Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Cardiol. Dec 26, 2015; 7(12): 875-881
Published online Dec 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.875
Published online Dec 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.875
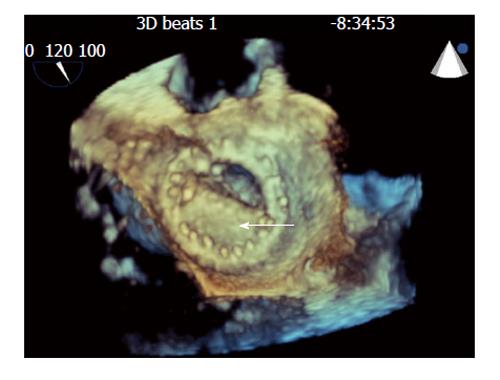
Figure 1 Still frames of 3-dimensional transesophogeal echocardiographic rendering of the mechanical bi-leaflet mitral valve as visualized from the left atrial perspective during diastole showing fixed mitral leaflet (arrow).
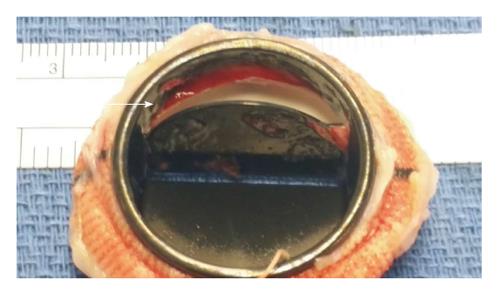
Figure 2 Gross sample of explanted mechanical mitral valve revealing the transesophogeal echocardiography finding residual organized thrombus, apparent on the mitral valve disc (arrow).
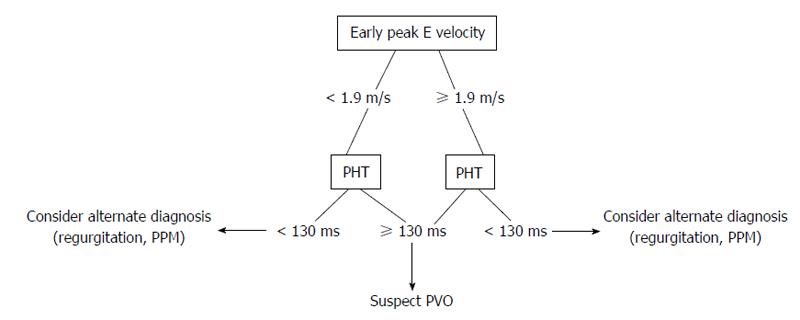
Figure 3 Proposed echocardiographic evaluation for suspected prosthetic mitral valve obstruction.
PHT: Pressure half-time; PVO: Prosthetic valve obstruction; PPM: Prosthetic patient mismatch.
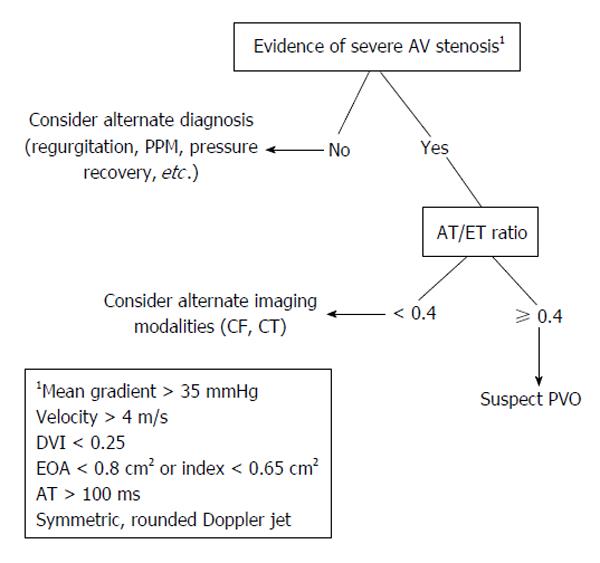
Figure 4 Proposed non-invasive evaluation for suspected prosthetic aortic valve obstruction.
AT: Acceleration time; ET: Ejection time; PPM: Prosthetic-patient mismatch; CF: Cine fluoroscopy; CT: Computed tomography; PVO: Prosthetic valve obstruction; EOA: Effective orifice area; DVI: Doppler velocity index; AV: Aortic valve.
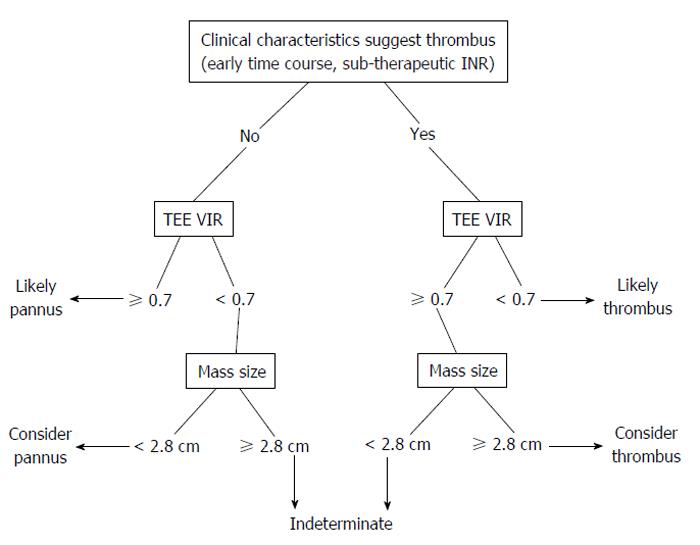
Figure 5 Proposed non-invasive evaluation for differentiating thrombus from pannus as underlying cause of prosthetic valve obstruction.
TEE: Transesophogeal echocardiography; VIR: Video intensity ratio; INR: International normalized ratio.
- Citation: Salamon J, Munoz-Mendoza J, Liebelt JJ, Taub CC. Mechanical valve obstruction: Review of diagnostic and treatment strategies. World J Cardiol 2015; 7(12): 875-881
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v7/i12/875.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.875