Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
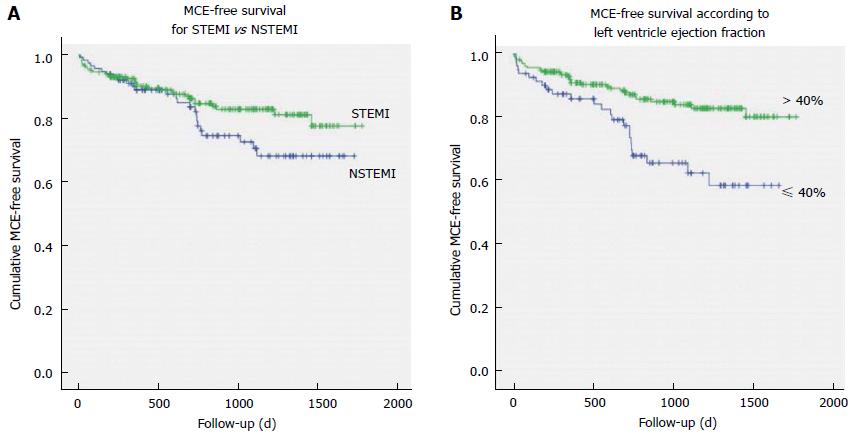
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier major clinical events-free survival curves for: Patients with recent ST-elevation myocardial infarction vs patients with recent non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (A), patients with preserved left ventricle ejection fraction (> 40%) vs patients with depressed left ventricle ejection fraction (≤ 40%) (B).
STEMI: ST-elevation myocardial infarction; NSTEMI: Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction; MCE: Major clinical events.
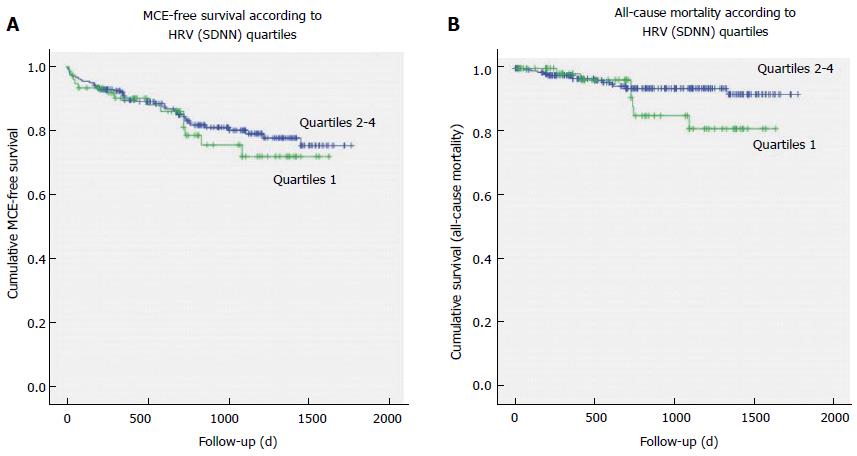
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for patients with lowest quartile of standard deviation of all normal-to-normal intervals vs patients in the other standard deviation of all normal-to-normal intervals quartiles: Major clinical events-free survival curves (A), all-cause mortality curves (B).
HRV: Heart rate variability; SDNN: Standard deviation of all normal-to-normal intervals; MCE: Major clinical events.
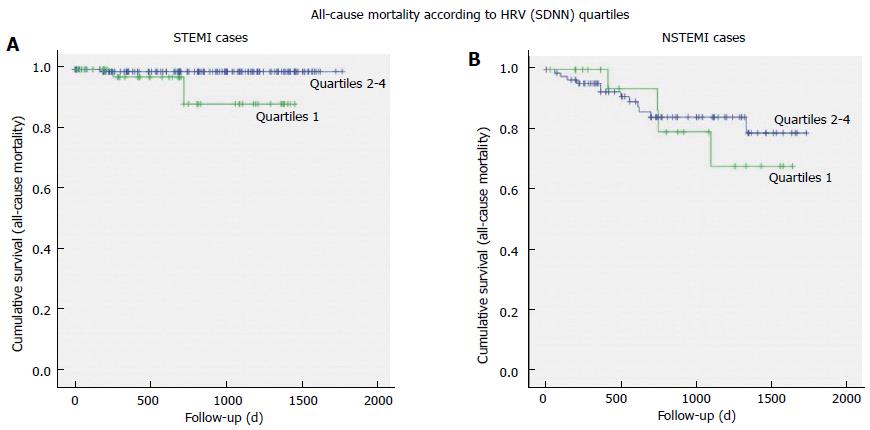
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier all-cause mortality curves for ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients (A) and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients (B) divided between cases with lowest quartile of standard deviation of all normal-to-normal intervals vs cases in the other standard deviation of all normal-to-normal intervals quartiles.
HRV: Heart rate variability; SDNN: Standard deviation of all normal-to-normal intervals; STEMI: ST-elevation myocardial infarction; NSTEMI: Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
- Citation: Compostella L, Lakusic N, Compostella C, Truong LVS, Iliceto S, Bellotto F. Does heart rate variability correlate with long-term prognosis in myocardial infarction patients treated by early revascularization? World J Cardiol 2017; 9(1): 27-38
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v9/i1/27.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i1.27