Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jul 27, 2023; 15(7): 1317-1330
Published online Jul 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i7.1317
Published online Jul 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i7.1317
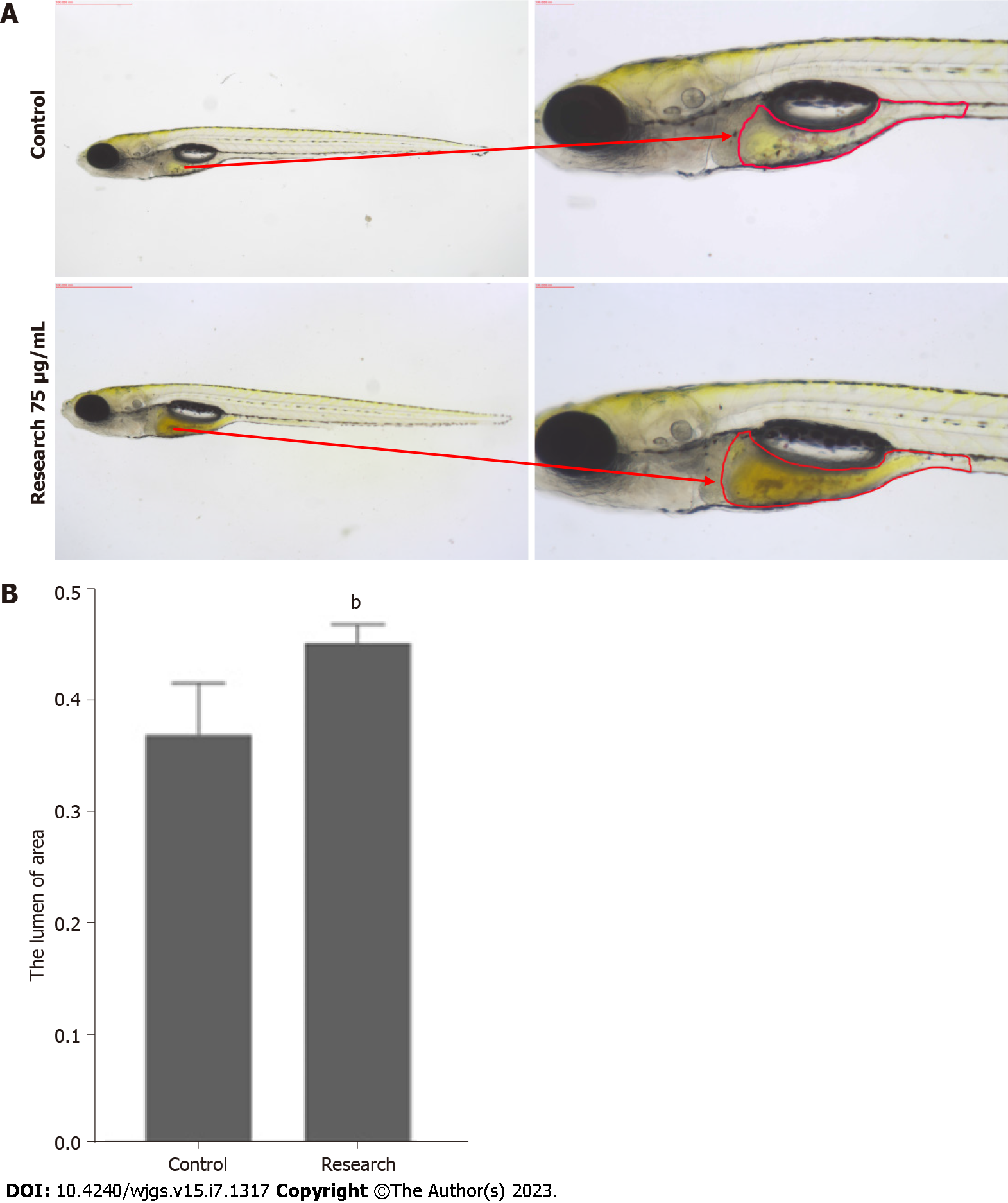
Figure 1 Observation of phenotypes of zebrafish in control group and zebrafish exposed to trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid in research group.
