Published online Jul 10, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i7.927
Peer-review started: October 21, 2014
First decision: November 14, 2014
Revised: February 25, 2015
Accepted: March 18, 2015
Article in press: March 20, 2015
Published online: July 10, 2015
Processing time: 261 Days and 21.7 Hours
Periodontal disease is a high prevalent disease. In the United States 47.2% of adults ≥ 30 years old have been diagnosed with some type of periodontitis. Longitudinal studies have demonstrated a two-way relationship between diabetes and periodontitis, with more severe periodontal tissue destruction in diabetic patients and poorer glycemic control in diabetic subjects with periodontal disease. Periodontal treatment can be successful in diabetic patients. Short term effects of periodontal treatment are similar in diabetic patients and healthy population but, more recurrence of periodontal disease can be expected in no well controlled diabetic individuals. However, effects of periodontitis and its treatment on diabetes metabolic control are not clearly defined and results of the studies remain controversial.
Core tip: Longitudinal studies have demonstrated a two-way relationship between diabetes and periodontitis, with more severe periodontal tissue destruction in diabetic patients and poorer glycemic control in diabetic subjects with periodontal disease. Periodontal treatment can be successful in diabetic patients, but more recurrence of periodontal disease can be expected in non well controlled diabetic individuals. However, effects of periodontitis and its treatment on diabetes metabolic control are not clearly defined and results of the studies remain controversial. Recommendations for future investigations are included in this review.
- Citation: Llambés F, Arias-Herrera S, Caffesse R. Relationship between diabetes and periodontal infection. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(7): 927-935
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i7/927.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i7.927
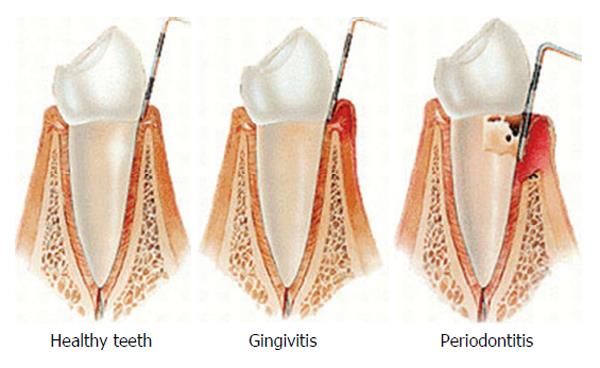
Periodontal disease is the destruction of the tissues that support the tooth by accumulation and maturation of oral bacteria on teeth.
Periodontal diseases include two major entities, gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is characterized by reversible inflammation of periodontal tissues whereas periodontitis also presents destruction of tooth supporting structures, and may lead to tooth loss. Exiting evidence indicates that gingival inflammation (gingivitis) is required for periodontitis, however some gingivitis never transform to periodontitis[1,2]. This is because bacterial plaque accumulation is necessary for the onset of both entities but individual susceptibility is required to develop periodontitis[2,3].
The currently used classification of periodontal diseases was introduced by the 1999 International Workshop for a Classification of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions[4]. Since the current classification has been used only in the last years, a substantial part of the existing literature on the prevalence and extent of periodontal diseases in various populations is still based on earlier classification systems.
Due to its high prevalence in current populations, it has become a public health priority. Epidemiologic studies have determined that about 50% of the population suffer from gingivitis and approximately 14% show periodontitis[5]. This percentage was higher in a recent study on United States population, which showed that 47.2% of adults ≥ 30 years old had periodontitis. Prevalence of periodontitis increased with age up to the point that 70.1% of adults ≥ 65 years old were affected by periodontal disease[6]. Men exhibit worse periodontal status than women [(56.4% vs 38.4%), as well as those with limited education (66.9%) and income (65.4%)]. These factors, together with cigarette smoking are increased risk factors for periodontal progression[7].
Microorganisms in combination with individual host susceptibility and environmental factors are the main etiologic factors of periodontal diseases.
Plaque accumulation on teeth produces gingivitis, but the degree of inflammation and destruction of the alveolar bone that supports teeth depend on the host susceptibility[8].
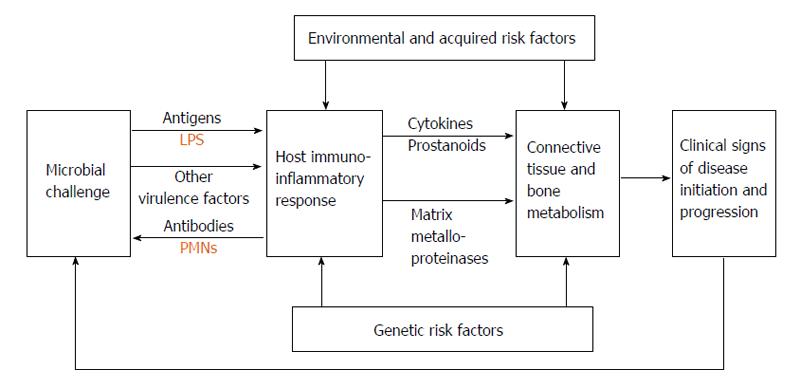
Oral bacteria can damage periodontal tissues through the action of matrix-degrading enzymes and molecules that affect host cells. The transition from gingivitis to periodontitis involves the spreading of the inflammatory front to deeper areas in the connective tissue. However the reason why this happens is not well established. One etiopathogenic mechanism could involve the presence of bacteria or their products, such as lipopolysaccharides, in the periodontal connective tissue. They may induce an immune response with production of interleukins and tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which play an important role in the regulation of inflammatory processes. This inflammation stimulates the production of secondary mediators, which amplify the inflammatory response. Simultaneously, the presence of these cytokines reduces the ability to repair damaged tissue by cells such as fibroblasts, and finally, bacterial products and this inflammatory cascade stimulate osteoclastogenesis, leading to alveolar bone destruction[9,10] (Figure 1).
