Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Mar 27, 2024; 16(3): 860-870
Published online Mar 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i3.860
Published online Mar 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i3.860
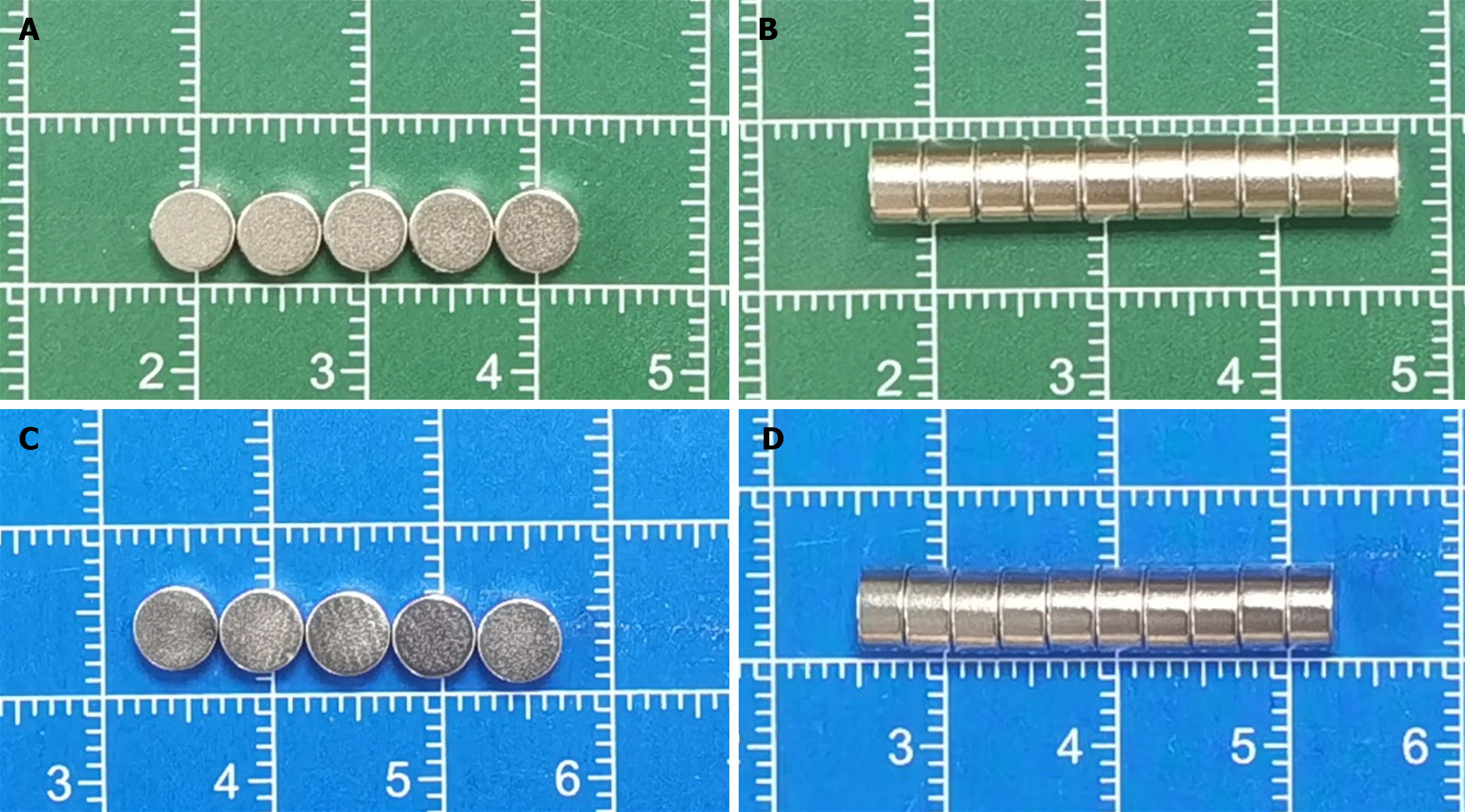
Figure 1 Magnets.
