Published online Sep 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i9.1082
Peer-review started: April 29, 2022
First decision: May 29, 2022
Revised: June 1, 2022
Accepted: August 15, 2022
Article in press: August 15, 2022
Published online: September 27, 2022
Processing time: 146 Days and 7.4 Hours
Acute portal venous system thrombosis (PVST) can cause acute mesenteric ischemia and even intestinal infarction, which are potentially fatal, and requires recanalization in a timely fashion. Herein, we report a 56-year-old man with acute non-cirrhotic symptomatic extensive PVST who achieved portal vein recanalization after systemic thrombolysis combined with anticoagulation. Initially, anticoagulation with enoxaparin sodium for 4 d was ineffective, and then systemic thrombolysis for 7 d was added. After that, his abdominal pain com
Core Tip: The present case suggests that systemic thrombolysis should be safe and effective for acute extensive portal venous system thrombosis, if it is unresponsive to anticoagulation.
- Citation: Gao FB, Wang L, Zhang WX, Shao XD, Guo XZ, Qi XS. Successful treatment of acute symptomatic extensive portal venous system thrombosis by 7-day systemic thrombolysis. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(9): 1082-1085
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i9/1082.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i9.1082
Acute portal venous system thrombosis (PVST) is potentially life-threatening and can achieve a good response to agitation thrombolysis combined with catheter-directed thrombolysis[1]. However, it should be acknowledged that systemic thrombolysis, a more convenient treatment approach, has been rarely attempted for the treatment of acute PVST in clinical practice due to its potential bleeding risk. Herein, we report a case of acute symptomatic extensive PVST successfully treated by systemic thrombolysis combined with anticoagulation to strengthen our confidence in its clinical efficacy and safety.
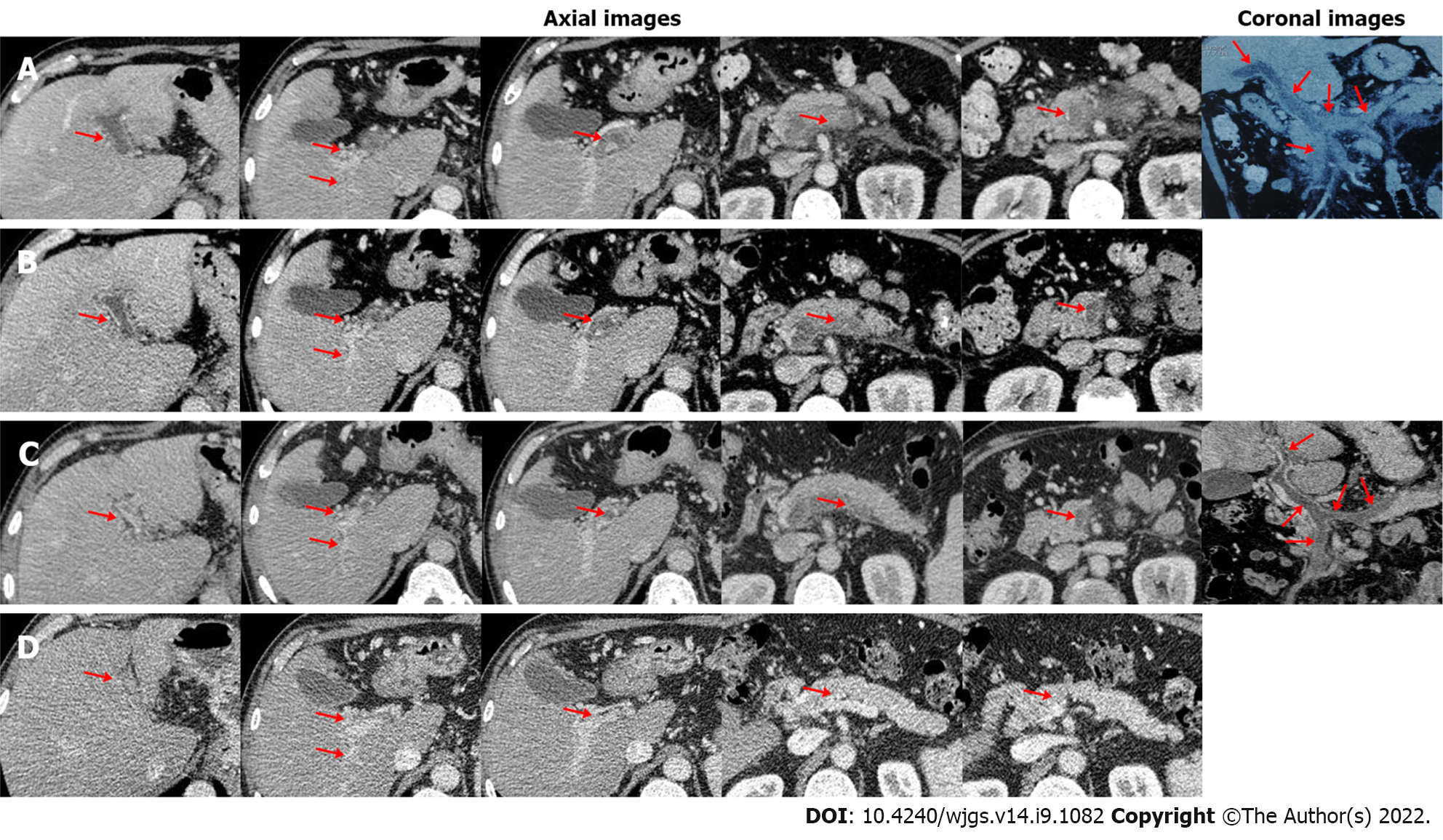
A 56-year-old man with a history of hepatitis B virus infection was admitted to the Department of Gastroenterology due to aggravating severe epigastric pain for nearly half a month. He had no other obvious medical history. On physical examinations, his abdomen was soft without abdominal tenderness, rebound, or tension. On day 1 of admission, laboratory tests were performed (Table 1). Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) showed no contrast agent filling within all vessels of the portal venous system, including the main portal vein (MPV), right portal vein (RPV), left portal vein (LPV), confluence of the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) and splenic vein (SV), SMV, and SV (Figure 1A), suggesting a diagnosis of occlusive PVST. Thus, subcutaneous injection of enoxaparin sodium was immediately initiated at a dose of 5000 IU (62.5 IU/kg) twice daily. On day 5, his abdominal pain was not relieved. Anti-Xa level was 0.05 IU/mL (reference range: 0-0.1 IU/mL). Contrast-enhanced CT showed no significant improvement of PVST (Figure 1B). Thus, systemic thro