Several studies have shown how gingival inflammation can be modulated by a number of conditions. Systemic diseases, steroid hormones variations, nutritional deficiency, the intake of drugs, diabetes, tobacco smoking and other conditions have comprehensive and profound effects on the host, resulting in an increased response to bacterial plaque accumulation[10].
The high prevalence of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) among the microorganisms isolated from the oral environment induce to think that it may have an effect in the development of periodontal disease. Umeda et al[11] determined that periodontal patients showed a higher level of H. pylori than healthy subjects but, there was no significant correlation between the presence of H. pylori and the severity of periodontitis[12]. The addition of periodontal treatment to eradication therapy may reduce H. pylori recurrence compared with eradication therapy alone in periodontal patients suffering from gastric diseases associated with H. pylori[13].
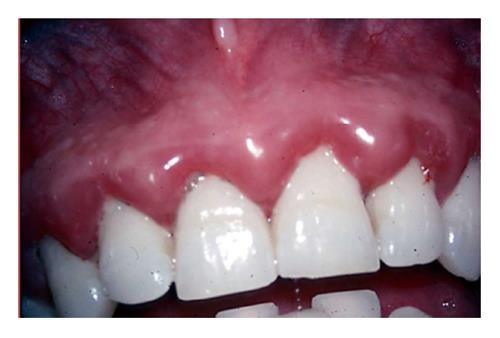
Clinical signs of gingival inflammation (gingivitis) involve enlarged gingival contours due to edema or fibrosis, color transition to a red and/or bluish red hue, elevated sulcular temperature, bleeding upon probing and, increased gingival exudates (Figure 2).
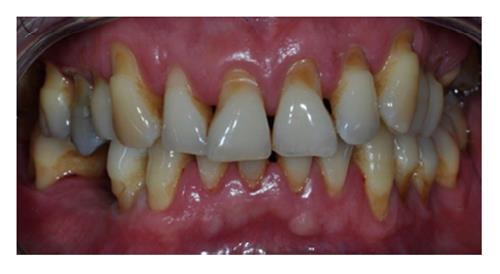
Periodontitis clinical features include clinical attachment loss (CAL), alveolar bone loss (BL), periodontal pocketing and gingival inflammation. In addition, enlargement or recession of the gingiva; increase tooth mobility, drifting, and even tooth exfoliation may occur (Figure 3)[14].
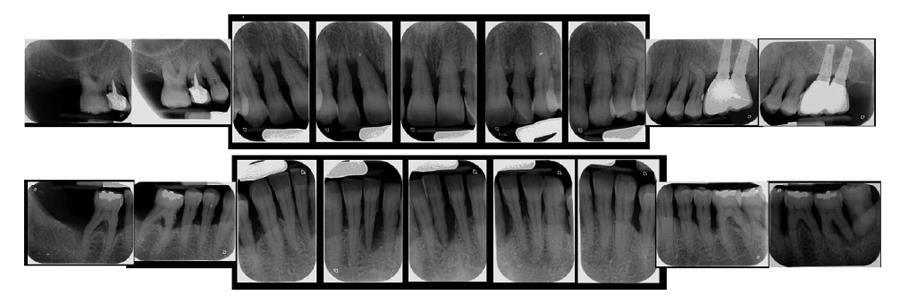
Clinical evaluation includes periodontal probing (Figure 4) to evaluate: (1) Probing depth: the distance a periodontal probe penetrates into a periodontal pocket measured from the gingival margin to its bottom; (2) Clinical attachment level: The distance from the cemento-enamel junction to the bottom of the periodontal pocket; (3) Bleeding on probing. Bleeding after probing to the base of the periodontal pocket has been a common way to identify presence of subgingival inflammation; and (4) Tooth mobility and furcations. The movement of a tooth in its socket resulting from an applied force can be classified into three categories. Furcation involvement is defined as BL affecting the base of the root trunk of a tooth where two or more roots meet.
Radiographic evaluation will show if alveolar bone that support tooth roots is lost. In a healthy situation alveolar bone will remain 1-2 mm below the crown of the teeth. If bone is located further from the crown, it means that loss has occurred (Figure 5).
In 1999, the American Academy of Periodontology organized an international symposium with the aim of reaching a consensus regarding the classification of periodontal diseases and disorders, resulting in eight categories: gingival diseases, chronic periodontitis, aggressive periodontitis, periodontitis as manifestation of systemic diseases, necrotizing periodontal diseases, periodontal abscesses, periodontitis associated with endodontic lesions and, developmental or acquired deformities and conditions[4,15,16].
It is possible to include in this classification additional subcategories such as “diabetes mellitus-associated chronic periodontitis” and “diabetes mellitus-associated aggressive periodontitis” under the category of periodontitis as manifestation of systemic diseases.
Investigations have demonstrated associations between periodontitis and various systemic diseases[17,18] such as cardiovascular disorders[19,20], respiratory diseases[21,22], osteoporosis[23,24], immunodeficiencies[25] and also diabetes mellitus[26].
As already mentioned, longitudinal studies have demonstrated a two-way relationship between diabetes and periodontitis, with more severe periodontal tissue destruction in diabetic patients and poorer glycemic control in diabetic subjects with periodontal disease[27-30].
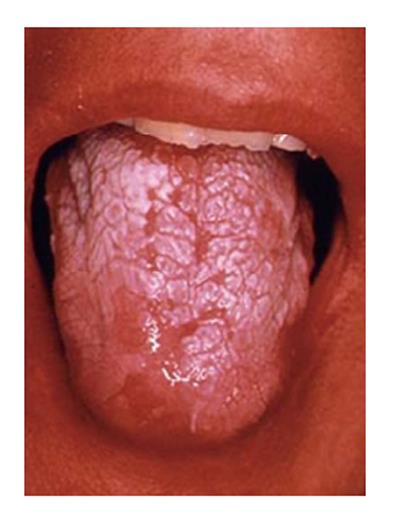
Diabetes has been associated to different oral diseases such as salivary and taste dysfunction, oral bacterial and fungal infections (i.e., candidiasis), and oral mucosa lesions (i.e., stomatitis, geographic tongue, traumatic ulcer, lichen planus,…)[31,32]. Diminished salivary flow and burning mouth are other oral characteristics in diabetic patients with poor glycemic control. Also, different oral pathologies such as, lichen planus, leukoplakia and lichenoid reactions are associated to diabetic subjects due to immunosuppression and/or drugs used. In addition, delayed mucosal wound healing, mucosal neuro-sensory disorders, decay lesions and tooth loss have been reported in diabetic patients[33]. Xerostomia is a frequent symptom found in diabetic patients on oral hypoglycemic agents, and it may facilitate the onset of some fungal opportunistic infection. Candidiasis has been reported in patients with poorly controlled diabetes (Figure 6).
Evidence suggests that diabetes leads to worsening of periodontal disease, and a significant association between diabetes and periodontitis has been demonstrated. Periodontal disease has a higher incidence in diabetic patients, and it is more prevalent and severe if compared with a healthy population[27,34]. Lalla et al[35] determined the prevalence of periodontitis in different age cohorts. It was 4.8 times higher among diabetic patients compared to non diabetics when the 15 to 24-year age cohort was considered, and 2.3 higher in the 25-34 year group. Also, CAL was higher in diabetic patients when the 15 to 55-year age cohort was considered. Lim et al[36] estimated that the glycemic control was the most important risk factor related to severity and extent of periodontitis. Other authors like Lalla et al[37] established that the rate of periodontal destruction is related to inappropriate glycemic control in diabetic patients so that accurate metabolic control could be important to prevent periodontal complications. Thus, glycemic control and the diabetes onset are critical factors in periodontal disease progression but it should be considered that substantial heterogeneity exists within diabetics[38].
Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) allows the control of serum glucose levels in an interval of 120 d and is a useful decision-making tool. Diabetes micro- and macrovascular complications are related to increased levels of HbA1c. The risk of periodontitis is 3-fold times higher among diabetic patients[39], being its prevalence and severity even greater in diabetic patients presenting elevated HbA1c levels[40].
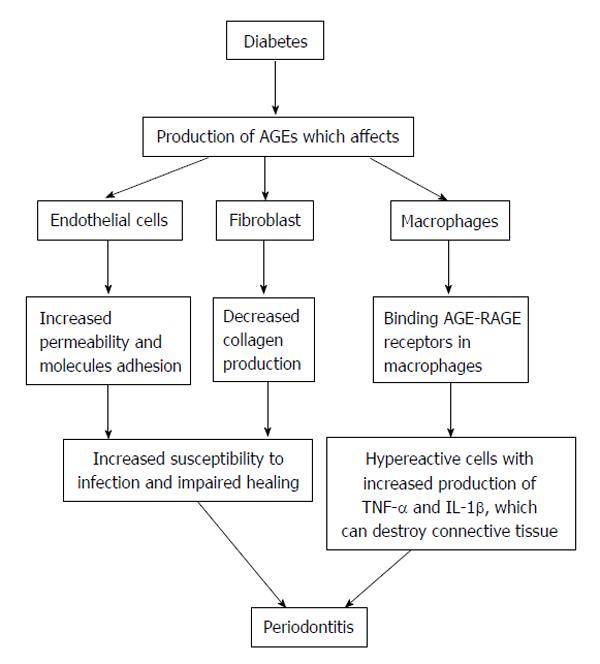
Different hypotheses have been proposed to explain the influence of diabetes mellitus on periodontitis but they are all currently under investigation and remain somewhat controversial. Two similar but distinct pathogenic pathways may justify the biologic plausibility, a possible common origin of the two diseases which results in a host susceptible to either diseases[41], or a direct causal relationship in which, through the effects of advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs), diabetes triggers an increased inflammatory phenotype in cells[5,27]. Studies have shown how chronic hyperglycemia produces AGEs that can bind to specific receptors (RAGE) on different cells such as fibroblast, endothelial cells and macrophages[42]. Thereby, macrophages are transformed into hypereactive cells that produce pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukins 1β and 6 (IL-1β, IL-6) and TNF-α. AGEs can also alter endothelial cells which will become hyperpermeable and hyperexpressive for adhesion molecules, while fibroblasts will show decreased collagen production[43]. Therefore, AGEs produced by chronic hyperglycemia can produce hyper inflammatory responses, vascular modifications, altered healing and increased predisposition to infections (Figure 7). Lalla et al[44] supported the hypothesis that the activation of RAGE contributes to pathogenesis of periodontitis in diabetic patients. Increased accumulation of AGEs and their interaction with RAGE in diabetic gingiva leads to hyper production of proinflammatory cytokines, vascular dysfunction, and loss of effective tissue integrity and barrier function.