A: Front view of the powerful magnet; B: Side view of the powerful magnet; C: Front view of the common magnet; D: Side view of the common magnet.
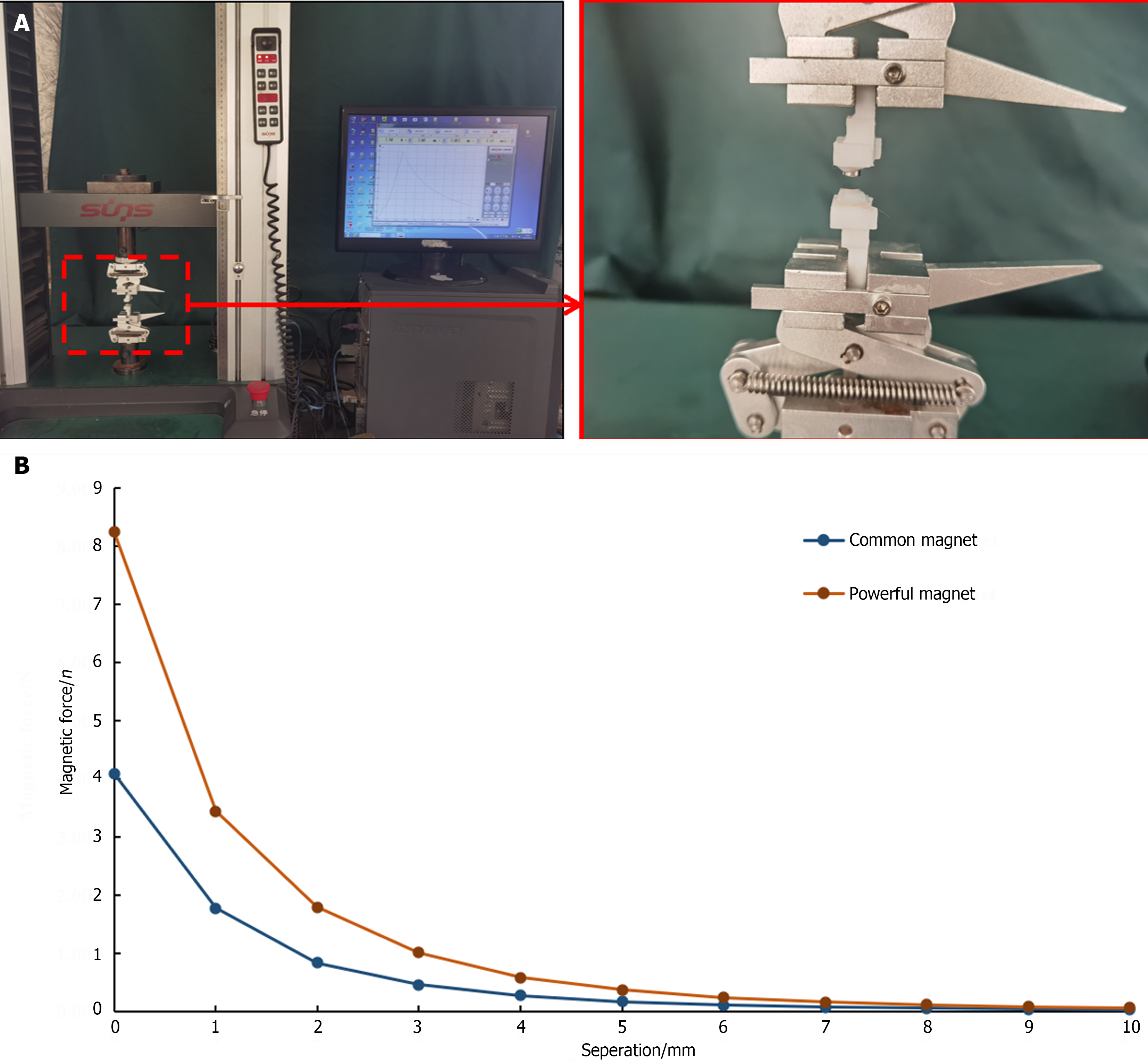
Figure 2 Magnetic force test.
