Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jul 27, 2023; 15(7): 1542-1548
Published online Jul 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i7.1542
Published online Jul 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i7.1542
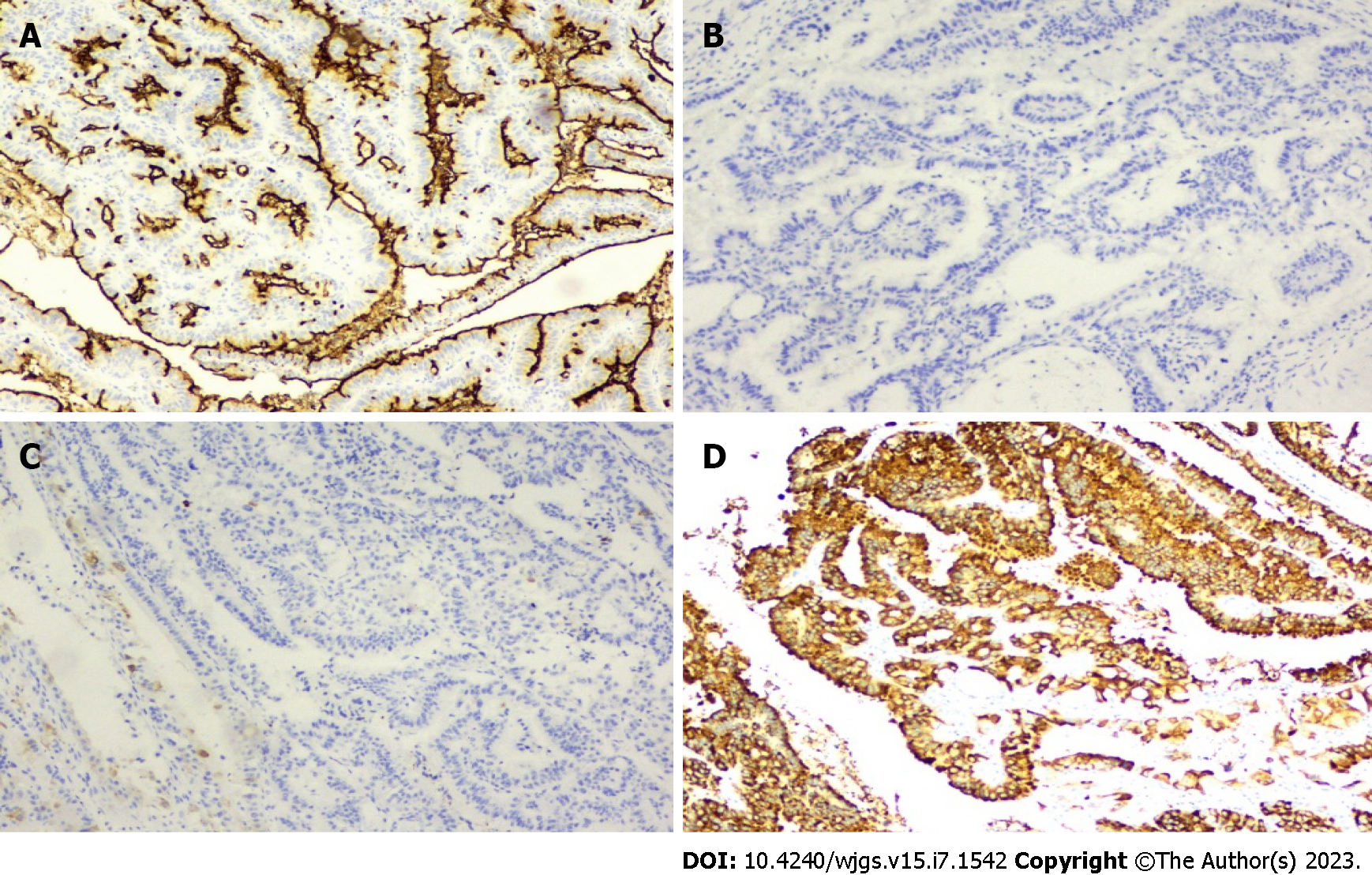
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical examination of the resected specimen.
