Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2024; 16(8): 362-370
Published online Aug 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i8.362
Published online Aug 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i8.362
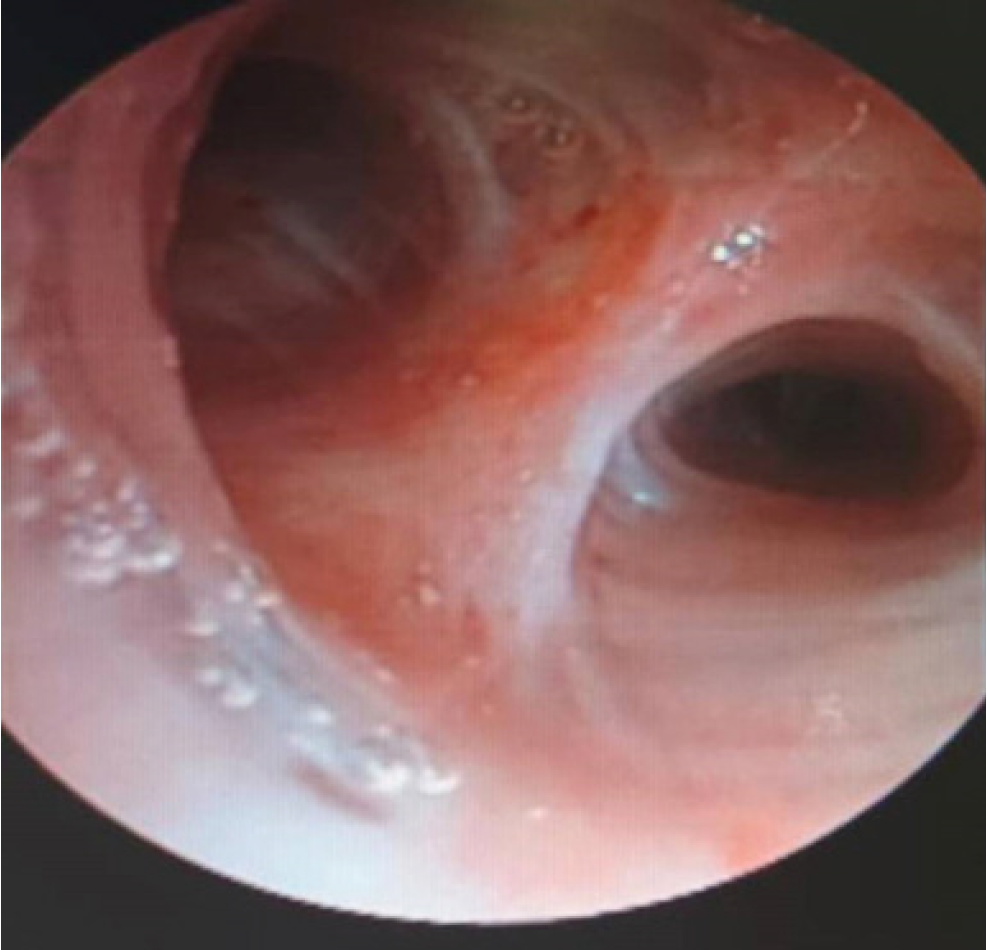
Figure 1 Bronchoscopic findings.
The tracheal mucosa of the upper lobe of the right lung is congested and edematous with a little sticky secretion.