A: Magnetic force test procedure; B: Magnetic force curve of the magnet.
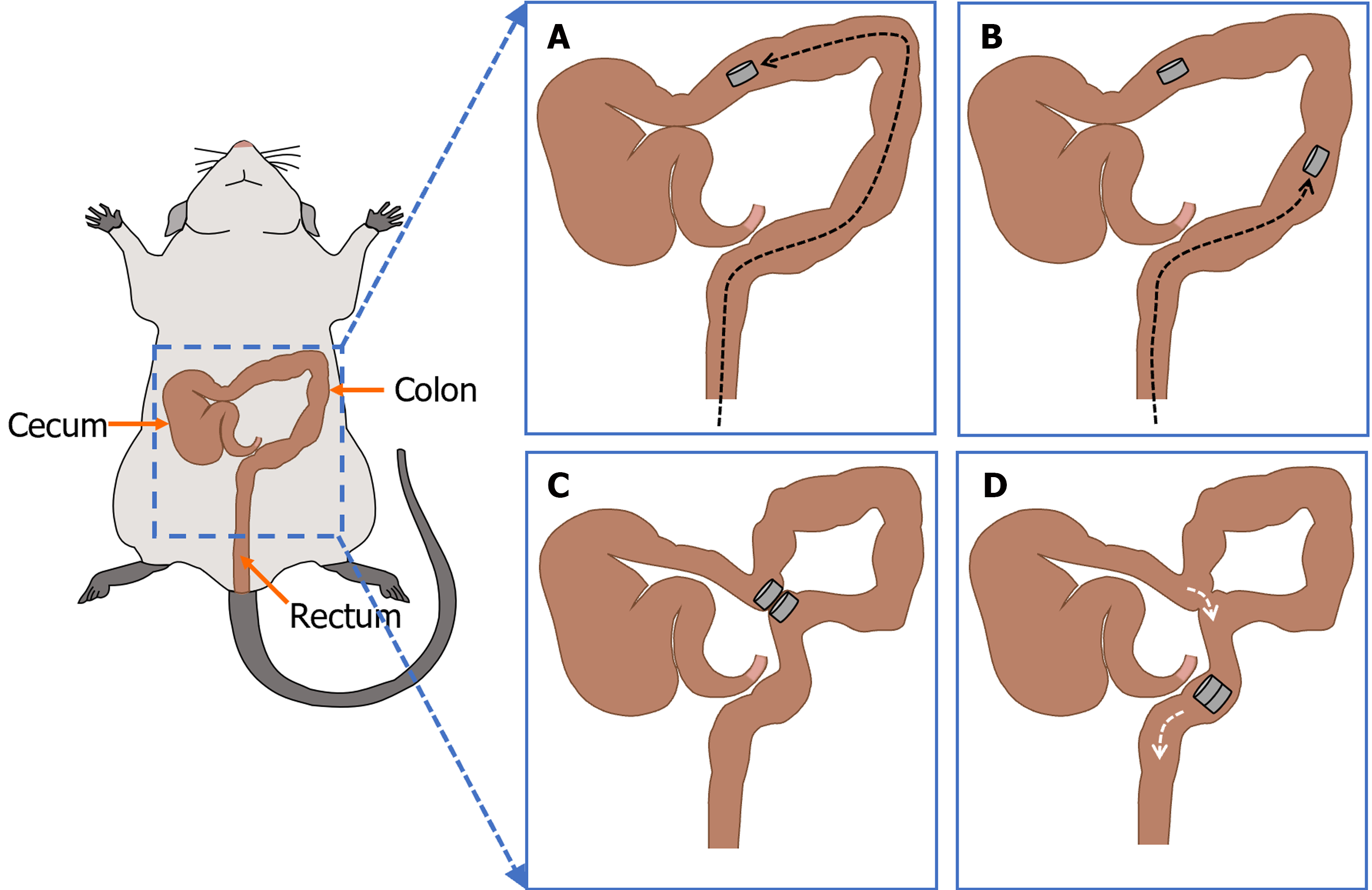
Figure 3 Schematic presentation of the surgical procedure.
