Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Nov 27, 2023; 15(11): 2646-2656
Published online Nov 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i11.2646
Published online Nov 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i11.2646
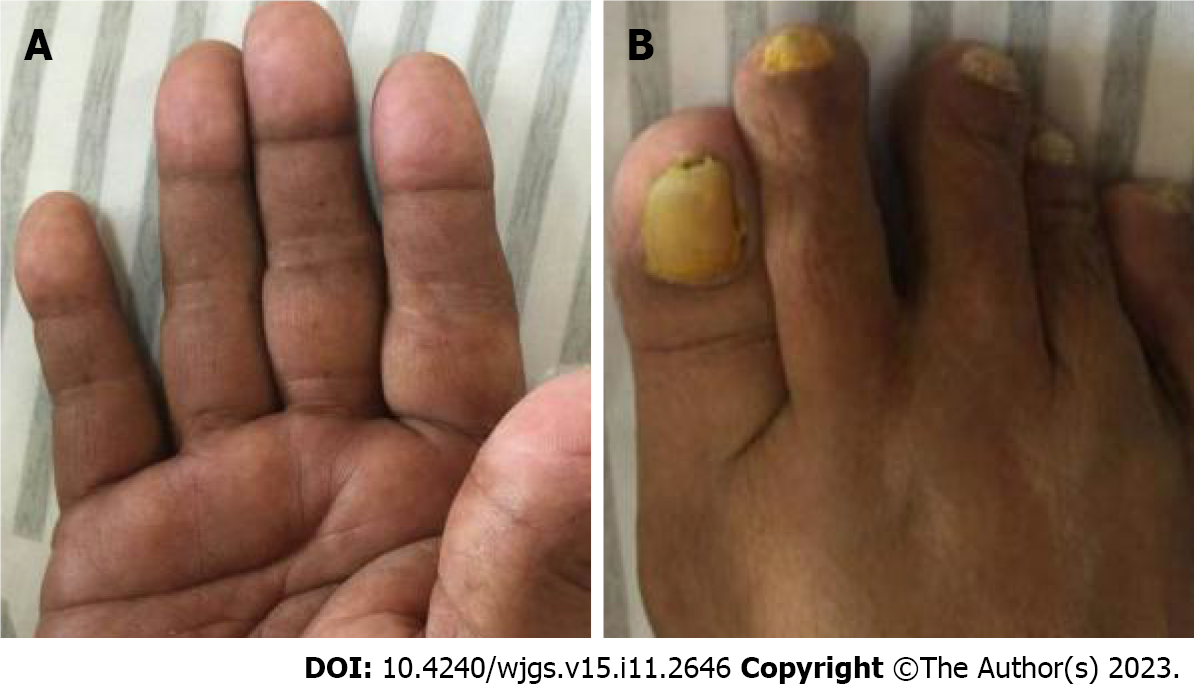
Figure 1 Cutaneous hyperpigmentation of Patient 1.
A: Hands; B: Feet (with nail dystrophy).
