Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Surg. May 27, 2021; 13(5): 419-428
Published online May 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i5.419
Published online May 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i5.419
Figure 1 Preparation of pancreatic stumps in all animals in the study.
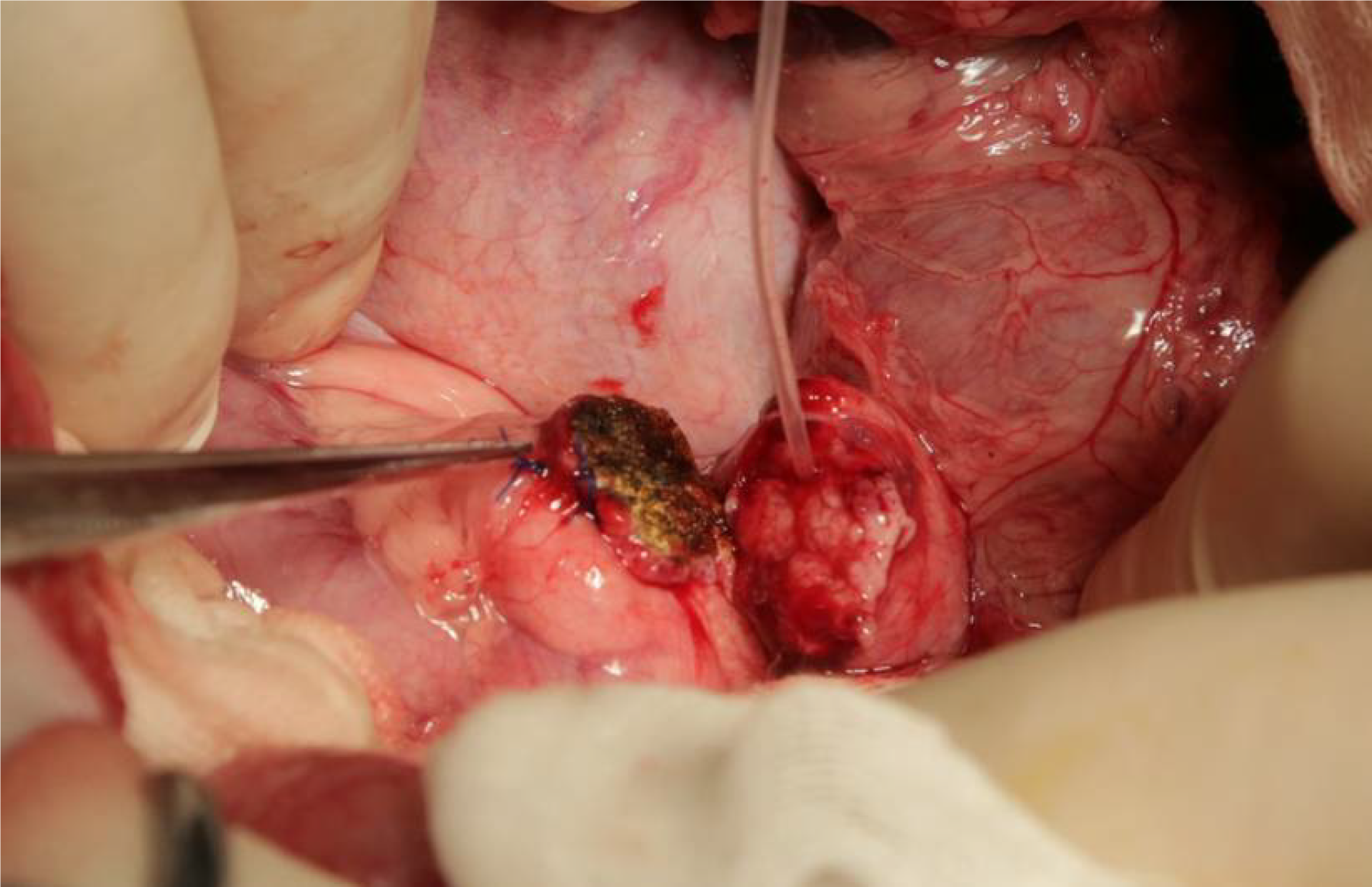
Figure 2 ”Bridging“ pancreaticogastrostomy was performed in the experimental group.