Despite these facts, periodontal treatment can be successful in diabetic patients. Short term effects of periodontal treatment are similar in diabetic patients and healthy population[45-47] but, more recurrence of periodontal disease can be expected in non well controlled diabetic individuals[26].
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2010 reported that prevalence of diabetes was 12.5% among periodontal patients, but only 6.3% in subjects without periodontitis[48].
If diabetic individuals are at a higher risk for periodontitis, it is also important to determine what effects periodontitis and its treatment may have on diabetes. It would be reasonable to think that periodontal inflammation, as any other infections, can have an adverse effect on diabetes glycemic control, compromising diabetes management in these individuals. Most evidence on this issue is derived from interventional and observational studies, indicating that periodontitis affects the glycemic control of diabetic patients. HbA1c values < 7% are related with proper glycemic levels whilst > 8% values represents poorly controlled glycemia.
Longitudinal studies have demonstrated that severe periodontitis is associated with poorly controlled glycemia, higher HbA1c levels and development of diabetic systemic complications[1,30,49]. It also has been reported that periodontitis is associated with a slight elevation of HbA1c in non-diabetic subjects (periodontitis may potentially increase the incidence of diabetes), although a clear-cut association could not be established[50].
Studies assumed that periodontal infection may impair glycemic control by increasing insulin tissue resistance[26]. Hence, glycemic level could be improved by non-surgical periodontal treatment removing bacterial plaque accumulation and decreasing gingival inflammation. This assumption is based on studies that observed an improvement in diabetes glycemic control following periodontal therapy[46,51]. It should be considered that other studies did not find such causal relationship, maybe due to inadequate time for periodontal tissues healing, or because periodontitis had not been properly resolved[30,52]. Another reason may be the influence of factors such as diet, physical exercise or use of antidiabetics that can alter significantly HbA1c, and make more difficult to observe the metabolic effect of periodontal treatment[45].
Several studies have investigated the effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy on the glycemic control of diabetic patients. Both non-diabetic and diabetic patients show similar short-term outcomes after non-surgical periodontal therapy in terms of probing depth reductions, gain in CAL and changes in subgingival microbiota[53]. If glycemic control is considered as treatment outcome after non-surgical periodontal therapy, results vary (Table 1).
| Ref. | Design | Sample | Follow-up | Outcome | Results | |
| Type 1 | Aldridge et al[55] | Randomized clinical trial | 23 subjects | 2 mo | HbA1c | No changes |
| Smith et al[47] | Controlled clinical trial | 18 subjects | 2 mo | HbA1c | No changes | |
| Christgau et al[53] | Cohort study | 7 subjects | 4 mo | HbA1c | No changes | |
| Llambés et al[45] | Randomized clinical trial | 30 subjects | 3 mo | HbA1c | 0.06% reduction (no changes) | |
| Type 2 | Stewart et al[75] | Controlled clinical trial | 72 subjects | 10 mo | HbA1c | 6% reduction |
| Kiran et al[51] | Randomized clinical trial | 44 subjects | 3 mo | HbA1c | 0.8% reduction | |
| Faria-Almeida et al[46] | Cohort study | 20 subjects | 6 mo | HbA1c | 5.7% reduction | |
| Dağ et al[56] | Controlled clinical trial | 45 subjects | 3 mo | HbA1c | No changes | |
| Auyeung et al[57] | Cohort study | 75 subjects | 12 mo | HbA1c | No changes | |
| Engebretson et al[58] | Randomized clinical trial | 257 subjects | 6 mo | HbA1c | No changes | |
| Gay et al[59] | Randomized clinical trial | 126 subjects | 4 mo | HbA1c | No changes |
Different studies on patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus have not found an additional beneficial effect of periodontal treatment in glycemic control. Llambés et al[45] obtained changes in mean HbA1c of about 0.07%, without statistical significant difference after non-surgical periodontal treatment in type 1 diabetic patients after 3-mo. Similarly, Seppälä et al[54] reported that in poorly-controlled type 1 diabetic patients, non-surgical periodontal therapy had no effect on HbA1c. The same results were observed in the study performed by Aldridge et al[55] who stated no changes in HbA1c levels after non-surgical periodontal therapy in 22 type 1 diabetics with severe periodontitis.
On the other hand, Faria-Almeida et al[46] reported that non-surgical periodontal therapy significantly reduce HbA1c levels about 5.7% in type 2 diabetics, while Dağ et al[56] and Auyeung et al[57] reported that this therapy alone significantly reduced HbA1c levels only in well-controlled diabetics. Smith et al[47] reported that mechanical periodontal therapy alone did not produce a significant change in glycemic control in diabetic patients.
Recently, Engebretson et al[58] indicated that non-surgical periodontal therapy in type 2 diabetics with chronic periodontitis did not improve diabetes glycemic control. According to these findings the use of nonsurgical periodontal treatment in order to reduce levels of HbA1c would not be justified. Lately, Gay et al[59] in a randomized clinical trial where 152 type 2 diabetic patients with periodontitis were treated, determined that no statistically significant differences were found in the changes of HbA1c levels.
Furthermore, current systematic reviews report glycemic control improvement, with a HbA1c reduction of approximately 0.4%, after non-surgical periodontal treatment[60]. A mean reduction of -0.36% of glycosylated HbA1c in subjects with type 2 diabetes has been determined recently[61]. However, the clinical significance of this effect is still unknown. It has been reported that each 1% reduction of HbA1c may be associated with 35% reduction in the risk of microvascular complications[62]. To the best of our knowledge, no studies have evaluated changes in HbA1c levels in non-diabetic patients after non-surgical periodontal therapy.