A: Area of intestinal lumen of zebrafish in two groups; B: Comparison of intestinal luminal area of zebrafish in control and research groups. bP < 0.01, compared with the control.
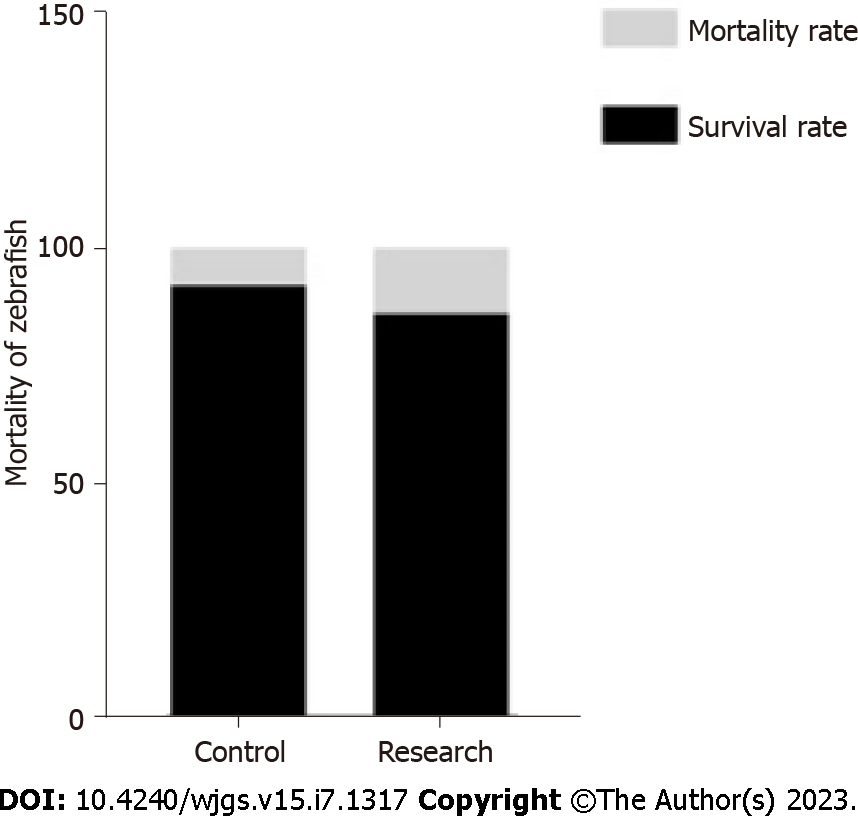
Figure 2 Mortality of zebrafish of the research and control groups.
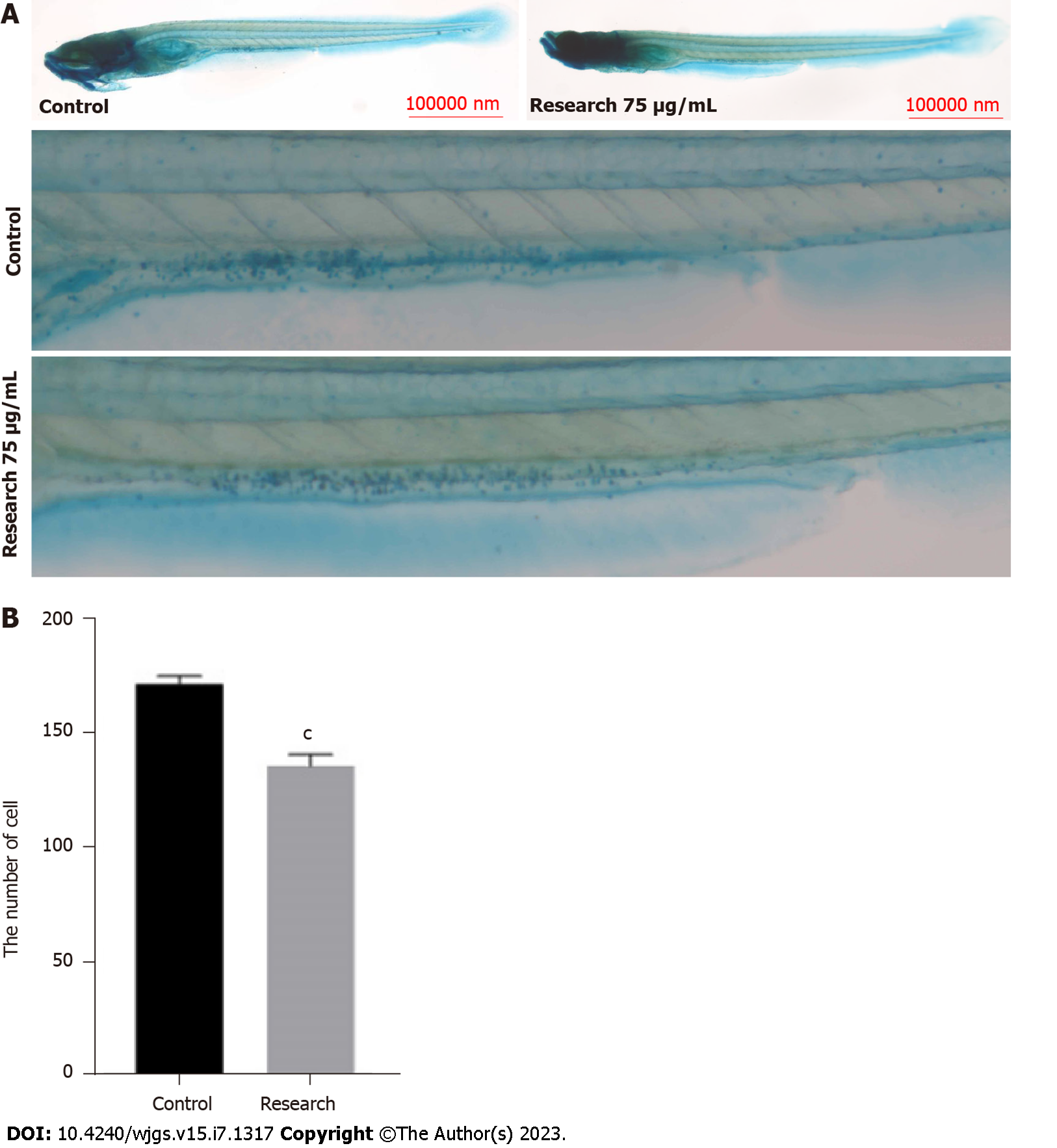
Figure 3 Comparison of the number of goblet cells in the intestinal lumen of zebrafish in control and research groups.