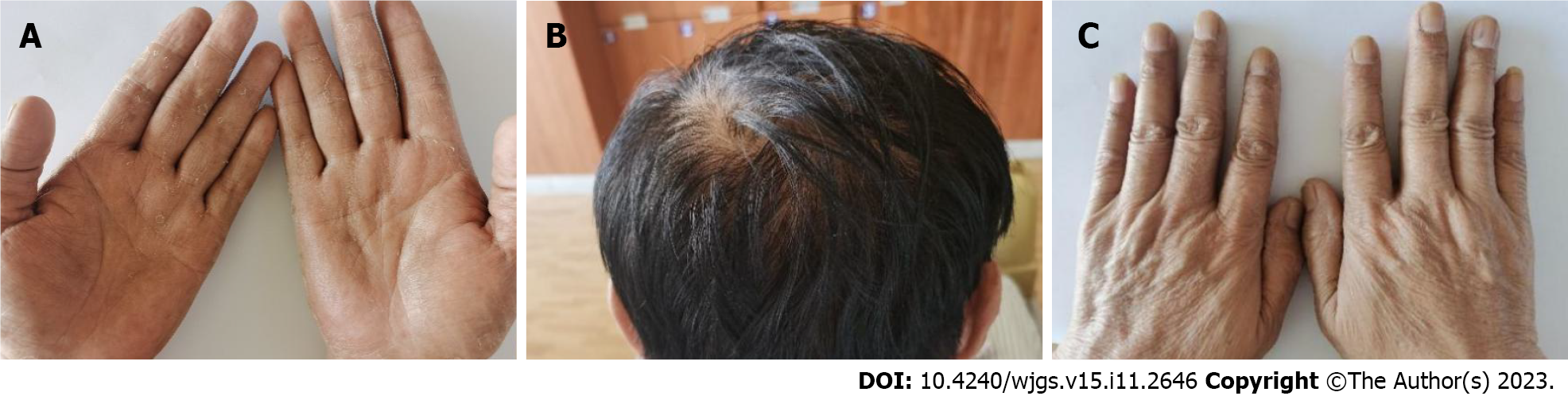
Figure 2 Physical examination findings of Patient 2.
A and C: Hyperpigmentation on the (A) palms and (C) back of the hands; B: Alopecia.
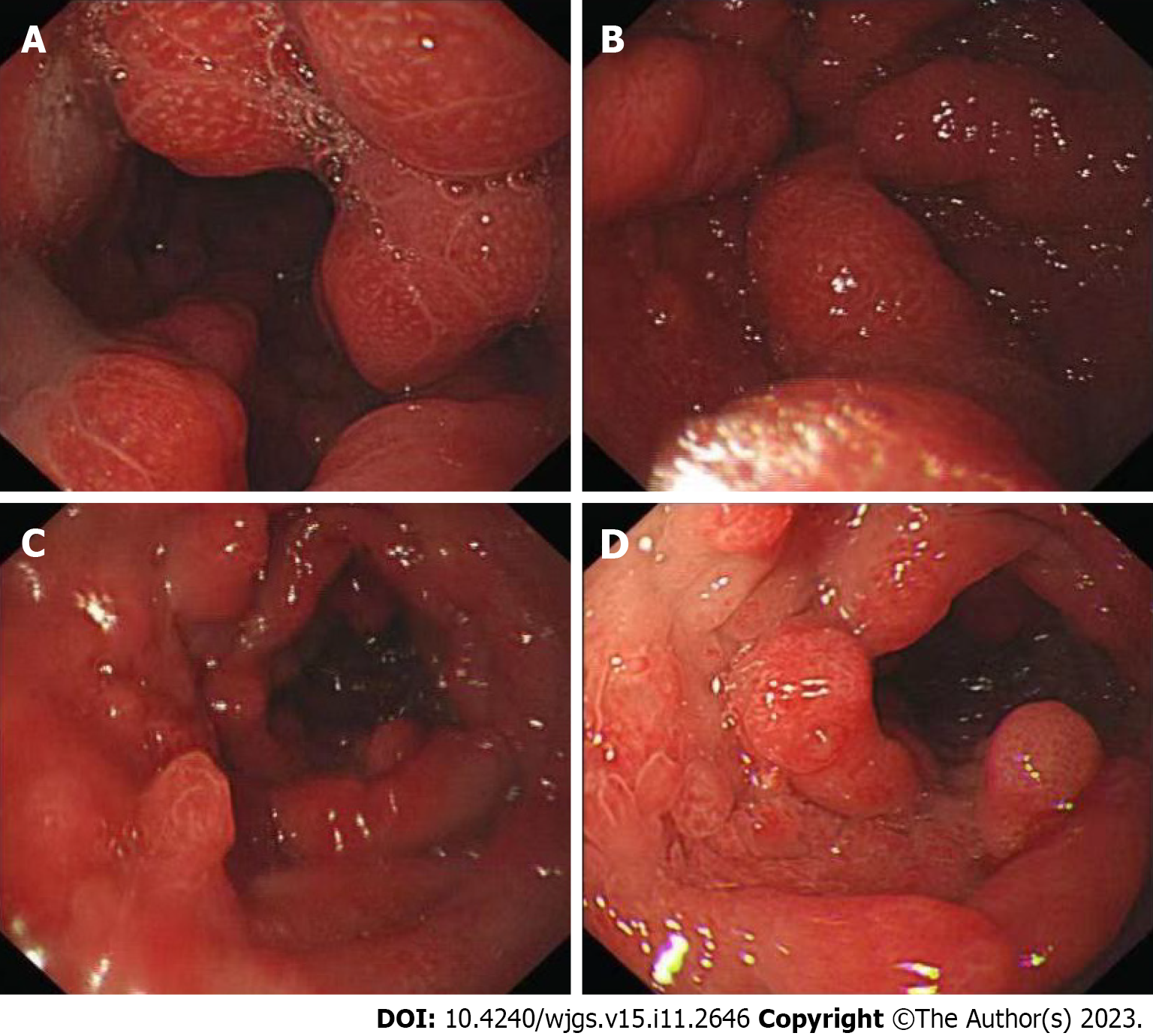
