Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Apr 27, 2023; 15(4): 600-620
Published online Apr 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.600
Published online Apr 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.600
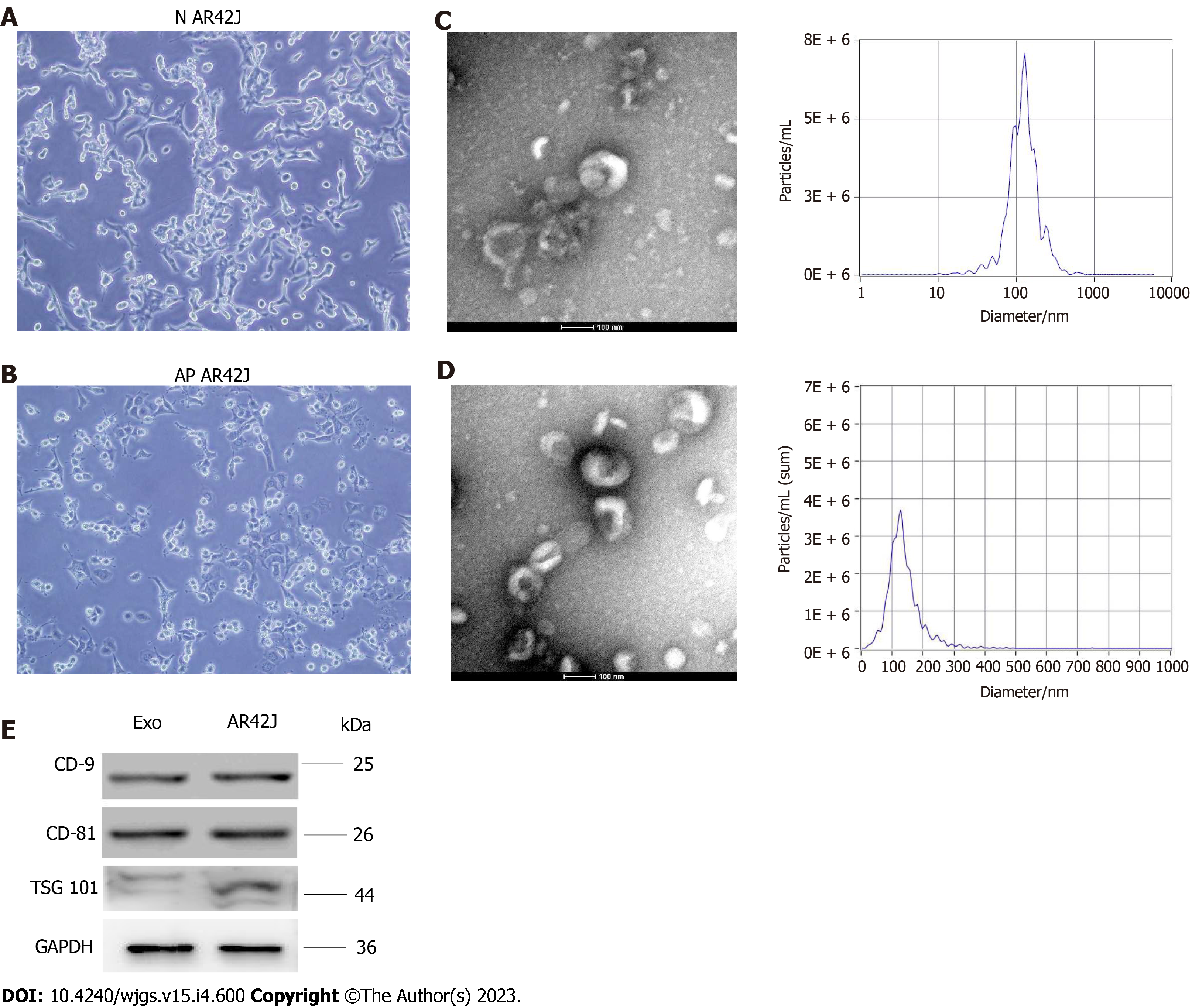
Figure 1 Isolation and characteristics of exosomes derived from normal acinous cell AR42J and active AR42J.
A: Morphology of AR42J cell line in the inactive state; B: Morphology of AR42J cell line in the activated state; C: Non-activated AR42J exosome morphology shown by transmission electron microscope (TEM) at 100nm scale. The diameter of exosomes derived from AR42J in the inactive state ranged from 68.3–181.9 nm, with an average of 121.4 nm, and the concentration of exosomes was 3.3 × 210 particles /mL; D: Morphology of AR42J exosomes in activated state as shown by TEM at 100 nm scale. The diameter of exosomes derived from AR42J in the activated state ranged from 82.1–197.5 nm, with an average of 132.8 nm, and the concentration of exosomes was 6.23 × 210 particles /mL; E: The positive expression of exosome marker, which include CD9, CD81 and TSG101, was confirmed by Western blot. AP: Acute pancreatitis; N: Normal.