Two studies have examined the added benefit of chlorhexidine as adjunct to non-surgical periodontal therapy in diabetic patients. Christgau et al[53] demonstrated that non-surgical periodontal therapy in combination with subgingival irrigation with 0.2% chlorhexidine did not improve HbA1c levels. The same results were achieved when 0.12% chlorhexidine was considered[63].
Iwamoto et al[64] demonstrated a 0.8% reduction in HbA1c in type 2 diabetics after non-surgical periodontal therapy and subgingival use of minocycline gel.
Studies in which systemic antibiotics were used along with mechanical therapy showed a significant improvement in glycemic control in diabetic patients. This may be due to the additional benefits of systemic antibiotics, such as their antimicrobial and host modulation effects, as well as their inhibition of non-enzymatic glycosylation[63,65-67].
Non-surgical periodontal therapy combined with 100 mg doxycycline is associated with a mean HbA1c reduction of 0.6% in type 2 diabetics patients[65]. There is not enough evidence about the use of tetracyclines but it seems to play a role in limiting tissue destruction. Lately, a modest improvement in glycemic control was detected after nonsurgical therapy plus azithromycin[68]. However, Llambés et al[45] show that non-surgical periodontal treatment combined with systemic doxycycline has no effect on HbA1c of type 1 diabetic patients[43].
Scarce available evidence makes it impossible to determine the response after periodontal surgical treatment in diabetic patients. Diabetic subjects usually show improved periodontitis after surgical periodontal treatment. However, if poor diabetic control is present, more recurrence of periodontal pockets and unfavorable long term response is expected after surgical treatment[53,69]. Effects of surgical periodontal treatment on HbA1c are currently unknown.
The exact mechanism linking periodontitis/periodontal inflammation and HbA1c levels is still not clearly known. In periodontitis, there is an increased production of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and interferon gamma (IF-α), and increased levels of acute-phase proteins, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). All these mediators have important effects on glucose and lipid metabolism. TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β are insulin antagonist and lipid metabolism is hampered by TNF-α. Elevated levels of CRP lead to insulin resistance. IF-α induces apoptosis of pancreatic β cells[70]. Non-enzymatic glycosylation of hemoglobin is not induced by inflammation, but rather results from hyperglycemia caused by insulin resistance[44]. Thus, this could explain why subjects with periodontitis have high HbA1c levels.
According to these reports, it can be presumed that control of periodontal inflammation after therapy may reduce the levels of local and circulatory mediators, such as IL-6 and TNF-α. Both may trigger acute phase proteins such as CRP, and impair intracellular insulin signaling. Consequently, if these mediators were reduced by periodontal treatment, this could theoretically, help in diabetes control. However, this mechanism remains to be confirmed. Some studies have shown that periodontal disease severity is correlated with blood CRP levels in diabetic patients[71,72], however CRP levels are not reduced after periodontal treatment[73,74].
Within the limits of this review we can conclude that: Periodontitis is a highly prevalent infectious disease that relates to some systemic disorders, including diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes has been associated to different oral diseases such as: xerostomia, neuro-sensory disorders, several oral mucosa diseases, tooth decay and periodontal disease. It is well documented in the literature that periodontal disease is more prevalent and severe in diabetic individuals than in healthy subjects. However, it has to be kept in mind that the level of metabolic control and duration of diabetes appear to influence the risk for periodontal disease, with a significant heterogeneity among diabetic individuals.
Periodontal treatment is effective in diabetic patients, but more long-term recurrence can be expected when diabetes is not well controlled.
Severe periodontitis is more frequently found in diabetic subjects with high HbA1c levels and systemic diabetic complications; however, the influence of periodontal treatment on HbA1c is not that well established. The beneficial effects of periodontal treatment on HbA1c levels seem to be more apparent in type 2 diabetics and when antibiotics are associated to local periodontal therapy, although other reports did not find any improvement in diabetes control after periodontal treatment. More research on type 1 and type 2 diabetic subjects will be needed to know how periodontal treatment affects diabetes metabolic control. In those, it will be paramount to control other factors that may affect HbA1c levels, such as diabetic medication, diet and physical exercise.
HbA1c reduction after periodontal treatment is usually less than 0.5%. New studies are needed to evaluate the clinical significance of this improvement.
Additionally, it may be necessary to explore the effects of different modalities of periodontal therapy in patients with different types of diabetes and different degrees of metabolic control.
Further analysis of inflammatory mediators, such as CRP, may help to explain the relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease, and the individual variations detected in samples from different severities of diabetes and periodontal disease.
Any improvement in the control of diabetes and/or periodontal disease has the potential to improve significantly the quality of life in diabetic subjects.
