Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2016; 7(4): 231-239
Published online Nov 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i4.231
Published online Nov 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i4.231
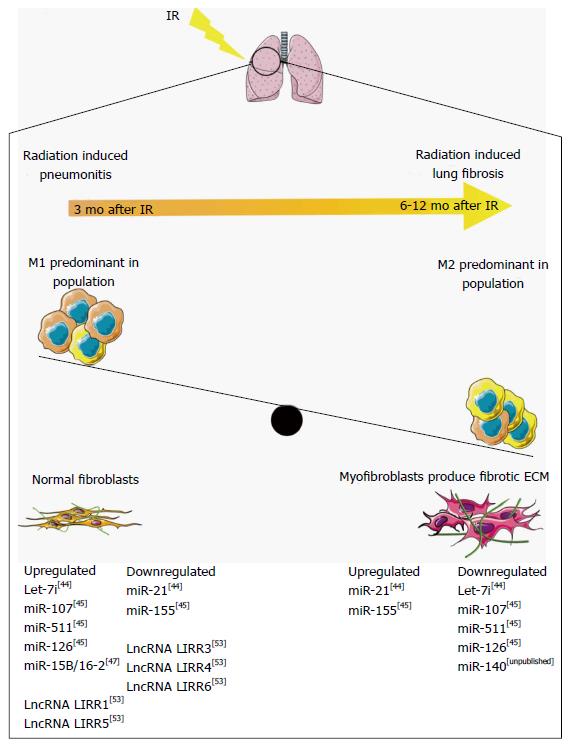
Figure 1 Non-coding RNAs regulation of macrophage polarization in radiation-induced lung fibrosis.
Radiation pneumonitis develops approximately 3 mo after ionizing radiation, resulting from the accumulation of M1 macrophages. Six to twelve months after ionizing radiation (IR) the accumulation of M2 macrophages activates myofibroblast differentiation, resulting in a fibrotic microenvironment and radiation-induced lung fibrosis (RILF). Non-coding RNAs regulate the pathways involved in RILF, and are temporally regulated through RILF development and progression. ECM: Extracellular matrix. This figure was produced using Servier medical art, available from http://www.servier.com/Powerpoint-image-bank.
- Citation: Duru N, Wolfson B, Zhou Q. Mechanisms of the alternative activation of macrophages and non-coding RNAs in the development of radiation-induced lung fibrosis. World J Biol Chem 2016; 7(4): 231-239
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v7/i4/231.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v7.i4.231