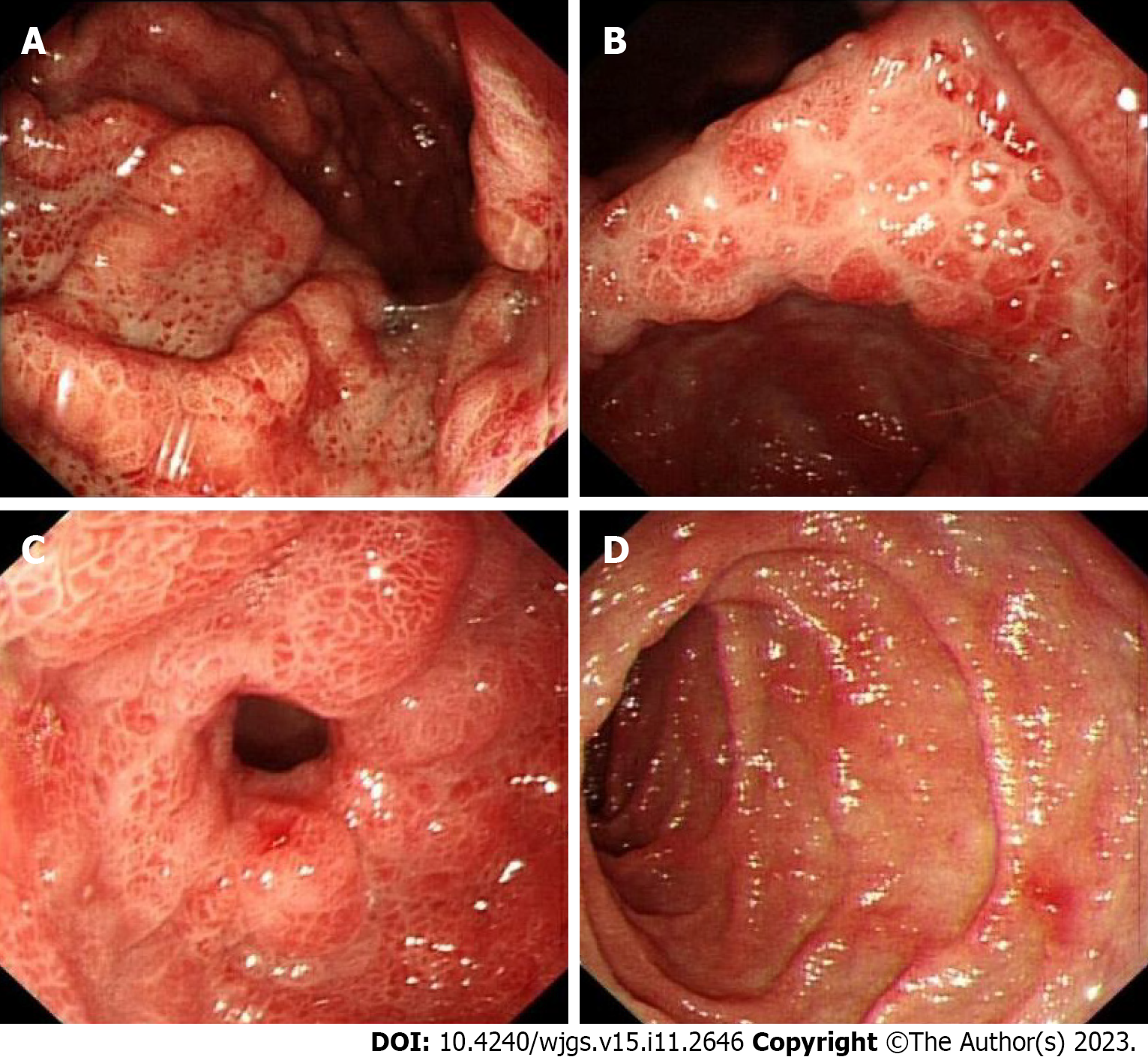
Figure 3 Gastroscopy of Patient 1.
A and B: Thickened edematous mucosa with extensive congestion in the gastric body and antrum, with scattered, nodular-like mucosal