P- Reviewer: Adler I, Kotsakis GA S- Editor: Song XX L- Editor: A E- Editor: Liu SQ
| 1. | Listgarten MA, Schifter CC, Laster L. 3-year longitudinal study of the periodontal status of an adult population with gingivitis. J Clin Periodontol. 1985;12:225-238. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Löe H, Anerud A, Boysen H, Morrison E. Natural history of periodontal disease in man. Rapid, moderate and no loss of attachment in Sri Lankan laborers 14 to 46 years of age. J Clin Periodontol. 1986;13:431-445. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 559] [Cited by in RCA: 543] [Article Influence: 13.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Page RC. Milestones in periodontal research and the remaining critical issues. J Periodontal Res. 1999;34:331-339. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Armitage GC. Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann Periodontol. 1999;4:1-6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3229] [Cited by in RCA: 3310] [Article Influence: 127.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Soskolne WA, Klinger A. The relationship between periodontal diseases and diabetes: an overview. Ann Periodontol. 2001;6:91-98. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 171] [Cited by in RCA: 169] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Eke PI, Dye BA, Wei L, Thornton-Evans GO, Genco RJ. Prevalence of periodontitis in adults in the United States: 2009 and 2010. J Dent Res. 2012;91:914-920. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1085] [Cited by in RCA: 1195] [Article Influence: 91.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Eke PI, Page RC, Wei L, Thornton-Evans G, Genco RJ. Update of the case definitions for population-based surveillance of periodontitis. J Periodontol. 2012;83:1449-1454. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 657] [Cited by in RCA: 961] [Article Influence: 73.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Trombelli L, Tatakis DN, Scapoli C, Bottega S, Orlandini E, Tosi M. Modulation of clinical expression of plaque-induced gingivitis. II. Identification of “high-responder” and “low-responder” subjects. J Clin Periodontol. 2004;31:239-252. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 102] [Cited by in RCA: 111] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Offenbacher S. Periodontal diseases: pathogenesis. Ann Periodontol. 1996;1:821-878. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 646] [Cited by in RCA: 628] [Article Influence: 21.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Socransky SS, Haffajee AD. The bacterial etiology of destructive periodontal disease: current concepts. J Periodontol. 1992;63:322-331. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 802] [Cited by in RCA: 783] [Article Influence: 23.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Umeda M, Kobayashi H, Takeuchi Y, Hayashi J, Morotome-Hayashi Y, Yano K, Aoki A, Ohkusa T, Ishikawa I. High prevalence of Helicobacter pylori detected by PCR in the oral cavities of periodontitis patients. J Periodontol. 2003;74:129-134. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Salehi MR, Shah Aboei M, Naghsh N, Hajisadeghi S, Ajami E. A Comparison in Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in the Gingival Crevicular Fluid from Subjects with Periodontitis and Healthy Individuals using Polymerase Chain Reaction. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2013;7:238-243. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Bouziane A, Ahid S, Abouqal R, Ennibi O. Effect of periodontal therapy on prevention of gastric Helicobacter pylori recurrence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39:1166-1173. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 14. | Mariotti A. Dental plaque-induced gingival diseases. Ann Periodontol. 1999;4:7-19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 169] [Cited by in RCA: 152] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Newman MG. Classification of diseases and conditions affecting the periodontium. In: Elsevier/Saunders. Carranza’s clinical periodontology. St. Louis, Mo 2012; 64-74. |
| 16. | Kinane DF, Lindhe J, Trombelli L. Chronic periodontitis. In: Blackwell. Clinical periodontology and implant dentistry. Oxford 2003; 420-428. |
| 17. | Mohangi GU, Singh-Rambirich S, Volchansky A. Periodontal disease: Mechanisms of infection and inflammation and possible impact on miscellaneous systemic diseases and conditions. SADJ. 2013;68:462, 464-467. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Linden GJ, Lyons A, Scannapieco FA. Periodontal systemic associations: review of the evidence. J Periodontol. 2013;84:S8-S19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 108] [Cited by in RCA: 132] [Article Influence: 14.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Figuero E, Sánchez-Beltrán M, Cuesta-Frechoso S, Tejerina JM, del Castro JA, Gutiérrez JM, Herrera D, Sanz M. Detection of periodontal bacteria in atheromatous plaque by nested polymerase chain reaction. J Periodontol. 2011;82:1469-1477. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 112] [Cited by in RCA: 143] [Article Influence: 10.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Aquino AR, Lima KC, Paiva MS, Rôças IN, Siqueira JF. Molecular survey of atheromatous plaques for the presence of DNA from periodontal bacterial pathogens, archaea and fungi. J Periodontal Res. 2011;46:303-309. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Si Y, Fan H, Song Y, Zhou X, Zhang J, Wang Z. Association between periodontitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a Chinese population. J Periodontol. 2012;83:1288-1296. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Sharma N, Shamsuddin H. Association between respiratory disease in hospitalized patients and periodontal disease: a cross-sectional study. J Periodontol. 2011;82:1155-1160. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Renvert S, Berglund J, Persson RE, Persson GR. Osteoporosis and periodontitis in older subjects participating in the Swedish National Survey on Aging and Care (SNAC-Blekinge). Acta Odontol Scand. 2011;69:201-207. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Fratzl P, Roschger P, Fratzl-Zelman N, Paschalis EP, Phipps R, Klaushofer K. Evidence that treatment with risedronate in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis affects bone mineralization and bone volume. Calcif Tissue Int. 2007;81:73-80. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Gonçalves LS, Gonçalves BM, Fontes TV. Periodontal disease in HIV-infected adults in the HAART era: Clinical, immunological, and microbiological aspects. Arch Oral Biol. 2013;58:1385-1396. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Bascones-Martínez A, Muñoz-Corcuera M, Bascones-Ilundain J. [Diabetes and periodontitis: A bidirectional relationship]. Med Clin (Barc). 2015;145:31-35. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Grossi SG, Genco RJ. Periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: a two-way relationship. Ann Periodontol. 1998;3:51-61. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 455] [Cited by in RCA: 445] [Article Influence: 16.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 28. | Lalla E, Papapanou PN. Diabetes mellitus and periodontitis: a tale of two common interrelated diseases. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7:738-748. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 526] [Cited by in RCA: 649] [Article Influence: 46.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Preshaw PM, Alba AL, Herrera D, Jepsen S, Konstantinidis A, Makrilakis K, Taylor R. Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship. Diabetologia. 2012;55:21-31. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 782] [Cited by in RCA: 1033] [Article Influence: 79.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Chapple IL, Genco R; working group 2 of the joint EFP/AAP workshop. Diabetes and periodontal diseases: consensus report of the Joint EFP/AAP Workshop on Periodontitis and Systemic Diseases. J Periodontol. 2013;84:S106-S112. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 190] [Cited by in RCA: 267] [Article Influence: 29.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Saini R, Al-Maweri SA, Saini D, Ismail NM, Ismail AR. Oral mucosal lesions in non oral habit diabetic patients and association of diabetes mellitus with oral precancerous lesions. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;89:320-326. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 32. | Sandberg GE, Sundberg HE, Fjellstrom CA, Wikblad KF. Type 2 diabetes and oral health: a comparison between diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2000;50:27-34. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 138] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Lamster IB, Lalla E, Borgnakke WS, Taylor GW. The relationship between oral health and diabetes mellitus. J Am Dent Assoc. 2008;139 Suppl:19S-24S. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 214] [Cited by in RCA: 209] [Article Influence: 13.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Papapanou PN. Periodontal diseases: epidemiology. Ann Periodontol. 1996;1:1-36. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 515] [Cited by in RCA: 494] [Article Influence: 17.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Lalla E, Lamster IB, Schmidt AM. Enhanced interaction of advanced glycation end products with their cellular receptor RAGE: implications for the pathogenesis of accelerated periodontal disease in diabetes. Ann Periodontol. 1998;3:13-19. [PubMed] |
| 36. | Lim LP, Tay FB, Sum CF, Thai AC. Relationship between markers of metabolic control and inflammation on severity of periodontal disease in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Clin Periodontol. 2007;34:118-123. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Lalla E, Cheng B, Lal S, Kaplan S, Softness B, Greenberg E, Goland RS, Lamster IB. Diabetes-related parameters and periodontal conditions in children. J Periodontal Res. 2007;42:345-349. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Taylor JJ, Preshaw PM, Lalla E. A review of the evidence for pathogenic mechanisms that may link periodontitis and diabetes. J Clin Periodontol. 2013;40 Suppl 14:S113-S134. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 118] [Cited by in RCA: 157] [Article Influence: 17.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Taylor GW, Burt BA, Becker MP, Genco RJ, Shlossman M, Knowler WC, Pettitt DJ. Severe periodontitis and risk for poor glycemic control in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Periodontol. 1996;67:1085-1093. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 402] [Cited by in RCA: 373] [Article Influence: 12.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 40. | Demmer RT, Holtfreter B, Desvarieux M, Jacobs DR, Kerner W, Nauck M, Völzke H, Kocher T. The influence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes on periodontal disease progression: prospective results from the Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP). Diabetes Care. 2012;35:2036-2042. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 108] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Emrich LJ, Shlossman M, Genco RJ. Periodontal disease in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Periodontol. 1991;62:123-131. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 437] [Cited by in RCA: 422] [Article Influence: 12.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 42. | Brownlee M. Glycation products and the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Diabetes Care. 1992;15:1835-1843. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 327] [Cited by in RCA: 312] [Article Influence: 9.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Seppälä B, Sorsa T, Ainamo J. Morphometric analysis of cellular and vascular changes in gingival connective tissue in long-term insulin-dependent diabetes. J Periodontol. 1997;68:1237-1245. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Lalla E, Lamster IB, Drury S, Fu C, Schmidt AM. Hyperglycemia, glycoxidation and receptor for advanced glycation endproducts: potential mechanisms underlying diabetic complications, including diabetes-associated periodontitis. Periodontol 2000. 2000;23:50-62. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 101] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Llambés F, Silvestre FJ, Hernández-Mijares A, Guiha R, Caffesse R. The effect of periodontal treatment on metabolic control of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clin Oral Investig. 2008;12:337-343. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Faria-Almeida R, Navarro A, Bascones A. Clinical and metabolic changes after conventional treatment of type 2 diabetic patients with chronic periodontitis. J Periodontol. 2006;77:591-598. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 89] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Smith GT, Greenbaum CJ, Johnson BD, Persson GR. Short-term responses to periodontal therapy in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. J Periodontol. 1996;67:794-802. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Arora N, Papapanou PN, Rosenbaum M, Jacobs DR, Desvarieux M, Demmer RT. Periodontal infection, impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance: results from the Continuous National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2010. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41:643-652. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Karjalainen KM, Knuuttila ML, von Dickhoff KJ. Association of the severity of periodontal disease with organ complications in type 1 diabetic patients. J Periodontol. 1994;65:1067-1072. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 64] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Wolff RE, Wolff LF, Michalowicz BS. A pilot study of glycosylated hemoglobin levels in periodontitis cases and healthy controls. J Periodontol. 2009;80:1057-1061. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 51. | Kiran M, Arpak N, Unsal E, Erdoğan MF. The effect of improved periodontal health on metabolic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Periodontol. 2005;32:266-272. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 212] [Cited by in RCA: 223] [Article Influence: 11.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 52. | Sgolastra F, Severino M, Pietropaoli D, Gatto R, Monaco A. Effectiveness of periodontal treatment to improve metabolic control in patients with chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Periodontol. 