Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Oncol. Oct 24, 2021; 12(10): 897-911
Published online Oct 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i10.897
Published online Oct 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i10.897
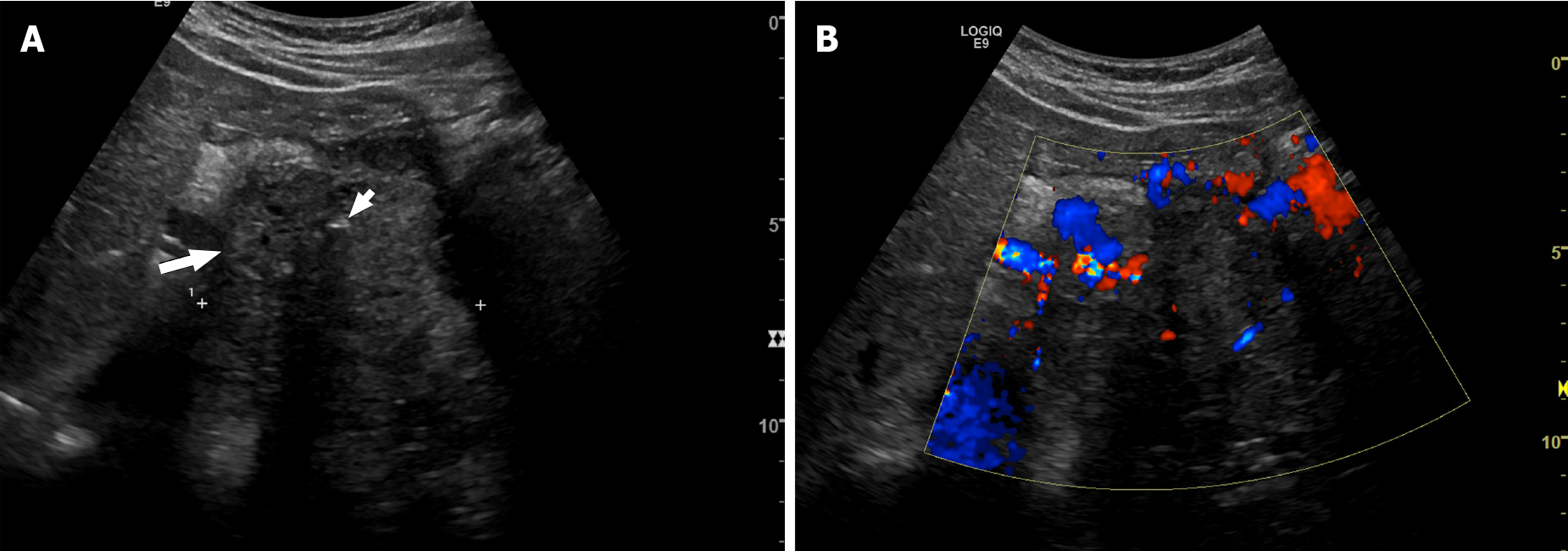
Figure 1 Forty-year-old man with pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm.
A: Axial ultrasound shows a large solid heterogeneous mass (long arrow). Internal calcification (small arrow) is seen, causing posterior acoustic shadowing; B: Doppler ultrasound shows increased vascularity within the pancreatic tumor.
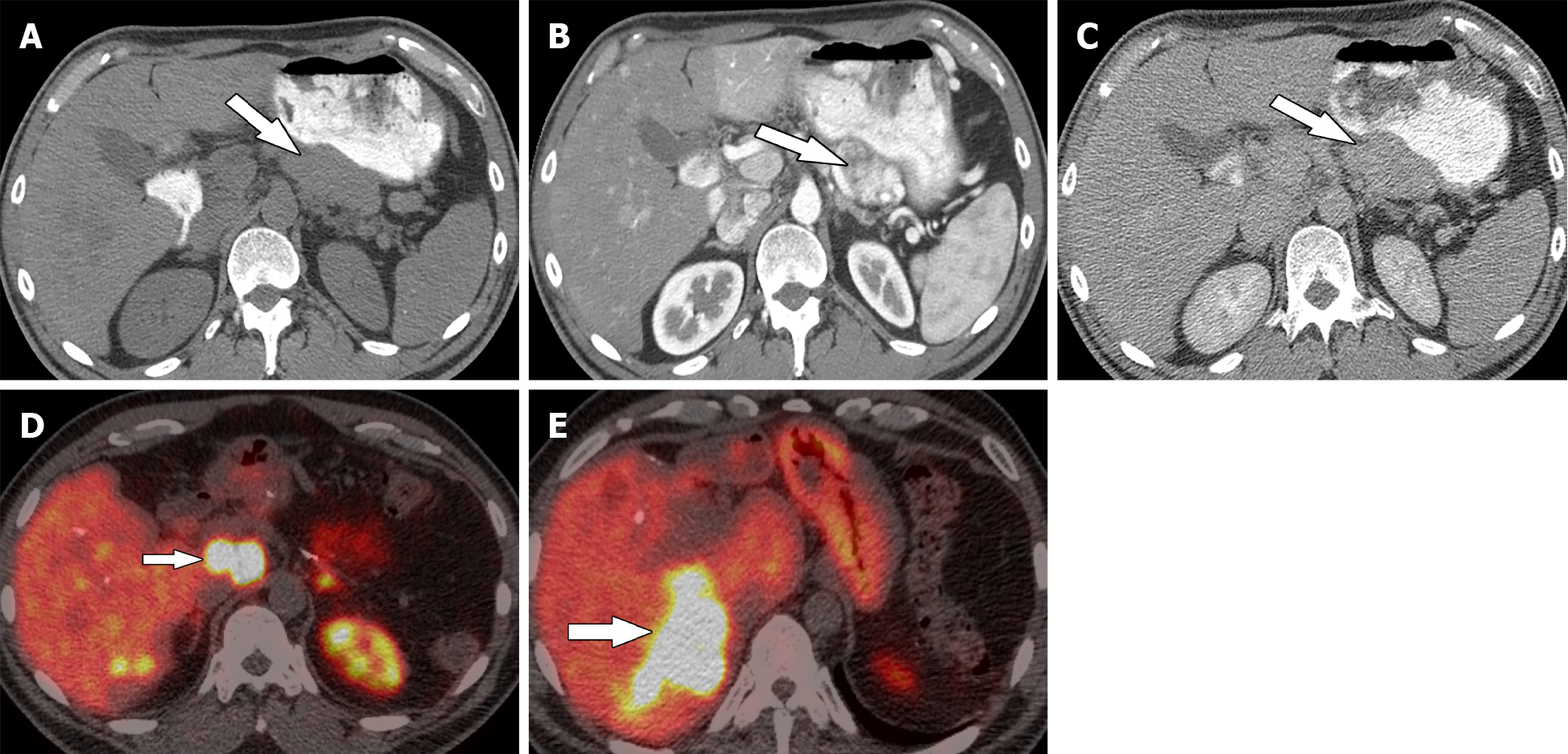
Figure 2 Thirty-eight-year-old woman with pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm.
A: Axial precontrast computed tomography; B and C: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography in the arterial phase (B) and delayed phase (C) demonstrate pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm (arrow). Patient underwent surgical resection; D and E: Follow-up Gallium-68 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid–octreotate positron emission tomography/computed tomography shows metastatic adenopathy (short arrow) and liver metastases (long arrow).
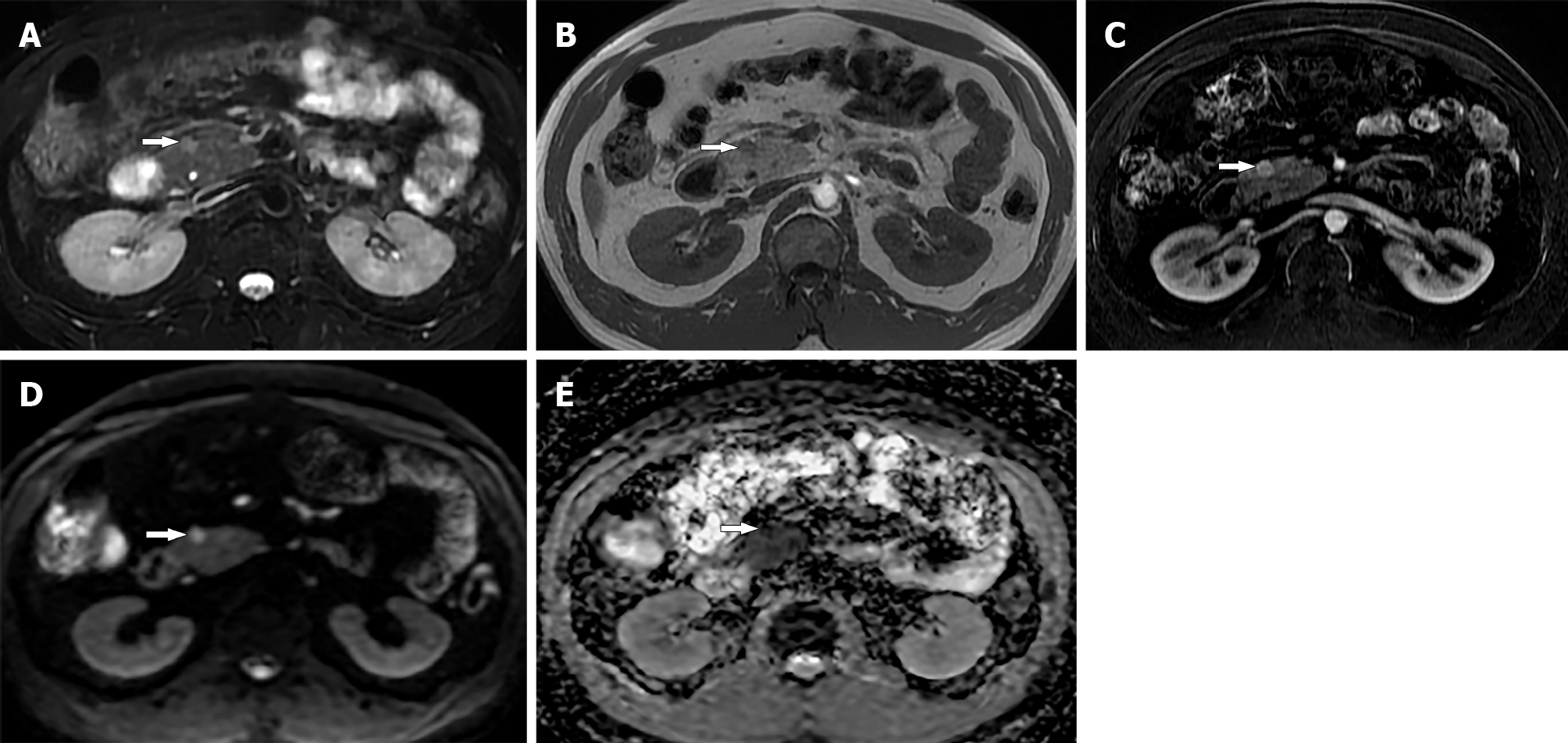
Figure 3 Thirty-five-year-old male with small pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm.