The distance between the pancreatic stump and the stomach was approximately 2 cm.
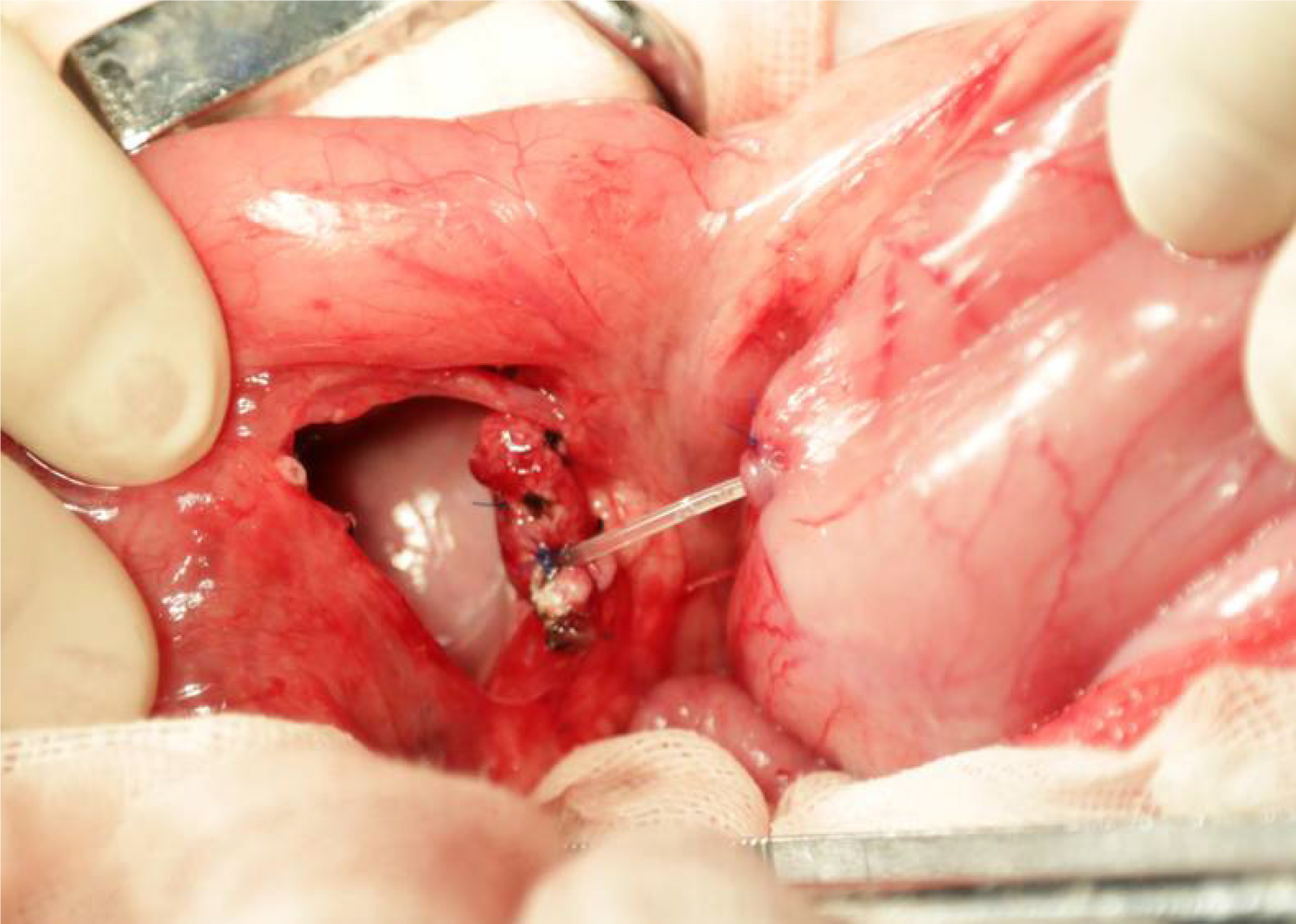
Figure 3 Routine mucosa-to-mucosa pancreaticogastrostomy was performed in the control group.