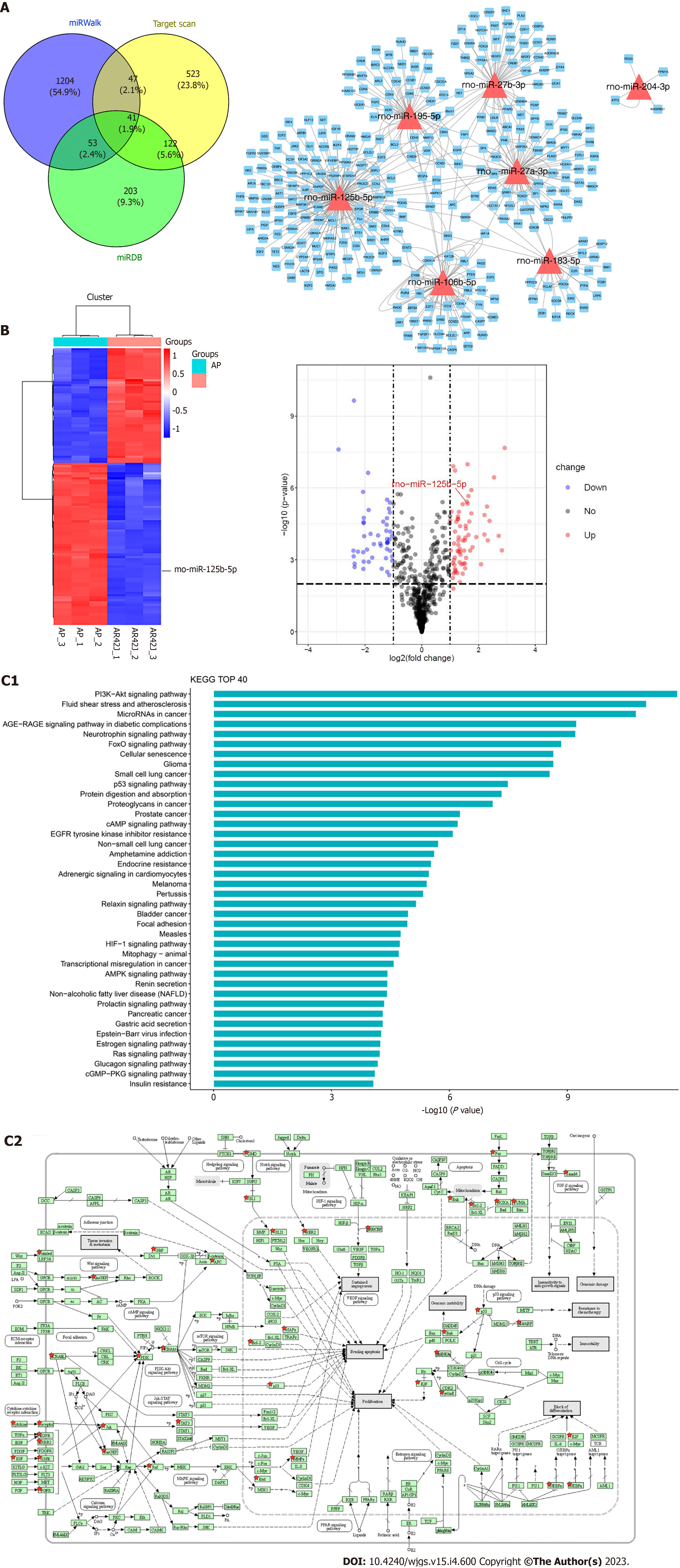
Figure 2 Differentially expressed miRNAs in AR42J cell lines between non-activated and activated states were screened.
A: RNA-seq was used to screen differentially expressed miRNAs. miRDB, miRWalk and Targetscan data were used to predict downstream binding target genes; B: The heat map and Volcano plot revealed that miR-125b-5p was up-regulated in activated state and down-regulated in non-activated state; C: The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis was performed on target genes of differentially expressed miR-125b-5p, and KEGG top 40 signaling pathways were enriched. Among them, PI3K/AKT signaling pathway may be the signaling pathway of miR-125b-5p. AP: Acute pancreatitis.
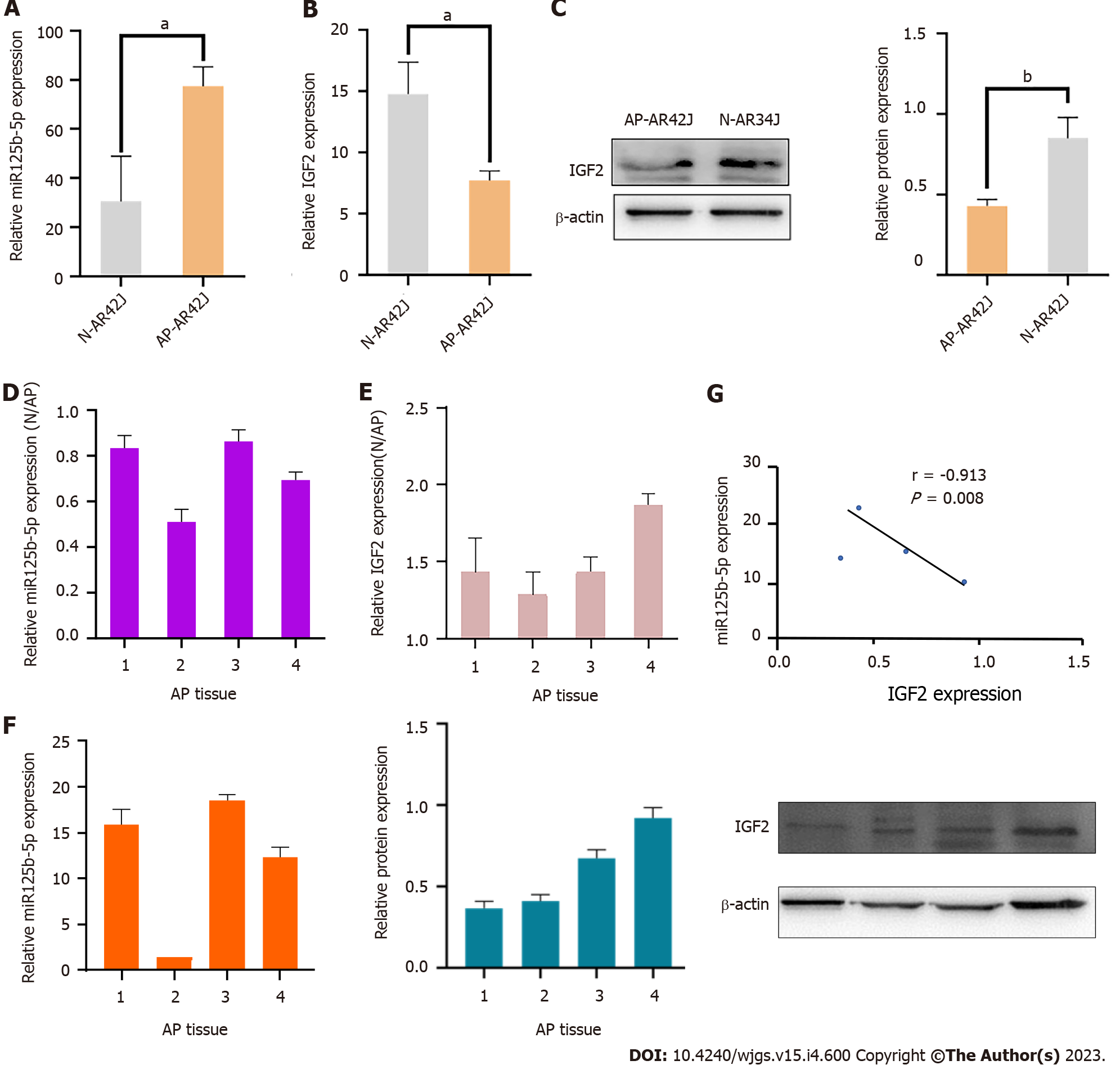
Figure 3 Expression of miR-125b-5p and insulin-like growth factor 2 in vitro and invivo.
A: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to detect the expression of miR-125b-5p in AR42J cell lines in activated and inactive state; B: RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) in AR42J cell lines under activated and inactive state; C: Western blot was used to