Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Apr 27, 2023; 15(4): 495-519
Published online Apr 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.495
Published online Apr 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.495
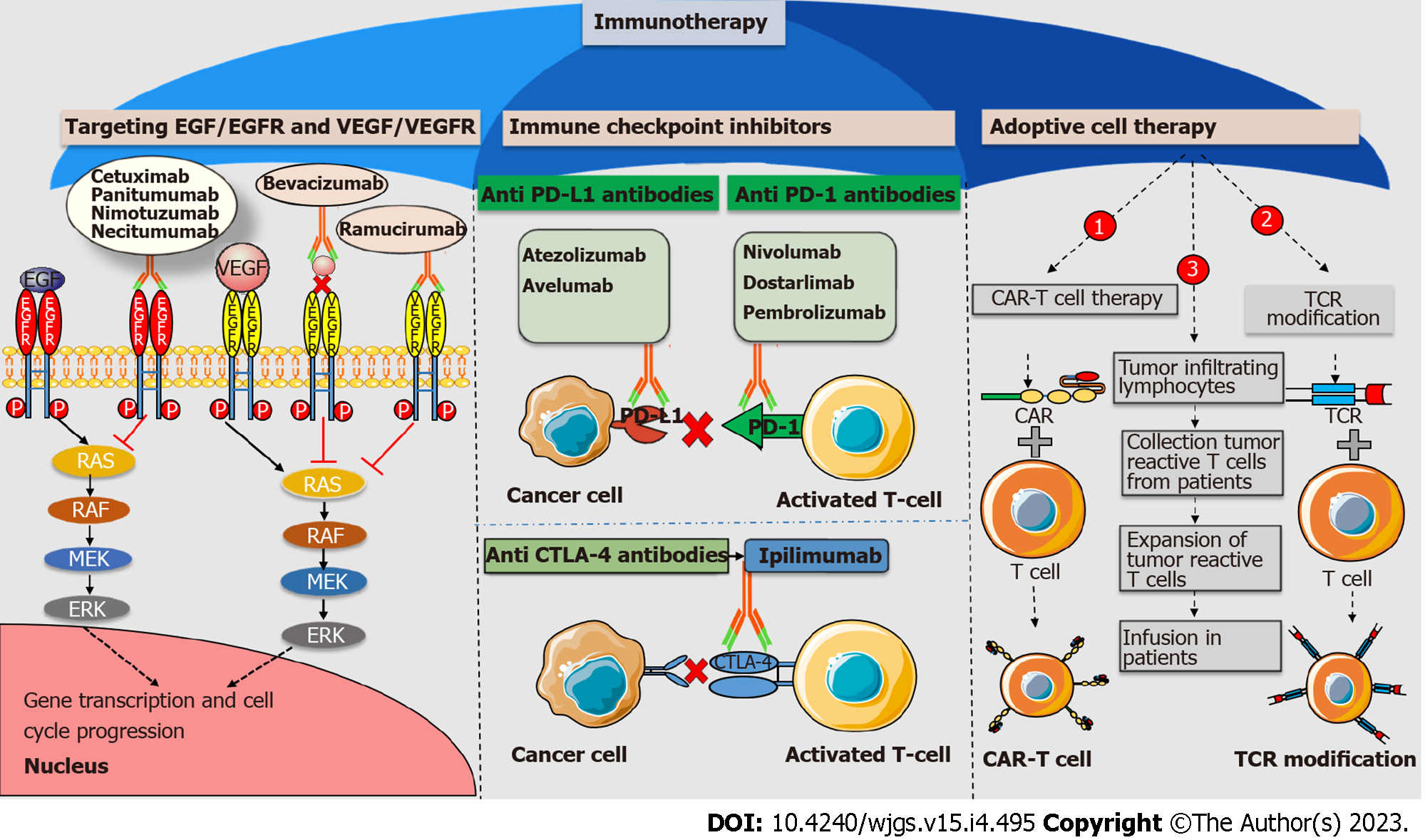
Figure 1 Immunotherapeutic approaches against colorectal cancer.
Antiangiogenic monoclonal antibodies like cetuximab, panitumumab, nimotuzumab, and necitumumab target epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor (EGFR). Antiangiogenic monoclonal antibodies such as bevacizumab and ramucirumab target vascular EGF and its receptor, respectively. All antiangiogenic monoclonal antibodies downregulate the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway and prevent the transcription of genes involved in cell cycle progression. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) like atezolizumab and avelumab target programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1). ICIs like nivolumab, dostarlimab, and pembrolizumab target programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1). The ICI ipilimumab targets cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4). ICIs act as immune brakes that prevent checkpoint proteins from interacting with their companion proteins, thus boosting T cell effector activity. T cell boosting therapy, like adoptive cell therapy, includes chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy (CAR-T), T cell receptor modification (TCR), and tumor infiltrating lymphocyte boost T cell activity to combat cancer cell growth. VEGF: Vascular epidermal growth factor; VEGFR: Vascular epidermal growth factor receptor.