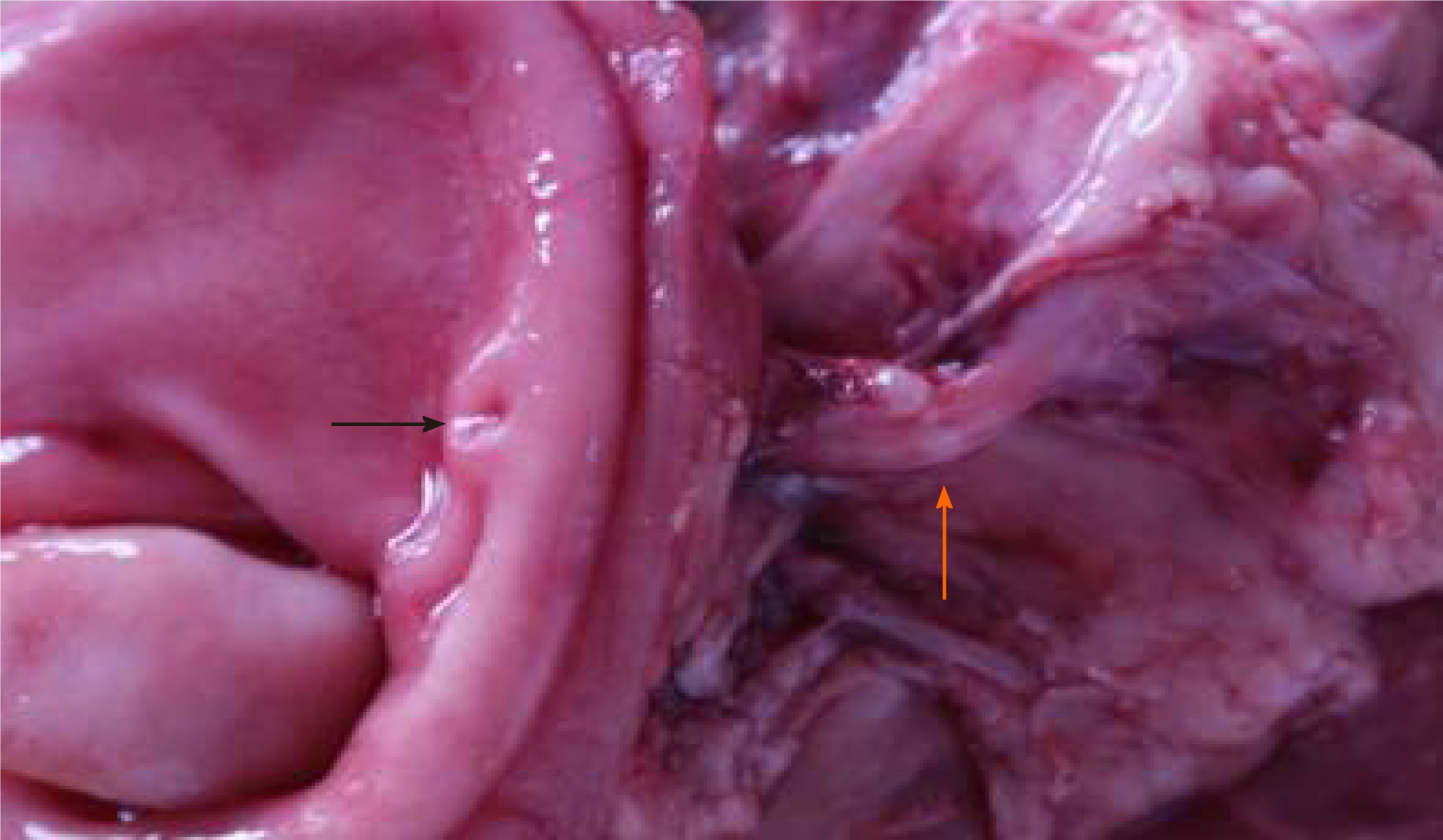
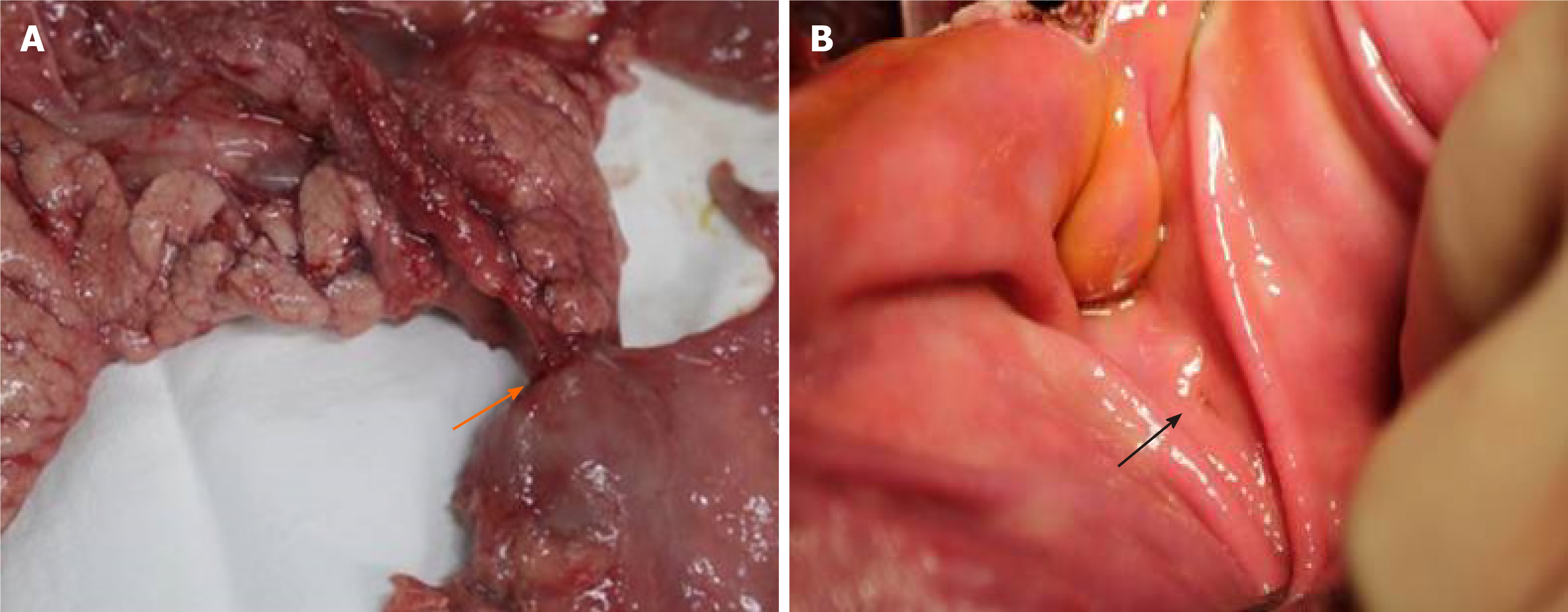
Figure 4 Sinus tract between the pancreas and stomach.
Orange arrows showed the sinus tract between the pancreas and stomach 1 mo after “bridging” pancreaticogastrostomy. Black arrows showed the sinus tract opening in the stomach.
