Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. Aug 26, 2014; 6(8): 713-727
Published online Aug 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i8.713
Published online Aug 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i8.713
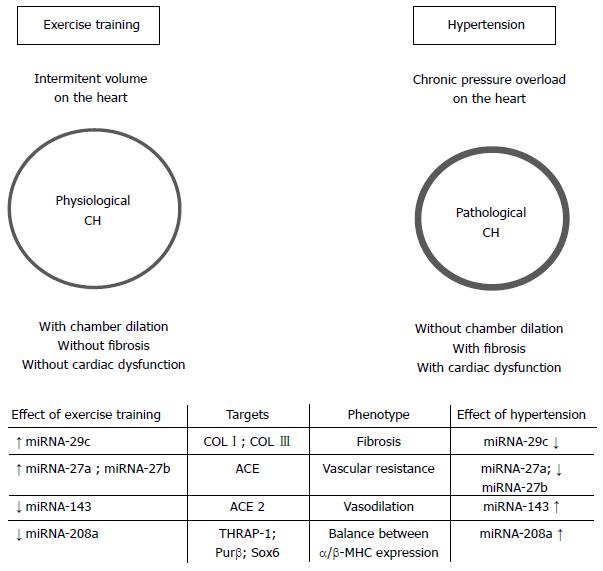
Figure 1 Effects of aerobic exercise training on the cardiac miRNAs in hypertension.
CH: Cardiac hypertrophy; COL I: Collagen 1; COL III: Collagen 3; ACE: Angiotensin-converting enzyme; ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; THRAP-1: Thyroid hormone-associated protein 1; Purβ: Purine-rich element binding protein B; α-MHC: α-Myosin heavy chain; β-MHC: β-Myosin heavy chain.
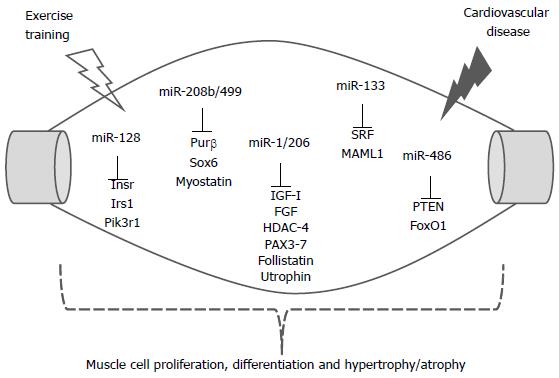
Figure 2 Skeletal muscle miRNAs and selected target genes regulating cell proliferation, differentiation and hypertrophy/ atrophy by exercise training and cardiovascular diseases.
The relationship between miRNAs and the mRNAs that encode proteins is shown. Insr: Insulin receptor; Irs1: Insulin receptor substrate 1; Pik3r1: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases regulatory 1; Purβ: Purine-rich element binding protein B; HDAC4: Histone deacetylase 4; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; SRF: Serum response factor; MAML1: Mastermind 1; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; FoxO1: Forkhead box protein O1.
- Citation: Neves VJD, Fernandes T, Roque FR, Soci UPR, Melo SFS, Oliveira EM. Exercise training in hypertension: Role of microRNAs. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(8): 713-727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i8/713.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i8.713