A: Goblet cells in the intestinal lumen of zebrafish; B: Comparison of number of goblet cells in the intestinal lumen of zebrafish. cP < 0.001, compared with the control.
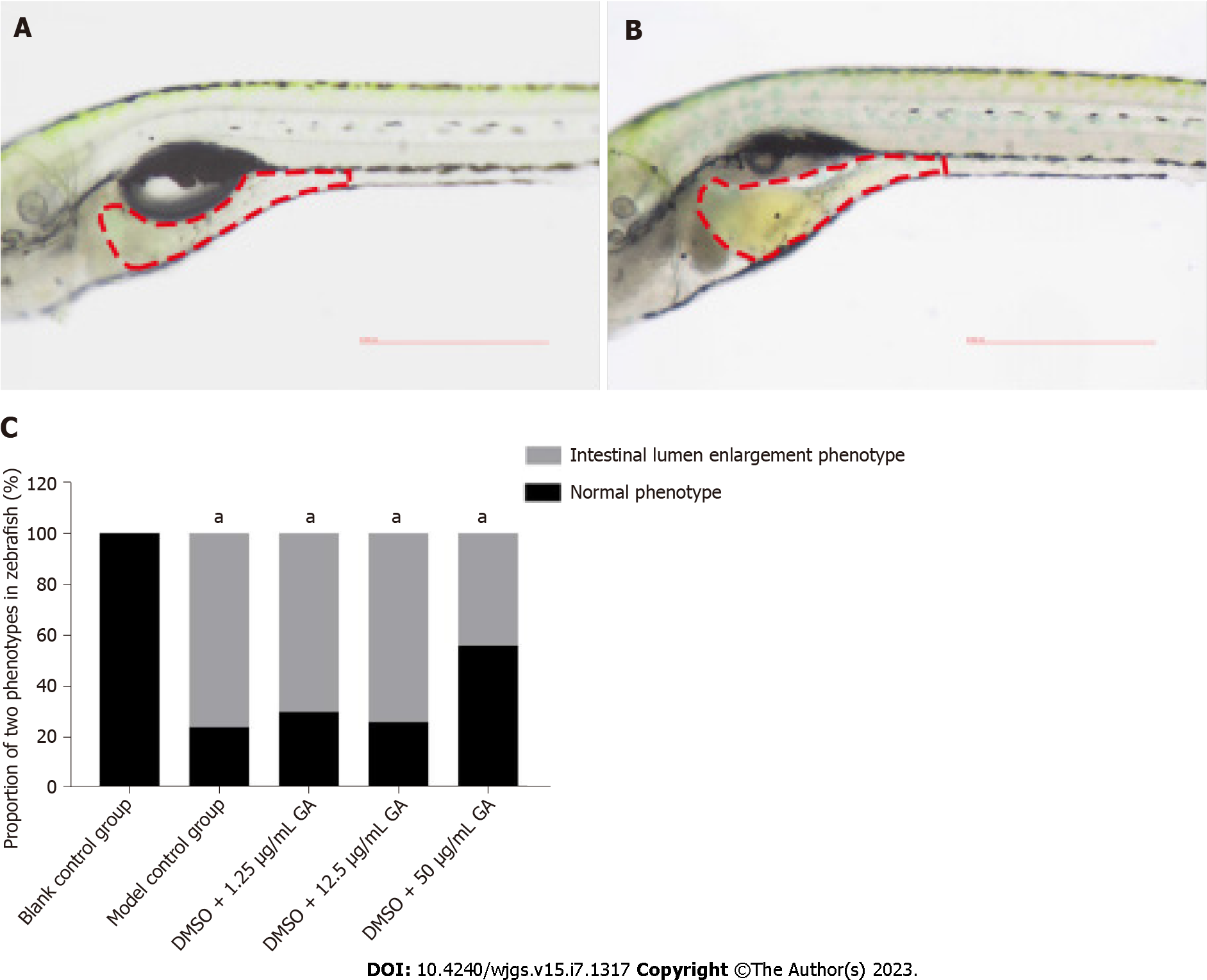
Figure 4 Typical examples of two phenotypes in zebrafish.
A: Normal phenotype; B: Intestinal lumen enlargement; C: Proportion of two phenotypes in zebrafish of all groups. aP < 0.05, model control, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) + 1.25 μg/mL glycyrrhizic acid group, DMSO + 12.5 μg/mL glycyrrhizic acid group and DMSO + 50 μg/mL glycyrrhizic acid group compared with the blank control; DMSO + 50 μg/mL glycyrrhizic acid group compared with the model control, DMSO + 1.25 μg/mL glycyrrhizic acid group and DMSO + 12.5 μg/mL glycyrrhizic acid group. DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; GA: Glycyrrhizic acid.