A: A magnet is inserted through the anus into the proximal portion of the colon; B: Another magnet is inserted through the anus to the distal end of the colon; C: The two magnets in the colon are attracted; D: The magnets enter the rectum after a side-to-side colonic anastomosis is established.
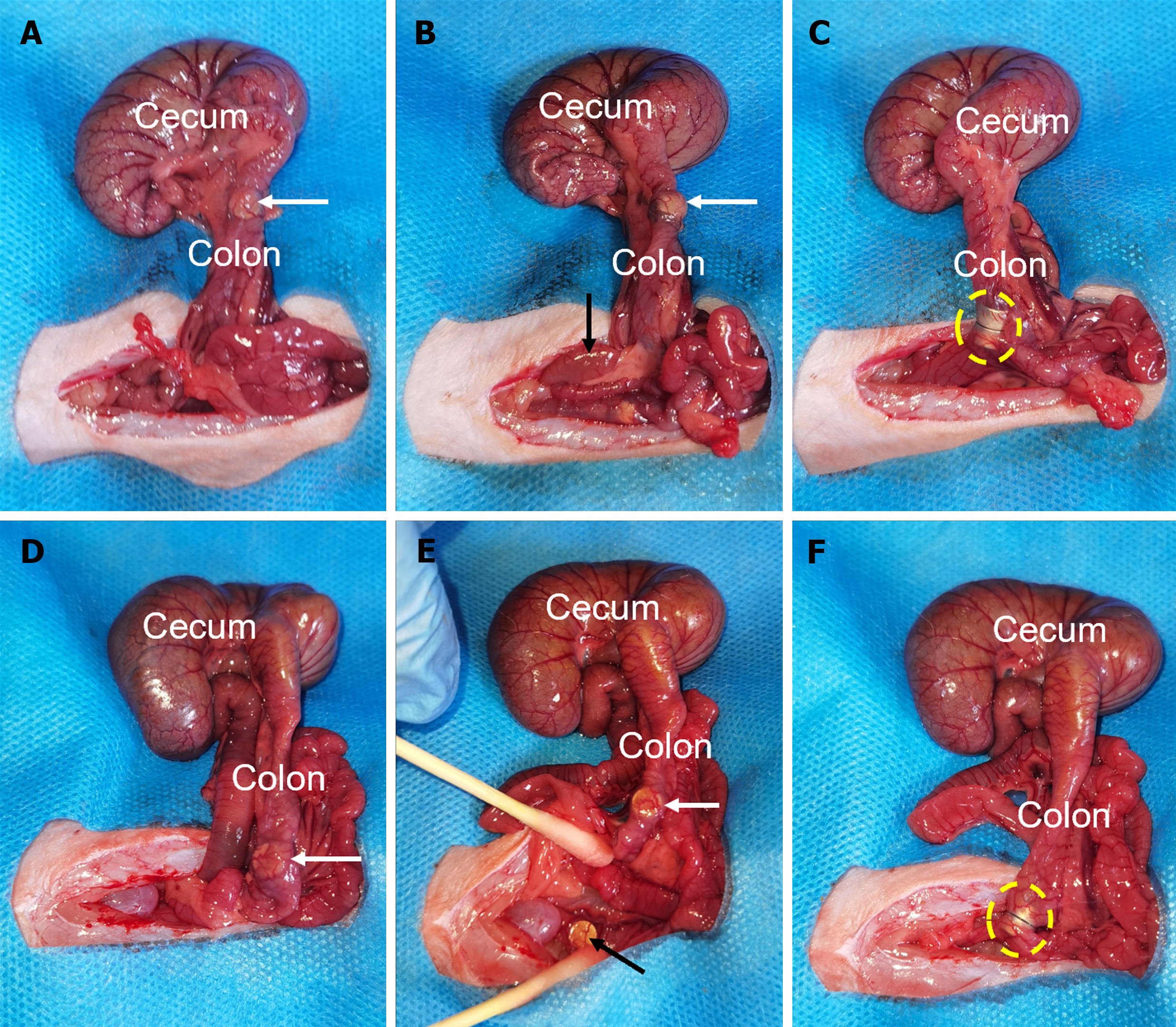
Figure 4 Surgical procedure.
A: A powerful magnet is placed in the proximal colon (white arrow); B: A powerful magnet is placed in the distal end of the colon (black arrow); C: The two powerful magnets are attracted (yellow circle); D: A common magnet in the proximal colon area (white arrow); E: A common magnet in the distal end of the colon (black arrow); F: The two common magnets are attracted (yellow circle).
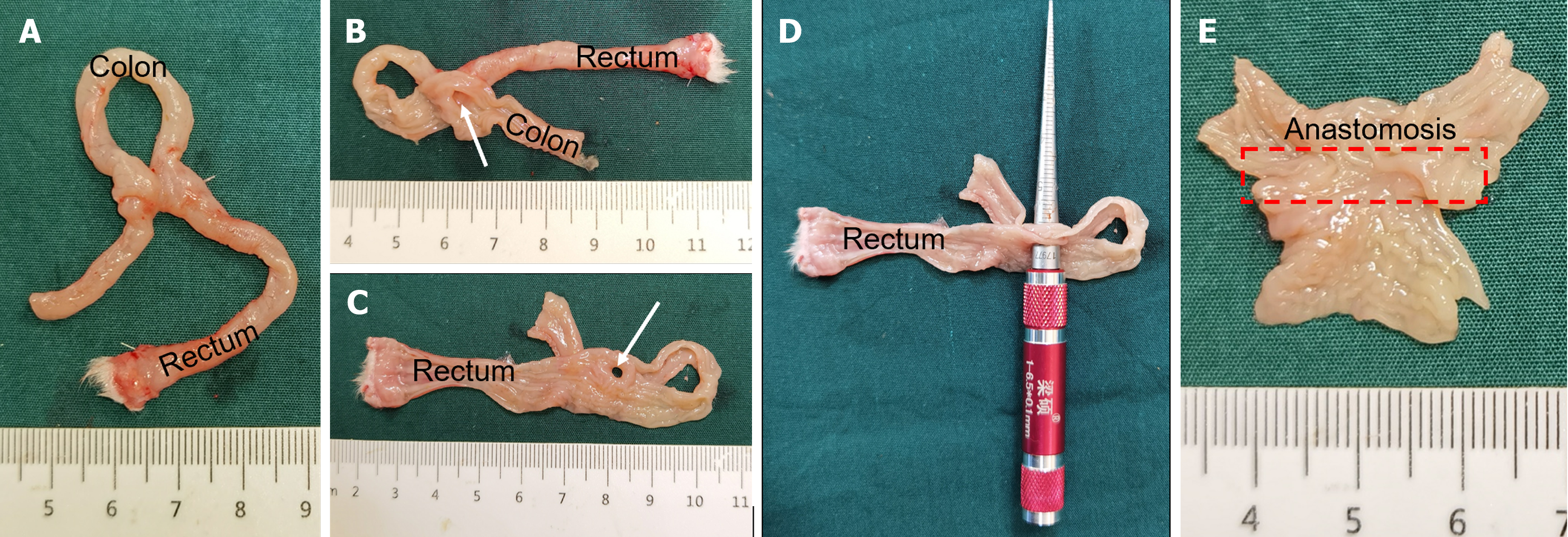
Figure 5 Anastomotic gross specimen of the powerful magnet group.