| Laboratory tests | Reference range | Before antithrombotic treatment | After 7-d thrombolysis | After 5-mo oral anticoagulants |
| White blood cell count (109/L) | 3.5-9.5 | 9.70 | 5.20 | 6.7 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 130-175 | 143 | 119 | 164 |
| Platelet count (109/L) | 125-350 | 230 | 242 | 123 |
| Total bilirubin (μmol/L) | 5.1-22.2 | 16.70 | 8.1 | 13.9 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 15-40 | 17.60 | 16.29 | 18.65 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 9-50 | 20.39 | 20 | 21.99 |
| International normalized ratio | 0.9-1.2 | 1.19 | 1.15 | 0.99 |
| Prothrombin time (s) | 11.0-13.7 | 14.80 | 14.4 | 13.1 |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time (s) | 31.5-43.5 | 32.30 | 38.9 | 34.6 |
| D-dimer (mg/L) | 0-0.55 | 7.71 | 4.77 | 0.27 |
| Antithrombin III (%) | 80-120 | 48 | - | 55 |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 2.0-4.0 | 3.09 | 4.87 | 3.09 |
| Protein C (%) | 70-140 | - | - | 89.3 |
| Protein S (%) | 75-130 | - | - | 90.4 |
Anticoagulation is the preferred choice of treatment for acute PVST[2], but 18% of patients still develop transmural intestinal necrosis after anticoagulation therapy, and 25%-50% will develop pre-hepatic portal hypertension[3,4]. Patients with acute PVST who do not respond to anticoagulation therapy may benefit from thrombolytic therapy[5]. However, thrombolytic therapy has a higher risk of bleeding, including upper gastrointestinal bleeding, abdominal bleeding, and epistaxis. Notably, the current evidence on systemic thrombolytic therapy for PVST is scare. In a retrospective cohort study[6], 33 patients with acute PVST were treated with intravenous injection of 750000 IU/d streptokinase or 100-150 mg/6-12 h recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA) for 2-3 d, followed with heparin infusion, and then received oral anticoagulants for 12 mo after discharge. Thrombosis recanalization was achieved in 23 patients. In a prospective cohort study[7], nine cirrhotic patients with recent PVST received continuous intravenous infusion of rt-PA at a dose of 0.25 mg/kg/d combined with subcutaneous injection of low molecular weight heparin for a maximum duration of 7 d. Thrombosis recanalization was achieved in eight patients. Besides, a stepwise thrombolysis regimen for PVST should be considered. In a study by Benmassaoud et al[8], 22 non-cirrhotic patients with acute PVST received systemic thrombolysis, of whom eight achieved portal vein recanalization, and the remaining 14 did not have any improvement of thrombosis or abdominal pain and were then treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) or local thrombolysis. Finally, the overall rate of portal vein recanalization was 86.4%. Notably, local thrombolysis and TIPS were employed in the study by Benmassaoud et al[8], but they are more invasive and technically complicated as compared to systemic thrombolysis. In our case, initial anticoagulation was less effective, and thus systemic thrombolysis was given. The symptoms improved significantly after thrombolysis, which avoided further vascular interventional procedures, and even surgery for intestinal infarction and necrosis[9].
