Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Cardiol. Jan 26, 2024; 16(1): 16-26
Published online Jan 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i1.16
Published online Jan 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i1.16
Figure 1 Flowchart of the present study.
PCI: Percutaneous coronary intervention; SPT: Spasm provocation test; VSA: Vasospastic angina.
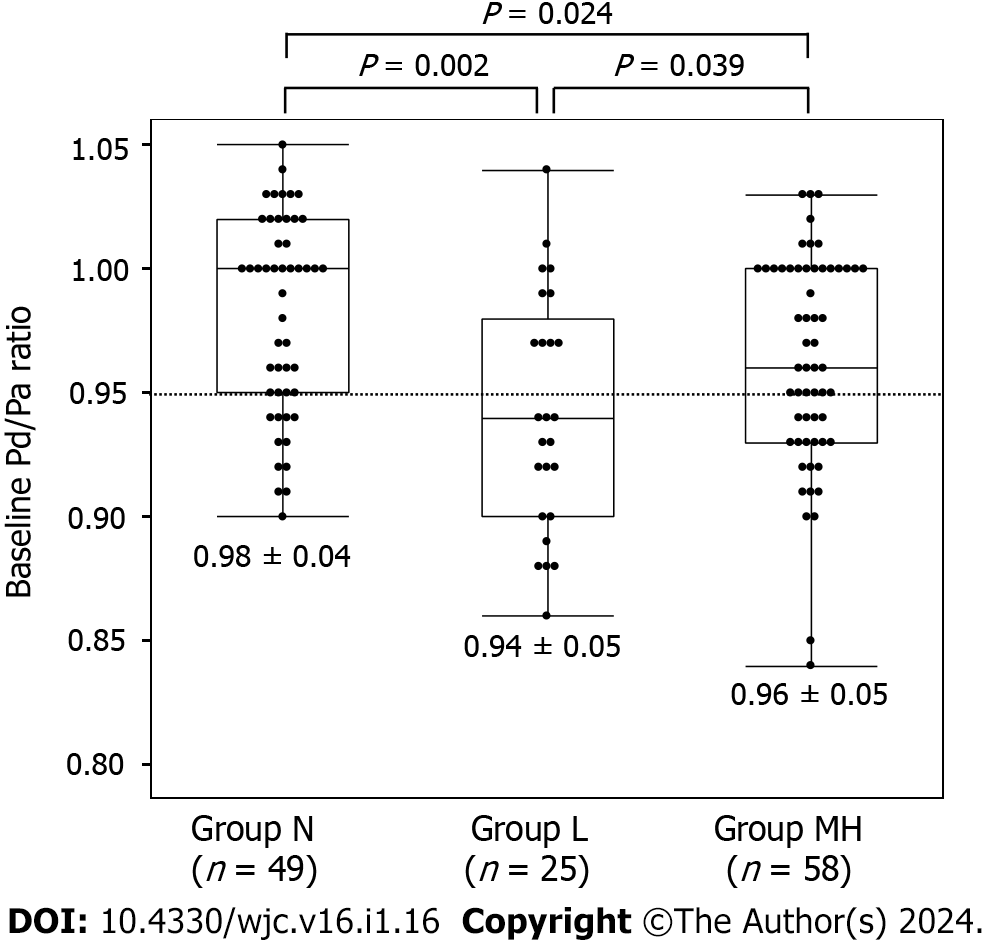
Figure 2 The distal pressure/aortic pressure ratio at baseline in lesions with no coronary spasm in response to spasm provocation test (group N), lesions in which coronary spasm was induced by a low dose of acetylcholine (group L), and lesions in which coronary spasm was induced by a moderate or high-dose acetylcholine (group MH).
This value was lower in group L than in groups MH and N. ACh: Acetylcholine; Pa: Aortic pressure; Pd: Distal pressure; SPT: Spasm provocation test.