uplift in the latter; C and D: Multiple mucosal protrusions of different shapes and sizes in the duodenal bulb and descending segment.
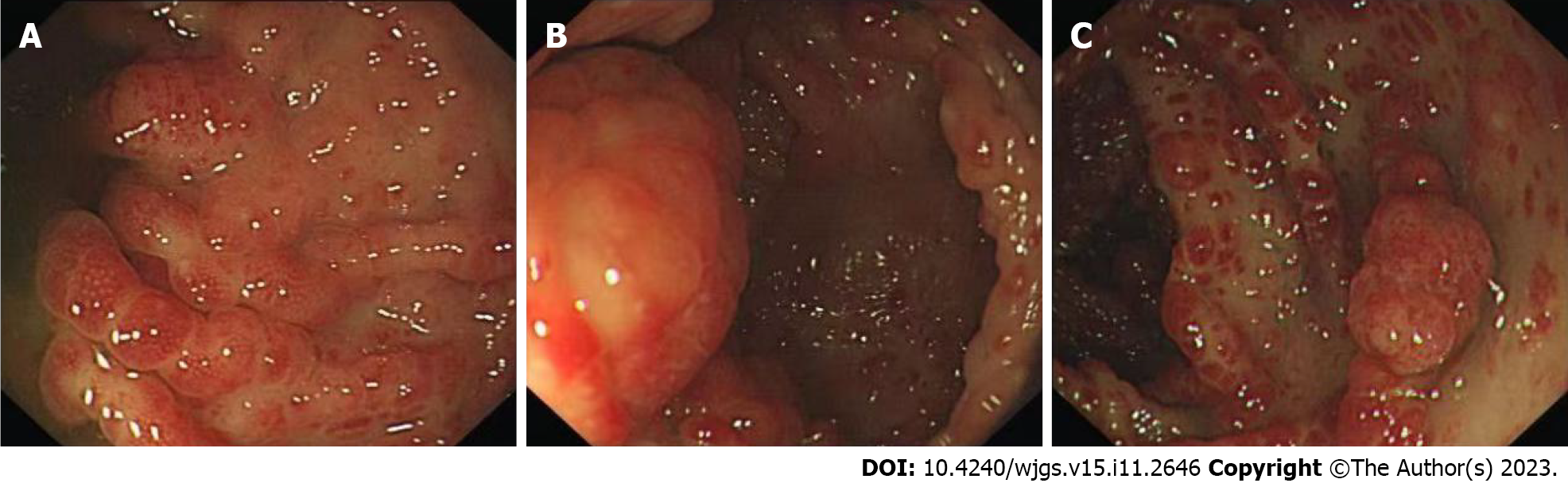
Figure 4 Colonoscopy of Patient 1.