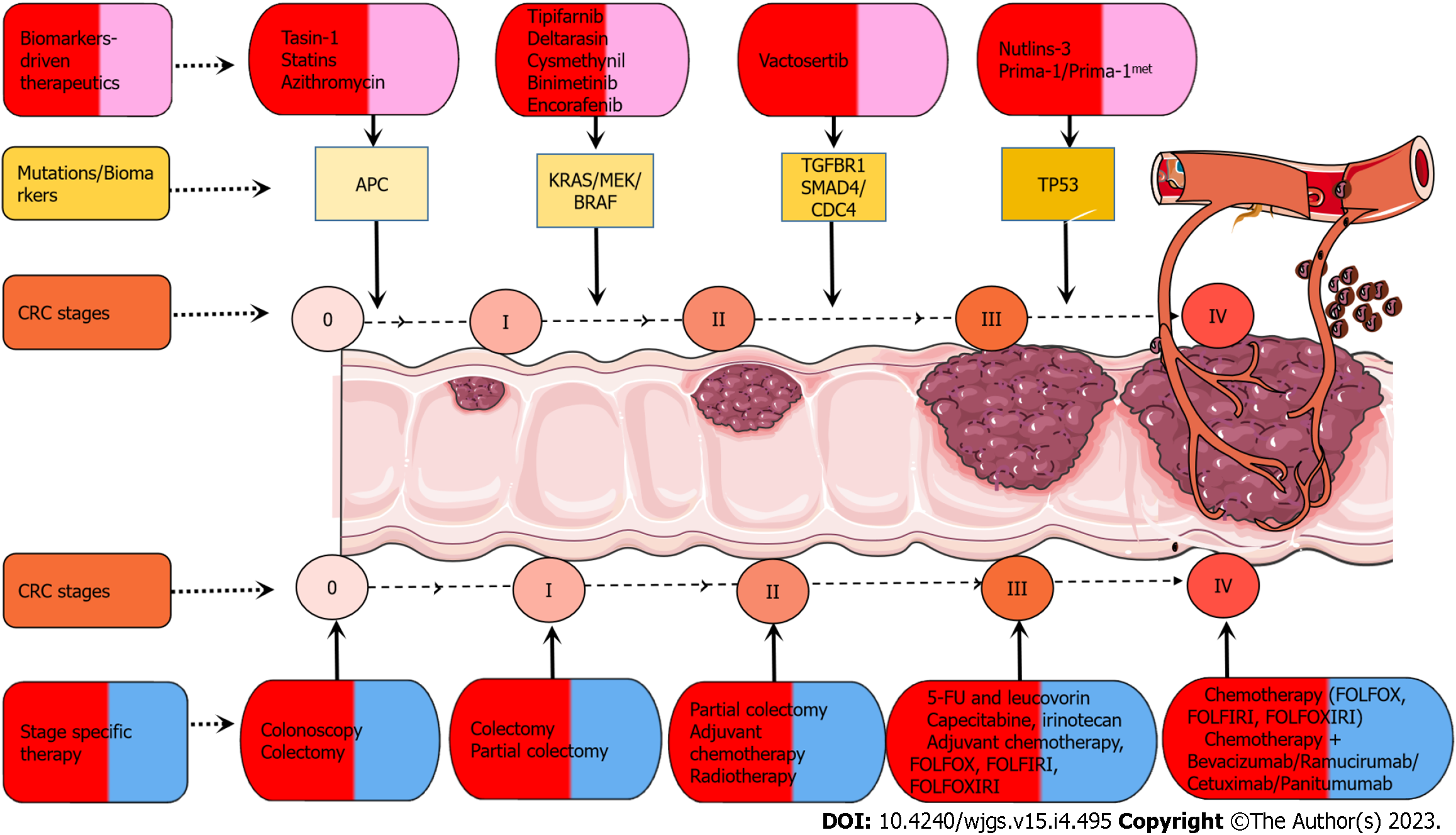
Figure 2 Biomarker-driven therapeutics and cancer stage specific therapeutic strategies.
Drugs like tasin-1, statins, and azithromycin specifically target adenomatous polyposis coli (APC). Drugs such as tipifarnib, deltarasin, and cysmethynil target KRAS mutations in colorectal cancer (CRC), and binimetinib and encorafenib target BRAF-V600 mutations in CRC. Vactosertib is a potent and selective transforming growth factor-beta receptor I kinase inhibitor. Small molecule nutlins-3 is an MDM2 antagonist blocking the interaction between MDM2 and p53. Small molecules prima-1/prima-1met convert mutant p53 to an active conformation. There are stage-specific therapies for different stages. For stage 0, colonoscopy and colectomy are recommended. For stage I, colectomy and partial colectomy are recommended. For stage II, partial colectomy, adjuvant chemotherapy, and radiotherapy are recommended. For stage III, chemotherapy includes 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), 5-FU/leucovorin, capecitabine, irinotecan, adjuvant chemotherapy, and combinational chemotherapy [5-FU + leucovorin + oxaliplatin (FOLFOX), 5-FU + leucovorin + irinotecan (FOLFIRI), 5-FU + leucovorin + oxaliplatin + irinotecan (FOLFOXIRI)]. For stage IV, chemotherapy, combinational chemotherapy, and immunotherapy include bevacizumab, ramucirumab, cetuximab, and panitumumab.
- Citation: Kumar A, Gautam V, Sandhu A, Rawat K, Sharma A, Saha L. Current and emerging therapeutic approaches for colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(4): 495-519
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i4/495.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.495