Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2020; 12(11): 247-260
Published online Nov 28, 2020. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i11.247
Published online Nov 28, 2020. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i11.247
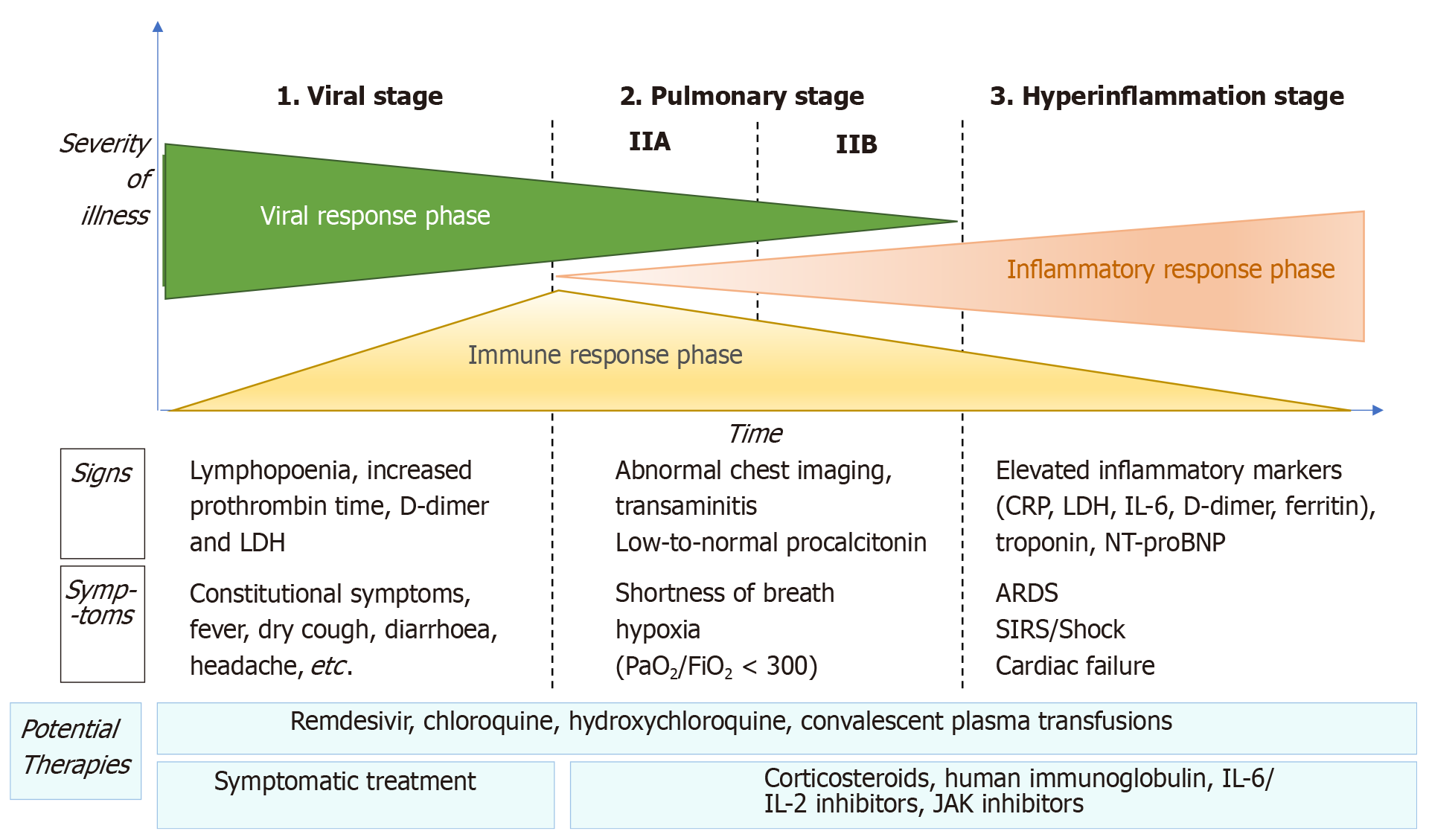
Figure 1 Adaptation of Siddiqi et al[29] the phases of coronavirus disease 2019 disease, including signs, symptoms, and potential therapeutic targets for each phase.
CRP: C-reactive protein; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; BNP: Brain natriuretic peptide; ARDS: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome; IL: Interleukin; JAK: Just another kinase.