Figure 5 Tight connection between the pancreas and stomach.
A: Orange arrows show the tight connection between the pancreas and stomach after routine mucosa-to-mucosa pancreaticogastrostomy; B: Black arrows show the anastomosis.
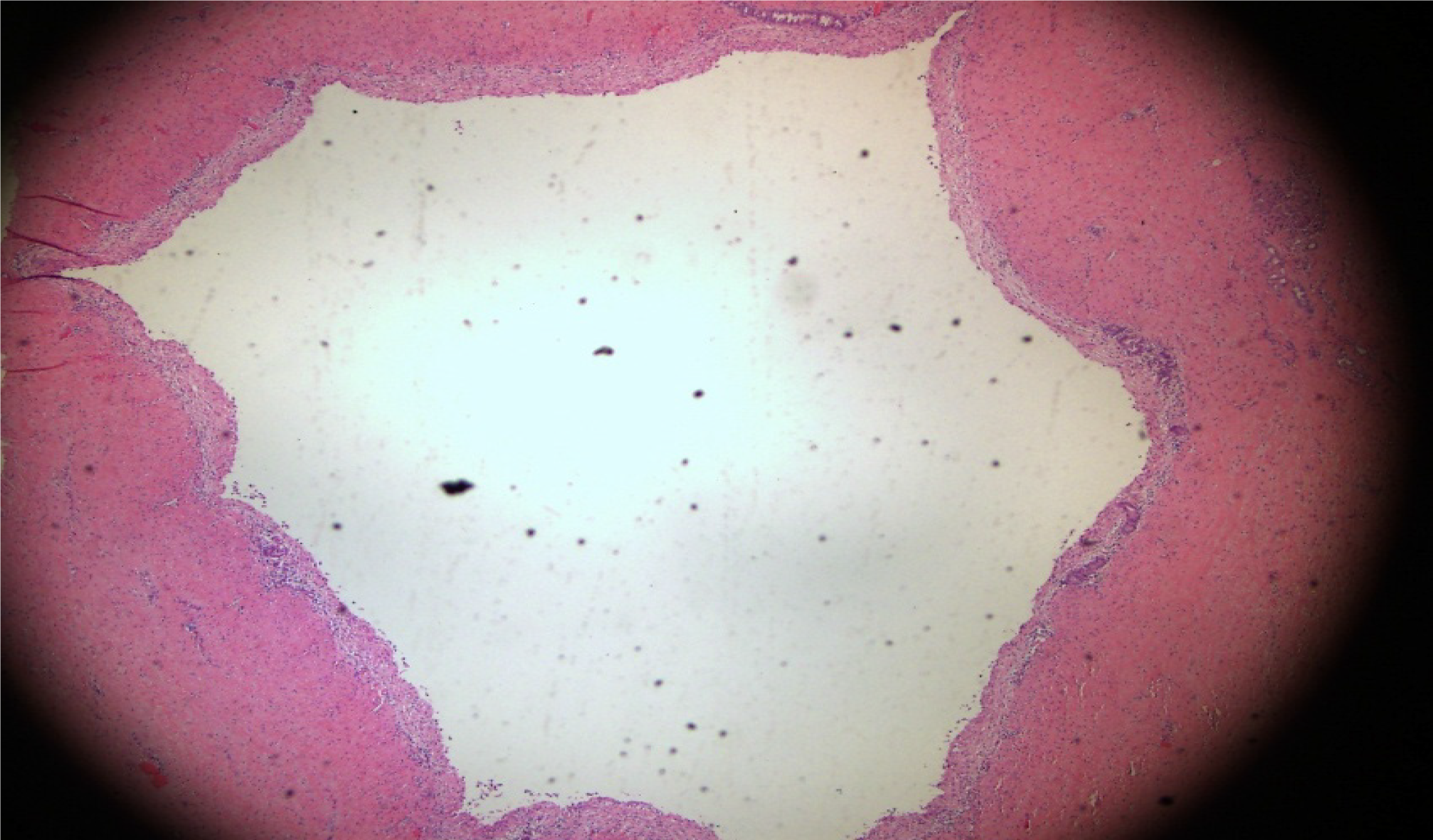
Figure 6 Significantly dilated pancreatic duct.
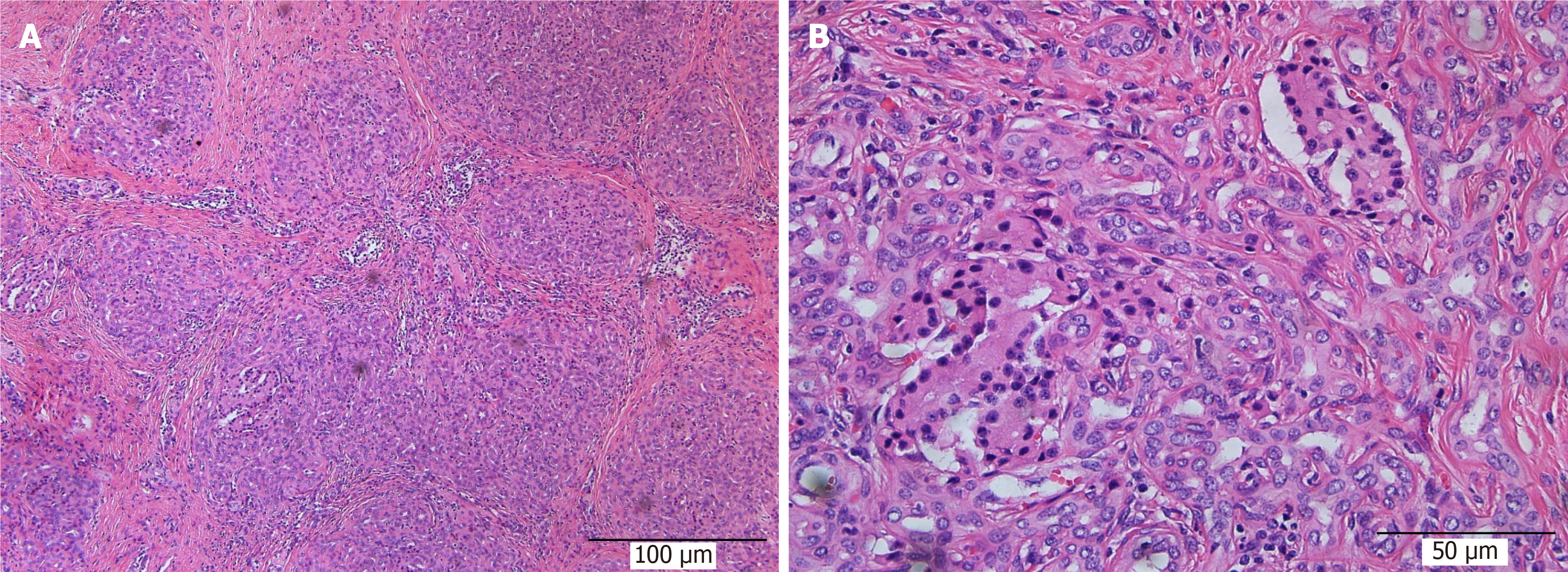
Figure 7 The pancreas was filled with large amounts of fibrous tissues and acinar atrophy with a drastic decrease in acinar cells and pancreatic islets.
A: × 100; B: × 400.
- Citation: Feng J, Zhang HY, Yan L, Zhu ZM, Liang B, Wang PF, Zhao XQ, Chen YL. Feasibility and safety of “bridging” pancreaticogastrostomy for pancreatic trauma in Landrace pigs. World J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 13(5): 419-428
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v13/i5/419.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v13.i5.419