Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Feb 27, 2025; 17(2): 100034
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i2.100034
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i2.100034
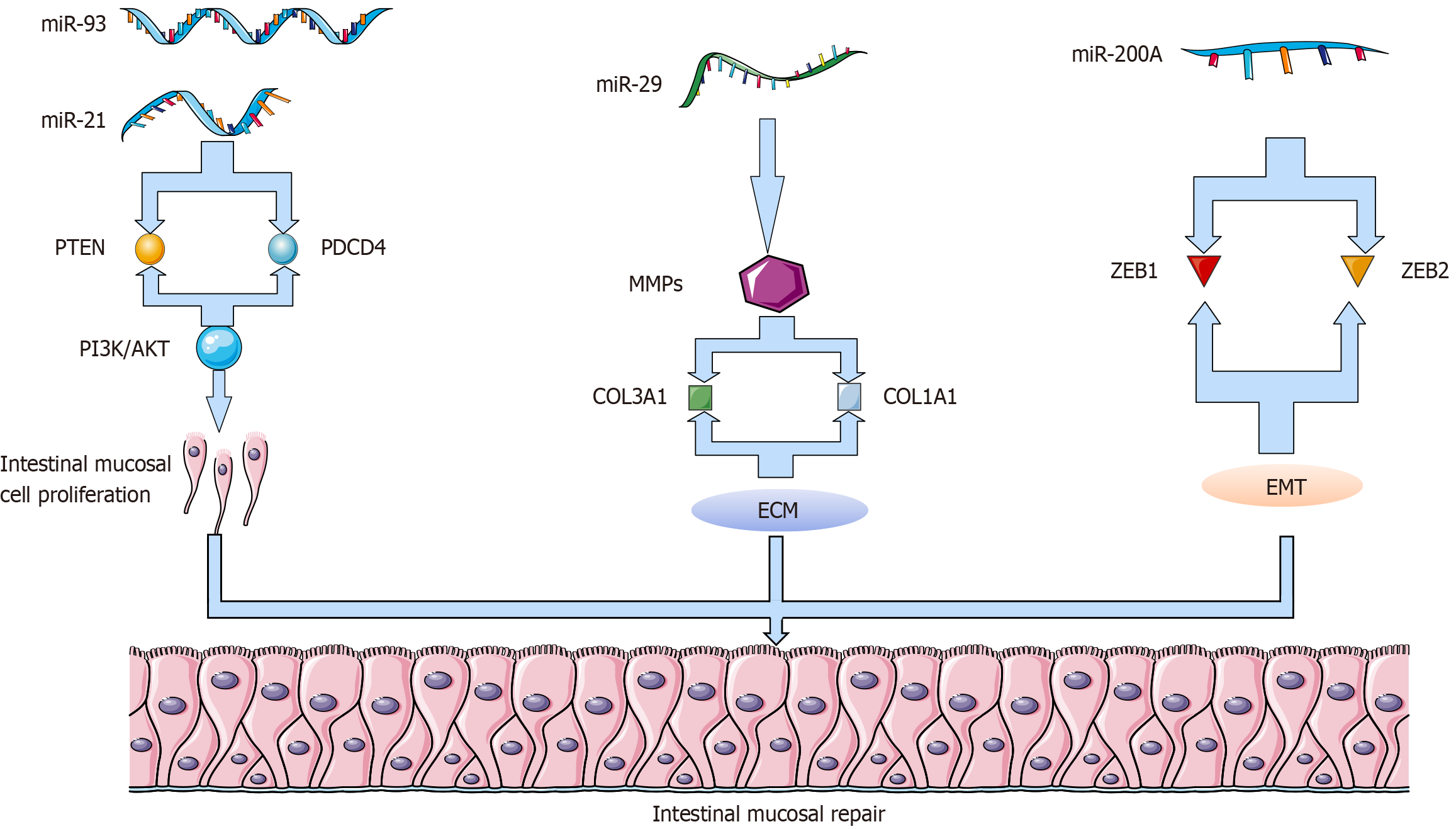
Figure 1 Effects exerted by some microRNAs (miR-21 and miR-93) in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury can inhibit PTEN and other negative regulatory gene expression, promoting activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway.
This facilitates vascular regeneration and suppresses apoptosis, contributing to the restoration of intestinal tissue function. miR-21 potentially inhibits reactive oxygen specie generation, alleviating cell apoptosis and inflammatory responses. miR-29a suppresses COL3A1 and COL1A1 expression to regulate matrix metalloproteinase expression, thereby modulating collagen content in the extracellular matrix. By adjusting collagen expression levels, it affects the repair and reconstruction processes of the intestinal mucosa. miR-200a participates in regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell migration by inhibiting ZEB1 and ZEB2 expression, thus promoting the restoration and protection of the intestinal mucosal barrier, which helps maintain its integrity and functionality. ECM: Extracellular matrix.
- Citation: Xu DJ, Wang GT, Zhong Q. Extracellular matrix gene set and microRNA network in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury: Insights from RNA sequencing for diagnosis and therapy. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(2): 100034
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i2/100034.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i2.100034