Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Sep 27, 2021; 13(9): 1039-1049
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i9.1039
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i9.1039
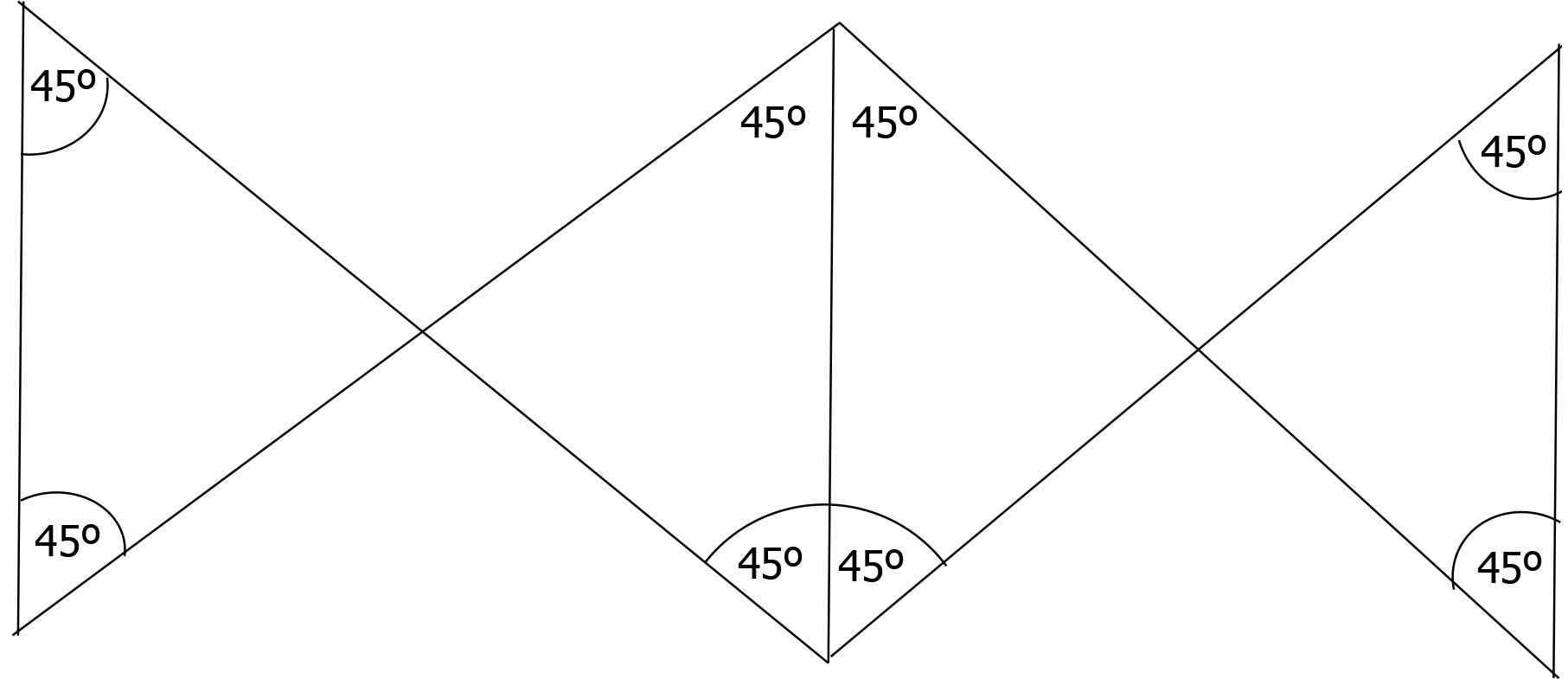
Figure 1 Theoretical model to reduce tension via an 8-angle suture pattern.