Acute PVST is often defined if PVST develops 1-3 wk since the onset of symptoms. Accordingly, our case should be diagnosed with acute PVST. Notably, the timing of antithrombotic therapy for acute PVST is very important. A shorter interval from the diagnosis of PVST to initiation of antithrombotic therapy indicates a higher probability of thrombus recanalization[10]. In our case, the interval was relatively long, which potentially compromised the efficacy of anticoagulation and forced the use of systemic thrombolysis.
In conclusion, systemic thrombolysis should be considered in the cases where anticoagulant therapy fails and interventional therapy is neither available nor feasible. The timing of systemic thrombolytic therapy and the dose of thrombolytic drugs should be further explored.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Dasuqi SA, Saudi Arabia; El-Karaksy H, Egypt S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Fan JR
| 1. | Wang CY, Wei LQ, Niu HZ, Gao WQ, Wang T, Chen SJ. Agitation thrombolysis combined with catheter-directed thrombolysis for the treatment of non-cirrhotic acute portal vein thrombosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24:4482-4488. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Wang L, Xu X, Hou Y, Shao X, Guo X, Qi X. Acute mesenteric vein thrombosis after endoscopic injection sclerotherapy for esophageal varices in a patient with liver cirrhosis. Drug Discov Ther. 2019;13:118-121. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Plessier A, Darwish-Murad S, Hernandez-Guerra M, Consigny Y, Fabris F, Trebicka J, Heller J, Morard I, Lasser L, Langlet P, Denninger MH, Vidaud D, Condat B, Hadengue A, Primignani M, Garcia-Pagan JC, Janssen HL, Valla D; European Network for Vascular Disorders of the Liver (EN-Vie). Acute portal vein thrombosis unrelated to cirrhosis: a prospective multicenter follow-up study. Hepatology. 2010;51:210-218. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 359] [Cited by in RCA: 390] [Article Influence: 26.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Condat B, Pessione F, Helene Denninger M, Hillaire S, Valla D. Recent portal or mesenteric venous thrombosis: increased recognition and frequent recanalization on anticoagulant therapy. Hepatology. 2000;32:466-470. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 342] [Cited by in RCA: 330] [Article Influence: 13.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Rössle M, Bettinger D, Trebicka J, Klinger C, Praktiknjo M, Sturm L, Caca K, Mücke VT, Radecke K, Engelmann C, Zipprich A, Heinzow H, Meyer C, Tappe U, Appenrodt B, Schmidt A, Lange C, Strassburg C, Zeuzem S, Grandt D, Schmidt H, Moessner J, Berg T, Lammert F, Thimme R, Schultheiß M. A prospective, multicentre study in acute non-cirrhotic, non-malignant portal vein thrombosis: comparison of medical and interventional treatment. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;52:329-339. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Malkowski P, Pawlak J, Michalowicz B, Szczerban J, Wroblewski T, Leowska E, Krawczyk M. Thrombolytic treatment of portal thrombosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003;50:2098-2100. [PubMed] |
| 7. | De Santis A, Moscatelli R, Catalano C, Iannetti A, Gigliotti F, Cristofari F, Trapani S, Attili AF. Systemic thrombolysis of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients: a pilot study. Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42:451-455. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Benmassaoud A, AlRubaiy L, Yu D, Chowdary P, Sekhar M, Parikh P, Finkel J, See TC, O'Beirne J, Leithead JA, Patch D. A stepwise thrombolysis regimen in the management of acute portal vein thrombosis in patients with evidence of intestinal ischaemia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;50:1049-1058. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Kumar S, Sarr MG, Kamath PS. Mesenteric venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1683-1688. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 400] [Cited by in RCA: 342] [Article Influence: 14.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 10. | Wang L, Guo X, Xu X, De Stefano V, Plessier A, Noronha Ferreira C, Qi X. Anticoagulation Favors Thrombus Recanalization and Survival in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis and Portal Vein Thrombosis: Results of a Meta-Analysis. Adv Ther. 2021;38:495-520. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 61] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 13.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |