Published online Jul 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i7.422
Revised: July 2, 2024
Accepted: July 4, 2024
Published online: July 26, 2024
Processing time: 62 Days and 5.4 Hours
Chronic heart failure is a complex clinical syndrome. The Chinese herbal com
To identify the effective active ingredients of Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe and ex
The effective active ingredients of eight herbs composing Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe were identified using the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform. The target genes of chronic heart failure were searched in the Genecards database. The target proteins of active ingredients were mapped to chronic heart failure target genes to obtain the common drug-disease targets, which were then used to construct a key chemical component-target network using Cytoscape 3.7.2 software. The protein-protein interaction network was constructed using the String database. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analyses were performed through the Metascape database. Finally, our previously published relevant arti
A total of 227 effective active ingredients for Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe were identified, of which quercetin, kaempferol, 7-methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone, formononetin, and isorhamnetin may be key active ingredients and involved in the therapeutic effects of TCM by acting on STAT3, MAPK3, AKT1, JUN, MAPK1, TP53, TNF, HSP90AA1, p65, MAPK8, MAPK14, IL6, EGFR, EDN1, FOS, and other proteins. The pathways identified by KEGG enrichment analysis include pathways in cancer, IL-17 signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, HIF-1 signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, cAMP signaling pathway, NF-kappaB signaling pathway, AMPK signaling pathway, etc. Previous studies on Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe suggested that this Chinese compound preparation can regulate the TNF-α, IL-6, MAPK, cAMP, and AMPK pathways to affect the mitochondrial structure of myocardial cells, oxidative stress, and energy metabolism, thus achieving the thera
The Chinese medicine compound preparation Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe exerts therapeutic effects on chronic heart failure possibly by influencing the mitochondrial structure of cardiomyocytes, oxidative stress, energy metabolism, and other processes. Future studies are warranted to investigate the role of the IL-17 signaling pa
Core Tip: Based on the clinical characteristics of patients, the dialectical treatment of chronic heart failure is often performed primarily by strengthening Qi and nourishing Yin, promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, resolving phlegm and alleviating water retention, and warming and tonifying heart Yang. In this study, the authors found that the Chinese medicine compound preparation Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe exerts therapeutic effects on chronic heart failure possibly by influencing the mitochondrial structure of cardiomyocytes, oxidative stress, energy metabolism, and other processes.
- Citation: Li SQ, Min DY, Jiang JW, Li XY, Yang XN, Gu WB, Jiang JH, Chen LH, Nan H, Chen ZY. Network pharmacology-based exploration of molecular mechanisms underlying therapeutic effects of Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe on chronic heart failure with spleen Qi deficiency syndrome. World J Cardiol 2024; 16(7): 422-435
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v16/i7/422.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i7.422
Chronic heart failure is a complex clinical syndrome due to abnormal changes in cardiac structure and/or function caused by multiple factors, resulting in ventricular systolic and/or diastolic dysfunction[1]. Its main manifestations are dyspnea, fatigue, and fluid retention. As the end-stage manifestation of cardiovascular disease and the main cause of death, chronic heart failure is thought to belong to "chest impediment", "palpitation", "true heart pain", and other categories in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Based on the clinical characteristics of patients, the dialectical treatment of chronic heart failure is often performed primarily by strengthening Qi and nourishing Yin, promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, resolving phlegm and alleviating water retention, and warming and tonifying heart Yang[2]. We have been studying the curative effect and mechanism of the Chinese herbal compound preparation Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe, which has the effects of strengthening the spleen, dissolving phlegm, and removing blood stasis, in the treatment of chronic heart failure. In order to further explore the therapeutic mechanism of this compound recipe, network pharmacology was applied in the present study to identify the effective active ingredients of eight herbs com
Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe is composed of eight Chinese herbs: Dangshen, Fuling, Baizhu, Zhigancao, Danshen, Qingbanxia, and Gualou. The effective active components of these eight herbs were searched using the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP)[3]. Oral bioavailability ≥ 30% and drug-likeness ≥ 0.18 were used as the screening criteria to ensure that the selected active ingredients have good oral absorption and high druggability.
The TCMSP database was used to identify the targets of the effective active ingredients as mentioned above. Human gene names and corresponding target proteins were downloaded from the UniProt database (https://www.uniprot.org/)[4]. The target genes of chronic heart failure were searched in the Genecards database (https://www.genecards.org/)[5]. The target proteins of active ingredients were mapped to chronic heart failure target genes to obtain the common drug-disease targets and to find out the key chemical components corresponding to these targets.
Common drug-disease targets and their corresponding key chemical components were sorted into a table, which was then imported into Cytoscape 3.7.2 software to obtain their relationship network.
Protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks can graphically describe the interactions between common drug-disease targets. The common drug-disease targets identified above were input into the String database (https://string-db.org/ Version 10.5)[6] to obtain the PPI network. The protein interaction score was further set to 0.9 to optimize the network diagram. Data on protein interactions were downloaded to screen out the top 15 core proteins.
The common drug-disease targets identified above were imported into the Metascape database (http: //metascape.org/gp/index.html)[7] for Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses, with the parameters set as follows: P value = 0.01, minimum overlap = 3, and minimum enrichment = 1.5, GO biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF) and KEGG pathways were enriched, respectively. Bubble maps were generated online using the ImageGP website tool. The target-pathway network was constructed with Cytoscape software.
According to the key targets and proteins belonging to the signal pathways identified above, our previously published relevant articles were analyzed to verify the therapeutic mechanism of Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe in the treatment of chronic heart failure.
There are eight herbs in the Chinese herbal compound preparation Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe: Huangqi, Dangshen, Fuling, Baizhu, Zhigancao, Danshen, Qingbanxia, and Gualou. As shown in Table 1, a total of 227 active ingredients were identified in the TCMSP database according to the oral bioavailability and drug-likeness.
| Molecule ID | Molecule name | Drug(s) | Molecule ID | Molecule name | Drug(s) |
| MOL007059 | 3-β-hydroxymethyllenetanshiquinone | Danshen, Dangshen | MOL001792 | DFV | Gancao |
| MOL004355 | Spinasterol | Dangshen, Gualou | MOL001484 | Inermine | Gancao |
| MOL003896 | 7-methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone | Dangshen, Gancao | MOL000500 | Vestitol | Gancao |
| MOL002776 | Baicalin | Banxia, Danshen | MOL000497 | Licochalcone a | Gancao |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | Banxia, Dangshen | MOL000359 | Sitosterol | Gancao |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | Gancao, Huangqi | MOL000300 | Dehydroeburicoic acid | Fuling |
| MOL000417 | Calycosin | Gancao, Huangqi | MOL000292 | Poricoic acid C | Fuling |
| MOL000392 | Formononetin | Gancao, Huangqi | MOL000291 | Poricoic acid B | Fuling |
| MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | Gancao, Huangqi | MOL000290 | Poricoic acid A | Fuling |
| MOL000296 | Hederagenin | Fuling, Huangqi | MOL000289 | Pachymic acid | Fuling |
| MOL000239 | Jaranol | Gancao, Huangqi | MOL000287 | 3-β-hydroxy-24-methylene-8-lanostene-21-oic acid | Fuling |
| MOL000211 | Mairin | Gancao, Huangqi | MOL000285 | (2R)-2-[(5R,10S,13R,14R,16R,17R)-16-hydroxy-3-keto-4,4,10,13,14-pentamethyl-1,2,5,6,12,15,16,17-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5-isopropyl-hex-5-enoic acid | Fuling |
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | Gancao, Huangqi | MOL000283 | Ergosterol peroxide | Fuling |
| MOL000033 | (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2R,5S)-5-propan-2-yloctan-2-yl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol | Baizhu, Huangqi | MOL000282 | Ergosta-7,22E-dien-3beta-ol | Fuling |
| MOL000006 | Luteolin | Danshen, Dangshen | MOL000280 | (2R)-2-[(3S,5R,10S,13R,14R,16R,17R)-3,16-dihydroxy-4,4,10,13,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,12,15,16,17-octahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5-isopropyl-hex-5-enoic acid | Fuling |
| MOL000442 | 1,7-dihydroxy-3,9-dimethoxy pterocarpene | Huangqi | MOL000279 | Cerevisterol | Fuling |
| MOL000439 | Isomucronulatol-7,2'-di-O-glucosiole | Huangqi | MOL000276 | 7,9(11)-Dehydropachymic acid | Fuling |
| MOL000438 | (3R)-3-(2-hydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)chroman-7-ol | Huangqi | MOL000275 | Trametenolic acid | Fuling |
| MOL000433 | FA | Huangqi | MOL000273 | (2R)-2-[(3S,5R,10S,13R,14R,16R,17R)-3,16-dihydroxy-4,4,10,13,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,12,15,16,17-octahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-6-methylhept-5-enoic acid | Fuling |
| MOL000398 | Isoflavanone | Huangqi | MOL008411 | 11-Hydroxyrankinidine | Dangshen |
| MOL000387 | Bifendate | Huangqi | MOL008407 | (8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-17-[(E,2R,5S)-5-ethyl-6-methylhept-3-en-2-yl]-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one | Dangshen |
| MOL000380 | (6aR,11aR)-9,10-dimethoxy-6a,11a-dihydro-6H-benzofurano[3,2-c]chromen-3-ol | Huangqi | MOL008406 | Spinoside A | Dangshen |
| MOL000379 | 9,10-dimethoxypterocarpan-3-O-β-D-glucoside | Huangqi | MOL008400 | Glycitein | Dangshen |
| MOL000378 | 7-O-methylisomucronulatol | Huangqi | MOL008397 | Daturilin | Dangshen |
| MOL000374 | 5'-hydroxyiso-muronulatol-2',5'-di-O-glucoside | Huangqi | MOL008393 | 7-(β-xylosyl)cephalomannine_qt | Dangshen |
| MOL000371 | 3,9-di-O-methylnissolin | Huangqi | MOL008391 | 5α-Stigmastan-3,6-dione | Dangshen |
| MOL007180 | Vitamin E | Gualou | MOL007514 | Methyl icosa-11,14-dienoate | Dangshen |
| MOL007179 | Linolenic acid ethyl ester | Gualou | MOL006774 | Stigmast-7-enol | Dangshen |
| MOL007175 | Karounidiol 3-O-benzoate | Gualou | MOL006554 | Taraxerol | Dangshen |
| MOL007172 | 7-oxo-Dihydrokaro-unidiol | Gualou | MOL005321 | Frutinone A | Dangshen |
| MOL007171 | 5-Dehydrokarounidiol | Gualou | MOL004492 | Chrysanthemaxanthin | Dangshen |
| MOL007165 | 10α-cucurbita-5,24-diene-3β-ol | Gualou | MOL003036 | ZINC03978781 | Dangshen |
| MOL006756 | Schottenol | Gualou | MOL002879 | Diop | Dangshen |
| MOL005530 | hydroxygenkwanin | Gualou | MOL002140 | Perlolyrine | Dangshen |
| MOL002881 | Diosmetin | Gualou | MOL001006 | Poriferasta-7,22E-dien-3β-ol | Dangshen |
| MOL001494 | Mandenol | Gualou | MOL007156 | Tanshinone Ⅵ | Danshen |
| MOL005020 | Dehydroglyasperins C | Gancao | MOL007155 | (6S)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,6-Dimethyl-8,9-dihydro-7H-naphtho[8,7-g]benzofuran-10,11-dione | Danshen |
| MOL005018 | Xambioona | Gancao | MOL007154 | Tanshinone iia | Danshen |
| MOL005017 | Phaseol | Gancao | MOL007152 | Przewaquinone E | Danshen |
| MOL005016 | Odoratin | Gancao | MOL007151 | Tanshindiol B | Danshen |
| MOL005013 | 18α-hydroxyglycyrrhetic acid | Gancao | MOL007150 | (6S)-6-hydroxy-1-methyl-6-methylol-8,9-dihydro-7H-naphtho[8,7-g]benzofuran-10,11-quinone | Danshen |
| MOL005012 | Licoagroisoflavone | Gancao | MOL007149 | NSC 122421 | Danshen |
| MOL005008 | Glycyrrhiza flavonol A | Gancao | MOL007145 | Salviolone | Danshen |
| MOL005007 | Glyasperins M | Gancao | MOL007143 | Salvilenone I | Danshen |
| MOL005003 | Licoagrocarpin | Gancao | MOL007142 | Salvianolic acid J | Danshen |
| MOL005001 | Gancaonin H | Gancao | MOL007141 | Salvianolic acid G | Danshen |
| MOL005000 | Gancaonin G | Gancao | MOL007140 | (Z)-3-[2-[(E)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)vinyl]-3,4-dihydroxy-phenyl]acrylic acid | Danshen |
| MOL004996 | Gadelaidic acid | Gancao | MOL007132 | (2R)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-[(Z)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acryloyl]oxy-propionic acid | Danshen |
| MOL004993 | 8-prenylated eriodictyol | Gancao | MOL007130 | Prolithospermic acid | Danshen |
| MOL004991 | 7-acetoxy-2-methylisoflavone | Gancao | MOL007127 | 1-methyl-8,9-dihydro-7H-naphtho[5,6-g]benzofuran-6,10,11-trione | Danshen |
| MOL004990 | 7,2',4'-trihydroxy-5-methoxy-3-arylcoumarin | Gancao | MOL007125 | Neocryptotanshinone | Danshen |
| MOL004989 | 6-prenylated eriodictyol | Gancao | MOL007124 | Neocryptotanshinone II | Danshen |
| MOL004988 | Kanzonol F | Gancao | MOL007123 | Miltirone II | Danshen |
| MOL004985 | Icos-5-enoic acid | Gancao | MOL007122 | Miltirone | Danshen |
| MOL004980 | Inflacoumarin A | Gancao | MOL007121 | Miltipolone | Danshen |
| MOL004978 | 2-[(3R)-8,8-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrano[6,5-f]chromen-3-yl]-5-methoxyphenol | Gancao | MOL007120 | Miltionone II | Danshen |
| MOL004974 | 3'-methoxyglabridin | Gancao | MOL007119 | Miltionone I | Danshen |
| MOL004966 | 3'-hydroxy-4'-O-methylglabridin | Gancao | MOL007118 | Microstegiol | Danshen |
| MOL004961 | Quercetin der. | Gancao | MOL007115 | Manool | Danshen |
| MOL004959 | 1-methoxyphaseollidin | Gancao | MOL007111 | Isotanshinone II | Danshen |
| MOL004957 | HMO | Gancao | MOL007108 | Isocryptotanshi-none | Danshen |
| MOL004949 | Isolicoflavonol | Gancao | MOL007107 | C09092 | Danshen |
| MOL004948 | Isoglycyrol | Gancao | MOL007105 | Epidanshenspiroketallactone | Danshen |
| MOL004945 | (2S)-7-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)chroman-4-one | Gancao | MOL007101 | Dihydrotanshinone I | Danshen |
| MOL004941 | (2R)-7-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chroman-4-one | Gancao | MOL007100 | Dihydrotanshinlactone | Danshen |
| MOL004935 | Sigmoidin-B | Gancao | MOL007098 | Deoxyneocryptotanshinone | Danshen |
| MOL004924 | (-)-medicocarpin | Gancao | MOL007094 | Danshenspiroketallactone | Danshen |
| MOL004917 | Glycyroside | Gancao | MOL007093 | Dan-shexinkum d | Danshen |
| MOL004915 | Eurycarpin A | Gancao | MOL007088 | Cryptotanshinone | Danshen |
| MOL004914 | 1,3-dihydroxy-8,9-dimethoxy-6-benzofurano[3,2-c]chromenone | Gancao | MOL007085 | Salvilenone | Danshen |
| MOL004913 | 1,3-dihydroxy-9-methoxy-6-benzofurano[3,2-c]chromenone | Gancao | MOL007082 | Danshenol A | Danshen |
| MOL004912 | Glabrone | Gancao | MOL007081 | Danshenol B | Danshen |
| MOL004911 | Glabrene | Gancao | MOL007079 | Tanshinaldehyde | Danshen |
| MOL004910 | Glabranin | Gancao | MOL007077 | Sclareol | Danshen |
| MOL004908 | Glabridin | Gancao | MOL007071 | Przewaquinone f | Danshen |
| MOL004907 | Glyzaglabrin | Gancao | MOL007070 | (6S,7R)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,6-dimethyl-8,9-dihydro-7H-naphtho[8,7-g]benzofuran-10,11-dione | Danshen |
| MOL004905 | 3,22-dihydroxy-11-oxo-delta(12)-oleanene-27-α-methoxycarbonyl-29-oic acid | Gancao | MOL007069 | Przewaquinone C | Danshen |
| MOL004904 | Licopyranocoumarin | Gancao | MOL007068 | Przewaquinone B | Danshen |
| MOL004903 | Liquiritin | Gancao | MOL007064 | Przewalskin B | Danshen |
| MOL004898 | (E)-3-[3,4-dihydroxy-5-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)phenyl]-1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | Gancao | MOL007063 | przewalskin a | Danshen |
| MOL004891 | Shinpterocarpin | Gancao | MOL007061 | Methylenetanshinquinone | Danshen |
| MOL004885 | Licoisoflavanone | Gancao | MOL007058 | Formyltanshinone | Danshen |
| MOL004884 | Licoisoflavone B | Gancao | MOL007051 | 6-O-syringyl-8-o-acetyl shanzhiside methyl ester | Danshen |
| MOL004883 | Licoisoflavone | Gancao | MOL007050 | 2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-5-(3-hydroxypropyl)-7-methoxy-3-benzofurancarboxaldehyde | Danshen |
| MOL004882 | Licocoumarone | Gancao | MOL007049 | 4-methylenemiltirone | Danshen |
| MOL004879 | Glycyrin | Gancao | MOL007048 | (E)-3-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-hydroxy-benzofuran-4-yl]acrylic acid | Danshen |
| MOL004866 | 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-6-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)chromone | Gancao | MOL007045 | 3α-hydroxytanshinone IIa | Danshen |
| MOL004864 | 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)chromone | Gancao | MOL007041 | 2-isopropyl-8-methylphenanthrene-3,4-dione | Danshen |
| MOL004863 | 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)chromone | Gancao | MOL007036 | 5,6-dihydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrophenanthren-4-one | Danshen |
| MOL004860 | Licorice glycoside E | Gancao | MOL006824 | α-amyrin | Danshen |
| MOL004857 | Gancaonin B | Gancao | MOL002651 | Dehydrotanshinone IIA | Danshen |
| MOL004856 | Gancaonin A | Gancao | MOL002222 | Sugiol | Danshen |
| MOL004855 | Licoricone | Gancao | MOL001942 | Isoimperatorin | Danshen |
| MOL004849 | 3-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-8-(1,1-dimethylprop-2-enyl)-7-hydroxy-5-methoxy-coumarin | Gancao | MOL001771 | Poriferast-5-en-3β-ol | Danshen |
| MOL004848 | Licochalcone G | Gancao | MOL001659 | Poriferasterol | Danshen |
| MOL004841 | Licochalcone B | Gancao | MOL001601 | 1,2,5,6-tetrahydrotanshinone | Danshen |
| MOL004838 | 8-(6-hydroxy-2-benzofuranyl)-2,2-dimethyl-5-chromenol | Gancao | MOL000569 | Digallate | Danshen |
| MOL004835 | Glypallichalcone | Gancao | MOL006967 | β-D-Ribofuranoside, xanthine-9 | Banxia |
| MOL004833 | Phaseolinisoflavan | Gancao | MOL006957 | (3S,6S)-3-(benzyl)-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)piperazine-2,5-quinone | Banxia |
| MOL004829 | Glepidotin B | Gancao | MOL006937 | 12,13-epoxy-9-hydroxynonadeca-7,10-dienoic acid | Banxia |
| MOL004828 | Glepidotin A | Gancao | MOL006936 | 10,13-eicosadienoic | Banxia |
| MOL004827 | Semilicoisoflavone B | Gancao | MOL005030 | Gondoic acid | Banxia |
| MOL004824 | (2S)-6-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-4-methoxy-2,3-dihydrofuro[3,2-g]chromen-7-one | Gancao | MOL003578 | Cycloartenol | Banxia |
| MOL004820 | Kanzonols W | Gancao | MOL002714 | Baicalein | Banxia |
| MOL004815 | (E)-1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(2,2-dimethylchromen-6-yl)prop-2-en-1-one | Gancao | MOL002670 | Cavidine | Banxia |
| MOL004814 | Isotrifoliol | Gancao | MOL001755 | 24-ethylcholest-4-en-3-one | Banxia |
| MOL004811 | Glyasperin C | Gancao | MOL000519 | Coniferin | Banxia |
| MOL004810 | Glyasperin F | Gancao | MOL000358 | β-sitosterol | Banxia |
| MOL004808 | Glyasperin B | Gancao | MOL000072 | 8β-ethoxy atractylenolide Ⅲ | Baizhu |
| MOL004806 | Euchrenone | Gancao | MOL000049 | 3β-acetoxyatractylone | Baizhu |
| MOL004805 | (2S)-2-[4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)phenyl]-8,8-dimethyl-2,3-dihydropyrano[2,3-f]chromen-4-one | Gancao | MOL000028 | α-amyrin | Baizhu |
| MOL004328 | Naringenin | Gancao | MOL000022 | 14-acetyl-12-senecioyl-2E,8Z,10E-atractylentriol | Baizhu |
| MOL003656 | Lupiwighteone | Gancao | MOL000021 | 14-acetyl-12-senecioyl-2E,8E,10E-atractylentriol | Baizhu |
| MOL002565 | Medicarpin | Gancao | MOL000020 | 12-senecioyl-2E,8E,10E-atractylentriol | Baizhu |
| MOL002311 | Glycyrol | Gancao |
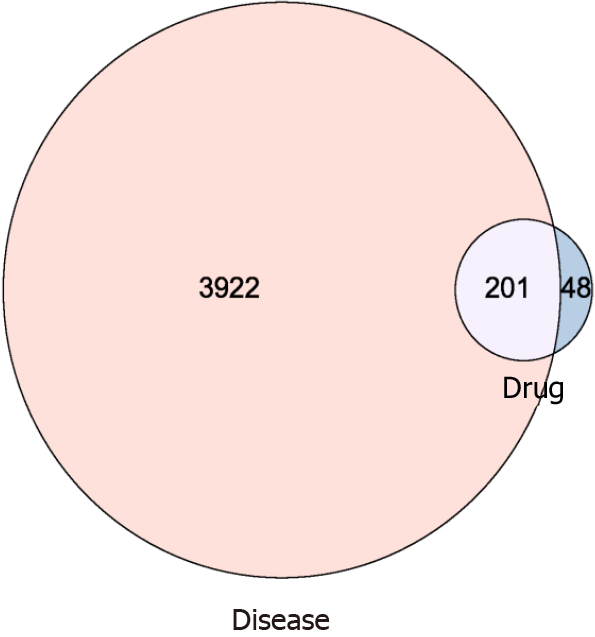
A total of 4123 genes were downloaded from the Genecard database and screened for genes with a score of 5 or greater, which might be associated with chronic heart failure. Mapping of the target proteins of active ingredients of Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe to chronic heart failure target genes led to the identification of 201 common targets. The Venn diagram indicating these common targets is shown in Figure 1.
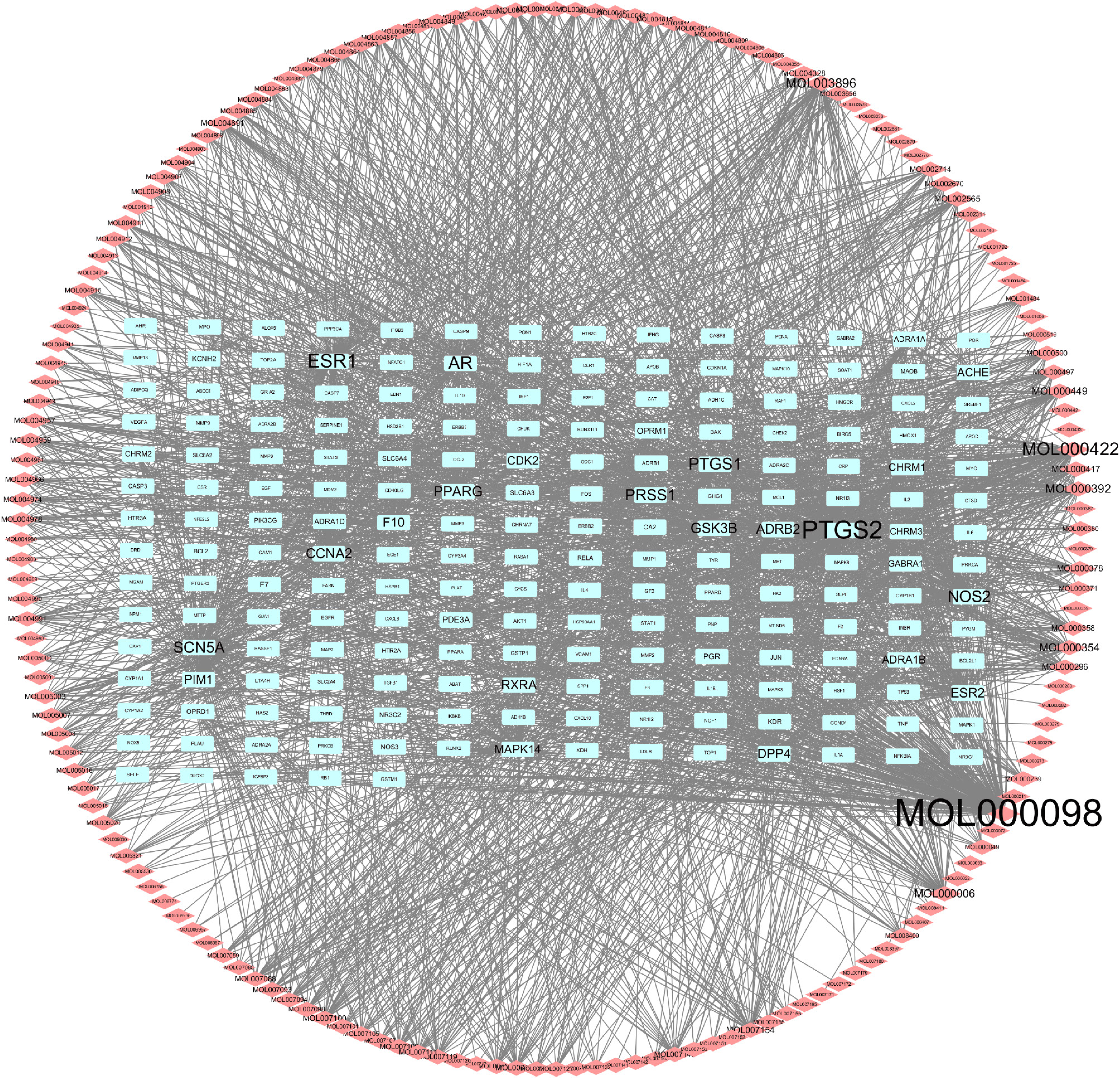
Cytoscape software was used to construct the relationship network of key active components in Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe and chronic heart failure associated genes. As shown in Figure 2, the top 5 key chemical components are as follows: Quercetin (MOL000098, degree = 236), kaempferol (MOL000422, degree = 94), 7-methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone, (MOL003896, degree = 60), formononetin (MOL000392, degree = 53), and isorhamnetin (MOL000354, degree = 47). The top 15 common target proteins are as follows: PTGS2, ESR1, AR, PTGS1, NOS2, SCN5A, PRSS1, GSK3B, PPARG, CCNA2, ESR2, ADRB2, DPP4, F10, and RXRA.
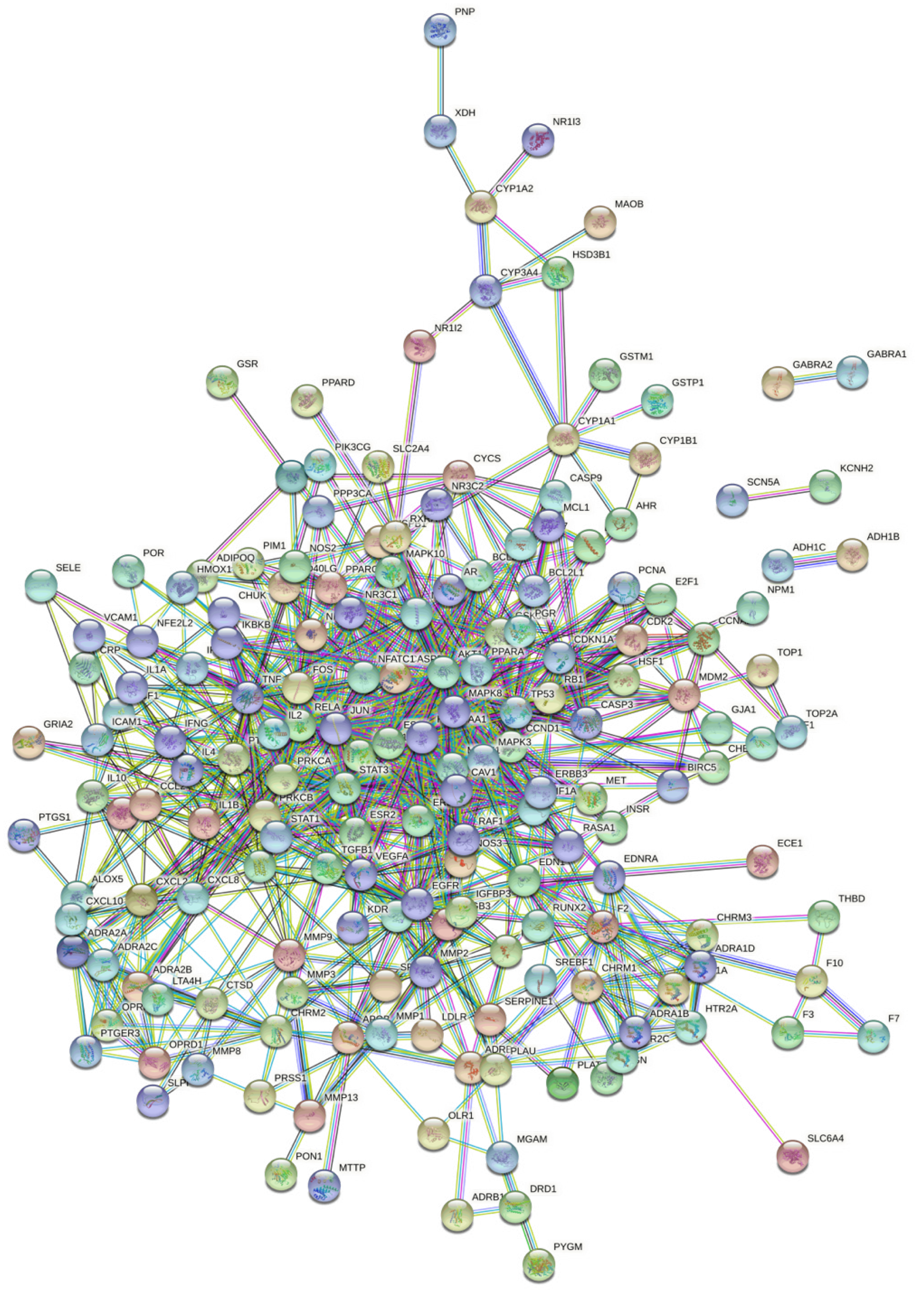
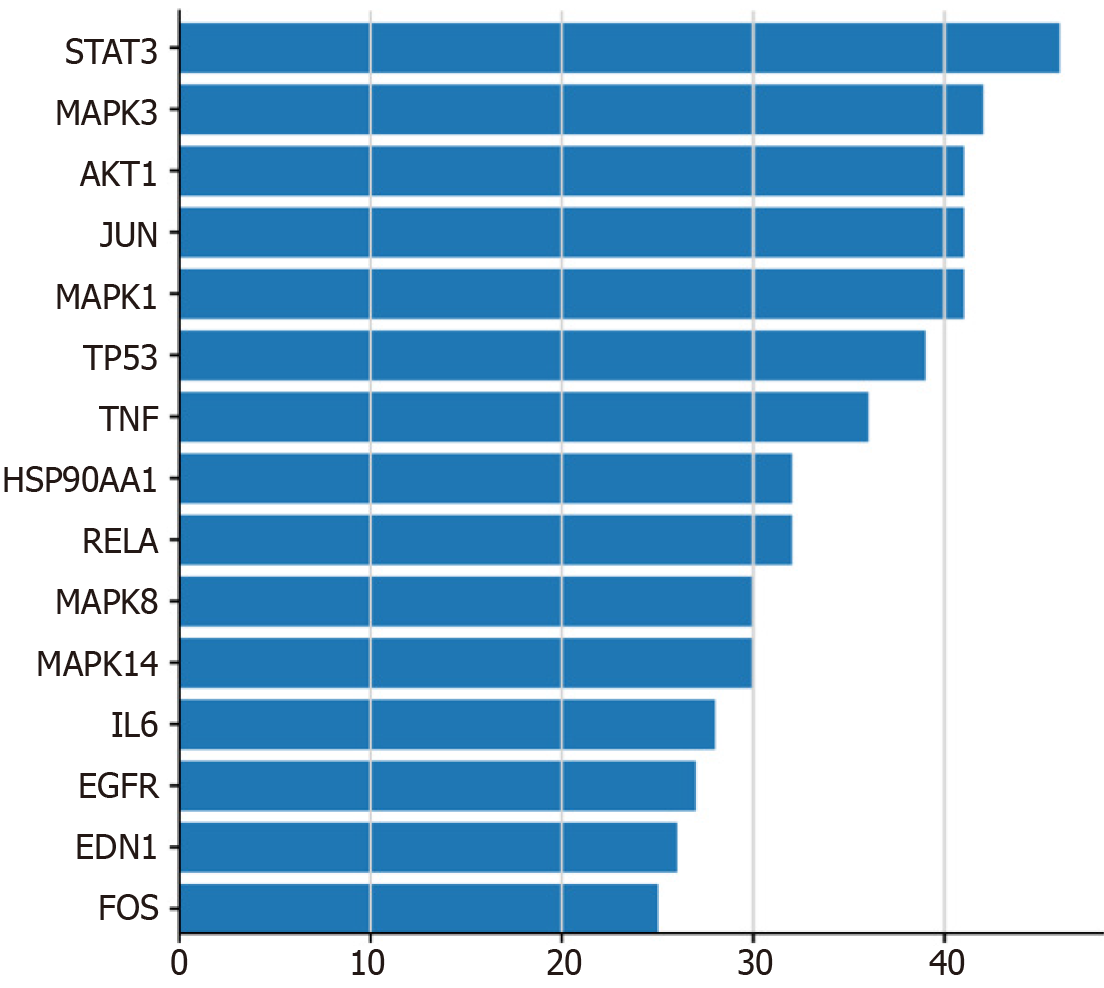
The PPI network was obtained by inputting the common drug-disease targets into the String database. As shown in Figure 3, the PPI network contains 200 nodes and 906 edges. Among them, the interacting protein pairs with a PPI score equal to 0.999 are AKT1-NOS3, AKT1-GSK3B, BCL2 L1-TP53, BCL2 L1-CASP8, CASP3-CASP8, CASP7-CASP8, CCNA2-CDK2, CCNA2-CDKN1A, CCND1-CDKN1A, CCND1-CDK2, CDK2-RB1, CDK2-CDKN1A, CDKN1A-TP53, CDKN1A-PCNA, E2F1-RB1, EDN1-EDNRA, EGF-EGFR, F3-F7, FOS-JUN, IKBKB-NFKBIA, IKBKB-TNF, JUN-MAPK8, KDR-VEGFA, MDM2-TP53, PLAT-SERPINE1, and PLAU-SERPINE1. By calculating the number of connection points in the network, the top 15 core proteins were identified: STAT3, MAPK3, AKT1, JUN, MAPK1, TP53, TNF, HSP90AA1, RELA, MAPK8, MAPK14, IL6, EGFR, EDN1, and FOS, which may be the core proteins mediating the therapeutic effects of Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe in treating chronic heart failure (Figure 4).
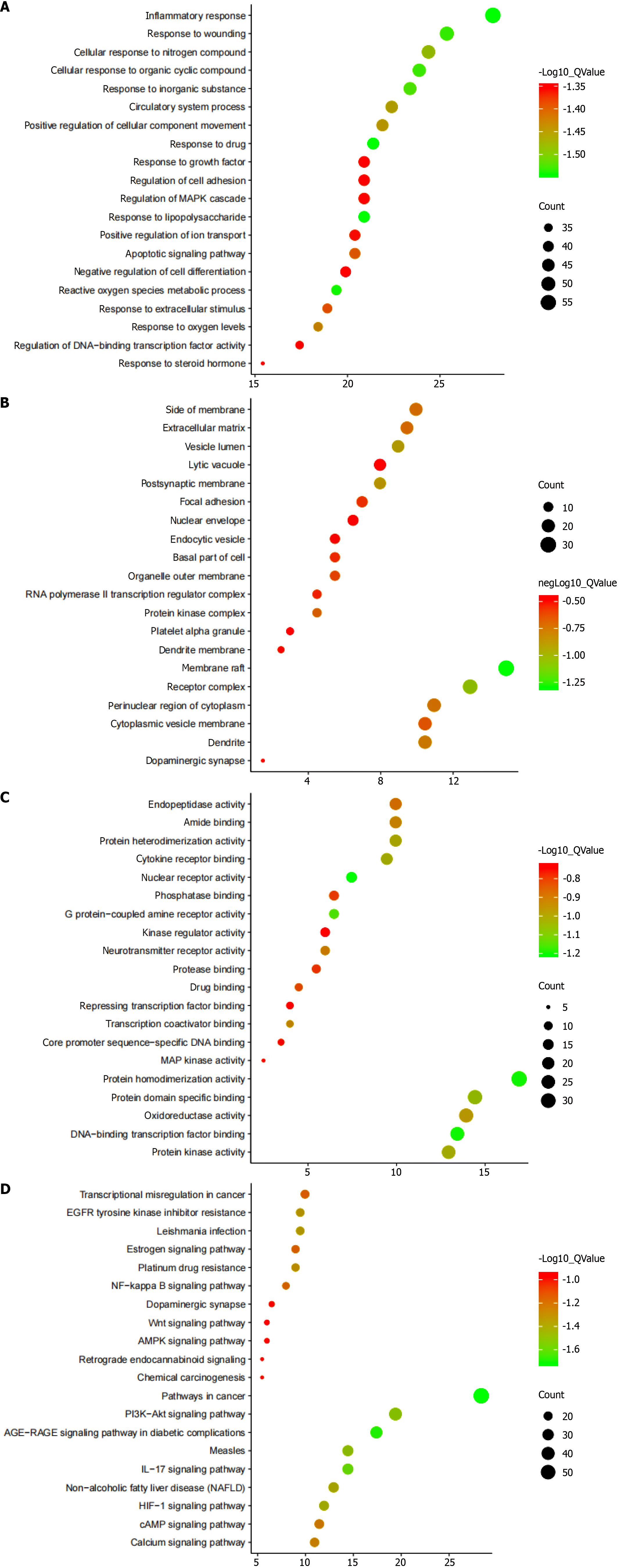
BP enrichment analysis results are shown in Figure 5A. The BPs enriched include response to lipopolysaccharide, inflammatory response, response to drug, reactive oxygen species metabolic process, response to wounding, cellular response to organic cyclic compound, response to inorganic substance, cellular response to nitrogen compound, circulatory system process, positive regulation of cellular component movement, response to oxygen levels, apoptotic signaling pathway, response to extracellular stimulus, positive regulation of ion transport, regulation of MAPK cascade, regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity, regulation of cell adhesion, response to growth factor, response to steroid hormone, fine negative regulation of cell differentiation, etc.
Figure 5B shows the results of CC enrichment analysis. The CCs enriched are membrane raft, receptor complex, vesicle lumen, postsynaptic membrane, dendrite, perinuclear region of cytoplasm, side of membrane, extracellular matrix, protein kinase complex, cytoplasmic vesicle membrane, organelle outer membrane, focal adhesion, basal part of cell, RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex, dendrite membrane, endocytic vesicle, dopaminergic synapse, etc.
Figure 5C shows the results of MF enrichment analysis. The MFs enriched include nuclear receptor activity, protein homodimerization activity, DNA-binding transcription factor binding, G protein-coupled amine receptor activity, protein domain specific binding, protein kinase activity, cytokine receptor binding, protein heterodimerization activity, oxidoreductase activity, transcription coactivator binding, amide binding, neurotransmitter receptor activation activity, endo
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis demonstrated that the pathways enriched include pathways in cancer, IL-17 signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, HIF-1 signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, cAMP signaling pathway, NF-kappaB signaling pathway, AMPK signaling pathway, etc. (Figure 5D).
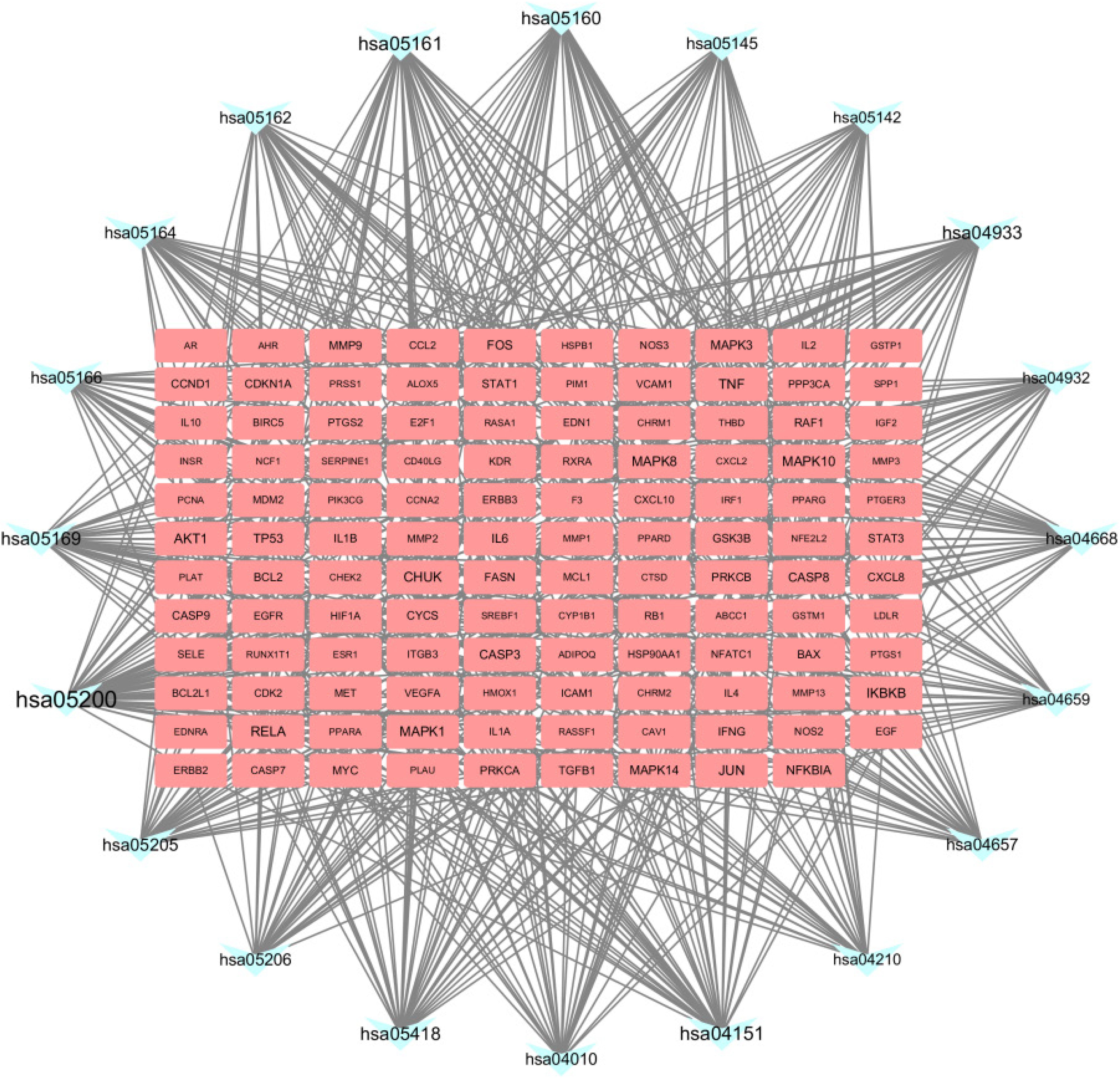
The target-pathway network constructed is shown in Figure 6. The selected core targets are IKBKB, RELA, AKT1, MAPK8, MAPK10, CHUK, JUN, MAPK1, TNF, CASP3, IL6, MAPK3, NFKBIA, MAPK14, TP53, CASP8, etc.
Our previous studies have explored the mechanism of action of Jianpi Huayu Qutan recipe in different conditions, which demonstrated that this recipe functions by regulating the expression of proteins involved in the TNF-α, IL-6, MAPK, cAMP, and AMPK pathways[8-11].
From the perspective of TCM, chronic heart failure is a disease characterized by deficiency in origin and excess in superficiality, which initially occurs in the heart, and then involves the lungs, spleen, and kidneys. With deficiency of heart Qi as the root cause, chronic heart failure mainly manifests as phlegm turbidity, fluid retention, and blood stasis[12]. The Chinese herbal compound preparation Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe, derived from the TCM preparation Sijunzi decoction, was initially used to treat the syndrome of deficiency of spleen Qi[13]. Correcting the deficiency of Qi and blood is essential for the treatment of diseases. The spleen and stomach are the sources of Qi and blood. In Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe, Huangqi, Dangshen, Baizhu, Fuling, and Zhigancao have strong spleen-strengthening effects and can promote blood circulation by flourishing the spleen Qi. Spleen dysfunction will lead to the accumulation of phlegm, so Qingbanxia is included in the recipe for removing dampness to reduce phlegm, and Gualou is used to relieve depression in the chest and regulate the flow of Qi, both of which can help eliminate the phlegm accumulated in the chest. Qi deficiency results in poor blood circulation and stagnation of blood stasis. Zhang et al[14] wrote in the ancient book "Thoroughly Revised Materia Medica" that "Danshen tonifies the heart, removes blood stasis, and promotes fresh blood production......having multiple therapeutic effects". Therefore, Danshen is included in the Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe to tonify the heart, promote blood circulation, and remove blood stasis. Combined use of all these herbs can achieve the effects of strengthening the spleen, tonifying the heart, eliminating phlegm, and removing blood stasis. Our previous studies have shown that Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe can effectively improve patients' blood lipids, improve myocardial function, and affect patients' myocardial mitochondrial energy metabolism[15,16]. This study further explored the molecular mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects of Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe in chronic heart failure.
In the present study, according to oral bioavailability and drug-likeness, 227 active ingredients of eight herbs com
To sum up, the Chinese herbal compound preparation Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe acts on multiple targets through a variety of active ingredients, exerting therapeutic effects on chronic heart failure via multiple pathways. The TNF-α, IL-6, MAPK, cAMP, and AMPK pathways have been experimentally verified to be involved in the therapeutic effects of Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe on chronic heart failure in previous studies. The pathways such as the IL-17, PI3K-Akt, and HIF-1 signaling pathways can be used as the targets in the treatment of chronic heart failure. Future research is warranted to further explore the mechanism of Jianpi Huatan Quyu recipe in the treatment of chronic heart failure.
| 1. | Heart Failure Group of Chinese Society of Cardiology of Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Heart Failure Association of Chinese Medical Doctor Association; Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Cardiology. [Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure 2018]. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2018;46:760-789. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 99] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Mao JY, Zhu MJ. [Consensus of Traditional Chinese Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment Experts on Chronic Heart Failure]. Zhongyi Zazhi. 2014;55:1258-1260. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 3. | Ru J, Li P, Wang J, Zhou W, Li B, Huang C, Li P, Guo Z, Tao W, Yang Y, Xu X, Li Y, Wang Y, Yang L. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1623] [Cited by in RCA: 3144] [Article Influence: 285.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | UniProt Consortium. UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51:D523-D531. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 3209] [Article Influence: 1604.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Stelzer G, Rosen N, Plaschkes I, Zimmerman S, Twik M, Fishilevich S, Stein TI, Nudel R, Lieder I, Mazor Y, Kaplan S, Dahary D, Warshawsky D, Guan-Golan Y, Kohn A, Rappaport N, Safran M, Lancet D. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016;54:1.30.1-1.30.33. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1289] [Cited by in RCA: 2890] [Article Influence: 321.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Szklarczyk D, Kirsch R, Koutrouli M, Nastou K, Mehryary F, Hachilif R, Gable AL, Fang T, Doncheva NT, Pyysalo S, Bork P, Jensen LJ, von Mering C. The STRING database in 2023: protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51:D638-D646. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1815] [Cited by in RCA: 3449] [Article Influence: 1724.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C, Chanda SK. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1523. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3766] [Cited by in RCA: 8765] [Article Influence: 1460.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Li R, Liu LP, Zhang LC, Yang AZ, Yang GL. [Effect of Different Formulae on GLUT-1 Protein of Heart in SAMP6 Mice]. Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi. 2018;45:2432-2434. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 9. | Zhang Q, Zhao QY, Sui GY, Zhao HH, Zhai YR, Yu N, Wang J, Qiu XY, Meng JW, Jia LQ. [Regulatory effect of Jianpi Huayu Qutan method on dyslipidemia improved by fatty acidβoxidation mediated by apoA-Ⅰ/AMPK/CPT1A signaling pathway and its mechanism]. Jilin Daxue Xuebao (Yixueban). 2022;48:1395-1402. |
| 10. | Leng X, Li Y, Song N, Wang Y. [Effect of Huayu Qutan Recipe in Regulating Aortic MAPK Pathway-related Gene Expression in Atherosclerosis Mice]. Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi. 2019;25:116-121. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 11. | Pei YP, Yang GL, Chen ZH, Dong JX, Shao Y, Zhang Z. [Effects of Jianpi Qutan Huayu Recipe on mitochondrial autophagy in cardiomyocytes of rats with spleen qi deficiency]. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi. 2020;35:1743-1746. |
| 12. | Tang Z, Zhang MX. [Research Progress of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure]. Shiyong Zhongyi Neike Zazhi. 2022;36:8-11. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 13. | Cai KZ, Zheng Q, Wei SF, Wu MQ, Xiong H, Zhao HT. [Research Progress of Sijunzi Decoction and Its Predictive Analysis of Quality Markers]. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan. 2023;41:161-168. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 14. | Zhang KT, Ding MG, Zhou JX, Fang CT, Zhang TT. [A clinical observation on modified Sijunzi decoction for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction of Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome]. Shiyong Yixue Zazhi. 2023;39:1982-1986. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 15. | Liu WH, Tang Y, Liu H, Cui JY. [Efficacy of Treating Phlegm Accumulating and Blood Stasis Syndrome of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Strengthening Spleen and Removing Phlegm and Removing Blood Stasis Method]. Liaoning Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao. 2014;16:7-9. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 16. | Kong DZ, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Liu Y, Meng FL, Gao XY, Pan JX, Tang J, Yang GL. [Effect of Treating Stable Angina Pectoris from Spleen on Quality of Life in Patients]. Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi. 2018;45:1345-1350. [DOI] [Full Text] |