detect the expression level of IGF2, and β-actin was used as the internal reference; D: RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of miR-125b-5p in normal pancreatic tissues and pancreatitis tissues; E: RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of IGF2 in normal pancreatic tissues and pancreatitis tissues; F: The mRNA and protein expression of miR-125b-5p and IGF2 in 4 cases of pancreatitis tissues were detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot. Among them, sample 2 was used as the standard to calculate the fold change of miR-125b-5p expression in other samples by comparing the miR-125b-5p/U6 ratio in sample 2. Western blot was used to detect the expression level of IGF2, and β-actin was used as the internal reference. The experiment was repeated three times and is expressed as mean ± SD; G: miR-125b-5p was negatively correlated with IGF2 protein expression level, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005. AP: Acute pancreatitis; IGF2: Insulin-like growth factor 2; N: Normal.
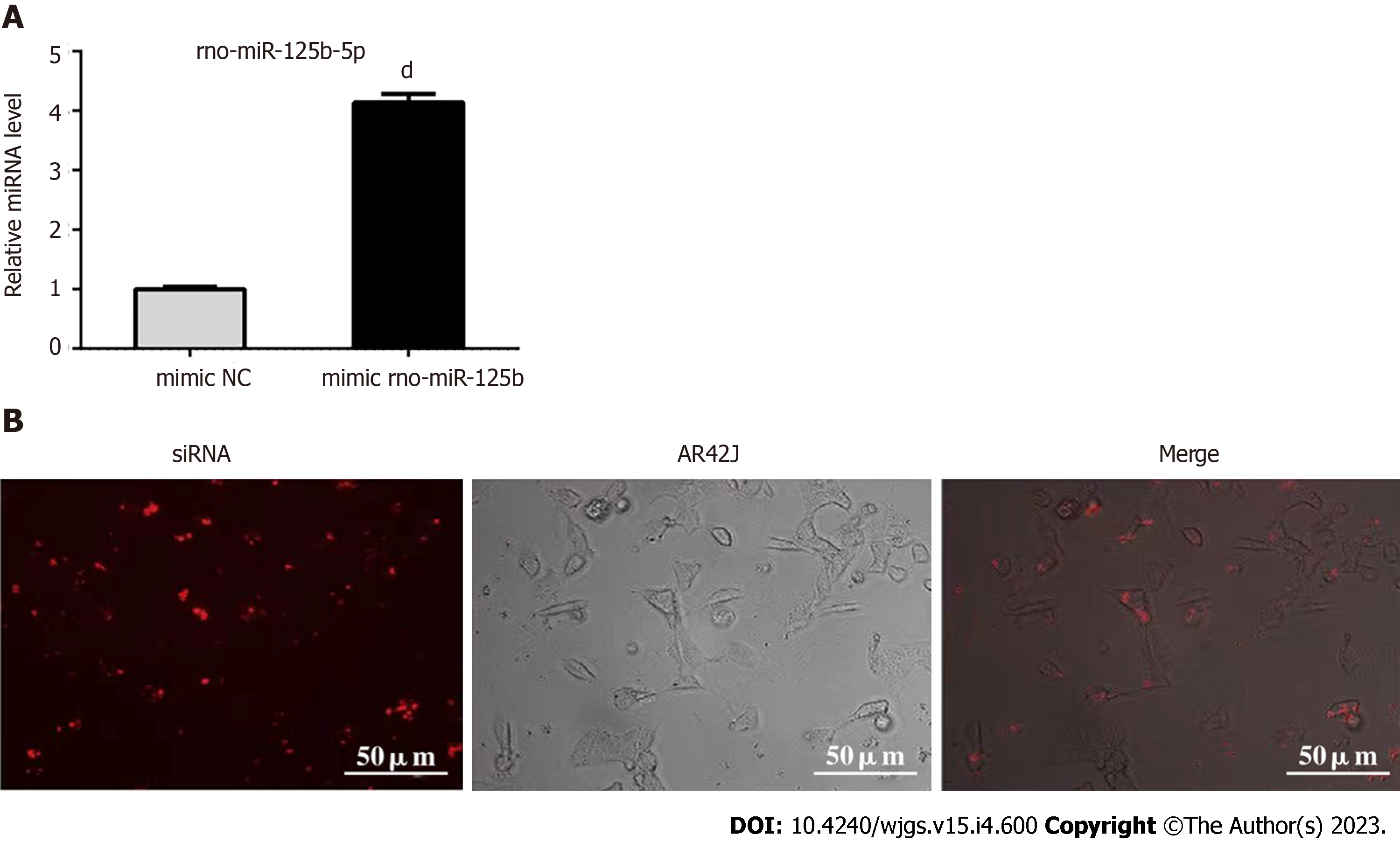
Figure 4 Establishment of exosome overexpression miR-125b-5p transfection system.
