Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Mar 26, 2025; 17(3): 103074
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i3.103074
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i3.103074
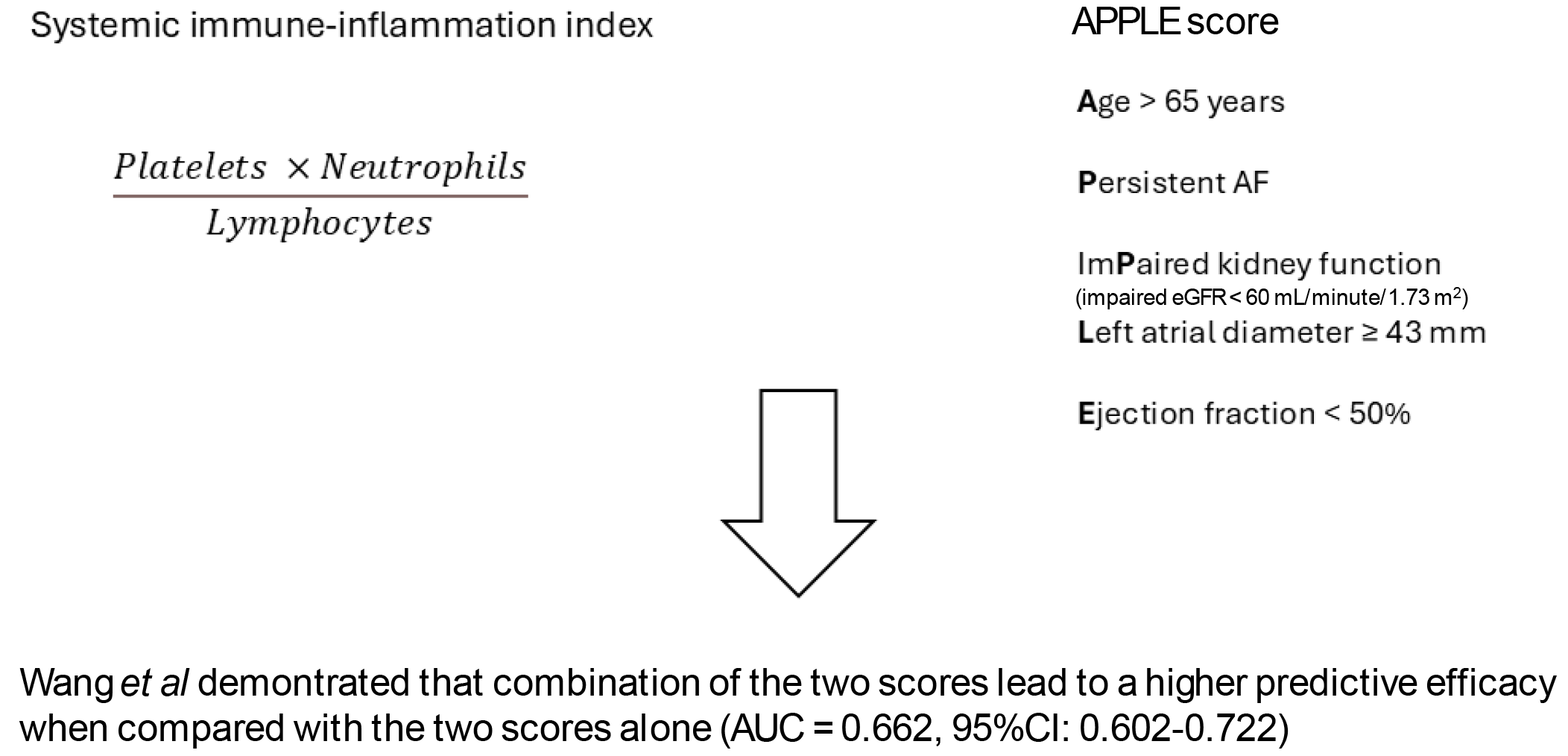
Figure 1 The implementation of the systemic immune-inflammation index in the APPLE score leads to a better prediction of atrial fibrillation recurrency after radiofrequency catheter ablation.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) recurrence can occur in up to 45% of patients after radiofrequency catheter ablation. The recurrence of AF in these patients is likely multifactorial. Inflammation is thought to play a key role in this setting. The systemic immune-inflammation index has been recently developed to evaluate the inflammatory status of the body. Conversely, the APPLE score has been developed to evaluate the risk of AF recurrence after radiofrequency catheter ablation. The study by Wang et al[14] proved that using the two scores together leads to a more precise evaluation of the AF recurrence risk. AF: Atrial fibrillation; AUC: Area under the curve; EGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate.
- Citation: Tirandi A, Carbone F, Liberale L, Montecucco F. Evaluating inflammatory status to predict atrial fibrillation recurrence following ablation: The role of systemic immune-inflammation index. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(3): 103074
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i3/103074.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i3.103074