INTRODUCTION
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a phosphorylated sphingolipid that is generated by the action of sphingosine kinase on sphingosine that is formed through the catabolism of ceramide derived from either a de novo pathway or from sphingomyelin breakdown[1]. S1P is secreted from cells and carried extracellularly on lipoprotein particles, particularly high-density lipoproteins (HDL)[2,3]. It acts upon a family of nine guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptors to stimulate heterotrimeric and small G-protein- and kinase-coupled intracellular events[4-6]. The nine members of the S1P receptor family include S1P1-5, Gpr3, Gpr6, Gpr12 and Gpr63. The latter four members of the family are the most recent to emerge and therefore there is rather little known about their roles in physiology and pathology[7,8].
The prototypic member of this S1P receptor family was first defined as a gene whose expression was upregulated during the process by which endothelial cells form capillary-like tubular structures in vitro, and given the name endothelial differentiation gene 1 (EDG-1)[9]. Subsequent studies have established that S1P is the ligand for EDG-1[10], and have led to it being referred to as S1P receptor 1 (S1P1). These seminal discoveries have spawned extensive research into S1P signaling and the involvement of S1P signaling in various aspects of vascular biology, including cell adhesive and motility activities associated with blood vessel formation; the subject of this review.
S1P SIGNALING AND ITS EFFECTS ON VASCULAR CELL ADHESION AND MOTILITY
S1P ligation with its receptors elicits a range of cell-type-specific adhesive and motility responses[5]. For example, when administered to endothelial cells, it stimulates the assembly of adherens junctions[10,11], induces formation of actin stress fibers and cortical actin[11], and promotes motility and barrier function[12,13]. Similarly, treatment of cultured fibroblasts with S1P induces formation of actin-containing stress fibers and assembly of focal adhesion contacts via tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and paxillin[14]. By contrast, treatment of vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) with S1P causes actin filament disassembly, inhibition of focal adhesion contact formation[15] and suppression of motility[15,16].
The basis for the differential effects of S1P on the motility of endothelial cells vs SMCs could relate to the disparate signaling activities of specific S1P receptors (Figure 1) and the stoichiometry of those receptors expressed by each cell type. For example, S1P signaling via S1P1 and S1P3 promotes endothelial cell migration[17] as demonstrated by experiments that have shown that S1P-dependent migration of endothelial cells is suppressed by treatment with the S1P1 antagonist, W146[17], or siRNAs targeting S1P1 and S1P3[18]. By contrast, S1P signaling via S1P2 inhibits endothelial cell migration as demonstrated by findings that have shown that treatment with the S1P2 antagonist, JTE-013, increases endothelial cell migration[19,20]. A high S1P2: S1P1 ratio may explain the differential effects of S1P on motility of endothelial cells vs SMCs. In adult medial SMCs, the ratio S1P2: S1P1 is indeed high and the cells do not migrate in response to S1P[21]. This is in contrast to neonatal SMCs that migrate in response to S1P and express higher levels of S1P1, similar levels of S1P2, and thus have a lower S1P2: S1P1 ratio. Differences in S1P receptor stoichiometry are also manifested in different types of endothelial cells. For example, human omental microvascular endothelial cells express relatively higher levels of S1P2 transcripts than human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) do, and have distinctly different migratory behavior[22].