A: The expression of miR-125b-5p was significantly increased in AR42J cells treated with miR-125b-5p mimic; B: Fluorescently-labeled siRNA was observed in the cytoplasm of the AR42J cell line. Data are representative of three independent experiments and presented as the mean ± SD of the mean, dP < 0.0001. NC: Negative control.
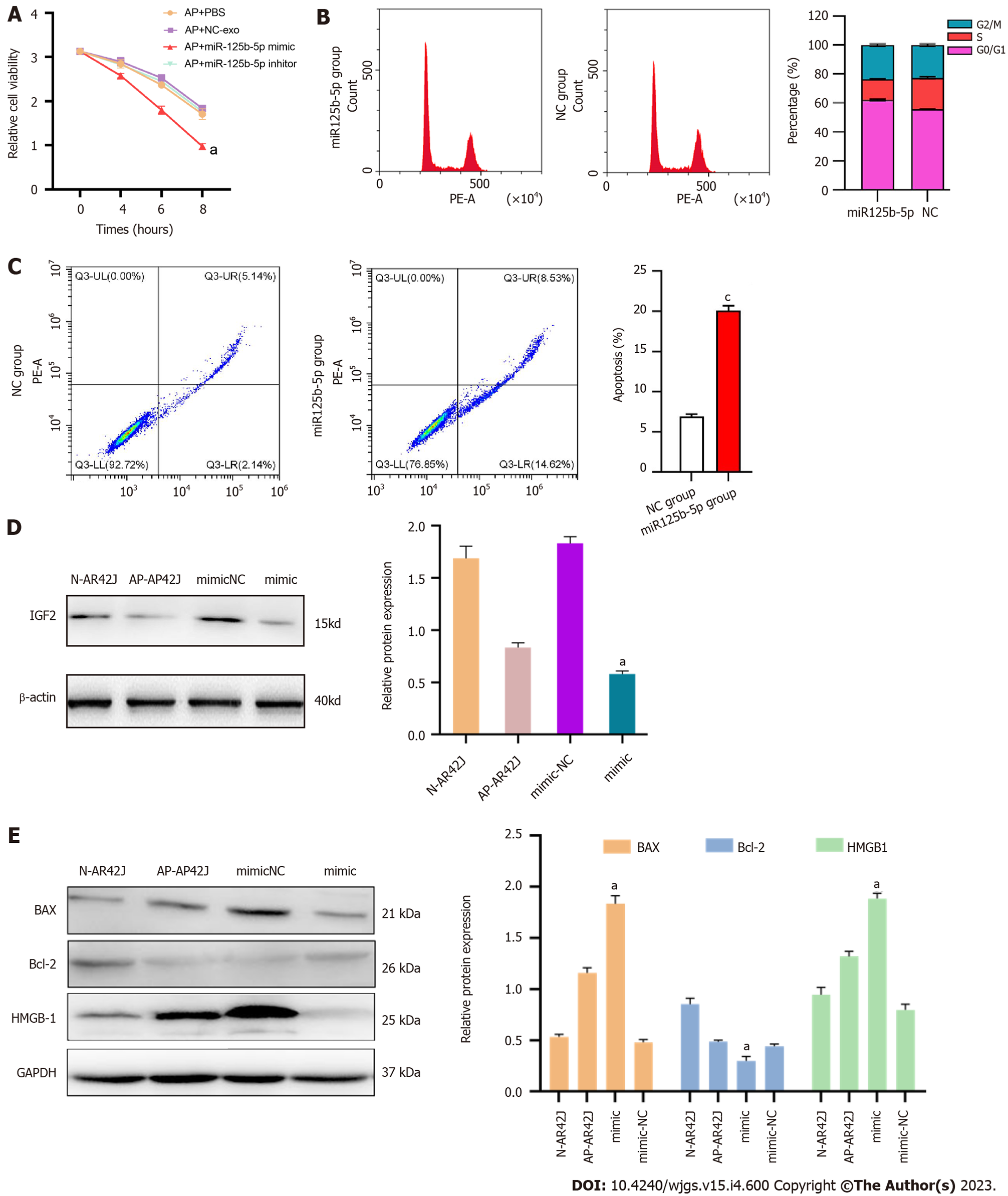
Figure 5 miR-125b-5p overexpression could promote necrosis and apoptosis of AR42J cells in the activated state.
