Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 27, 2021; 12(6): 114-130
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i6.114
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i6.114
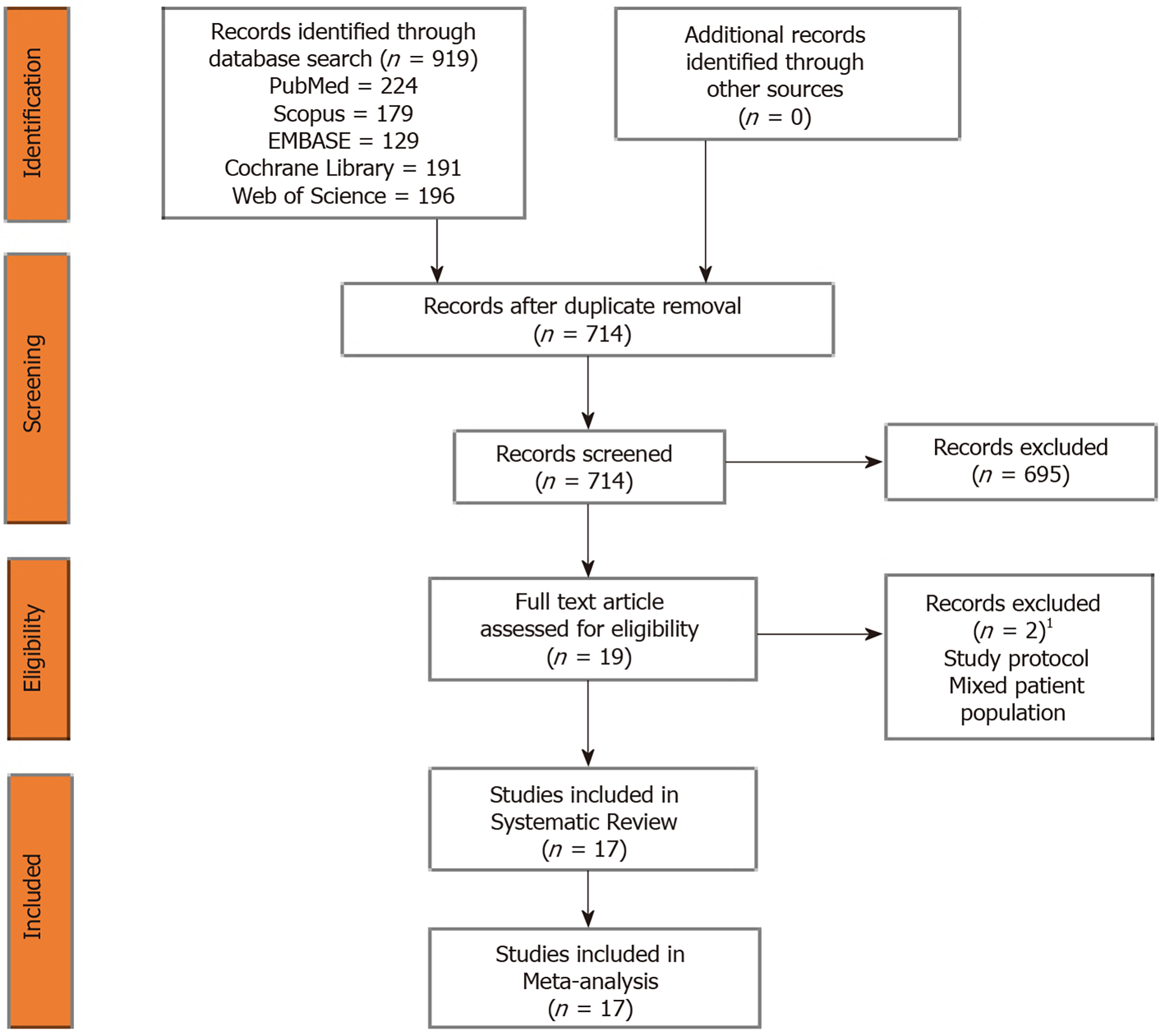
Figure 1 Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses flow diagram of the included studies.
1List of excluded studies given in Supplementary File 2.
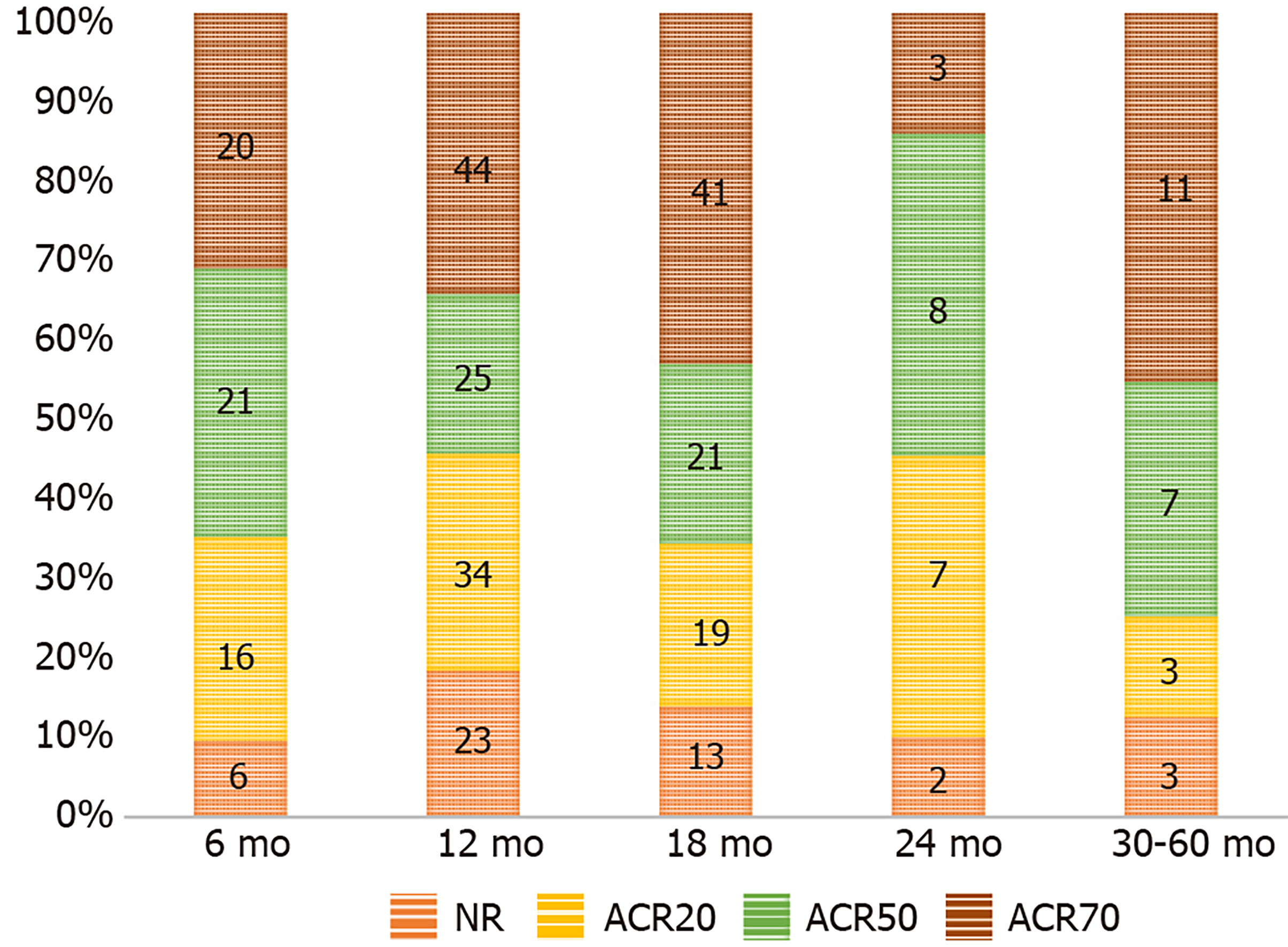
Figure 2 Transition trend of American College of Rheumatology criteria in the included studies across various time points.
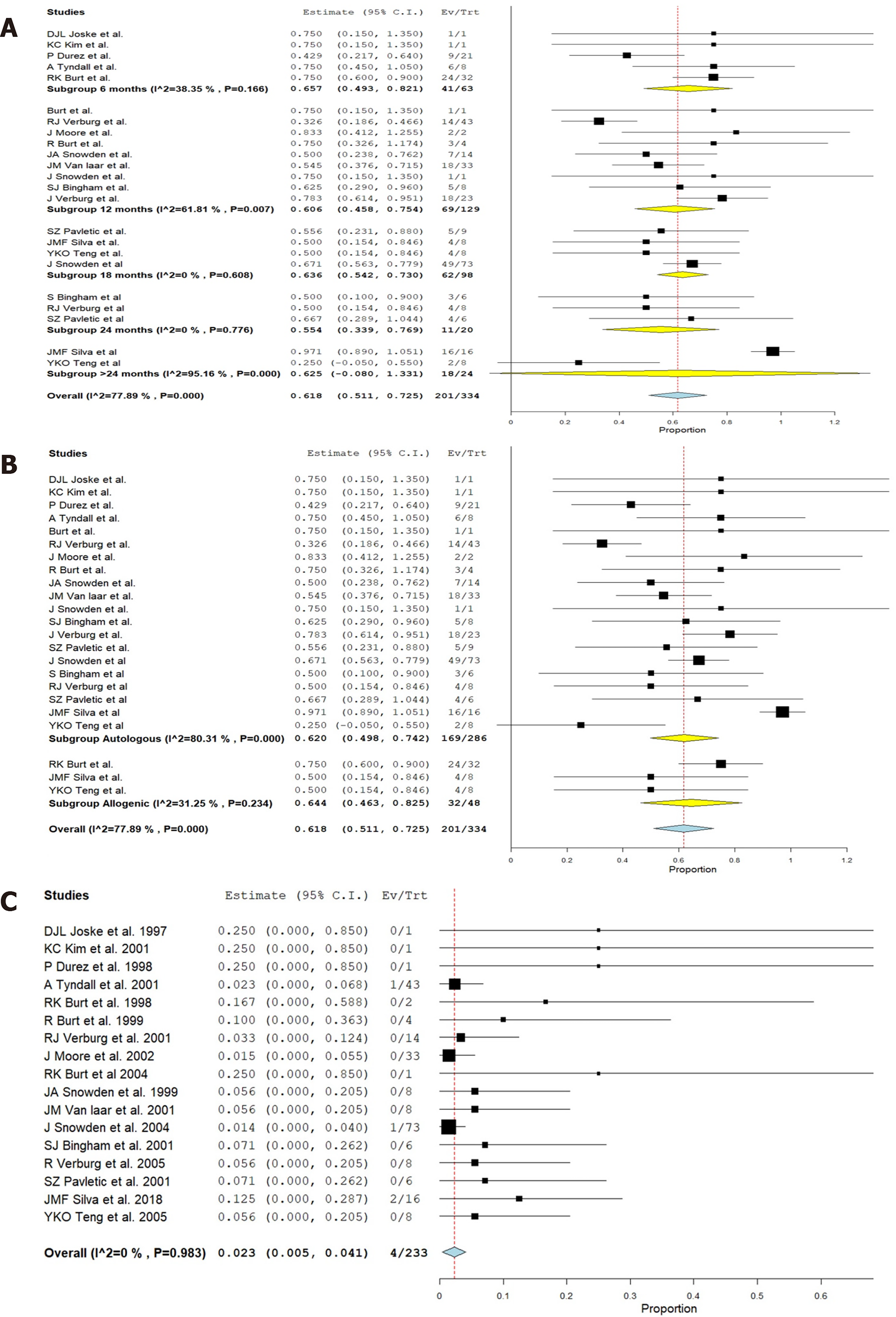
Figure 3 Forest plot.
A: Analysis of results of included studies at various time points following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in comparison to their pre-operative status of rheumatoid arthritis using a random binary effects model; B: Sub-group analysis of the results based on the nature of HSCT (autologous and allogeneic types); C: Major complications noted in the included studies.
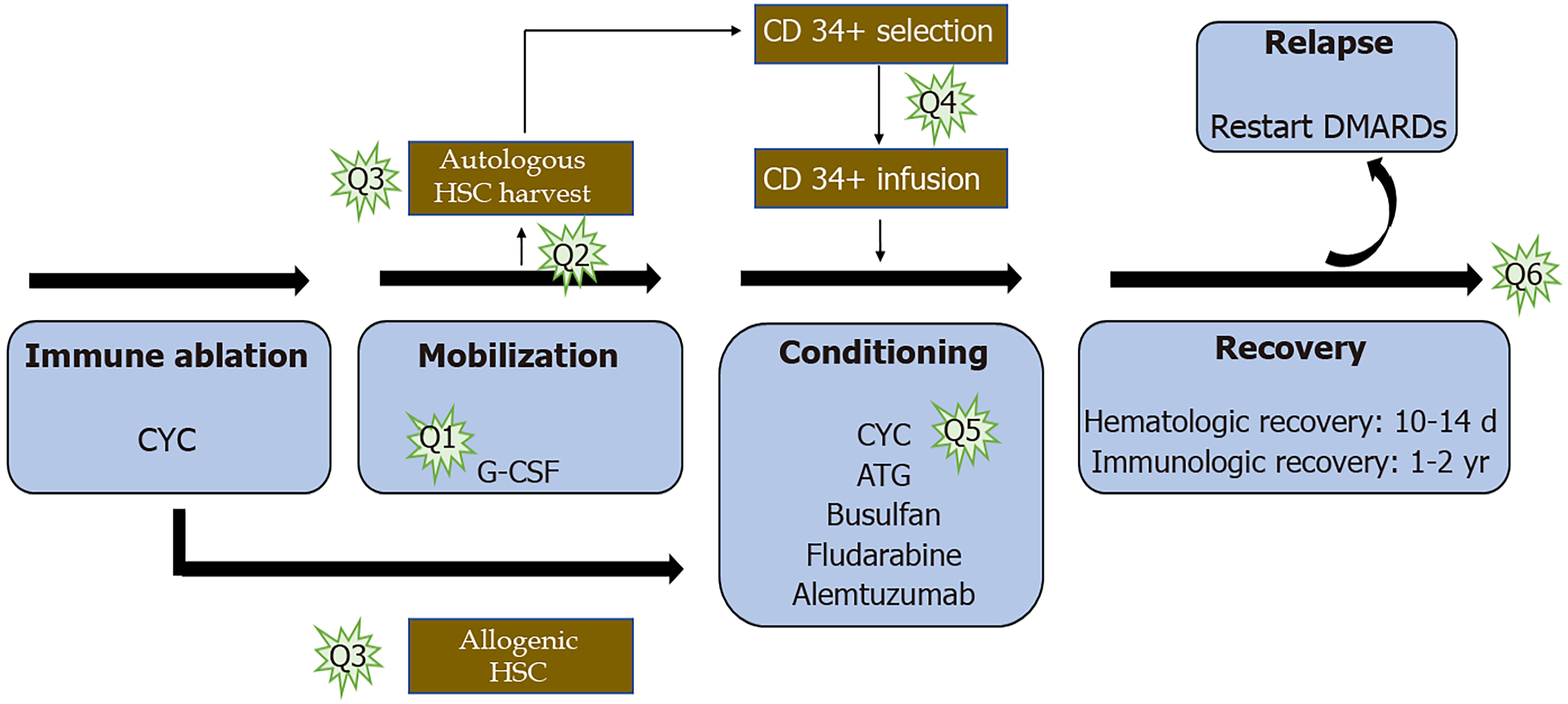
Figure 4 Potential areas of future research to optimize hematopoietic stem cell transplantation treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.
Q1 is to evaluate whether stem cell rescue is necessary after high dose immune ablation; Q2 is to assess the ideal source of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs); Q3 deals with either autologous or allogeneic source; Q4 deals with the need for T cell depletion from the harvested material; Q5 probes into the ideal conditioning regimen; and Q6 evaluates the ideal timing of HSC transplantation in the course of the disease. HSC: Hematopoietic stem cell.
- Citation: Muthu S, Jeyaraman M, Ranjan R, Jha SK. Remission is not maintained over 2 years with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. World J Biol Chem 2021; 12(6): 114-130
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v12/i6/114.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v12.i6.114