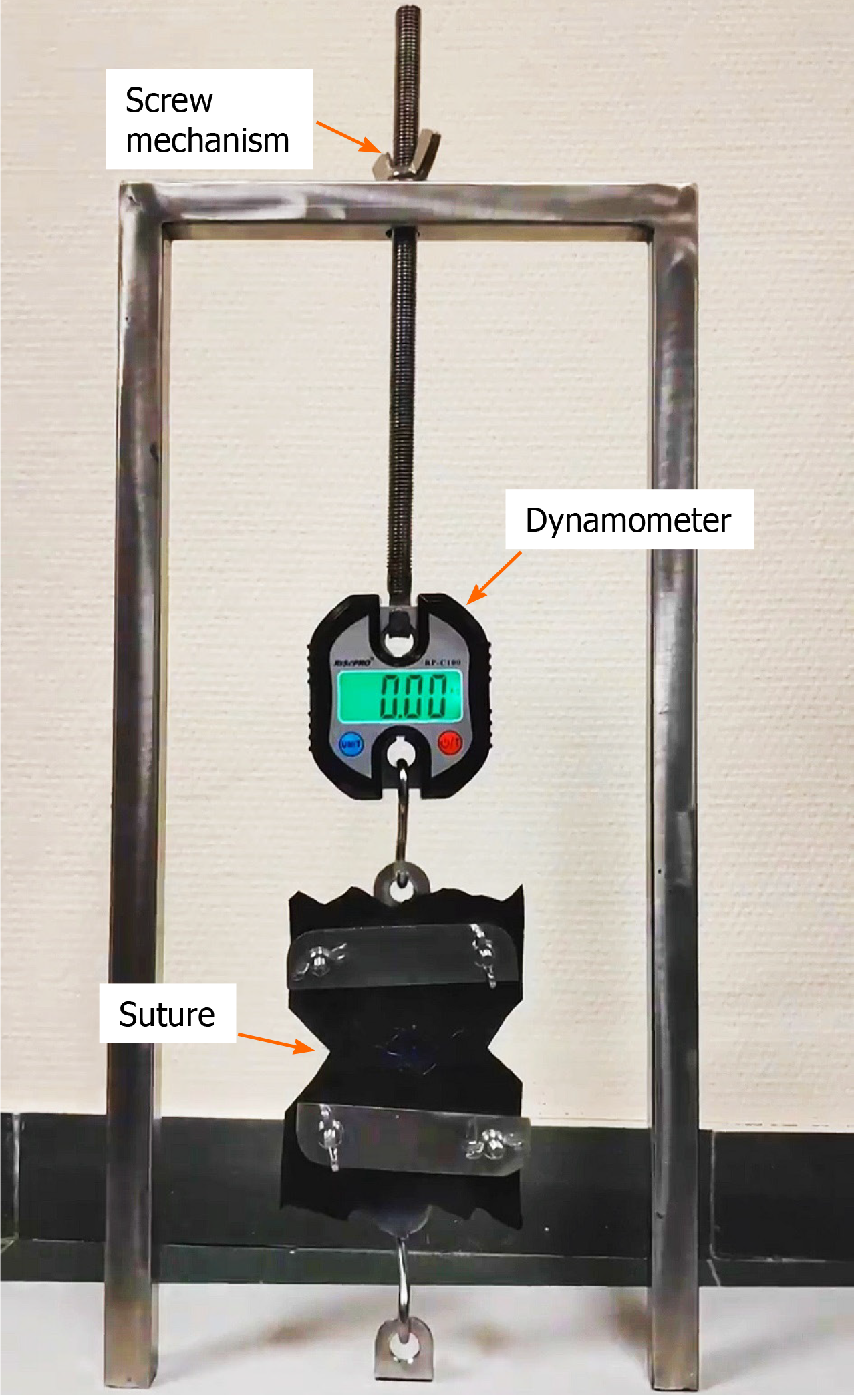
Figure 2 Device to apply a progressively-increasing separation force to the suture surfaces, and to measure the tension exerted until the breaking point is reached.
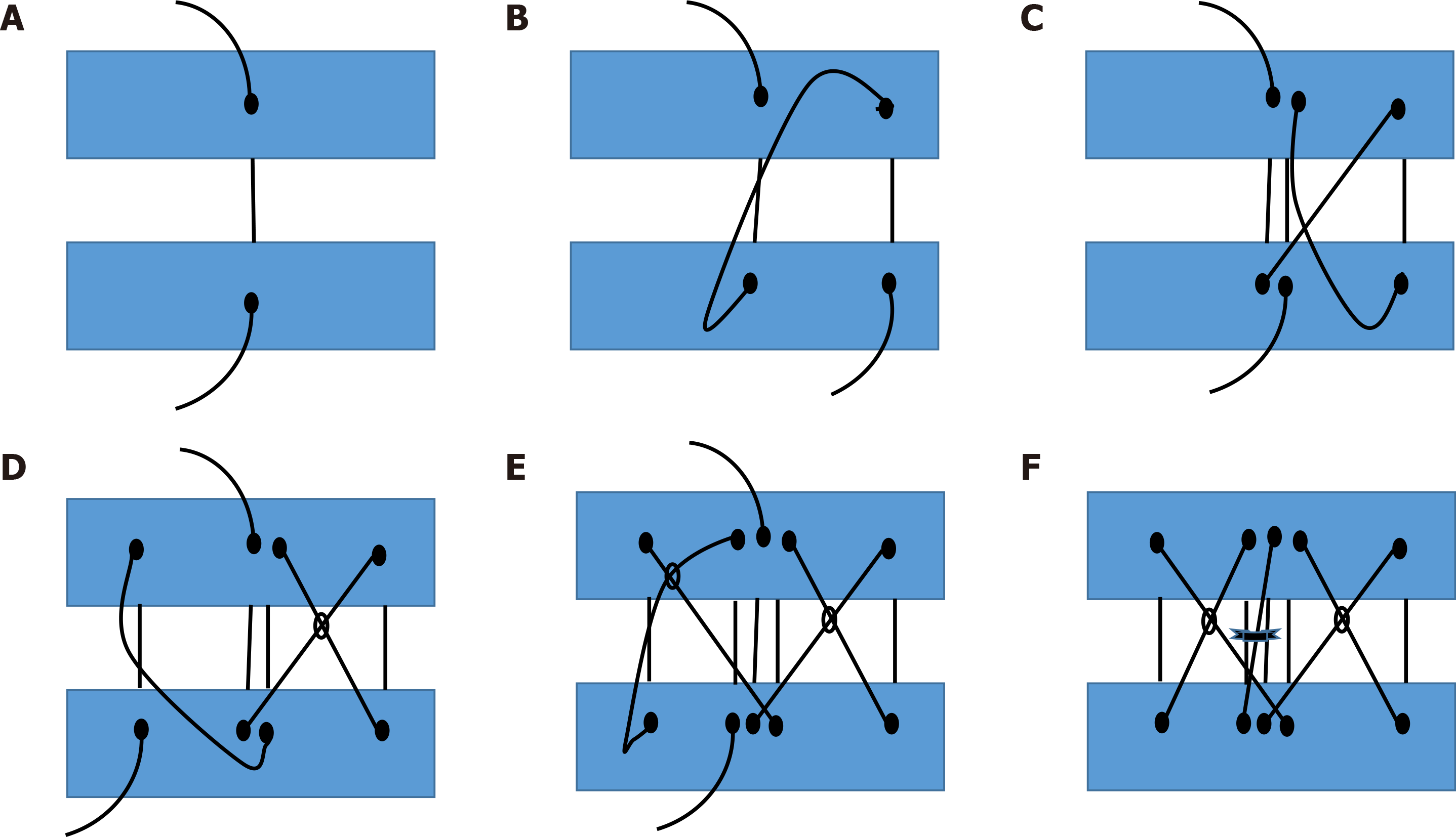
Figure 3 Steps to create the proposed “double-diabolo” suture.
A: We started with a central stitch that was perpendicular to the surfaces to be joined; B: Then we created an X-shaped stitch to the right; C: We returned with a second central stitch; D: We created another X-shaped stitch, this time to the left; E: We finally returned with a third central stitch to complete the “central column”; F: Then the stitch assembly was knotted with the thread that was centrally located at the outset.