A: miR-125b-5p overexpression promoted the necrosis of AR42J cells in the activated state; B: Flow cytometry analysis confirmed that the percentage of cells in G0/G1 phase increased in AR42J cells in the activated state treated with the miR-125b-5p overexpression group; C: The percentage of apoptotic cells increased as confirmed by flow cytometry; D and E: The expression of insulin-like growth factor 2, BAX, Bcl-2 and HMGB-1 was confirmed by Western blot, aP < 0.05, cP < 0.0005. AP: Acute pancreatitis; IGF2: Insulin-like growth factor 2; N: Normal; NC: Negative control.
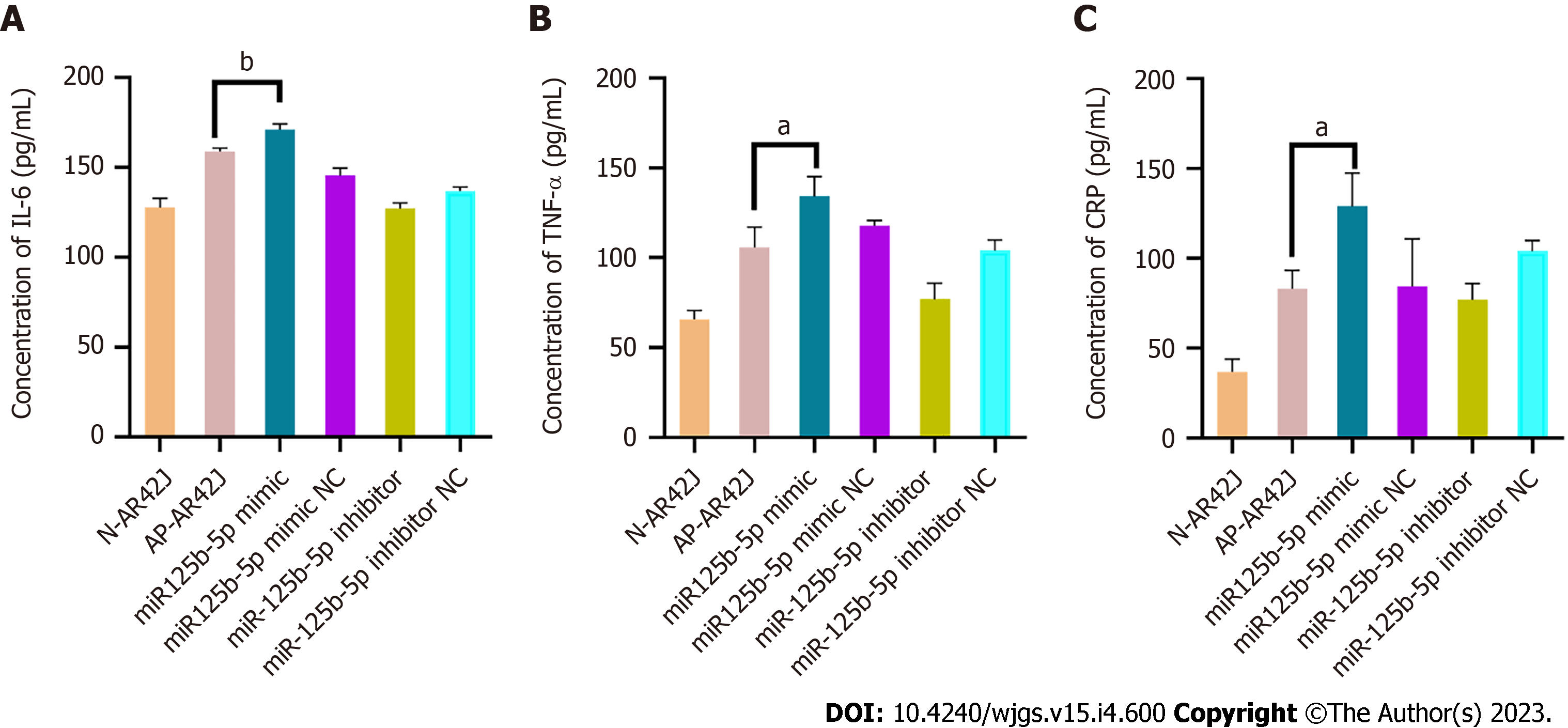
Figure 6 miR-125b-5p overexpression promotes inflammatory injury of AR42J cells in activated state.
A: Interleukin-6 level was determined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); B: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha level was determined by ELISA; C: C-reactive protein level was determined by ELISA, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005. IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; CRP: C-reactive protein.