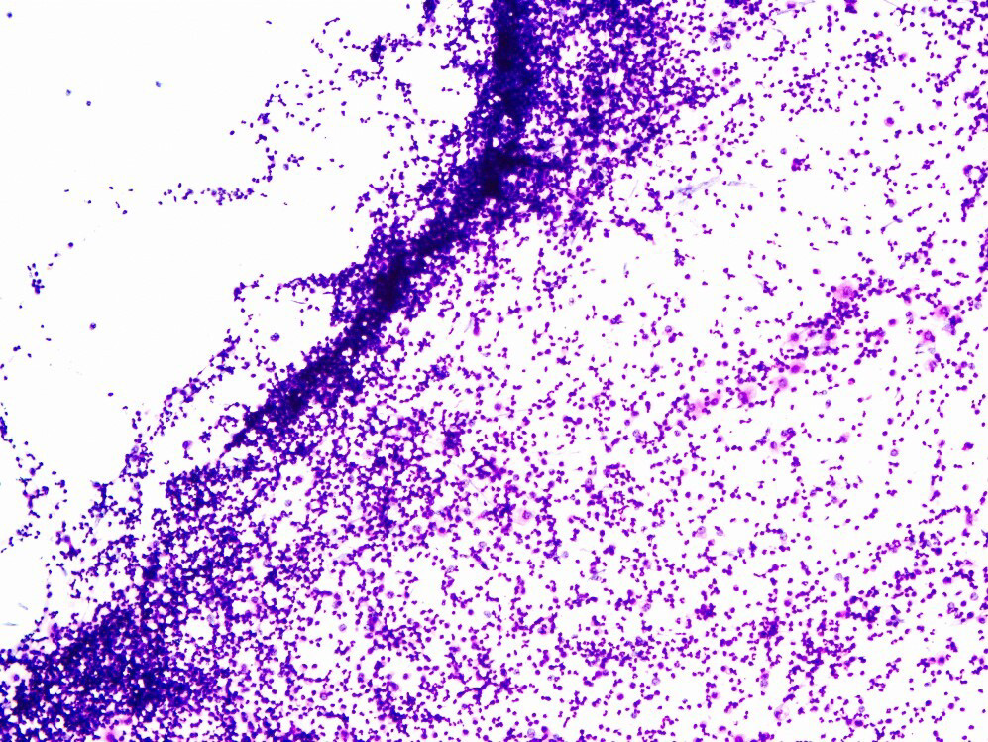
Figure 2 Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid pathological smear.
Smear showing neutrophils (90%), mononuclear phagocytes (9%), and lymphocytes (1%).
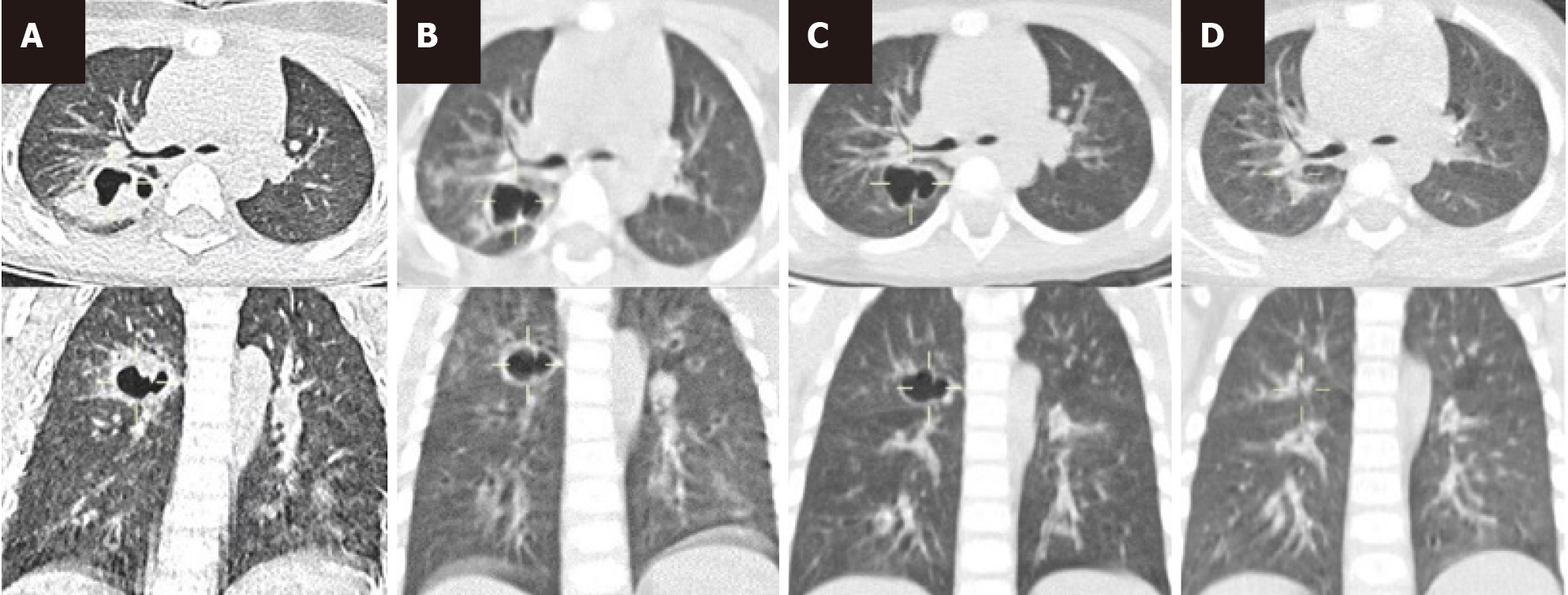
Figure 3 Computed tomography findings.