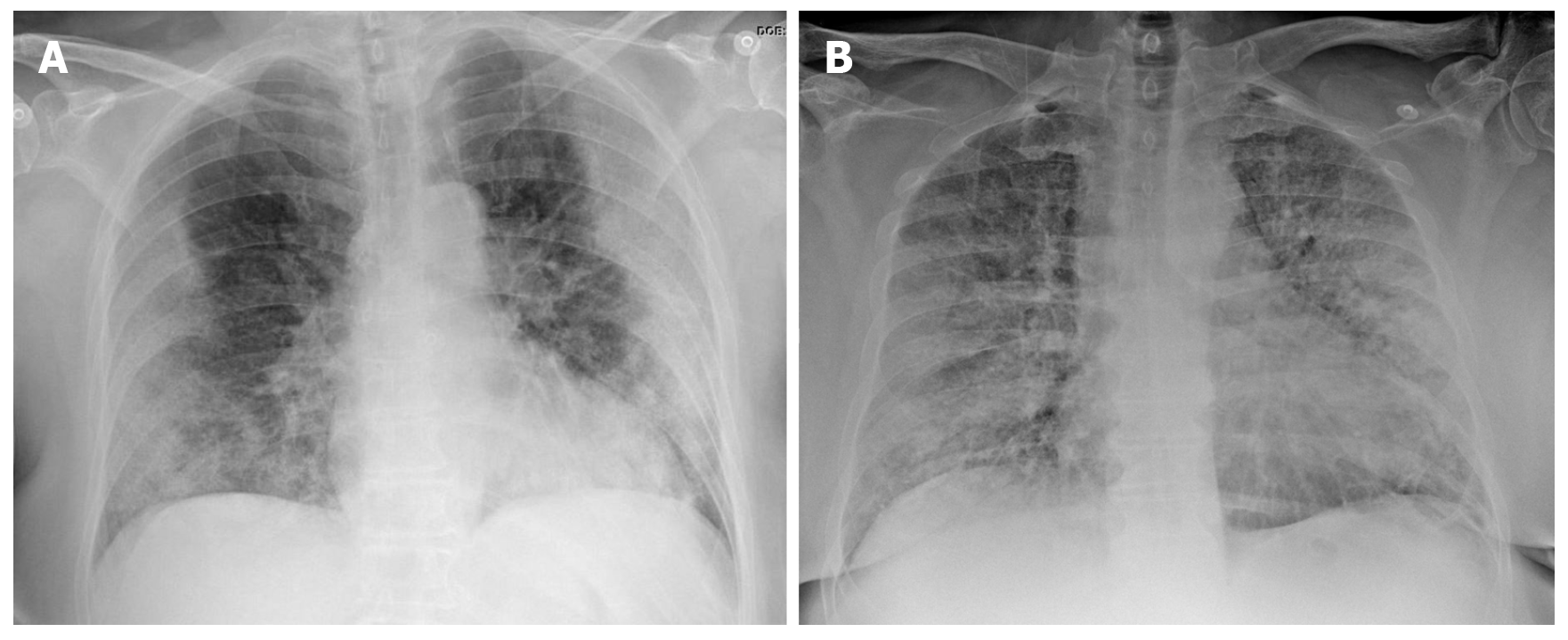
Figure 2 Chest X-ray findings in two patients with confirmed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pneumonia (positive reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction test).
A: 73-year-old diabetic woman. General malaise, myalgia and diarrhea of 8 d clinical course. Dyspnea in the last 2 d, no fever. AP X-ray: Peripherally-distributed bilateral lung opacities; B: 60-year-old man, fever and cough, progressive dyspnea. The patient presented at the emergency department with acute respiratory failure requiring admission to intensive care. AP X-ray: Alveolar infiltrates and diffusely-distributed, bilateral ground-glass opacities.