A-C: The mucosa of the large intestine was rough, with nodular and polypoid protuberances of different shapes and sizes. The mucosa at the protuberances was hyperemic and edematous, and the vascular texture of the intestinal wall between the protuberances disappeared and turned white.
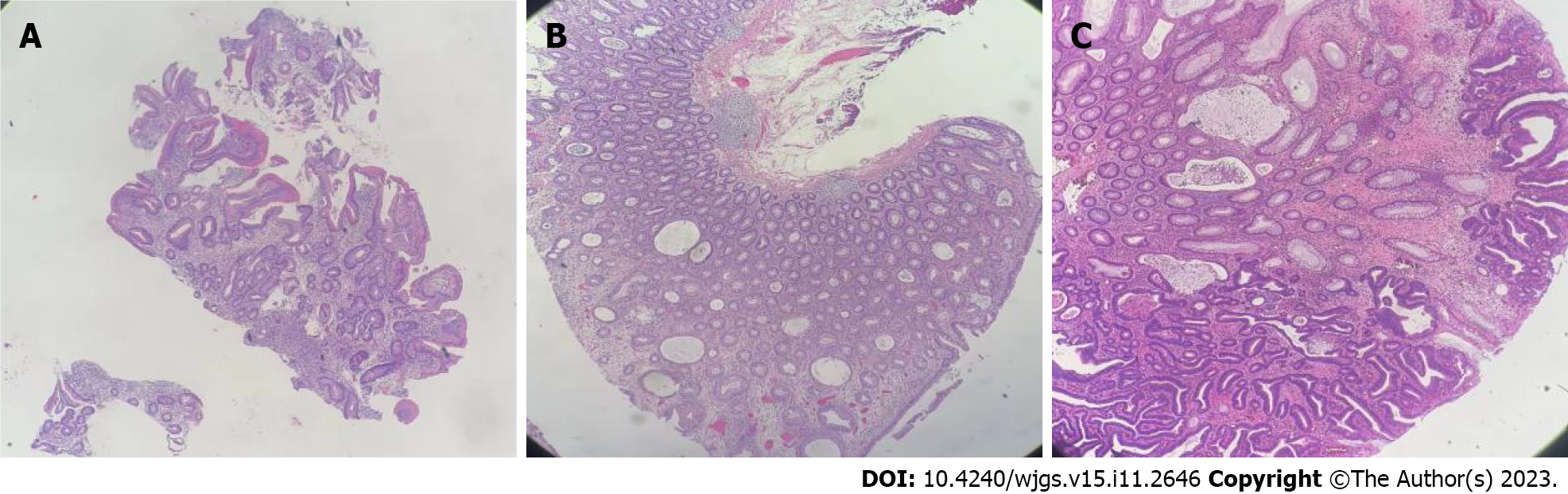
Figure 5 Biopsy from Patient 1 shows atrophic and dilated mucosal glands with infiltration of lymphocytes and eosinophils.
A: Stomach; B: Intestine. Magnification: 4 ×.
Figure 6 Endoscopic examination of Patient 2.
A-D: Mucosae of the body (A), angle (B), antrum (C), and duodenal (D) descending segment were hyperemic and edematous, with a hyperplastic and nodular appearance.
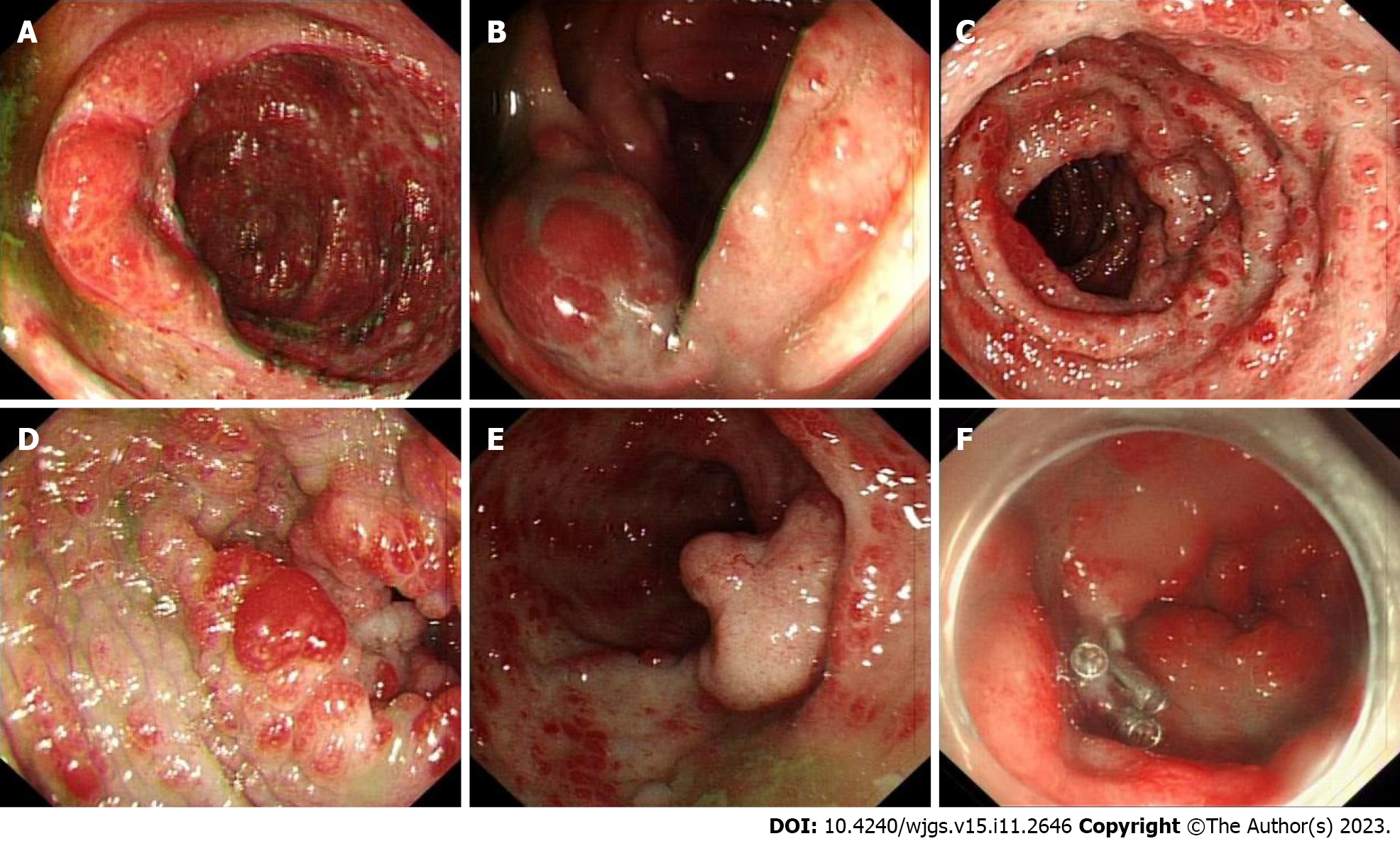
Figure 7 Colonoscopic examination of Patient 2.
A-F: Mucosa of the entire colon was diffusely hyperemic and edematous, with nodules of different sizes. A mucosal intumescent lesion measuring 2.5 cm × 2.5 cm was observed 10 cm from the anal verge.
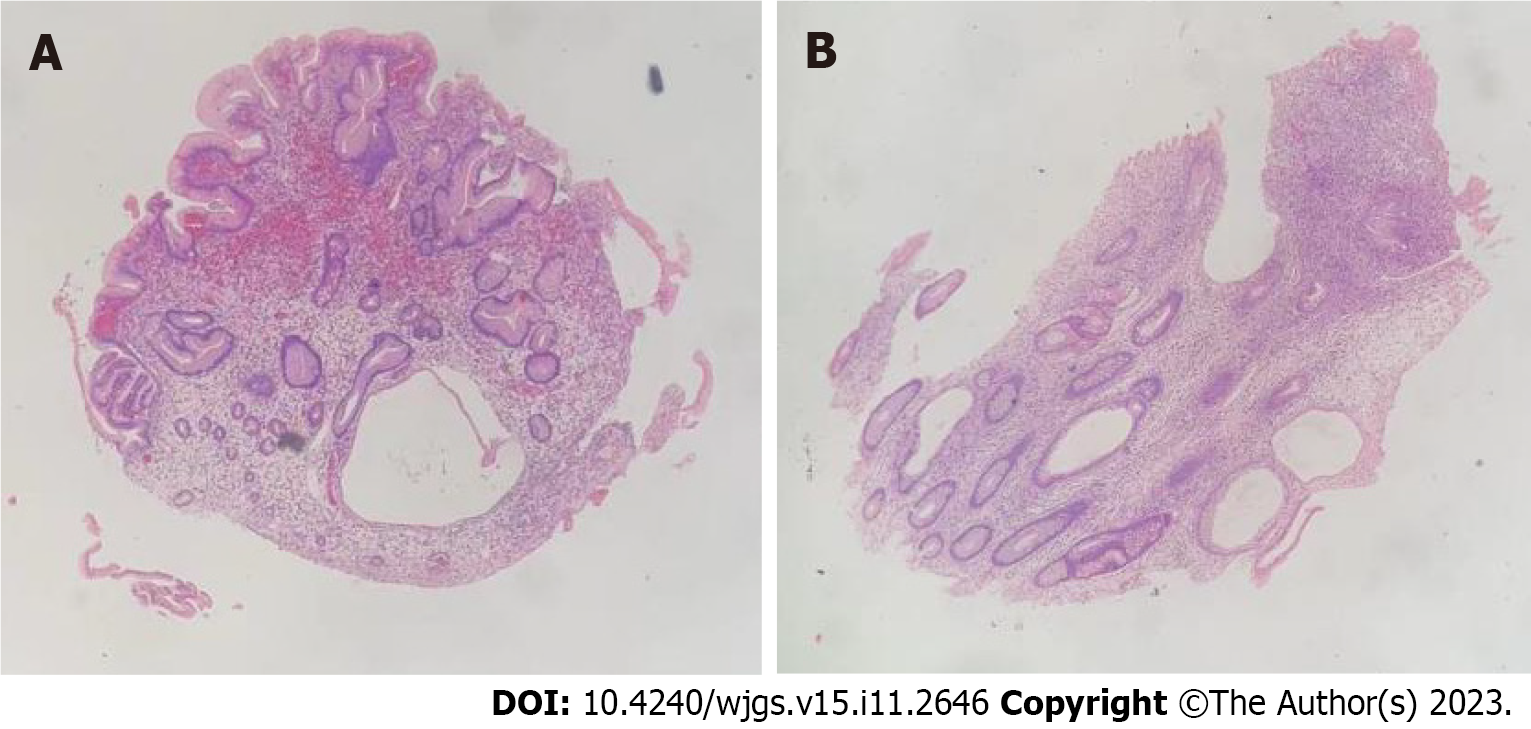
Figure 8 Histologic examination of biopsy samples from Patient 2.
A: Gastroscopic pathology, suggesting active chronic inflammation with distorted, branched, and hyperplastic glands; B: Presence of active chronic colitis, cryptitis and crypt abscesses, with hyperplastic or atrophic, dilated, and distorted glands. Interstitial edema and eosinophil infiltration were also observed; C: The rectal mass was a villous tubular adenoma, indicative of high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, with no apparent involvement of blood vessels or surgical margins. Magnification: 4 ×.
- Citation: Lv YQ, Wang ML, Tang TY, Li YQ. Comprehensive treatment and a rare presentation of Cronkhite–Canada syndrome: Two case reports and review of literature. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(11): 2646-2656
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i11/2646.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i11.2646