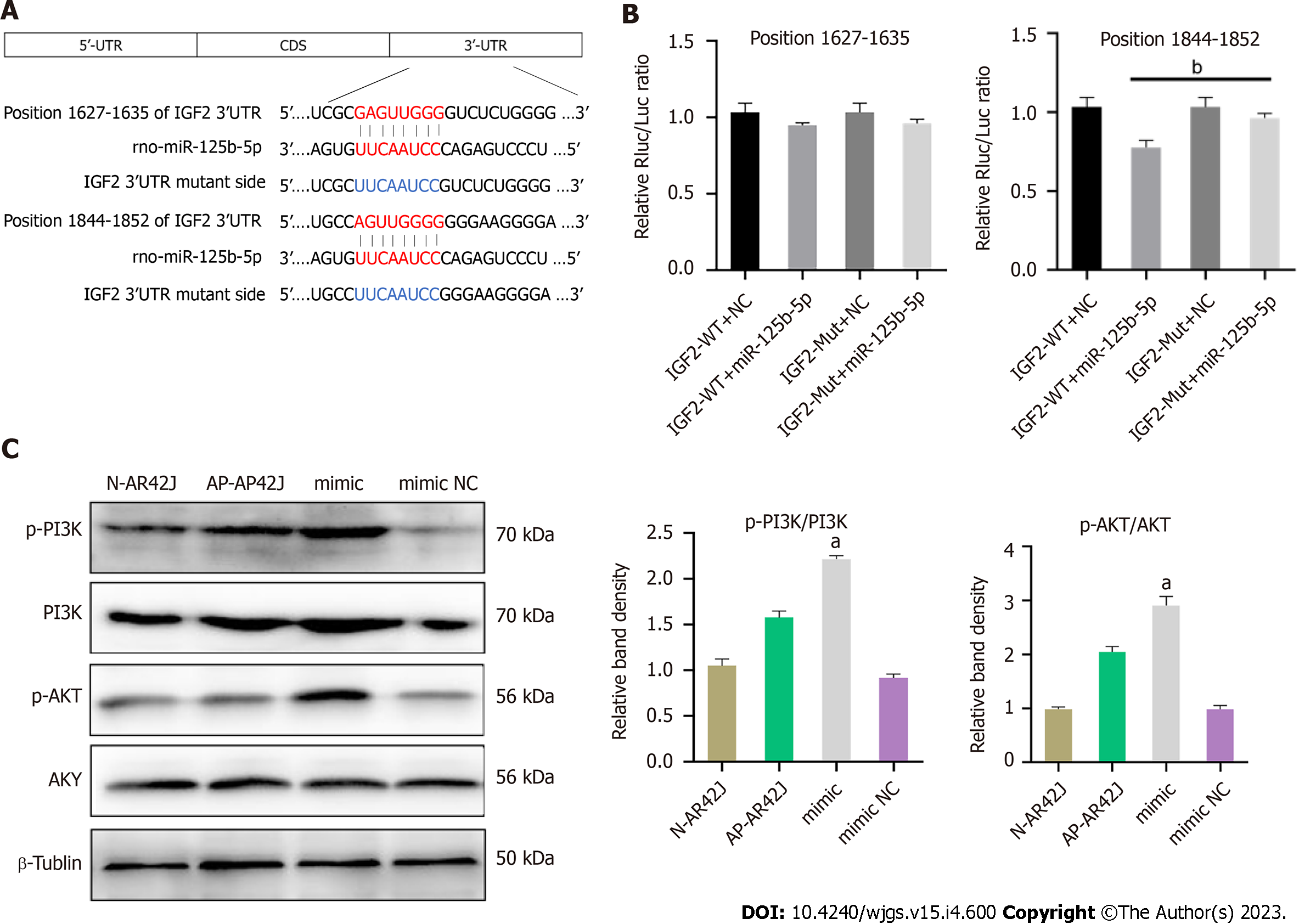
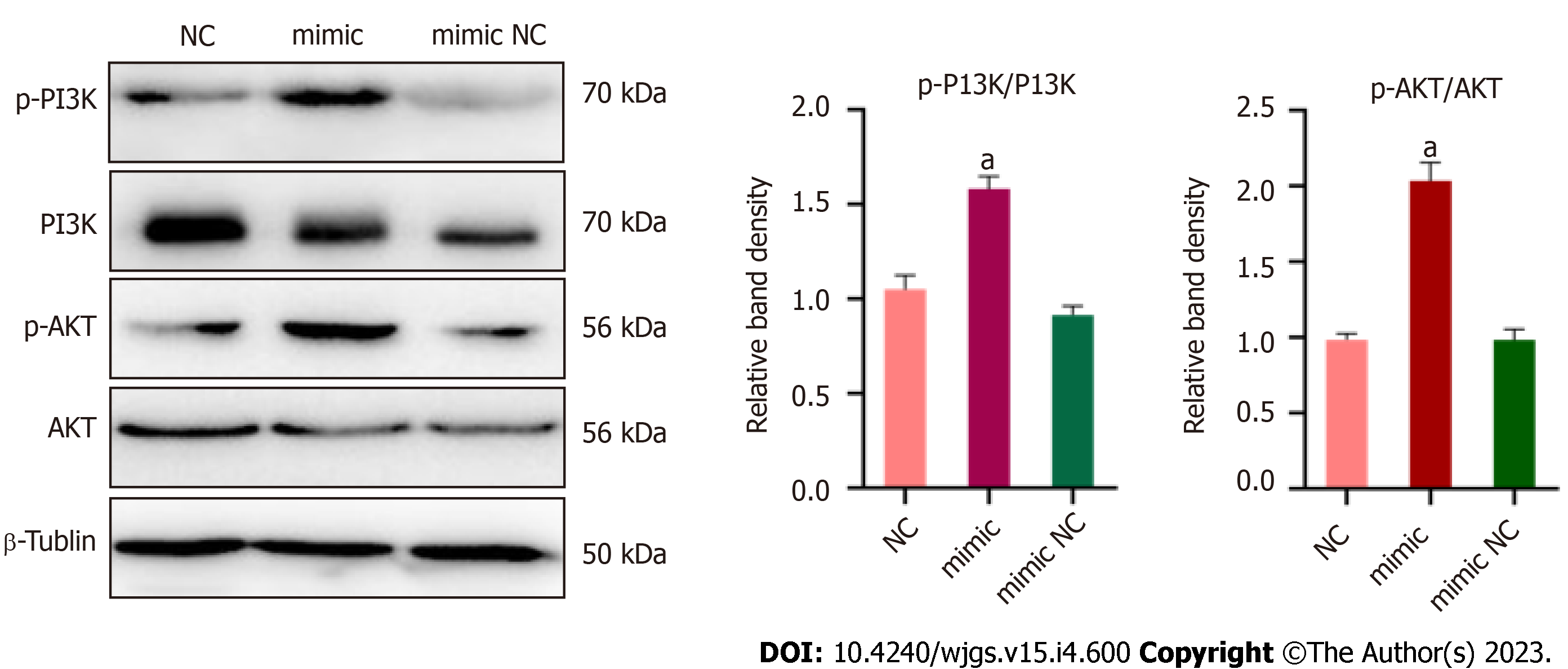
Figure 7 miR-125b-5p promotes acute pancreatitis exacerbation by inhibiting insulin-like growth factor 2 protein expression in PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
A: The potential binding sites of miR-125b-5p in the 3¢-untranslated regions (UTR) of wild-type insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) (red part). The blue section is the mutation site in mutant IGF2 3¢-UTR sequence; B: Luciferase activity in IGF2 3¢-UTR of wild-type and mutant was detected after transfection of miR-125b-5p mimics and negative control miRNAs. The normalized luciferase activity of the transfected control miRNA was set to a relative luciferase activity of 1; C: The protein expression of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway was confirmed by western blot. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005. AP: Acute pancreatitis; IGF2: Insulin-like growth factor 2; N: Normal; NC: Negative control; WT: Wild-type; MUT: Mutant; UTR: Untranslated regions; CDS: Coding sequence.
