Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Nov 27, 2022; 14(11): 1310-1319
Published online Nov 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i11.1310
Published online Nov 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i11.1310
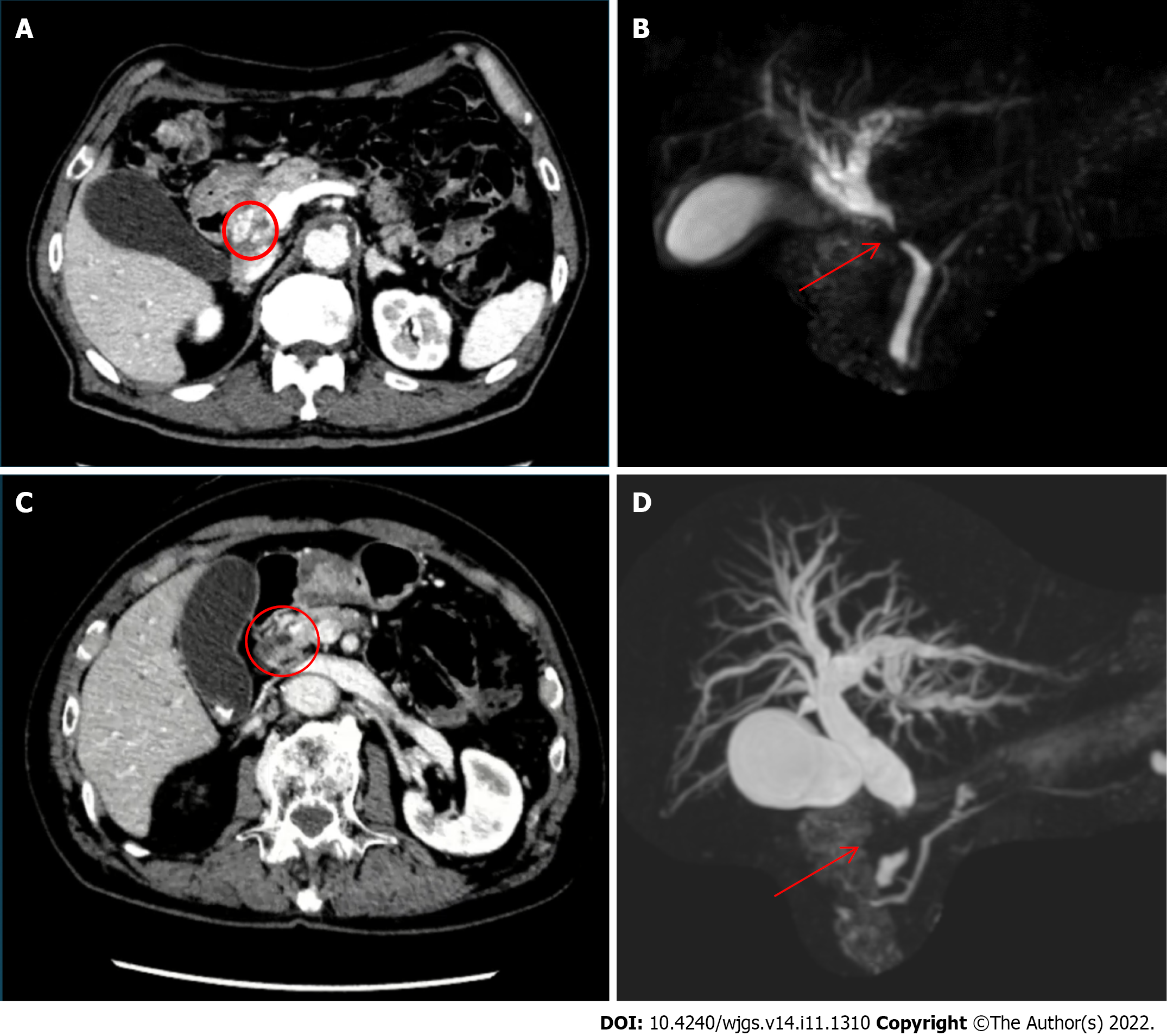
Figure 1 Imaging examinations.