2013;84:958-973. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 97] [Cited by in RCA: 107] [Article Influence: 8.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Christgau M, Palitzsch KD, Schmalz G, Kreiner U, Frenzel S. Healing response to non-surgical periodontal therapy in patients with diabetes mellitus: clinical, microbiological, and immunologic results. J Clin Periodontol. 1998;25:112-124. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 157] [Cited by in RCA: 158] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 54. | Seppälä B, Ainamo J. A site-by-site follow-up study on the effect of controlled versus poorly controlled insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Periodontol. 1994;21:161-165. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 55. | Aldridge JP, Lester V, Watts TL, Collins A, Viberti G, Wilson RF. Single-blind studies of the effects of improved periodontal health on metabolic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Periodontol. 1995;22:271-275. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | Dağ A, Firat ET, Arikan S, Kadiroğlu AK, Kaplan A. The effect of periodontal therapy on serum TNF-alpha and HbA1c levels in type 2 diabetic patients. Aust Dent J. 2009;54:17-22. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 57. | Auyeung L, Wang PW, Lin RT, Hsieh CJ, Lee PY, Zhuang RY, Chang HW. Evaluation of periodontal status and effectiveness of non-surgical treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Taiwan for a 1-year period. J Periodontol. 2012;83:621-628. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 58. | Engebretson SP, Hyman LG, Michalowicz BS, Schoenfeld ER, Gelato MC, Hou W, Seaquist ER, Reddy MS, Lewis CE, Oates TW. The effect of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on hemoglobin A1c levels in persons with type 2 diabetes and chronic periodontitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;310:2523-2532. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 170] [Cited by in RCA: 179] [Article Influence: 14.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 59. | Gay IC, Tran DT, Cavender AC, Weltman R, Chang J, Luckenbach E, Tribble GD. The effect of periodontal therapy on glycaemic control in a Hispanic population with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41:673-680. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 60. | Simpson TC, Needleman I, Wild SH, Moles DR, Mills EJ. Treatment of periodontal disease for glycaemic control in people with diabetes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;CD004714. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 114] [Article Influence: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Engebretson S, Kocher T. Evidence that periodontal treatment improves diabetes outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Periodontol. 2013;84:S153-S169. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 71] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 62. | Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, Hadden D, Turner RC, Holman RR. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000;321:405-412. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5819] [Cited by in RCA: 5964] [Article Influence: 238.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 63. | Grossi SG, Skrepcinski FB, DeCaro T, Robertson DC, Ho AW, Dunford RG, Genco RJ. Treatment of periodontal disease in diabetics reduces glycated hemoglobin. J Periodontol. 1997;68:713-719. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 339] [Cited by in RCA: 313] [Article Influence: 11.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 64. | Iwamoto Y, Nishimura F, Nakagawa M, Sugimoto H, Shikata K, Makino H, Fukuda T, Tsuji T, Iwamoto M, Murayama Y. The effect of antimicrobial periodontal treatment on circulating tumor necrosis factor-alpha and glycated hemoglobin level in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Periodontol. 2001;72:774-778. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 188] [Cited by in RCA: 173] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 65. | Miller LS, Manwell MA, Newbold D, Reding ME, Rasheed A, Blodgett J, Kornman KS. The relationship between reduction in periodontal inflammation and diabetes control: a report of 9 cases. J Periodontol. 1992;63:843-848. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 139] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 66. | Jones JA, Miller DR, Wehler CJ, Rich SE, Krall-Kaye EA, McCoy LC, Christiansen CL, Rothendler JA, Garcia RI. Does periodontal care improve glycemic control? The Department of Veterans Affairs Dental Diabetes Study. J Clin Periodontol. 2007;34:46-52. [PubMed] |
| 67. | Llambés F, Silvestre FJ, Hernández-Mijares A, Guiha R, Caffesse R. Effect of non-surgical periodontal treatment with or without doxycycline on the periodontium of type 1 diabetic patients. J Clin Periodontol. 2005;32:915-920. [PubMed] |
| 68. | Botero JE, Yepes FL, Ochoa SP, Hincapie JP, Roldan N, Ospina CA, Castrillon CA, Becerra MA. Effects of periodontal non-surgical therapy plus azithromycin on glycemic control in patients with diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. J Periodontal Res. 2013;48:706-712. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Tervonen T, Knuuttila M, Pohjamo L, Nurkkala H. Immediate response to nonsurgical periodontal treatment in subjects with diabetes mellitus. J Clin Periodontol. 1991;18:65-68. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 55] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 70. | Souza KL, Gurgul-Convey E, Elsner M, Lenzen S. Interaction between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in insulin-producing cells. J Endocrinol. 2008;197:139-150. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Llambés F, Silvestre FJ, Hernández-Mijares A, Guiha R, Bautista D, Caffesse R. Efect of periodontal disease and non surgical periodontal treatment on C-reactive protein. Evaluation of type 1 diabetic patients. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012;17:e562-e568. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 72. | Priyanka N, Kumari M, Kalra N, Arjun P, Naik SB, Pradeep AR. Crevicular fluid and serum concentrations of progranulin and high sensitivity CRP in chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes. Dis Markers. 2013;35:389-394. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 73. | Dasanayake AP. C-reactive protein levels are elevated in patients with periodontitis and their CRP levels may go down after periodontal therapy. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2009;9:21-22. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 74. | Pejcic A, Kesic L, Milasin J. Association between Periodontopathogens and CRP Levels in Patients with Periodontitis in Serbia. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2011;5:10-16. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 75. | Stewart JE, Wager KA, Friedlander AH, Zadeh HH. The effect of periodontal treatment on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Periodontol. 2001;28:306-310. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 168] [Cited by in RCA: 167] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |