Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Feb 26, 2014; 5(1): 1-11
Published online Feb 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i1.1
Published online Feb 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i1.1
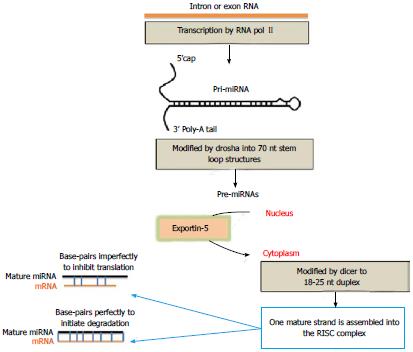
Figure 1 Schematic representation of microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis.
miRNA genes are transcribed into large pre-miRNA (capital R) that are cleaved by a protein complex containing the endonuclease Drosha into shorter pre-miRNAs. The latter are then transported to the cytoplasm by exportin-5. A complex containing the endonuclease, Dicer, then cleaves the loop portion of the pre-miRNA (capital R) to form a short duplex molecule that is unwound, and the single-stranded mature mirNA is then passed to Argonaute to from a functional mature, approximately 22 nucleotide, miRNA that inhibit translation after base-pairing with the 3’ UTR of the miRNA (capital R) target.
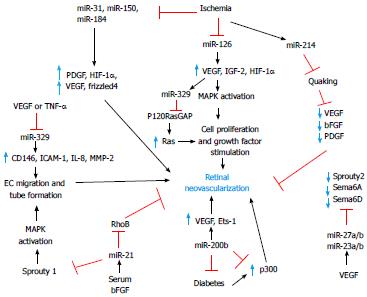
Figure 2 Overview of major angiogenic and antiangiogenic miRNAs and their targets in promoting or suppressing retinal neovascularization.
VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; IGFs: Insulin-like growth factors; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; PDGF: Platelet derived growth factor; IL-8: Interleukin 8; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor-alpha; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
- Citation: Agrawal S, Chaqour B. MicroRNA signature and function in retinal neovascularization. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(1): 1-11
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i1.1