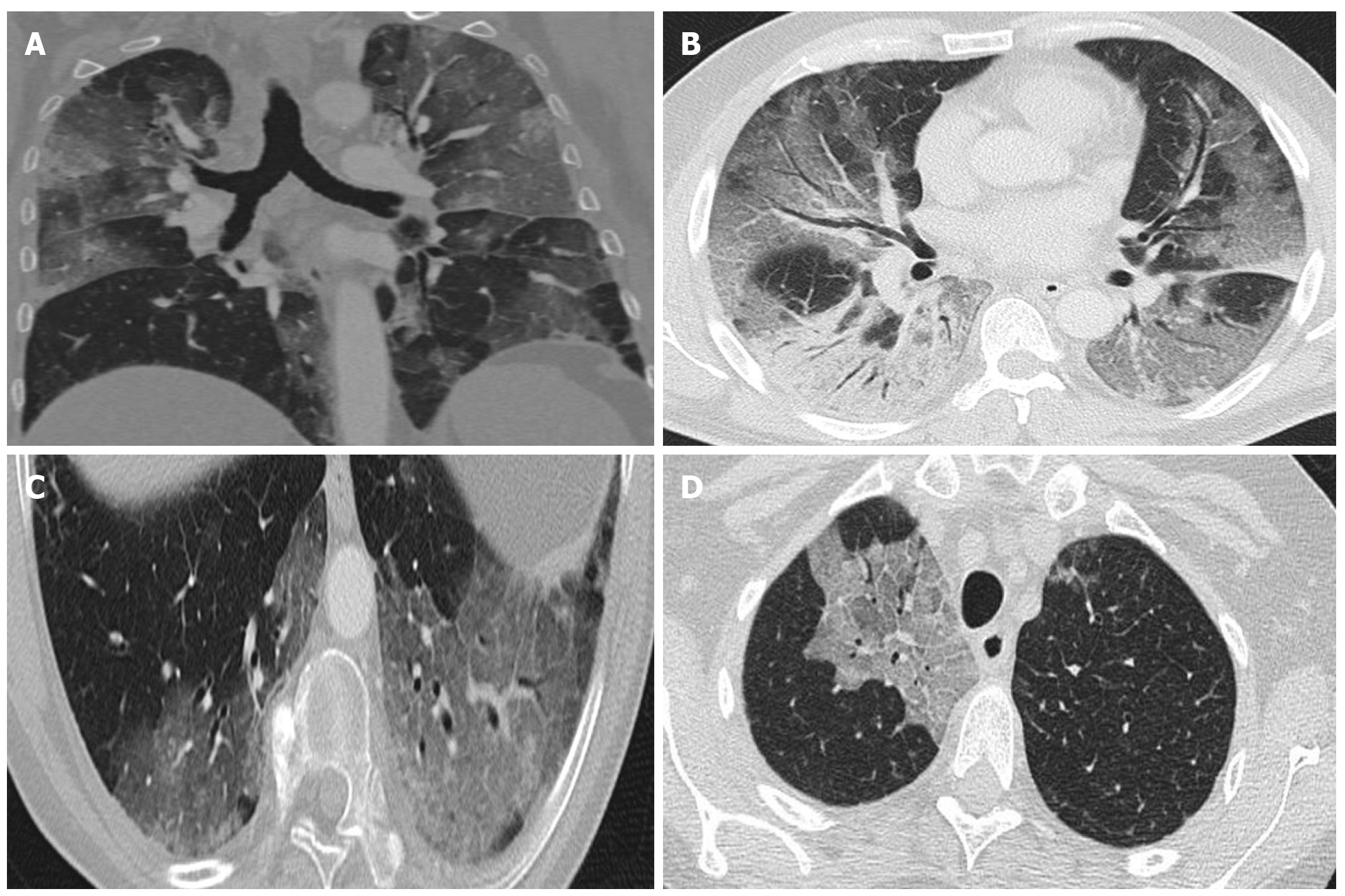
Figure 3 Computed tomography findings.
A: Extensive bilateral ground-glass opacities, one with poorly-defined margins and another with clearly defined borders; B: Multilobar ground-glass opacities and consolidation with air bronchogram in the right lower lobe. Band of subpleural parenchyma respected in the left lung; C: Microvascular dilation sign in the middle of ground-glass opacity in the left lower lobe; D: Crazy-paving pattern in the right upper lobe.
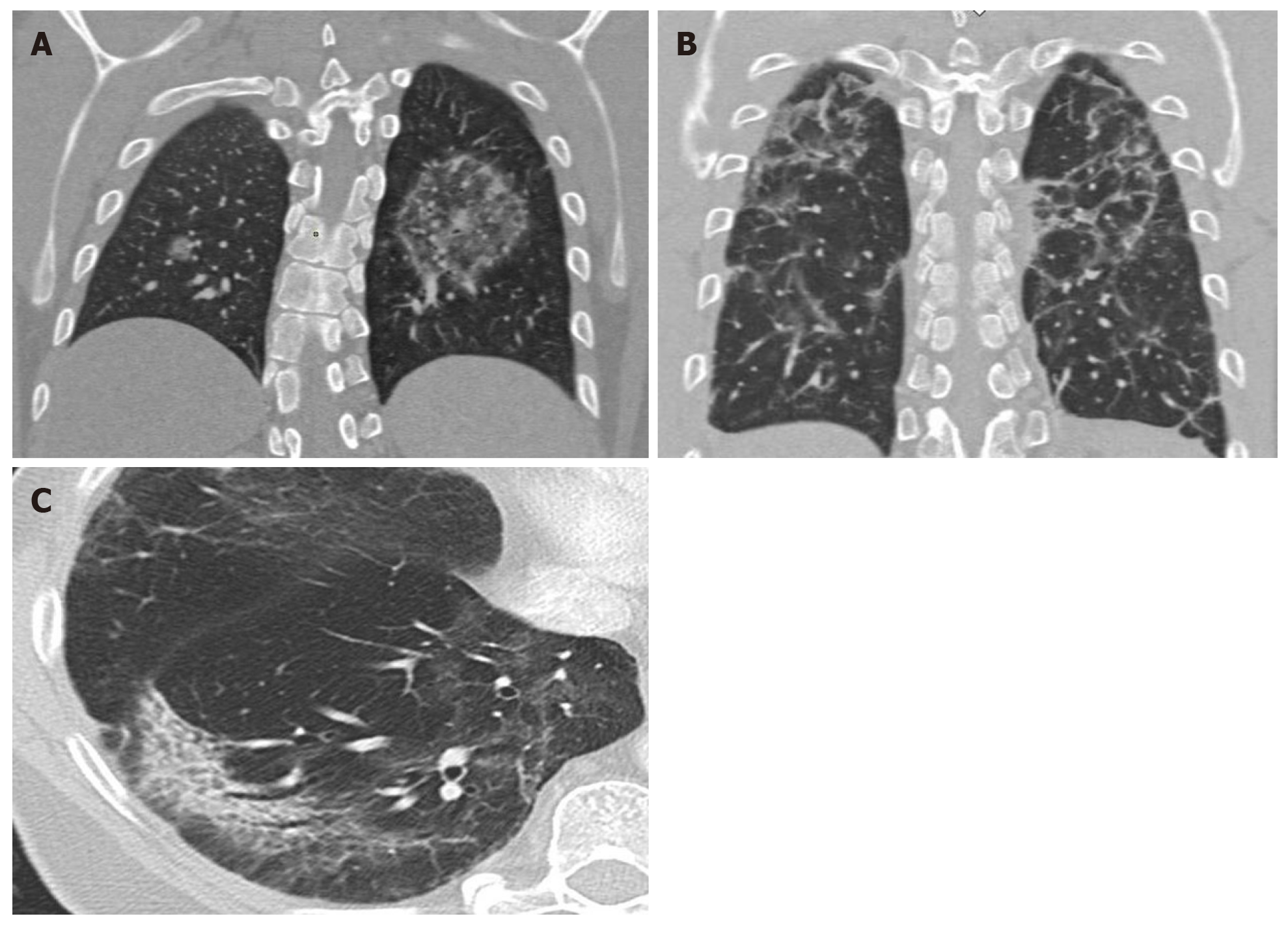
Figure 4 Computed tomography findings late stage disease.
A: Reverse halo or atoll sign: Rounded opacity in the left lung with ground-glass attenuation in the center demarcated by a denser, fine ring. Small, homogeneous rounded opacity in the right lung; B: Bilateral perilobular pattern: Polygonal (irregular, linear or band-like) peripheral opacities in secondary pulmonary lobules; C: Peripheral, elongated, curved consolidation in the right lower lobe containing dilated bronchi.