A: Axial magnetic resonance T2 weighted image; B: T1 weighted image show a small 1 cm mass (arrow) in the head of pancreas; C: Arterial phase image shows avid enhancement in the tumor; D: Diffusion-weighted image; E: Apparent diffusion coefficient map show restricted diffusion within the tumor (arrow). Biopsy confirmed diagnosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm.
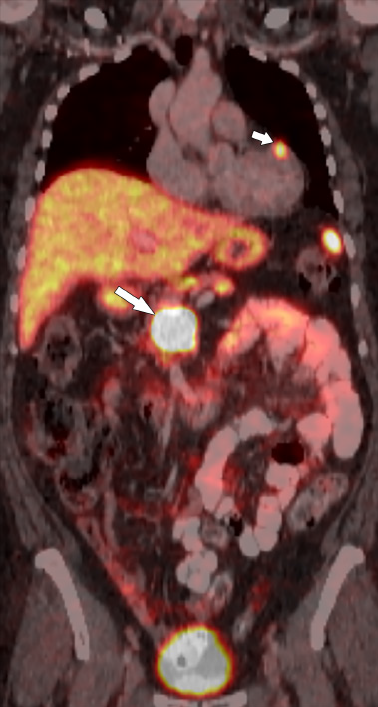
Figure 4 Sixty-two-year-old female with metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm.
Coronal fused Gallium-68 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclodo
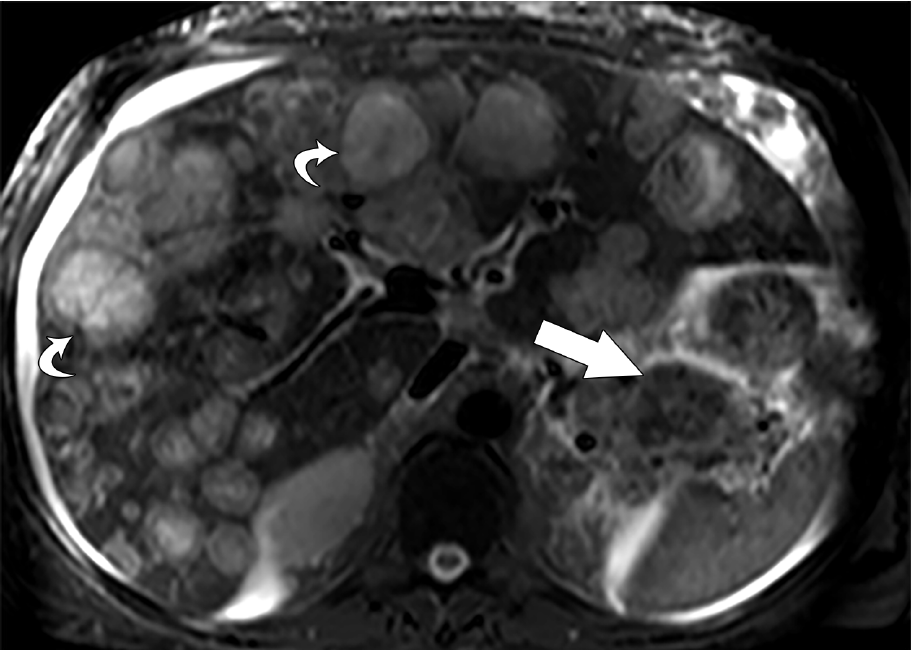
Figure 5 Thirty-nine-year-old male with metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm.
Axial T2 weighted image shows innumerable bilobar metastases (curved arrows). Note the heterogeneous primary pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (straight arrow). Patient was treated with capecitabine and temozolomide.
- Citation: Segaran N, Devine C, Wang M, Ganeshan D. Current update on imaging for pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. World J Clin Oncol 2021; 12(10): 897-911
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v12/i10/897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v12.i10.897