A-D: Immunohistochemical staining for Muc-1 (A), Muc-2 (B), Muc-5AC (C), and Muc-6 (D), × 200.
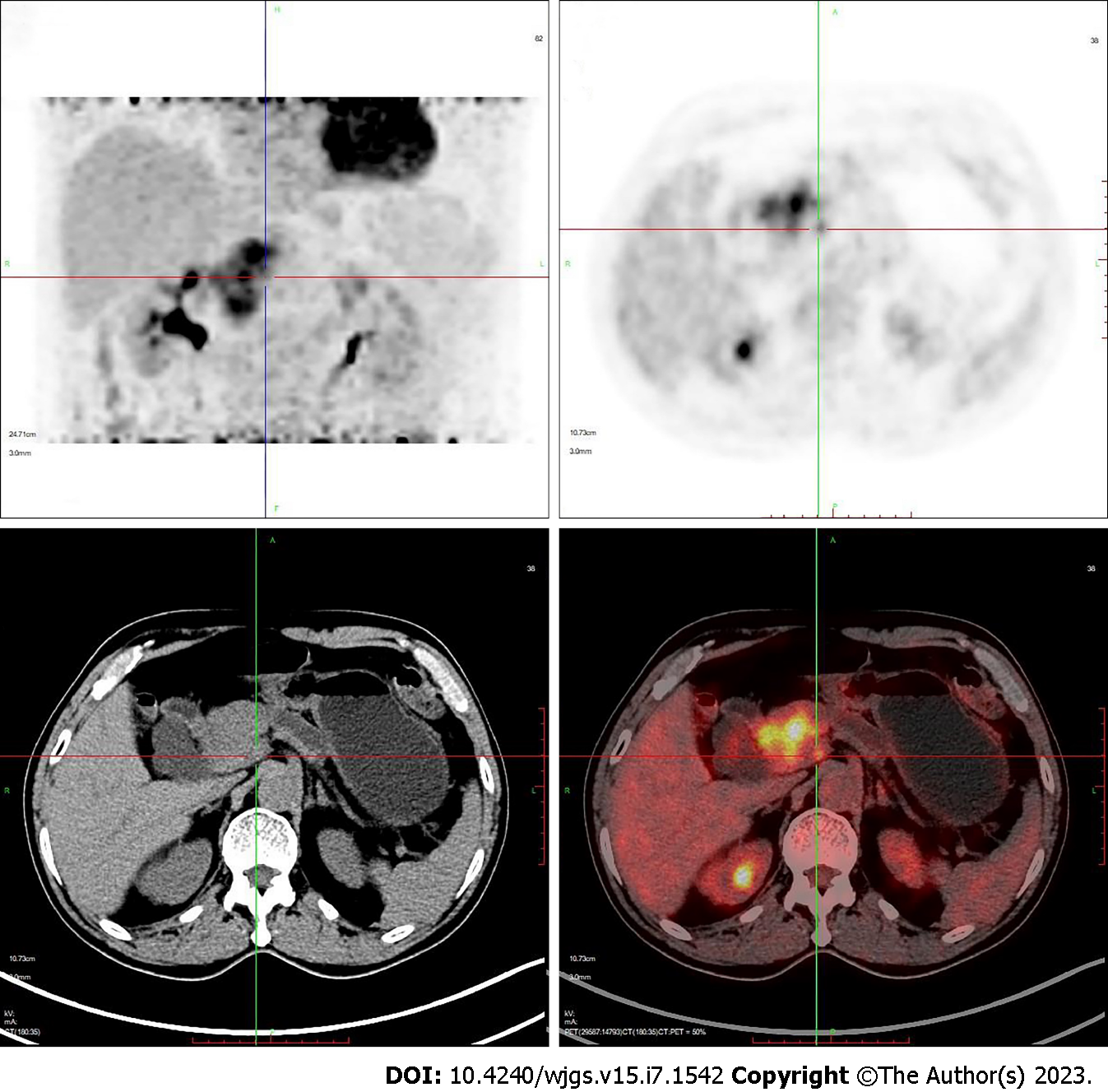
Figure 2 Positron emission tomography showed a mass in the head of the pancreas.