A: Gross specimen of colon anastomosis; B and C: The anastomosis observed after a longitudinal dissection of the colon (white arrow); D: Measurement of the anastomotic diameter; E: Colonic anastomosis observed on the mucosal surface.
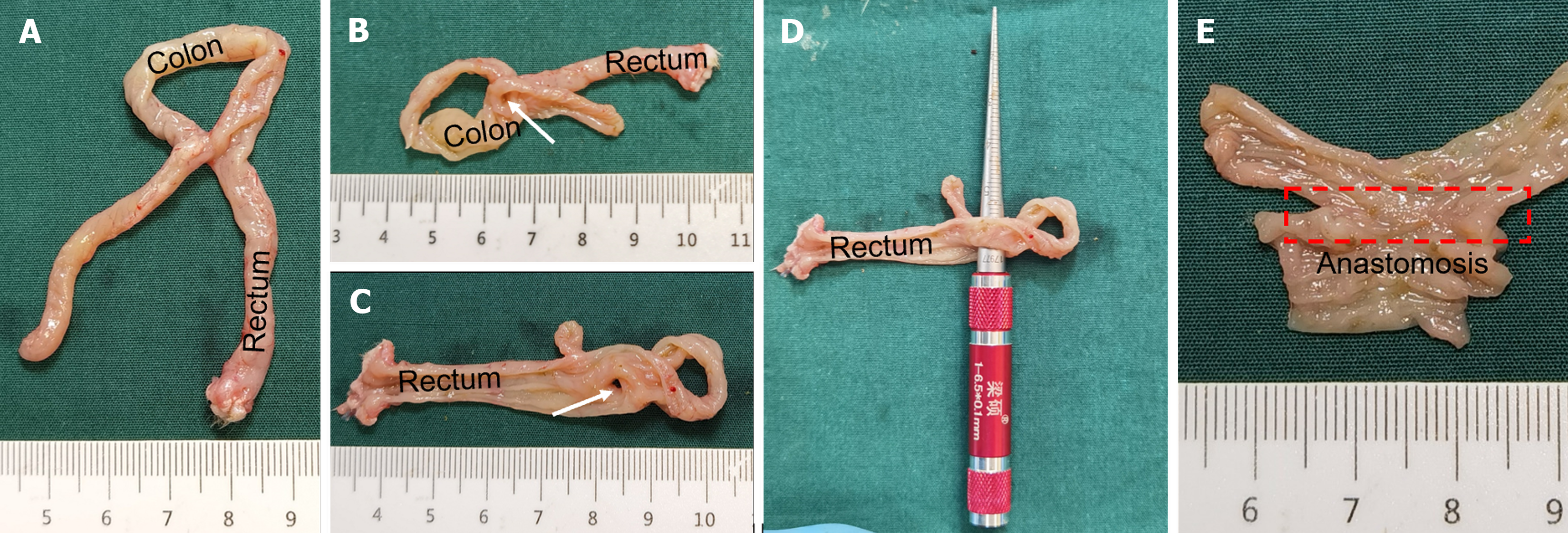
Figure 6 Anastomotic gross specimen of the common magnet group.
A: Gross specimen of colon anastomosis; B and C: The anastomosis observed after a longitudinal dissection of the colon (white arrow); D: Measurement of the anastomotic diameter; E: Colonic anastomosis observed on the mucosal surface.
