recurrence in the retroperitoneal lymph nodes, arrow.
- Citation: Yamamoto K, Takada Y, Kobayashi T, Ito R, Ikeda Y, Ota S, Adachi K, Shimada Y, Hayashi M, Itani T, Asai S, Nakamura K. Rapid transformation of branched pancreatic duct-derived intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm into an invasive carcinoma: A case report. World J Clin Oncol 2023; 14(12): 620-627
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v14/i12/620.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v14.i12.620