Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Oncol. Jul 24, 2020; 11(7): 428-449
Published online Jul 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i7.428
Published online Jul 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i7.428
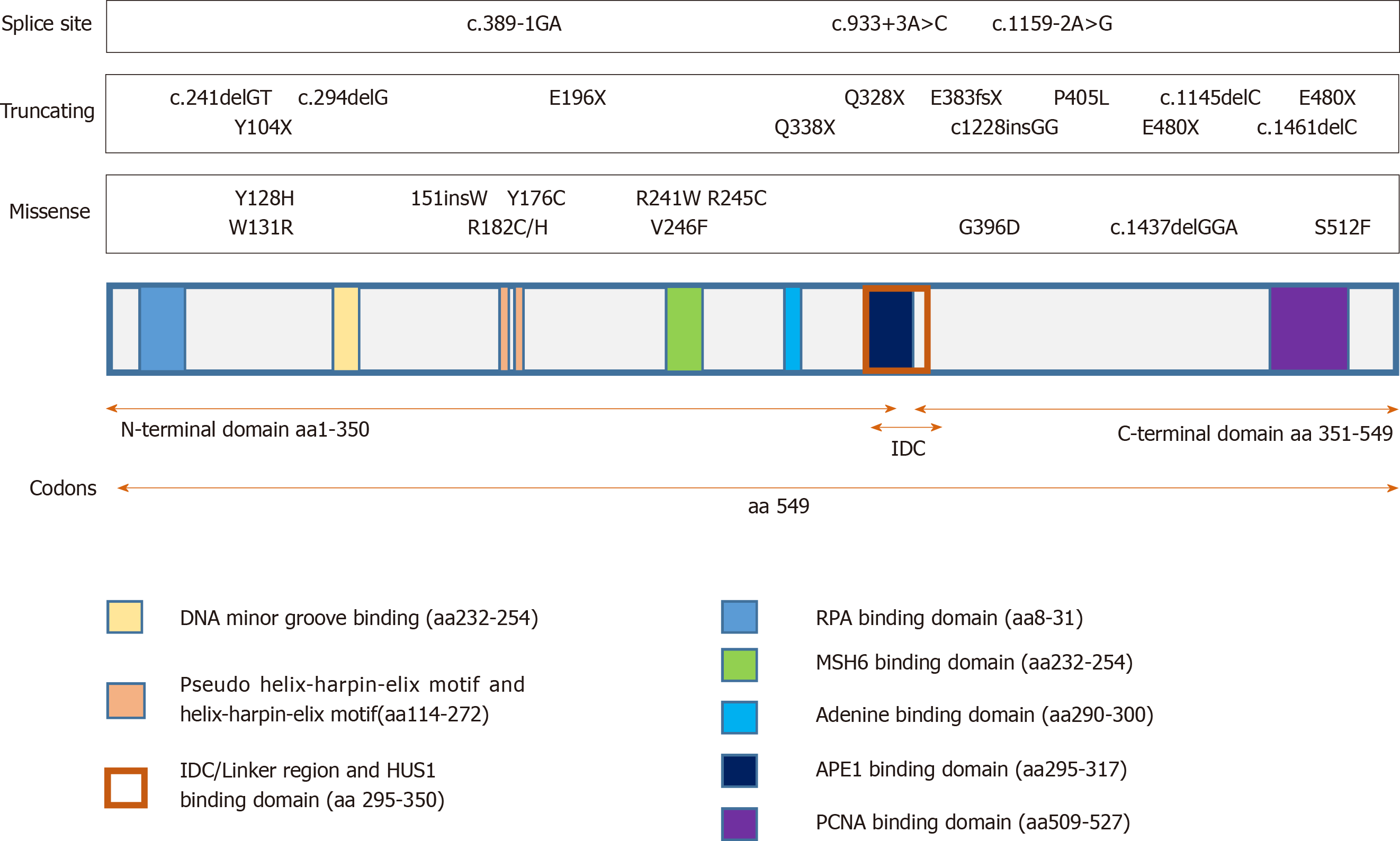
Figure 1 MUTYH functional domains and its binding partners (see UniProtKB - E5KP25).
RPA: Replication protein A; MSH6: MutS 6 homolog; APE1: AP endonuclease 1; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; HUS1: Checkpoint clamp component. APE1, PCNA and well-known representative typical mutations of MUTYH (see all variants in ClinVar database); the mutation nomenclature is based on MUTYH longest transcript.
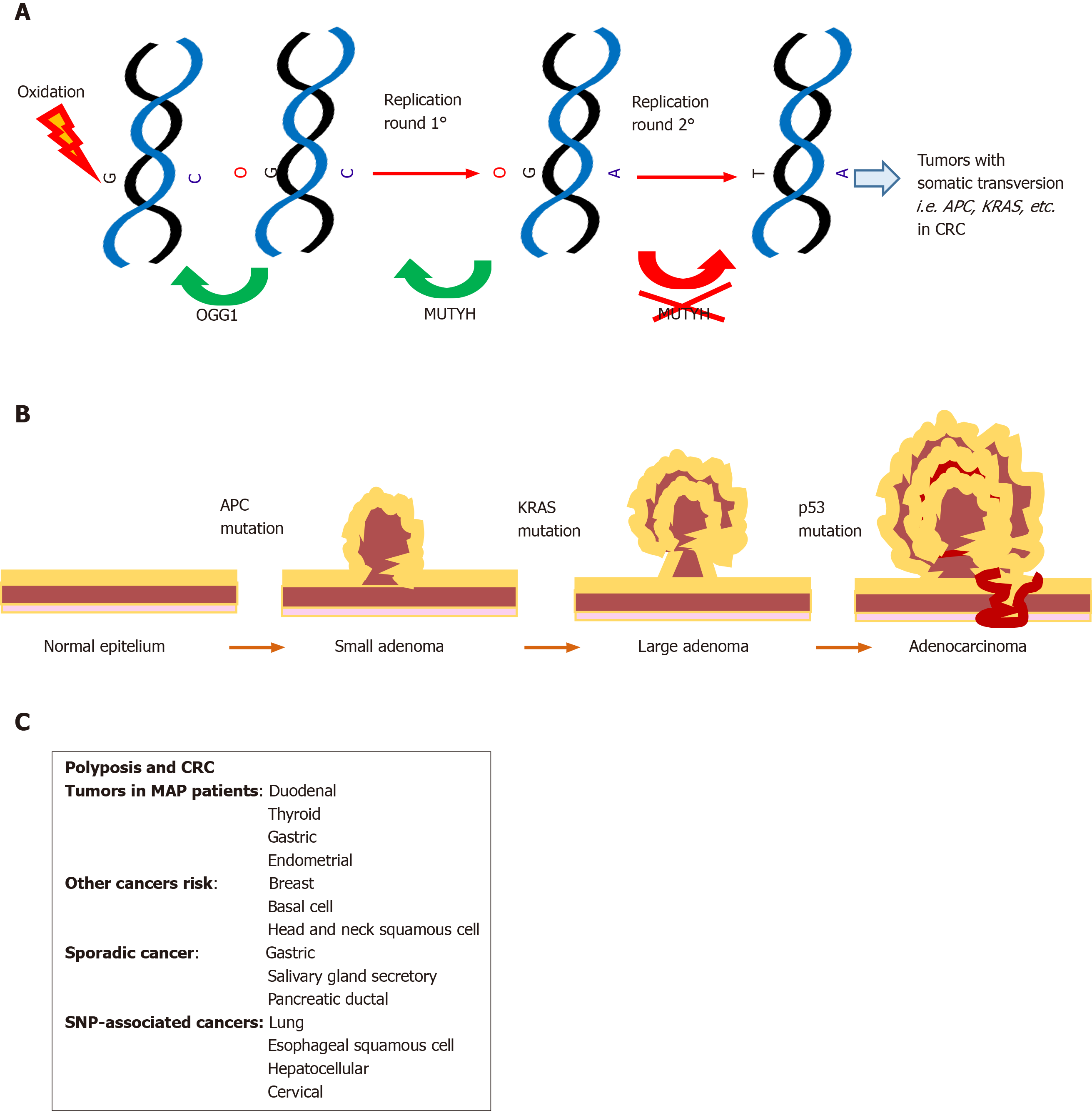
Figure 2 Roles of MUTYH in cancer.
CRC: Colorectal cancer; MAP: MUTYH associated polyposis syndrome; SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism. A: Functional MUTYH prevents G:C > A:T transversion caused by oxidative stress; B: Non-functional MUTYH predisposes to G:C > A:T somatic transversion and carcinogenesis; i.e. polyposis and CRC; C: Tumor risk from non-functional MUTYH.
- Citation: Curia MC, Catalano T, Aceto GM. MUTYH: Not just polyposis. World J Clin Oncol 2020; 11(7): 428-449
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v11/i7/428.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v11.i7.428