Maximum standard uptake value: 11.8.
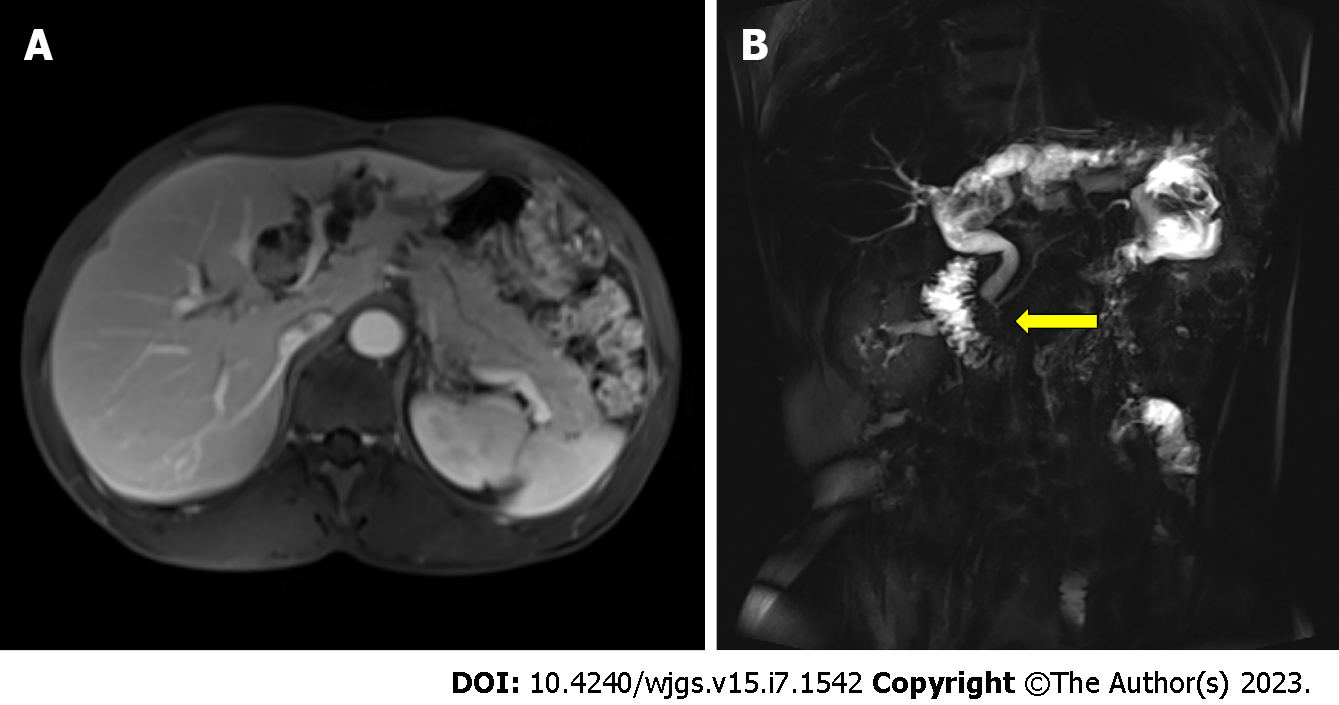
Figure 3 Preoperative imaging findings for the initial surgery.
A: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showed a left hepatobiliary mass with dilatation of the upstream bile duct; B: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography indicated pancreaticobiliary maljunction (indicated by arrow). The junction of the pancreatic and the bile duct was outside the duodenal wall with a long common channel.
Figure 4 Gross specimens showed pancreaticobiliary maljunction (indicated by arrow).
The pancreatic duct and bile duct shared a long common channel. The intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm was located in the neck of the pancreas.
- Citation: Xiao G, Xia T, Mou YP, Zhou YC. Reoperation for heterochronic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas after bile duct neoplasm resection: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(7): 1542-1548
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i7/1542.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i7.1542