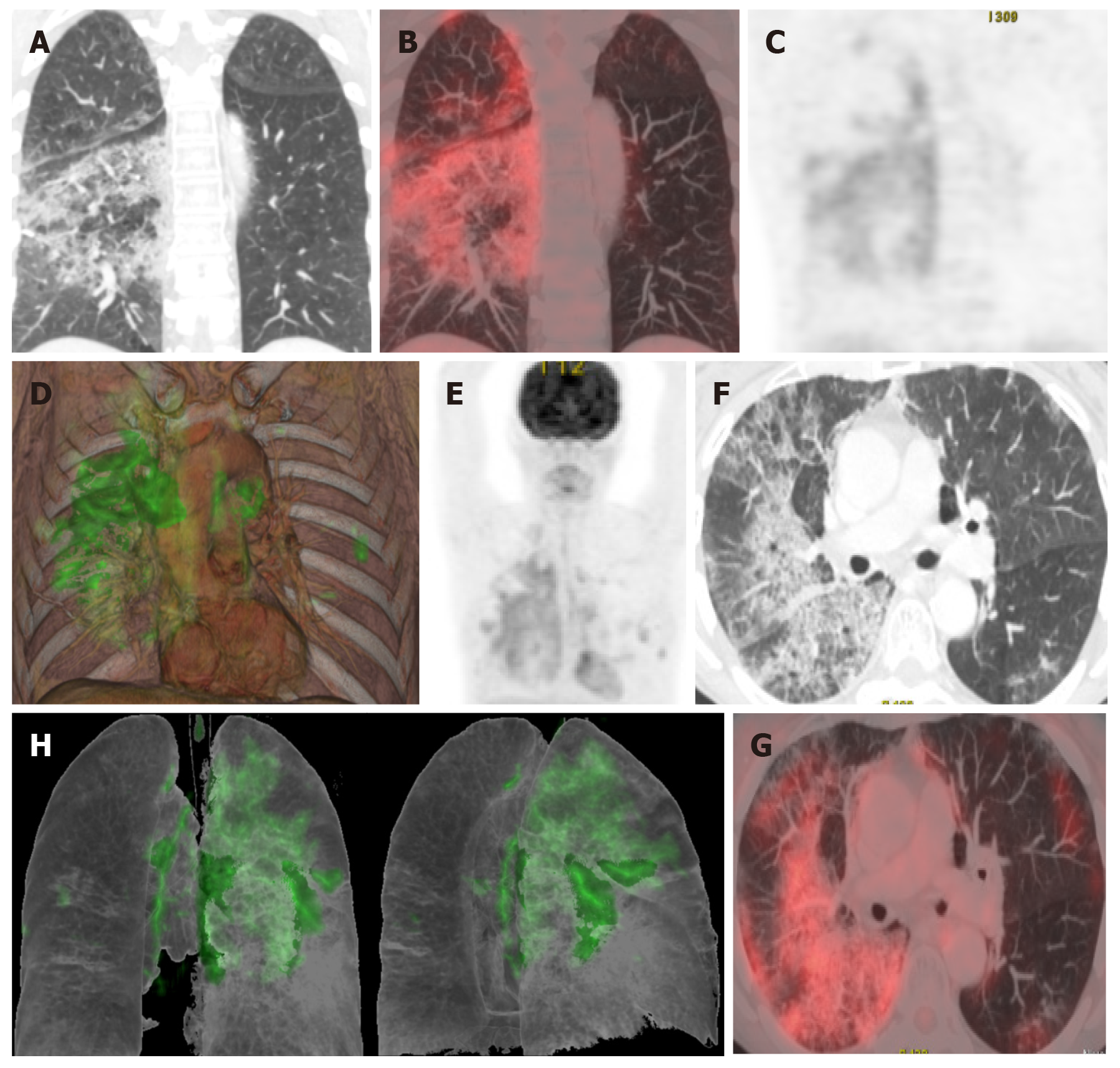
Figure 5 A 65-year-old patient with a history of invasive lepidic-predominant adenocarcinoma (stage pT1bNxM0) treated with surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
A: Coronal computed tomography showing the crazy-paving pattern (with interstitial septal thickening and increased density of ground-glass opacities) with a markedly asymmetric bilateral distribution, mainly affecting the right side; B: Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) coronal section; C: Metabolic PET; D: Volume rendering 3D PET-CT; E: MIP, PET; B-E: Reveals increased cellular activity [standard uptake value (SUV) 4-6] related to the associated inflammatory process. PET-CT pattern of bilateral coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) viral pneumonitis, predominantly right-sided; F: Axial computed tomography showing crazy-paving pattern (with interstitial septal thickening and increased ground-glass density) with a bilateral, but markedly asymmetric distribution, predominant right-sided; G and H: Axial section and 3D volume rendering from PET-CT metabolic imaging that reveals increased cellular activity (SUV 4-6) related to the associated inflammatory process. PET-CT pattern of bilateral, predominantly right-sided, COVID-19 viral pneumonitis.
- Citation: Landete P, Quezada Loaiza CA, Aldave-Orzaiz B, Muñiz SH, Maldonado A, Zamora E, Sam Cerna AC, del Cerro E, Alonso RC, Couñago F. Clinical features and radiological manifestations of COVID-19 disease. World J Radiol 2020; 12(11): 247-260
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v12/i11/247.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v12.i11.247