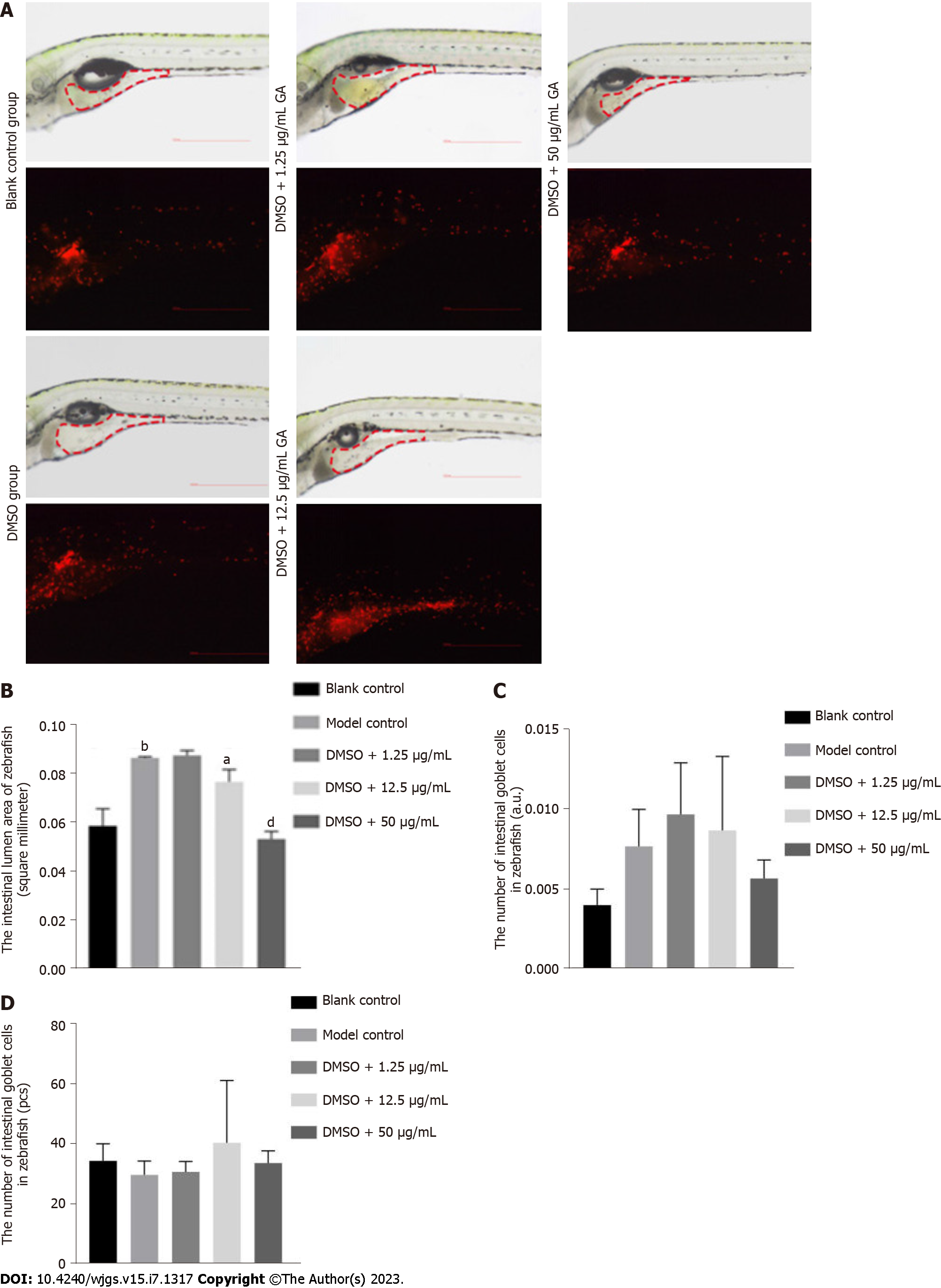
Figure 5 Photography of intestinal lumen of zebrafish after glycyrrhizic acid administration using stereo and stereo fluorescence microscopy.
A: Photographs of intestinal lumen of zebrafish using stereo and stereo fluorescence microscopy; B: Area of intestinal lumen of zebrafish of all groups; C: Fluorescence intensity in the intestinal lumen of zebrafish of all groups; D: Number of fluorescent neutrophils in the intestinal lumen of zebrafish of all groups. aP < 0.05, compared with the model control; bP < 0.01, compared with the blank control; dP < 0.0001, compared with the model control. DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; GA: Glycyrrhizic acid.
Figure 6 Alcian blue staining for zebrafish after glycyrrhizic acid administration.
A: Phenotypes of zebrafish stained with Alcian blue solution; B: Number of goblet cells in the intestinal lumen of zebrafish. aP < 0.05, compared with the model control; cP < 0.001, compared with the model control; dP < 0.0001, compared with the blank control. DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; GA: Glycyrrhizic acid.
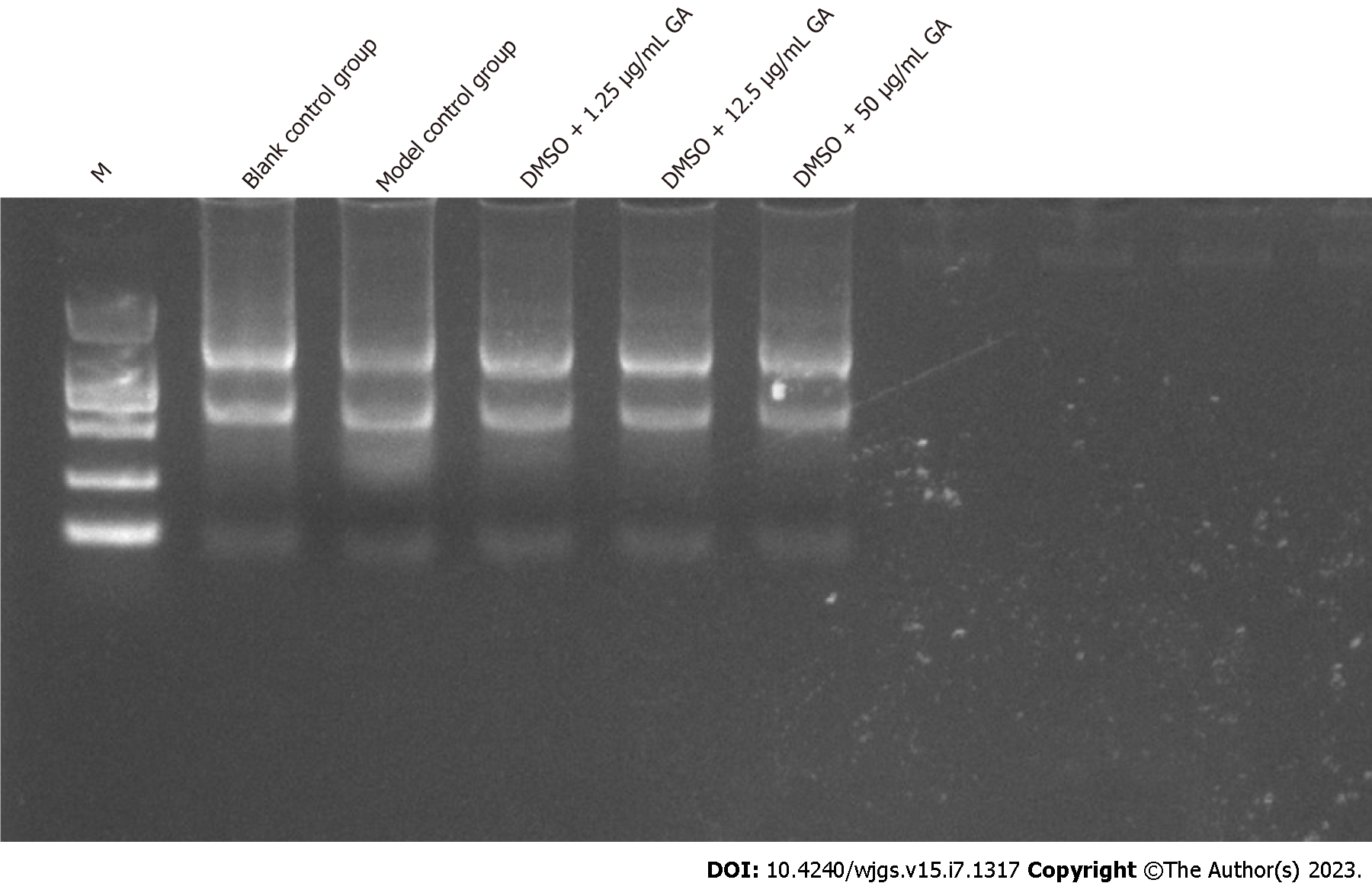
Figure 7 Quality test of RNA extracted from larvae after 3 d of glycyrrhizic acid administration.
DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide.