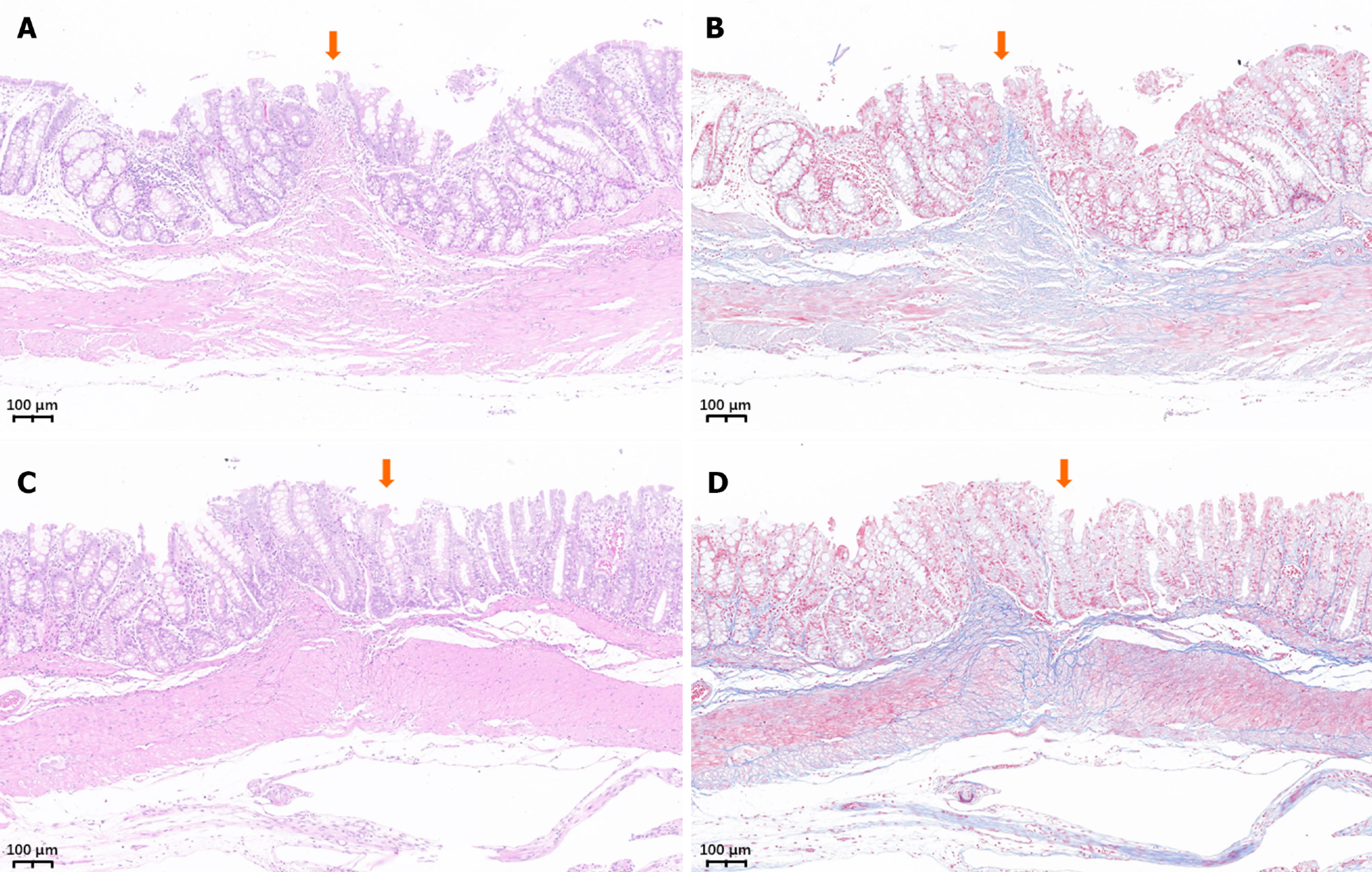
Figure 7 Histological images of the colonic anastomosis.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the colonic anastomosis in the powerful magnet group; B. Masson’s staining of the colonic anastomosis in the powerful magnet group; C: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the colonic anastomosis in the common magnet group; D: Masson’s staining of the colonic anastomosis in the common magnet group.
- Citation: Tian BY, Zhang MM, Ma J, Lyu Y, Yan XP. Influence of different magnetic forces on the effect of colonic anastomosis in rats. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(3): 860-870
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i3/860.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i3.860