A: Computed tomography (CT) scan showing inflammation of the posterior upper lobe of the right lung with abscess formation on September 2; B: CT scan showing an abscess in the posterior segment of the upper lobe of the right lung on September 8, which was more noticeable than that around the abscess on September 2; C: CT scan on September 22, showing the cystic cavity structure of the posterior segment of the upper lobe of the right lung, which was more absorbed than that around the film on September 8; D: CT scan showing focal pneumonitis in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe on October 9; Compared to the film on September 22, the thin-walled transparent focus of the posterior segment of the right upper lobe disappeared, and mild bronchitis was found in both lungs.
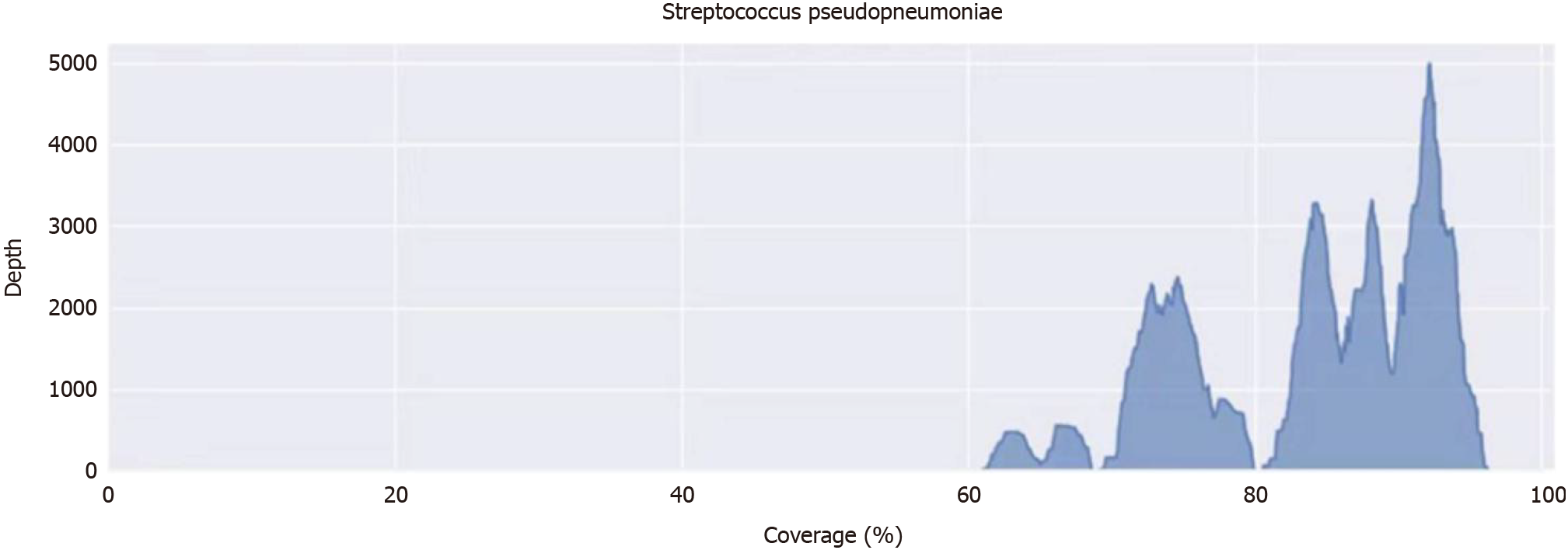
Figure 4 Information of metagenomic next-generation sequencing.
The abscissa is the expansion subregion, and the ordinate is the sequence number multiplied by the sequencing length 50. Gene number of Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae: CP002925.1, information on the metagenomic next-generation sequencing is shown in the supplementary file.
- Citation: Ma R, Wang YM, Guan H, Zhang L, Zhang W, Chen LC. Pulmonary abscess caused by Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae in a child: A case report and review of literature. World J Radiol 2024; 16(8): 362-370
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v16/i8/362.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v16.i8.362