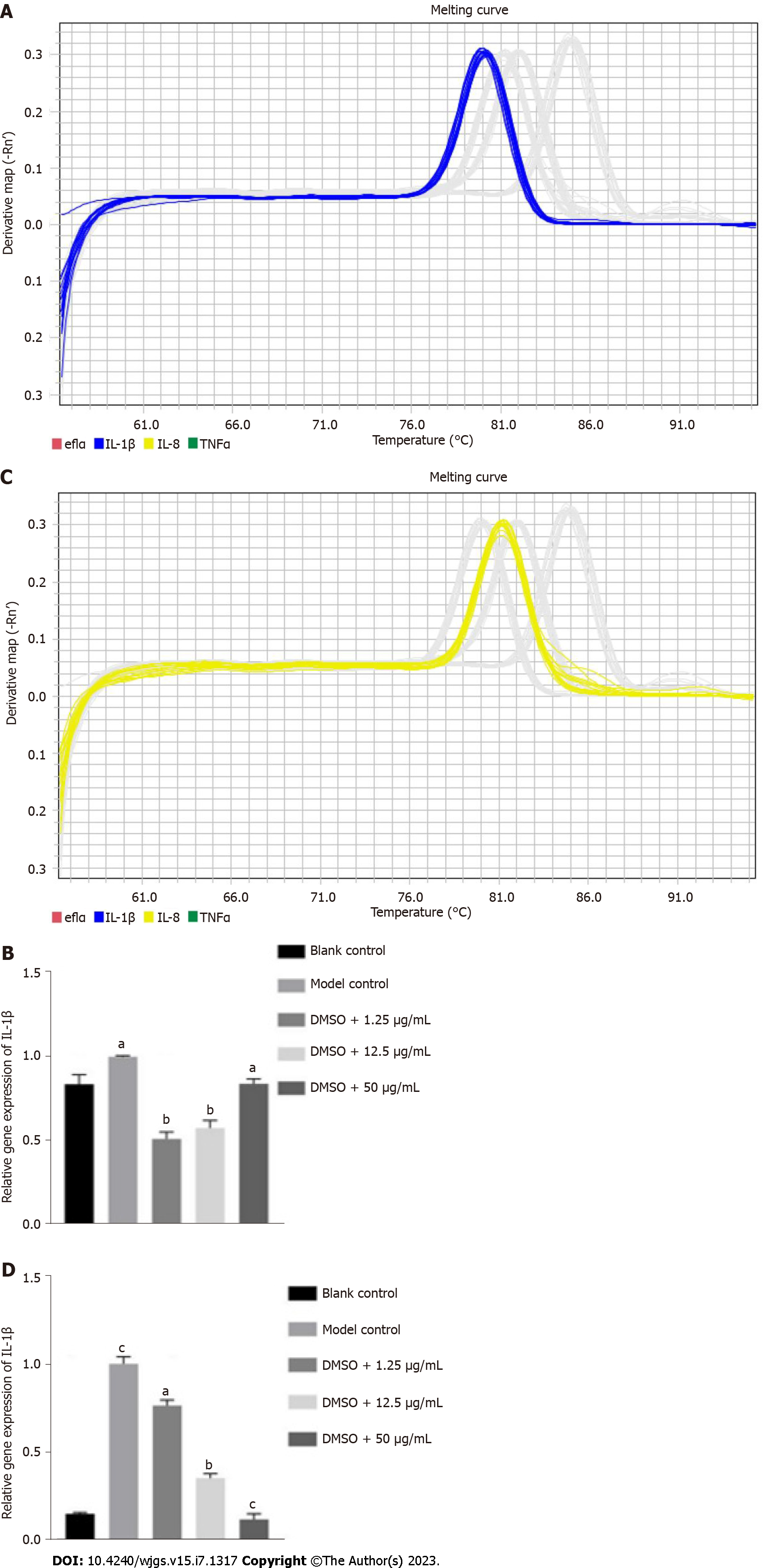
Figure 8 Gene expression detected by quantitative polymerase chain reaction after 3 d of glycyrrhizic acid administration.
A: Dissolution curve of interleukin (IL)-1β; B: Expression level of IL-1β; C: Dissolution curve of IL-8; D: Expression level of IL-8. aP < 0.05, compared with the blank control, compared with the model control; bP < 0.01, compared with the model control; cP < 0.001, compared with the blank control, compared with the model control. DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumour necrosis factor.
- Citation: Liu MK, Chen YJ, Chen F, Lin ZX, Zhu ZC, Lin Y, Fang YF, Wu DM. Intervention effects and related mechanisms of glycyrrhizic acid on zebrafish with Hirschsprung-associated enterocolitis. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(7): 1317-1330
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i7/1317.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i7.1317