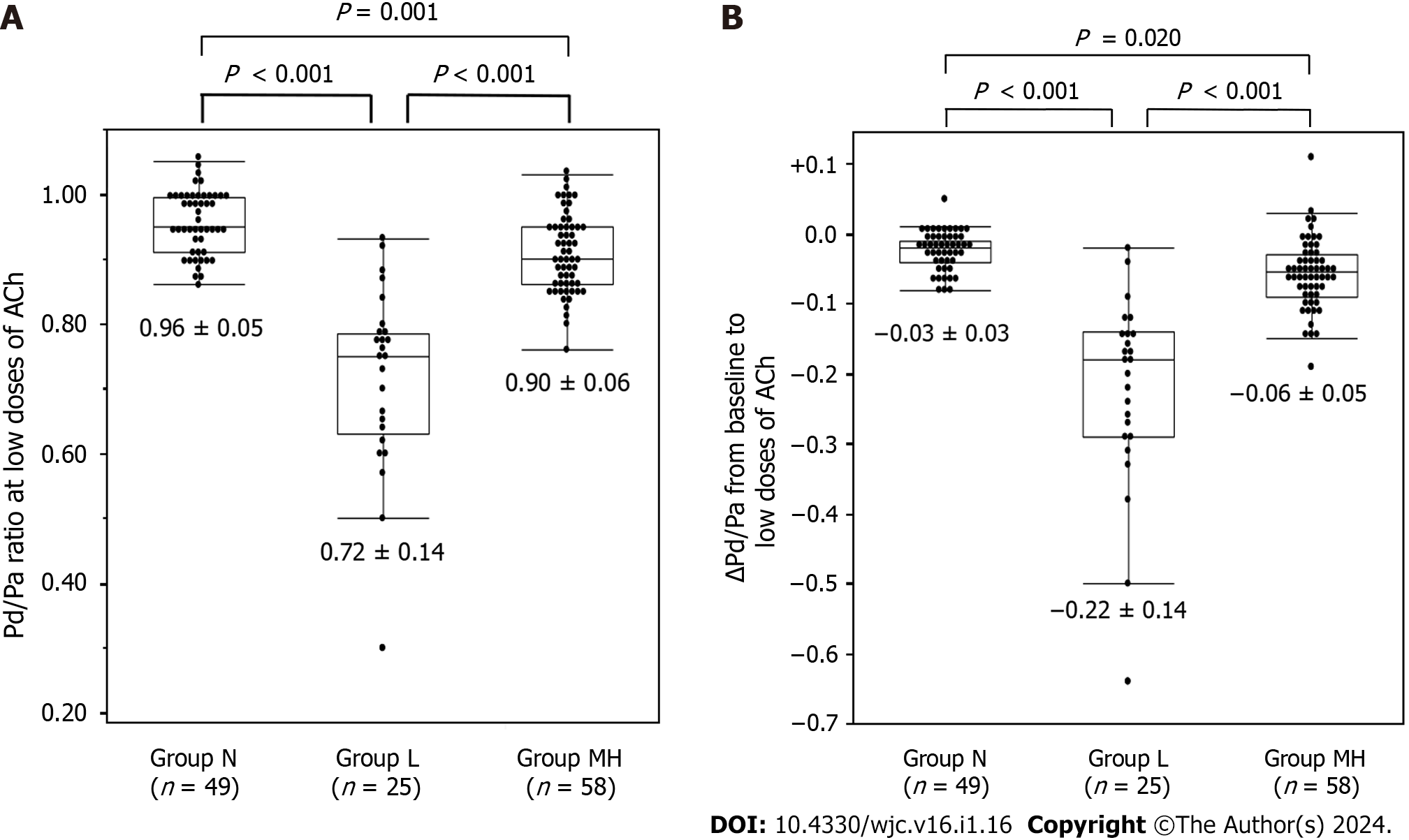
Figure 3 The distal pressure/aortic pressure ratio at low doses of acetylcholine and Pd/Pa between baseline and low doses of acetylcholine in the three coronary spasm groups.
A: Shows distal pressure/aortic pressure (Pd/Pa) at low doses of acetylcholine (ACh). The value was lowest in group L and highest in group N; B: Shows the Pd/Pa between baseline and low doses of ACh. This value was also lowest in group L and highest in group N. ACh: Acetylcholine; Pa: Aortic pressure; Pd: Distal pressure.
Figure 4 The results of a receiver-operating characteristics analysis of the data from this study.
A: Shows the cutoff value of the distal pressure/aortic pressure (Pd/Pa) ratio at baseline for the prediction of coronary spasms induced by low doses of acetylcholine (ACh); B: Shows the cutoff value of the Pd/Pa between baseline and low-doses ACh. ACh: Acetylcholine; Pa: Aortic pressure; Pd: Distal pressure; ROC: Receiver-operating characteristics; AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Teragawa H, Oshita C, Uchimura Y. Do changes in intracoronary pressure aid coronary spasm diagnosis using the spasm provocation test? World J Cardiol 2024; 16(1): 16-26
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v16/i1/16.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i1.16