A: Dynamic computed tomography (case 1) showing common bile duct wall thickening at the ductal confluence (circle) and mild dilatation of the intrahepatic bile duct; B: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showing stricture of common bile duct (arrow) and dilatation of the intrahepatic bile duct; C: Dynamic computed tomography (case 2) showing bile duct wall thickening at the upper pancreatic margin level (circle) with dilatation of the entire bile duct system without pancreatic duct dilatation; D: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showing stenosis of the distal common hepatic duct (arrow) and dilatation of the intrahepatic bile duct.
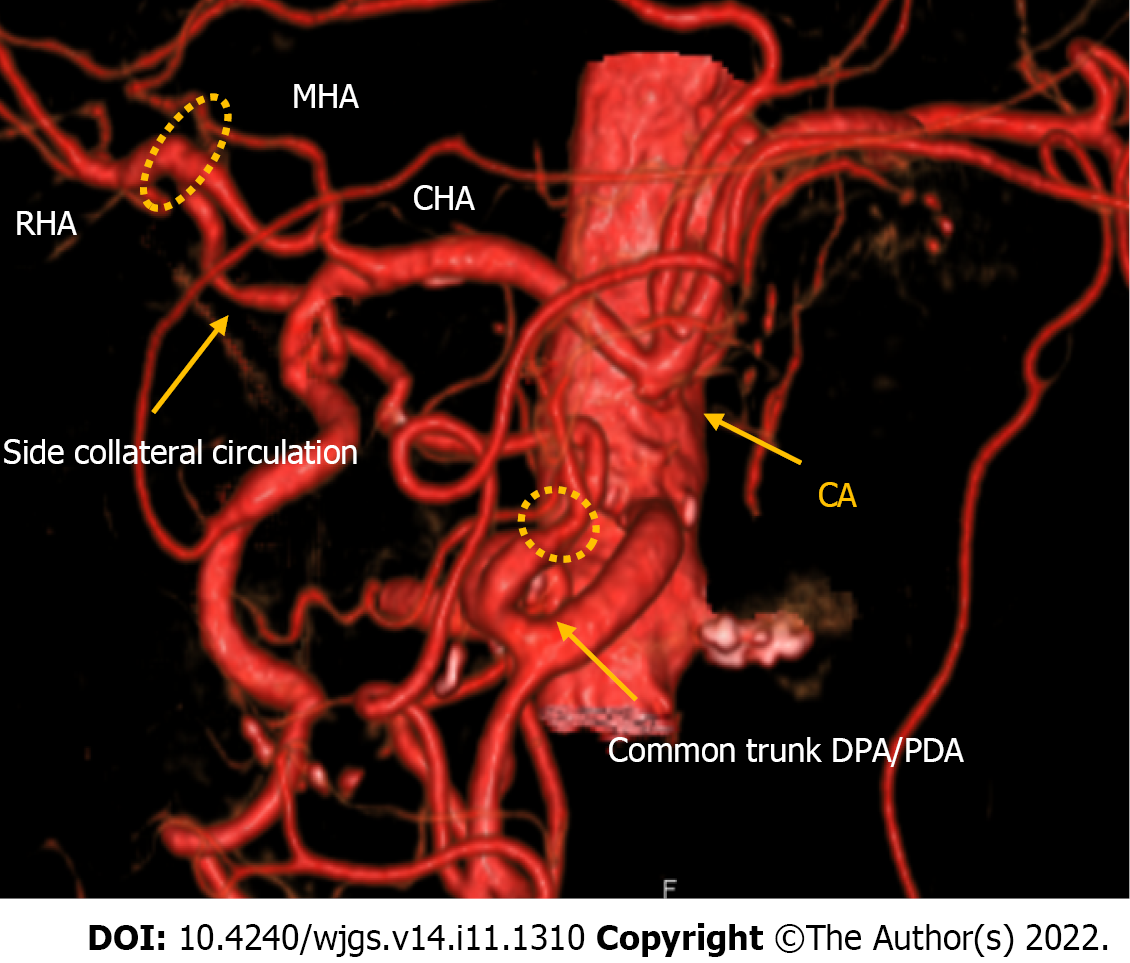
Figure 2 Computed tomography with 3D reconstruction of the vascular anatomy in case 1.
Computed tomography showed a right hepatic artery (RHA) and middle hepatic artery originating from the common hepatic artery, the usual pancreaticoduodenal arcade originating from the gastroduodenal artery, a common trunk between the dorsal pancreatic artery and pancreaticoduodenal artery originating from the superior mesenteric artery, an additional arcade originating from the common trunk and passing through the dorsal surface of the pancreatic head and linking directly to the RHA, and a replaced left hepatic artery originating from the left gastric artery. RHA: Right hepatic artery; MHA: Middle hepatic artery; CHA: Common hepatic artery; PDA: Pancreaticoduodenal artery; SMA: Superior mesenteric artery.
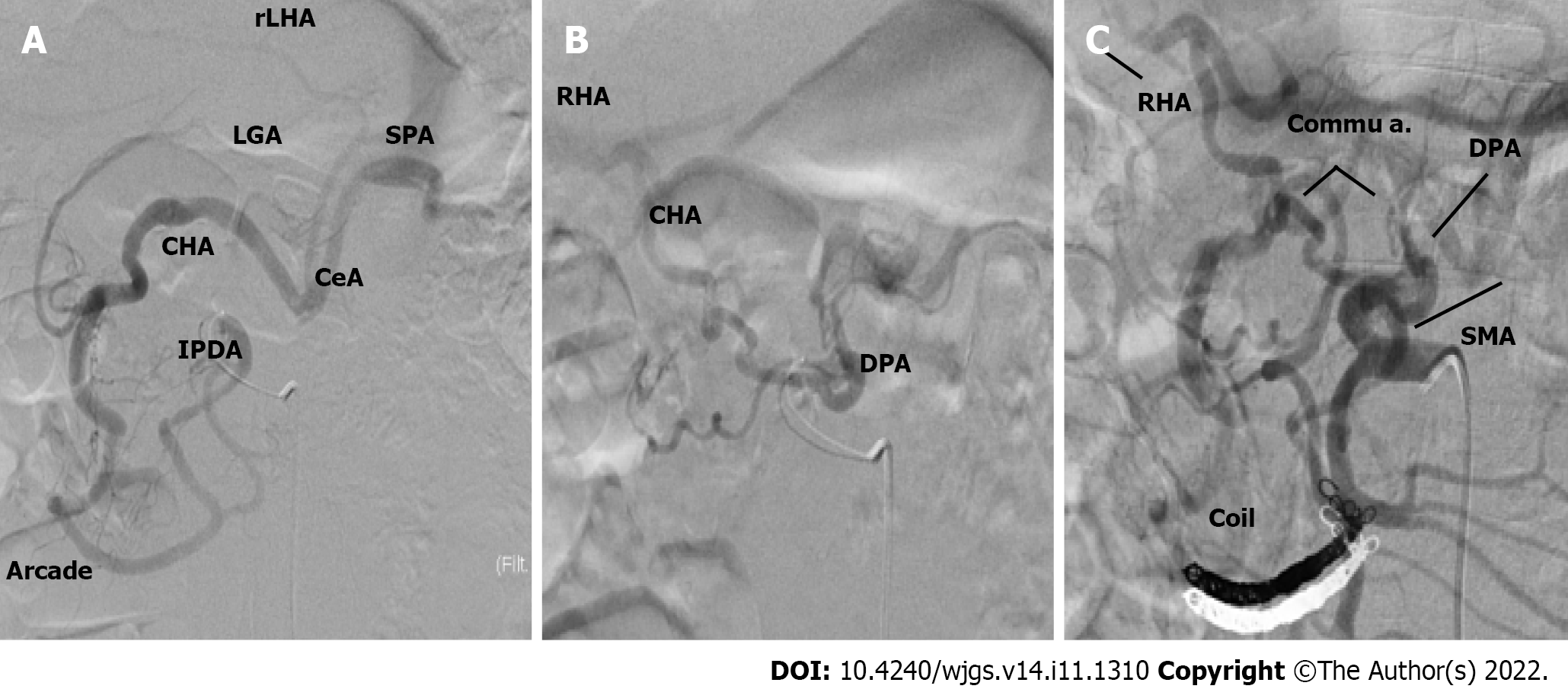
Figure 3 Angiographic study.
A: The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery was responsible for the main back flow to the celiac artery; B: The dorsal pancreatic artery (DPA) was responsible for the blood flow of the right hepatic artery; C: Blood re-flow post embolization and the DPA was responsible for the main flow to the celiac artery. IPDA: Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery; DPA: Dorsal pancreatic artery; SPA: Splenic arteries; RHA: Right hepatic artery; MHA: Middle hepatic artery; CHA: Common hepatic artery; GDA: Gastroduodenal artery; SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; LHA: Left hepatic artery; LGA: Left gastric artery; CeA: Celiac artery.
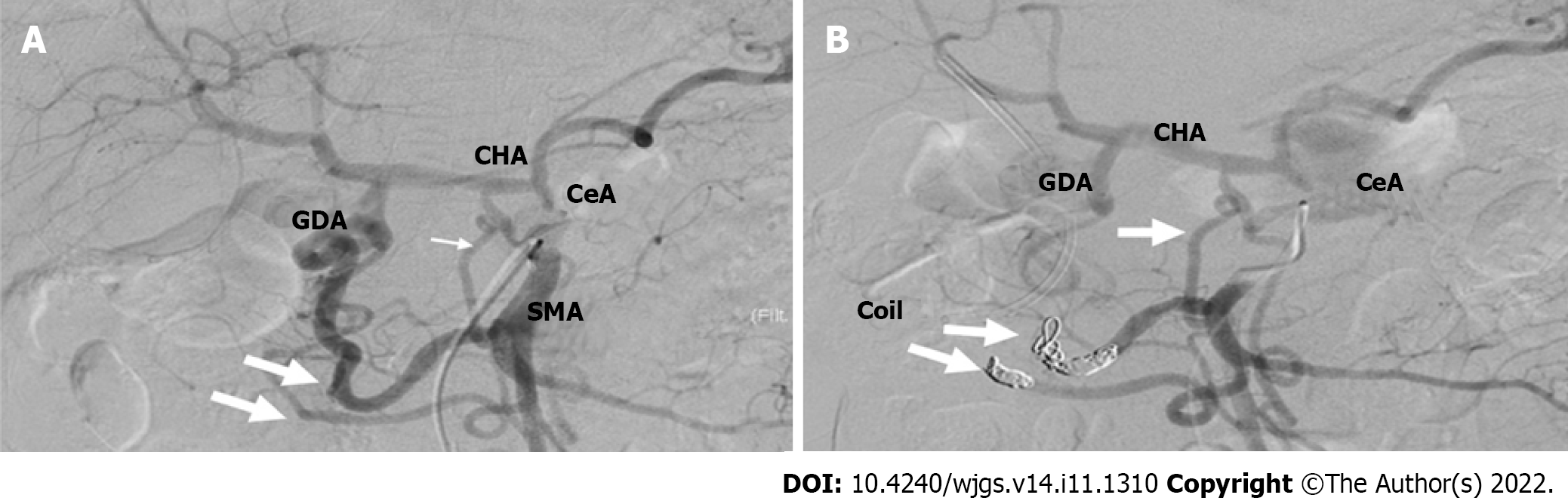
Figure 4 Angiographic study.
A: Pre-embolization angiography showed that the main backflow to the celiac artery was granted from the GDA; B: Post embolization angiography showed that after blood flow modification, the main backflow was granted from the dorsal pancreatic artery (arrow). CHA: Common hepatic artery; GDA: Gastroduodenal artery; SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; CeA: Celiac artery.
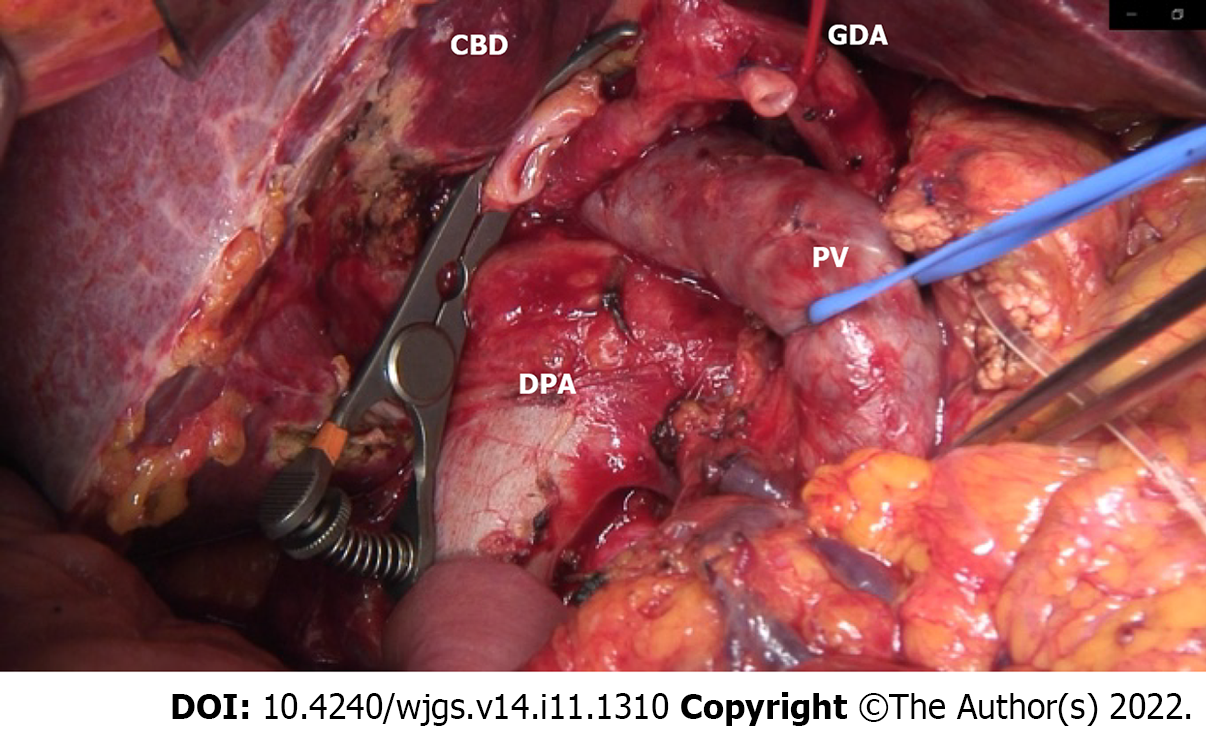
Figure 5 Intraoperative image.
The common bile duct was clipped with a bulldog, the gastroduodenal artery was ligated, and the portal vein was surrounded by a vessel loop at the bottom of the dorsal pancreatic artery hypertrophy. DPA: Dorsal pancreatic artery; CBD: Common bile duct; PV: Portal vein; GDA: Gastroduodenal artery.
- Citation: Colella M, Mishima K, Wakabayashi T, Fujiyama Y, Al-Omari MA, Wakabayashi G. Preoperative blood circulation modification prior to pancreaticoduodenectomy in patients with celiac trunk occlusion: Two case reports. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(11): 1310-1319
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i11/1310.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i11.1310