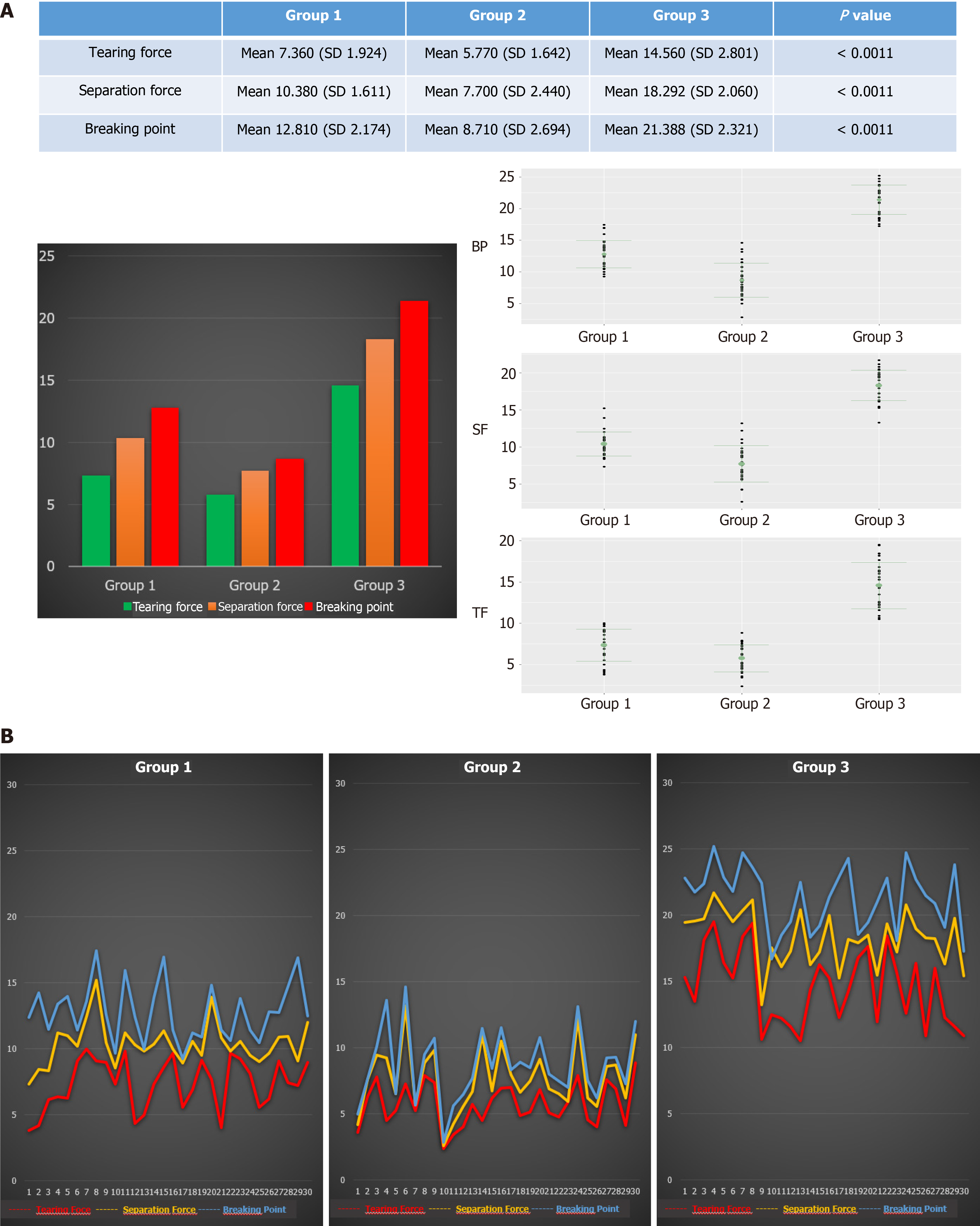
Figure 4 Results of the comparative analysis (A and B).