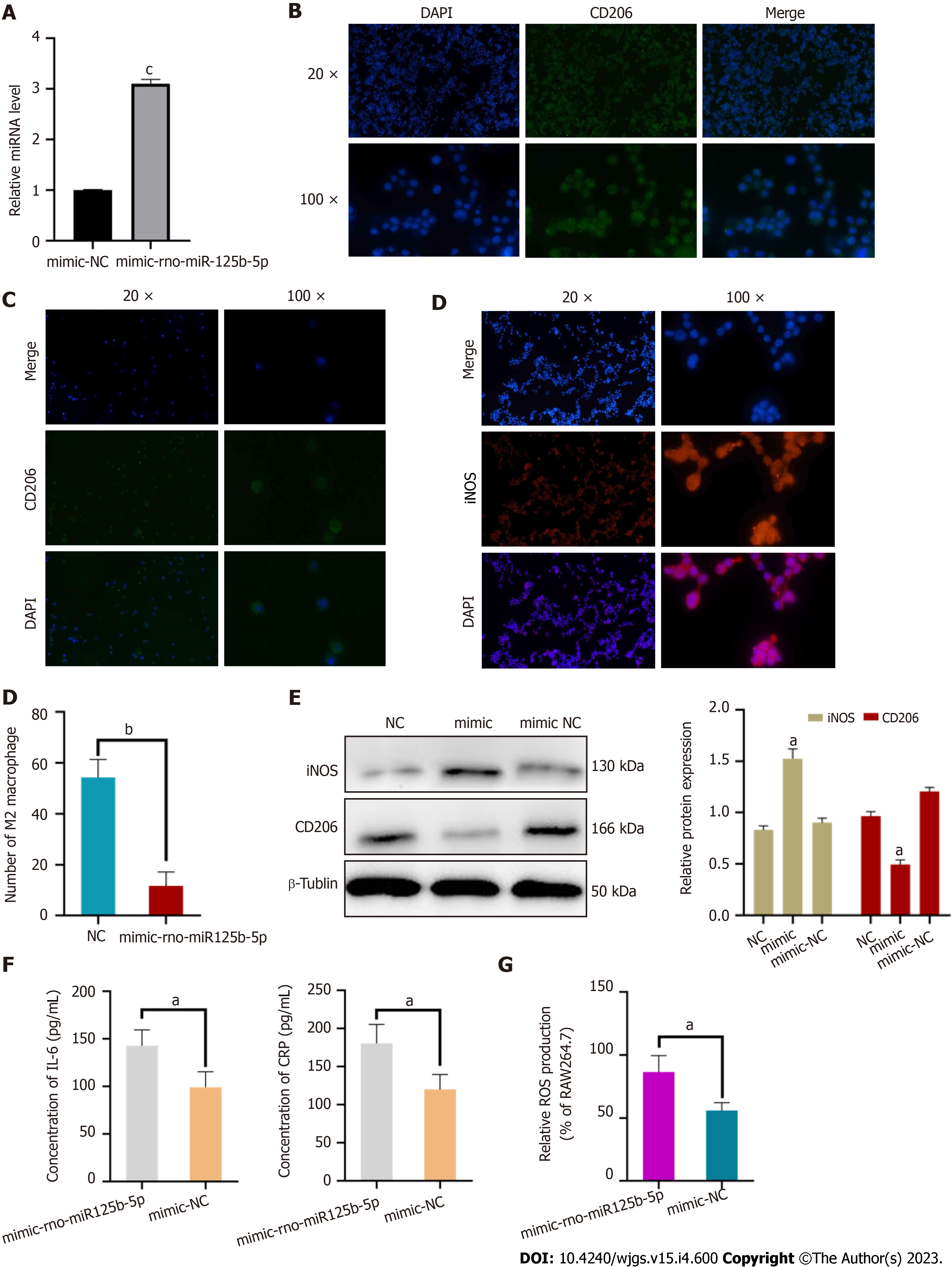
Figure 8 miR-125b-5p promoted M1-type polarization of macrophages and the release of inflammatory factors.
A: Construction of overexpression miR-125b-5p in RAW264.7 cell line; B: Negative control group: RAW264.7 cells stimulated with interleukin (IL)-4 for 24 h showed M2 polarization of macrophages; C: miR-125b-5p overexpression group: exosomes overexpressing miR-125b-5p were added to RAW264.7 cell line stimulated with IL-4 to inhibit M2 polarization of macrophages; D: miR-125b-5p overexpression group: Exosomes overexpressing miR-125b-5p were added to RAW264.7 cell line stimulated with IL-4 to promote M1 polarization of macrophages. Immunofluorescence counting showed that the number of M2 macrophages in the overexpression group was decreased compared with the control group; E: Western blot showed that the protein expression level of inducible nitric oxide synthase and CD206 in the RAW264.7 cell line; F: IL-6 and C-reactive protein level were determined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; G: miR-125b-5p overexpression promoted reactive oxygen species accumulation in the RAW264.7 cell line (P = 0.0224), aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005, cP < 0.0005. NC: Negative control; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL: Interleukin; CRP: C-reactive protein; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
Figure 9 miR-125b-5p promotes PI3K/AKT signaling pathway phosphorylation and inflammatory response in RAW264.
7 cell line. A western blot was used to confirm the protein expression of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cell line, aP < 0.05. NC: Negative control.
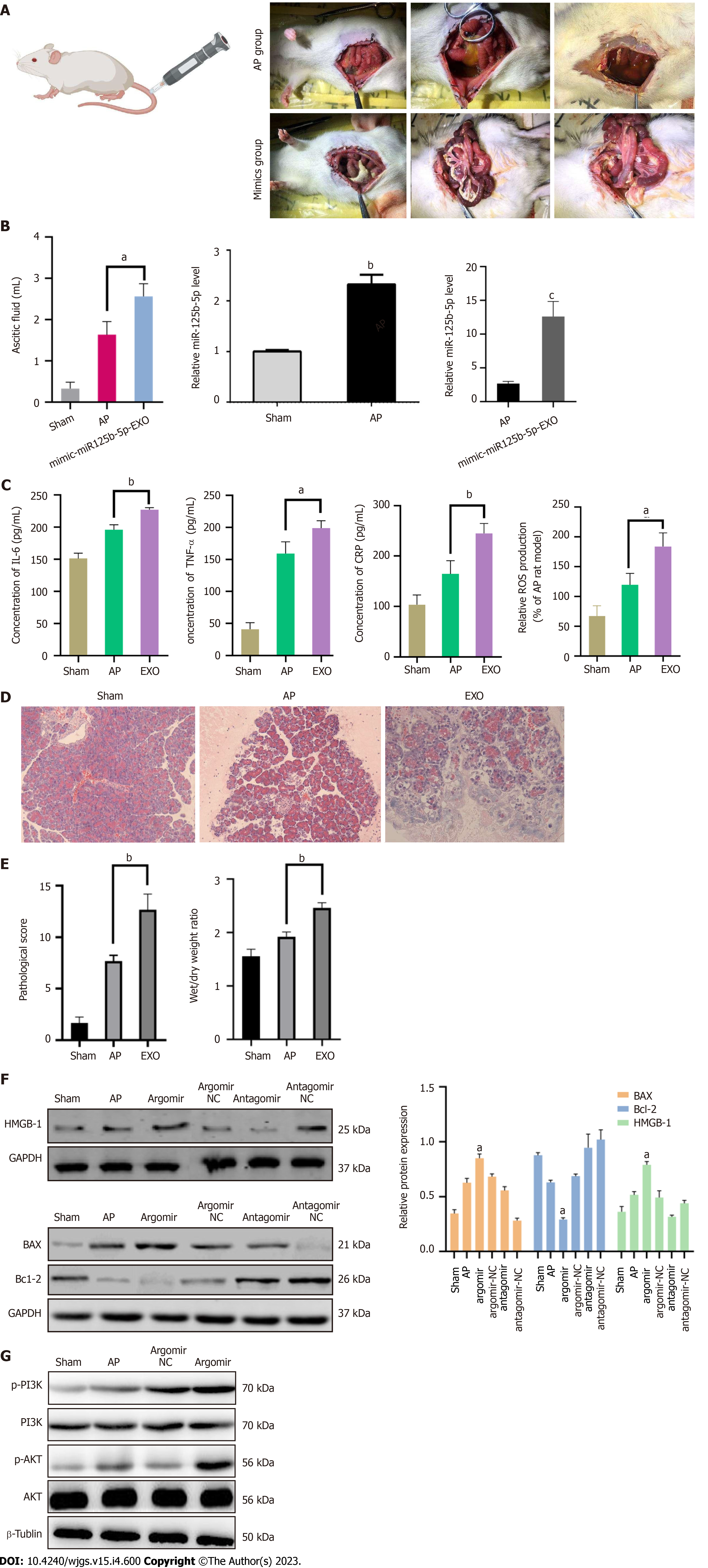
Figure 10 miR125b-5p promotes the aggravation of inflammation in vivo.
A: Intraperitoneal condition of rats in acute pancreatitis (AP) group and overexpression group; B: Ascites volume of rats in the three groups. The expression of miR-125b-5p in pancreatic tissues of sham group, AP group and overexpression group was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; C: The level of interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, C-reactive protein and reactive oxygen species was determined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; D: Histopathological image of rat pancreas in three groups; E: Pancreatic histopathology score and dry/wet ratio; F: Western blot showing the expression of BAX, Bcl-2, HMGB-1 and insulin-like growth factor 2 in the pancreatic tissues; G: Western blot showing the expression of p-PI3K, PI3K, p-AKT and AKT in the pancreatic tissues, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005, cP < 0.0005. IGF2: Insulin-like growth factor 2; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; AP: Acute pancreatitis; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; CRP: C-reactive protein; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; NC: Negative control.
- Citation: Zheng Z, Cao F, Ding YX, Lu JD, Fu YQ, Liu L, Guo YL, Liu S, Sun HC, Cui YQ, Li F. Acinous cell AR42J-derived exosome miR125b-5p promotes acute pancreatitis exacerbation by inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(4): 600-620
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i4/600.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.600