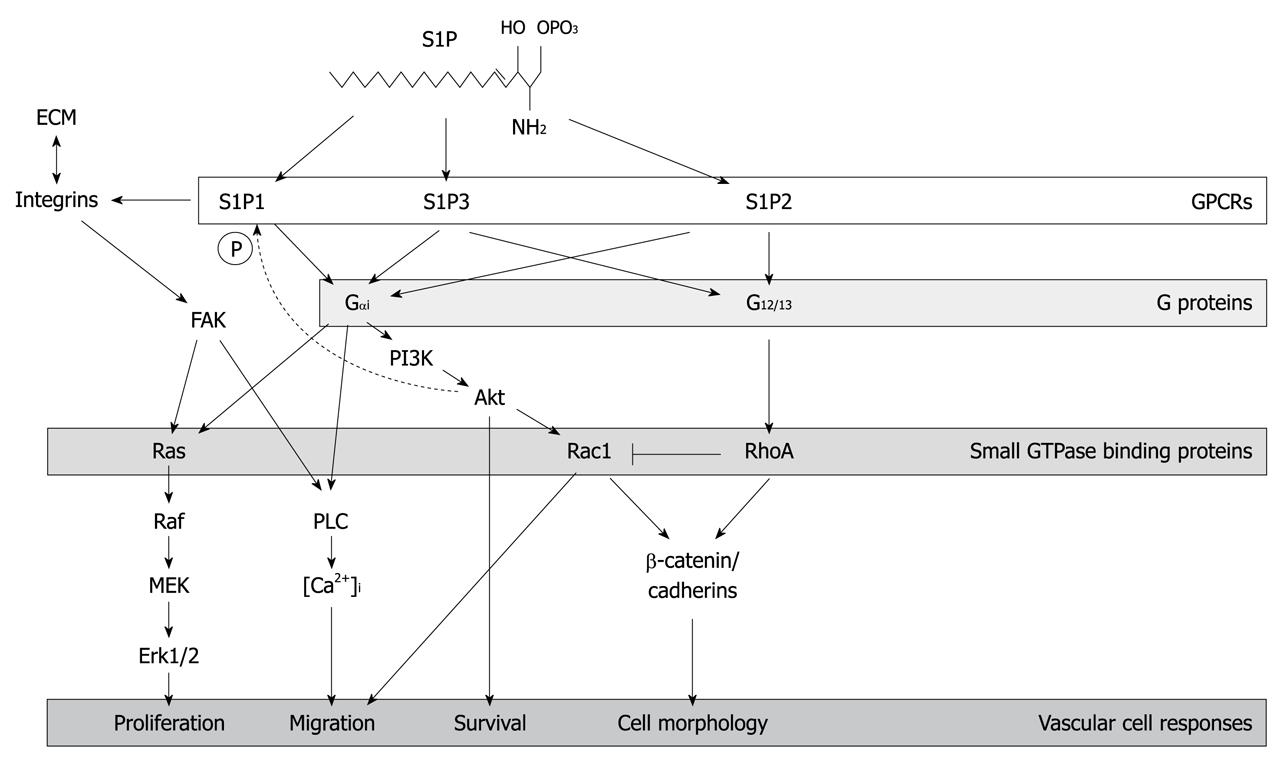
Figure 1 Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling.
The figure shows salient aspects of the signaling cascades that are mediated by three members of the sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor family, S1P1-3. Given the focus of this review, the cascades depicted emphasize the effects of S1P signaling on modulation of cadherin and actin cytoskeletal protein rearrangements, as well as integrin-extracellular matrix interactions that collectively mediate S1P-dependent adhesive and motility responses that are important for vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; GPCRs: G-protein-coupled receptors; PLC: phospholipase C; ECM: Extracellular matrix; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase.
In addition to S1P receptor stoichiometry, it is also possible that G protein subunit availability is a determining factor in the migratory outcome of S1P signaling in vascular cells. For example, S1P1 receptor coupling through G protein subunit, Gαi, leads to activation of the Rho family GTPase, Rac1, which promotes migration[23]. By contrast, S1P2 coupling through the G protein subunit α13 (G13) activates RhoA and negatively regulates Rac1 activity, which leads to suppression of migration[23]. Differential effects of S1P signaling may also relate to expression of regulators of G protein-signaling-Rho guanine exchange factors such as LARG, leukemia-associated RhoGEF, which in SMCs, is activated downstream of S1P2 and mediates activation of RhoA[24].
S1P effects on vascular cell adhesion and motility also integrate signaling mediated by integrins. For example, S1P activates the integrin, αvβ3, as evidenced by ligation of αv and β3 subunits in endothelial cells after S1P treatment[25]. S1P also stimulates the association of αvβ3 with FAK and cytoskeletal proteins including α-actinin[25]. These events do not occur in S1P1-deficient endothelial cells, which indicates the essential role of S1P1 in the adhesion process. In addition to αvβ3, β1 integrins also participate in S1P-induced endothelial cell migration[18,26]. Work by Bayless et al[26] has shown that S1P-induced endothelial cell invasion into collagen matrices involves α2β1, while invasion in fibrin involves a combination of α5β1 and αvβ3 integrins. Inter-related with integrin activation is S1P activation of phospholipase C (PLC) and mobilization of calcium from intracellular stores, which mediate both FAK phosphorylation and endothelial cell migration[11,27].
S1P signaling also mediates the formation of N-cadherin-based junctions that are important in cell-cell adhesion that is required for vascular stabilization. S1P induces plasma membrane trafficking and activation of N-cadherin and p120-catenin in endothelial cells[28]. The translocation process facilitates endothelial-cell interaction with other N-cadherin-expressing cells, including endothelial cells and SMCs[28]. S1P-induced N-cadherin-dependent adhesion involves S1P-stimulated phosphorylation of N-cadherin and p120-catenin and the formation of protein complexes of N-cadherin, α-catenin, β-catenin and p120-catenin[28].
The process of S1P-induced cell-membrane trafficking of N-cadherin is also dependent on Rho family GTPases, in particular Rac1[28]. Indeed, Rac1 is translocated to endothelial cell junctions together with β-catenin and VE-cadherin within minutes of S1P treatment[11,29]. In cells that overexpress a dominant negative Rac1 mutant, S1P does not promote increased transendothelial electrical resistance; an indication that the Rac-dependent translocation of junctional components is required to mediate endothelial barrier function[29].
In addition to activating Rac1, S1P also activates Src kinase in endothelial cells[30]. Together, activation of Rac1 and Src pathways are essential for the process of polymerization of actin filaments behind the leading edge of the cell to drive the extension of lamellipodia during migration. In particular, both Src and Rac pathways are necessary for lamellipodia targeting of the F-actin-binding protein, cortactin[30]. In addition to mediating cytoskeletal protein rearrangements involved with migration, S1P-mediated activation of Rac1 is also required for formation of the cortical actin ring which functions in endothelial cell barrier[13]. Specifically, S1P mediates redistribution of FAK, paxillin, and the ADP-ribosylation factor GTP-ase activating protein, GIT2, to the cell periphery to form a focal adhesion complex that is associated with the cortical actin ring[13].
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway in endothelial cells is also activated by S1P, which leads to migration[31]. Indeed, activation of PI3K is required for S1P-mediated endothelial cell migration on collagen[32]. S1P activation of PI3K leads to Akt phosphorylation, which is required for relocalization of cortactin to the lamellipodia of cultured HUVECs[31]. In this context, S1P mediated activation of Akt leads to S1P1 receptor phosphorylation. By contrast, in microvascular endothelial cells, Akt does not appear to be required for migration in response to S1P-mediated activation of PI3K[32]. S1P-dependent Akt activation in these cells may therefore be facilitating other Akt-dependent activities such as cell survival or endothelial barrier function[33].
Besides activating Rho kinase, PI3K and Akt pathways, S1P also activates endothelial cell extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling through a Gαi-dependent pathway[34] and increases in [Ca2+]i due to either intracellular Ca2+ release from stores, extracellular Ca2+ influx, or both[35,36]. Work by Ambesi et al[32] has revealed that ERK activation by S1P stimulates endothelial cell cycle progression. This finding has emerged from studies in which a peptide from fibronectin, called anastellin, was found to inhibit specifically ERK-mediated endothelial cell proliferation in response to S1P, while having no effect on S1P-induced cell migration or Akt activation.
S1P signaling has also been shown to increase endothelial cell expression of CCN1 (Cyr61)[37], an extracellular matrix protein that promotes both endothelial cell and endothelial progenitor cell adhesion and migration in vitro[38,39]. The mechanism by which S1P induces CCN1 expression involves internalization and nuclear trafficking of S1P1[37]. Estrada et al[37] have shown that, in nuclear lysates from S1P-treated endothelial cells, the transcription of CCN1 requires S1P and is pertussis-toxin-sensitive. These findings suggest that S1P-S1P1-Gαi signaling responsible for CCN1 transcription occurs in the nucleus.
VASCULOGENESIS AND S1P SIGNALING
Blood vessels are formed by either vasculogenesis or angiogenesis[40]. These two processes are distinguished by the source of the endothelial cells that form the new vessels. In vasculogenesis, endothelial cells are generated de novo from endothelial progenitor cells that are known as angioblasts, whereas in angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels occurs through the sprouting and proliferation of existing endothelial cells.
Vasculogenesis is initiated in the mammalian embryo at different places and times in development. In the mouse, the earliest events in vasculogenesis occur in the yolk sac beginning at embryonic day (E) 6-6.5, as demonstrated by the appearance of Tal1+/Flk1+ angioblasts[41]. Subsequently (between E6.5 and 7.3), primary networks of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM)-positive endothelial tubes form in the yolk sac. These networks remodel and the blood vessels stabilize between E8.4 and E8.5 through a process that involves expression of VE-cadherin[42]. Following vasculogenesis in the yolk sac, de novo blood vessel formation is initiated next in the allantois (E7), followed by the endocardium (E7.3) and dorsal aorta (E7.6), and then in the head vessels (E8.2) and cardinal veins (E8.3)[41]. Later in development, vasculogenesis mediates the formation of the coronary arteries (E9)[43] and the pulmonary vasculature (E10.5)[44].
At each site of vasculogenesis, blood vessel formation occurs via a process that can be separated into a number of discrete steps. Initially, the differentiation of splanchnic mesoderm occurs to form angioblasts (i.e. Tal1+/Flk1+ cells)[41]. As a result, angioblasts emerge as isolated cells; typically within sites of presumptive vasculogenesis. Isolated angioblasts move and coalesce to form aggregates and the angioblasts within these aggregates extend cellular protrusions that connect with cells of adjacent aggregates. Concomitantly, angioblasts differentiate and express endothelial cell proteins (e.g. PECAM and VE-cadherin) and also undergo lumen formation[26]. Isolated nascent vessel elements interact to form a capillary-like network of vessels referred to as a primary vascular network. Through an iterative process that involves extension of cell protrusions into avascular spaces that result in progressive loss of avascular spaces, and fusion of small diameter vessels, capillary-like blood vessels give rise to vascular sinuses or large vessels[45].
Indirect evidence for the involvement of S1P signaling in the earliest events of de novo blood vessel formation comes from the finding that transcripts that encode S1P1, S1P2 and S1P3, as well as the S1P biosynthesis enzyme, sphingosine kinase 2 (Sphk2) are expressed in the E7.5 allantois[46]. At this stage, the allantois has angioblasts engaged in coalescence to form aggregates, but lacks endothelial cells and primary vascular networks. The early events of vasculogenesis that occur in the E7.5 allantois resemble those in the yolk sac between E6 and E6.5, however, it remains to be determined whether S1P receptors and Sphk2 are expressed in the E6-6.5 yolk sac. Clearly, S1P1, S1P2 and S1P3 and Sphk2 are all expressed during later phases of vasculogenesis (i.e. during primary network formation and stabilization phases) that occur at a number of sites including the murine yolk sac at E7.5 and allantois at E8.5[46].
The role of S1P receptors and Sphk2 expressed during early phases of vasculogenesis is not well defined. Evidence from a study of E7.8 allantois explants cultured in serum-free medium (i.e. lacking S1P from serum) has revealed that exogenously added S1P can induce blood vessel formation without affecting differentiation of the endothelial lineage or the proliferation of angioblasts and early endothelial cells[46]. Specifically, S1P has been found to promote adhesive activities that are required for the expansion of primary networks, including the elongation and migration of early endothelial cells[46]. It is not known whether S1P signaling is involved in the movement of isolated angioblasts within sites of presumptive vasculogenesis in vivo. Angioblast movement has been described in a number of sites of embryonic vasculogenesis. For example, the formation of the mouse dorsal aorta (between E7.5 and 8.5) involves movement and aggregation of isolated angioblasts that are dispersed throughout the splanchnic mesoderm that lies lateral to the embryo axis. A similar process occurs in zebrafish in which angioblasts undergo movement to the midline where they aggregate to form the trunk axial vessels, the dorsal aorta, and posterior cardinal vein[47]. Another example is the vascularization of the neural tube in avian embryos, in which there is dorsal immigration of isolated angioblasts[48]. Remarkably, very little is known about the mechanisms that govern angioblast movement. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is known to regulate angioblast protrusive activity[49] and promote chemotaxis[50], but angioblasts remain able to aggregate in the presence of antagonists of VEGF signaling[51]. Whether angioblast motility is dependent on S1P signaling is an open question.
In contrast to findings that indicate the importance of S1P signaling in aspects of vasculogenesis that occur in allantois explant cultures, phenotypic analysis of mice deficient in the S1P receptors, S1P1, S1P2, S1P3 and S1P5 have not implicated S1P signaling as being required for vasculogenesis. For example, S1P1 deficiency leads to a hemorrhagic phenotype that is apparent at E12.5, with lethality occurring after E13.5[52,53]. Deficiency of either S1P2 or S1P3 does not lead to bleeding or embryonic lethality[53]. However, in S1P2/S1P3 double nulls, bleeding is apparent in embryos as early as E13.5, and in S1P1/S1P2/S1P3 triple nulls, bleeding is apparent at E10.5. Overall, either the lack of vascular defects or the relatively advanced level of vascular development that occurs before the appearance of vascular abnormalities (i.e. morphological or onset of bleeding) in all of these nulls is an indication that S1P receptors 1, 2, 3 and 5 are not essential for the earliest events in embryonic vasculogenesis, which is completed by E9.5, although vasculogenesis does occur later in development to generate lung and coronary blood vessels. However, it remains to be established whether any of the other S1P receptors (i.e. Gpr3, Gpr6, Gpr12 and Gpr63) plays a role in vasculogenesis. In this regard, it is interesting to note that deficiency of G13, which participates in S1P signaling mediated by S1P2, 3 and 4[54] and perhaps some of the S1P-binding Gprs, leads to lethality after E9.5, with complete absence of blood vessels in the E8.5 yolk sac[55]. Similarly, endothelial-specific knockout of Rac1 results in embryonic lethality at E9.5, and a failure of primary networks of yolk sac blood vessels to remodel[56]. The vascular defects of the G13 and the Rac1 nulls bear similarity to abnormalities of vasculogenesis that occur as a result of deficiency of a number of other genes[57].
Findings from phenotypic analysis of mice deficient in the enzymes responsible for S1P biosynthesis, Sphk1 and Sphk2, do not implicate S1P synthesis by the embryo as being required for vasculogenesis. For example, deficiency of either Sphk1 or Sphk2 does not lead to vascular defects during development, and deficiency of both Sphk1 and Sphk2 leads to embryos that show mid-gestational hemorrhage (i.e. E11.5)[58]. The relatively advanced level of vascular development achieved in the sphingosine kinase double nulls indicates that embryonic expression of these enzymes is not essential for the earliest events in vasculogenesis. Although sphingosine kinase double null embryos are incapable of S1P biosynthesis, there remains the question of whether maternal-derived S1P might contribute to S1P signaling during vasculogenesis. Female mice deficient in sphingosine kinases display defective uterine decidualization and blood vessel formation and do not support embryonic development beyond E8.5, with approximately 50% embryonic death seen at E7.5[59]. These findings underline the crucial importance of S1P for the formation of normal vasculature that comprises the maternal-fetal interface, and also raises the possibility that maternally derived S1P, carried on HDL, may contribute to embryonic development. HDL, the predominant carrier of S1P[2] is transported from the maternal circulation across the yolk sac visceral endoderm via the action of an endocytic receptor, cubilin[60]. Cubilin-deficient embryos fail to take up maternal HDL and also display severe defects of the yolk sac vasculature (i.e. failure of E8.5 primary networks to remodel)[60]. Whether these apparent defects of vasculogenesis are the result of embryonic deficiency of maternal derived S1P is not yet known.
S1P SIGNALING IN ANGIOGENESIS
In addition to promoting angiogenesis through its effects on endothelial cell migration and proliferation, S1P also promotes angiogenesis by stimulating endothelial morphogenesis. For example, S1P acts to induce the formation capillary-like networks of endothelial cells cultured on Matrigel[11]. It also promotes endothelial cell invasion, lumen formation, and branching morphogenesis into 3D collagen and fibrin matrices[26]. These findings are consistent with others that show that selective absorption and neutralization of S1P using anti-S1P monoclonal antibody blocks capillary-like network formation of cultured endothelial cells, as well as in vivo angiogenesis induced by basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and VEGF in a Matrigel implant model of subcutaneous angiogenesis[61].
Mechanistically, the effects of S1P on in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis have been shown to be mediated via S1P1 and S1P3 signaling. In experiments by Lee et al[11], S1P1 and S1P3 antisense oligonucleotides have been shown to inhibit S1P enhancement of blood vessel formation by FGF-2 and VEGF in a Matrigel implant model. These findings are consistent with those from studies that have shown that functional antagonism of S1P1 inhibits angiogenesis[62,63]. For example, oral administration of the S1P1 binding compound, FTY720, to mice inhibits angiogenesis in corneal micropocket assays and implanted chambers filled with VEGF-containing agar[63]. In mice inoculated with B16/BL6 melanoma cells, oral administration of FTY720 reduces the density of blood vessels associated with metastatic tumors[63]. Similarly, in mice implanted with B16-F10 melanoma cells and treated with the anti-S1P monoclonal antibody, there is a substantial reduction in tumor microcapillary density[61]. Recently, an S1P1 antagonist (referred to as chemical lead 2) derived from a small molecule library screen, has been shown to inhibit the in vitro formation of capillary-like networks by endothelial cells, as well as inhibit VEGF-induced corneal angiogenesis in vivo[62]. While there is general consensus that S1P signaling via S1P1 and S1P3 is pro-angiogenic, there are reports that S1P2 can act to both promote and inhibit angiogenesis in different in vivo settings. In one study, S1P2-deficient mice have been shown to have increased tumor growth that is attributable to increased angiogenesis[64]. By contrast, another study using S1P2-deficient mice has shown reduced angiogenesis associated with retinopathy[65].
A key aspect of the effect of S1P in angiogenesis relates to its ability promote intercellular interactions between endothelial cells and SMCs that are necessary for stabilization of newly formed blood vessels. This role is evident in embryos that are constitutively deficient in S1P1 in which there is incomplete SMC coverage of nascent blood vessels, which is accompanied by hemorrhage and edema[52]. By contrast, analysis of embryos that are deficient in S1P2 and S1P3 indicates that their blood vessels appear normally invested with SMCs, and that endothelial cell-cell junctions are intact, however endothelial cell morphology is aberrant[53].
CONCLUSION
Clearly, S1P signaling is a potent effector of vascular cell adhesion and motility that are important for blood vessel formation. Overall, most data support the concept that S1P signaling via specific S1P receptors orchestrates apparently discrete events along the continuum of blood vessel formation. Strong evidence exists for S1P serving as a pro-angiogenic factor as well as an inducer of vascular maturation. The question of whether S1P signaling plays a crucial role in the earliest events in vasculogenesis remains to be answered conclusively. In this regard, it will be important to establish the extent to which signaling mediated by the lesser-studied S1P receptors (i.e. GPR3, GPR6, GPR12[8] and GPR63[66]) contribute along the continuum of blood vessel formation.
Peer reviewer: Bradley K McConnell, PhD, Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, University of Houston, College of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 4800 Calhoun Road, Bldg SR-2, Room 460, Houston, TX 77204-5037, United States
S- Editor Cheng JX L- Editor Kerr C E- Editor Zheng XM