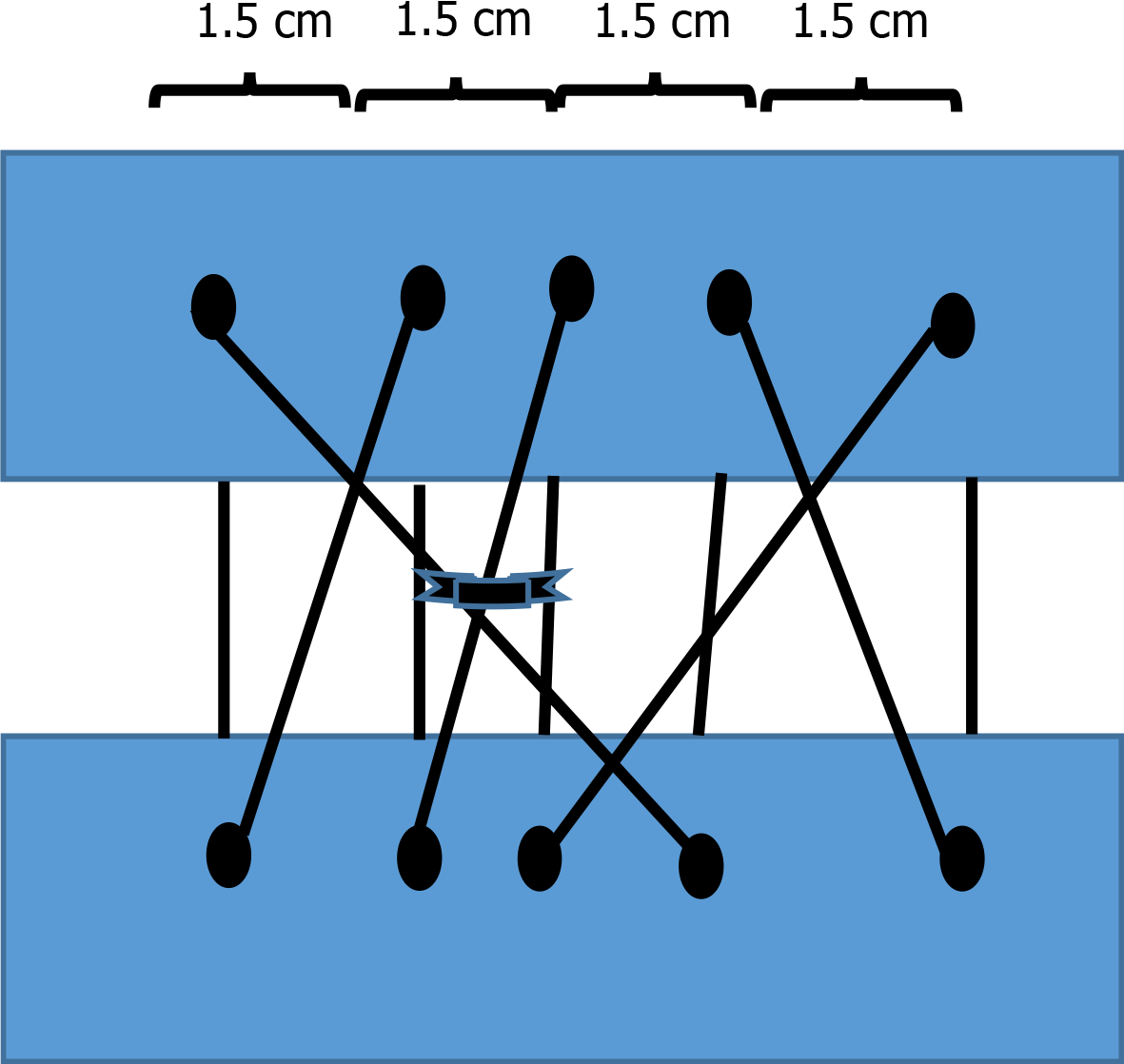
Figure 5 Final model of “double-diabolo” suture with central points sited approximately 1-1.
5 cm.
- Citation: Pérez Lara FJ, Zubizarreta Jimenez R, Moya Donoso FJ, Hernández Gonzalez JM, Prieto-Puga Arjona T, Marín Moya R, Pitarch Martinez M. Novel suturing technique, based on physical principles, achieves a breaking point double that obtained by conventional techniques . World J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 13(9): 1039-1049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v13/i9/1039.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v13.i9.1039