Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2025; 16(6): 104665
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.104665
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.104665
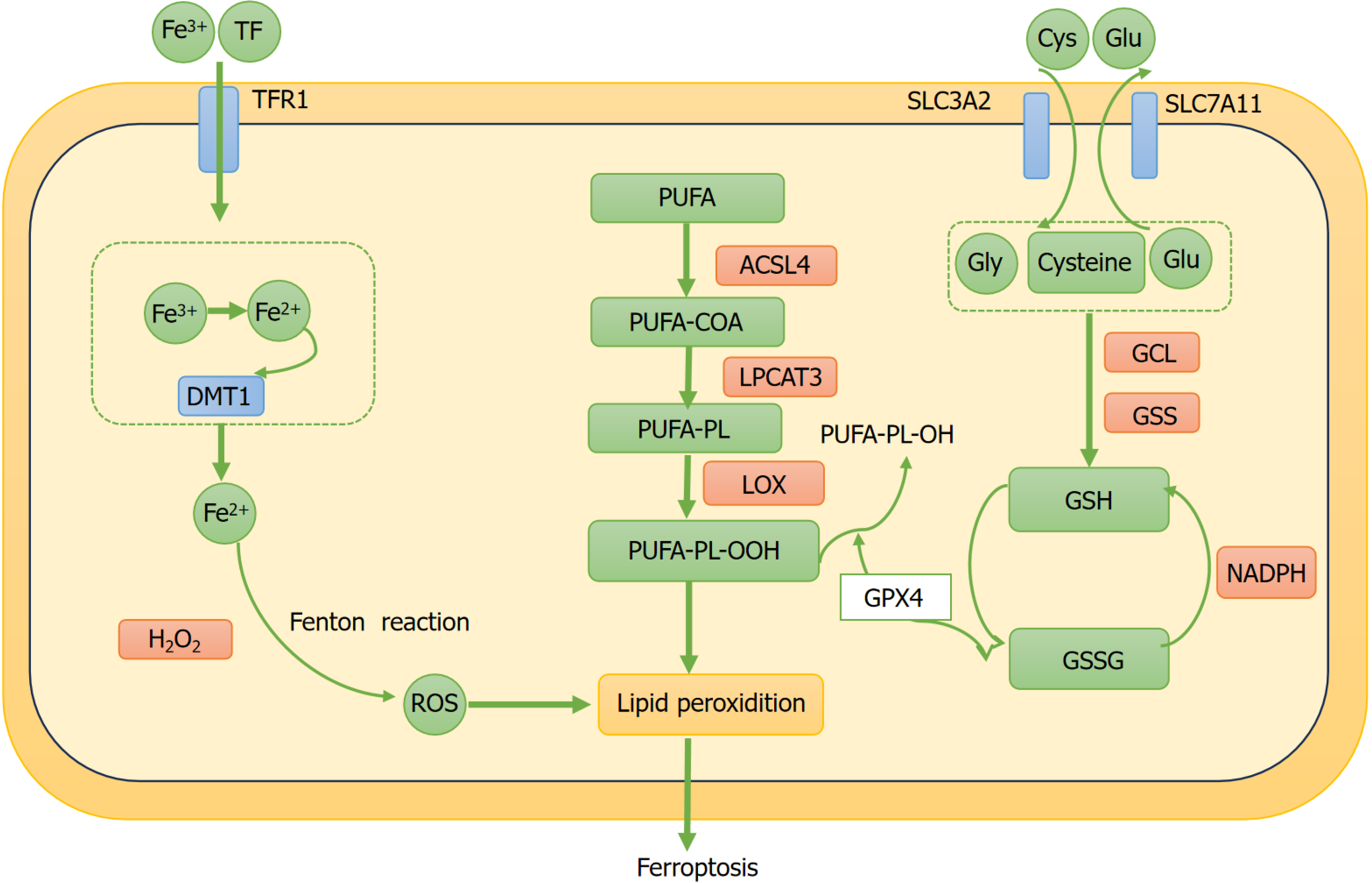
Figure 1 The primary signaling pathways and key regulatory factors of ferroptosis.
TF: Transferrin; TFR1: Transferrin receptor1; DMT1: Divalent 311 metal transporter 1; ACSL4: Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; LPCAT3: Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; LOX: Lipoxygenase; SLC3A2: Solute carrier family 3 member 2; SLC7A11: Solute carrier family 7 member 11; GCL: Glutamate cysteine ligase; GSS: Glutathione synthase; Cys: Cystine; Glu: Glutamate; Gly: Glycine; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; PUFA: Polyunsaturated fatty acid; PUFA-PL: Polyunsaturated fatty acid-phospholipid; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase; GSH: Glutathione.
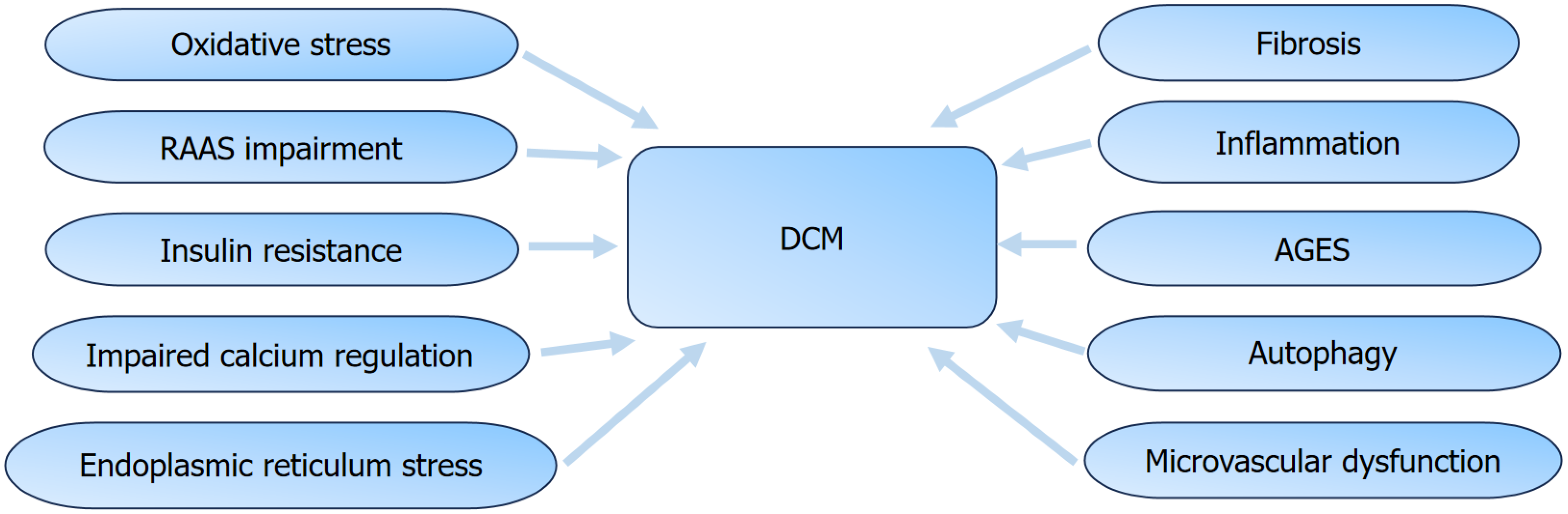
Figure 2 Pathophysiological mechanism of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
AGEs: Advanced glycation end products; RAAS: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; DCM: Diabetic cardiomyopathy.
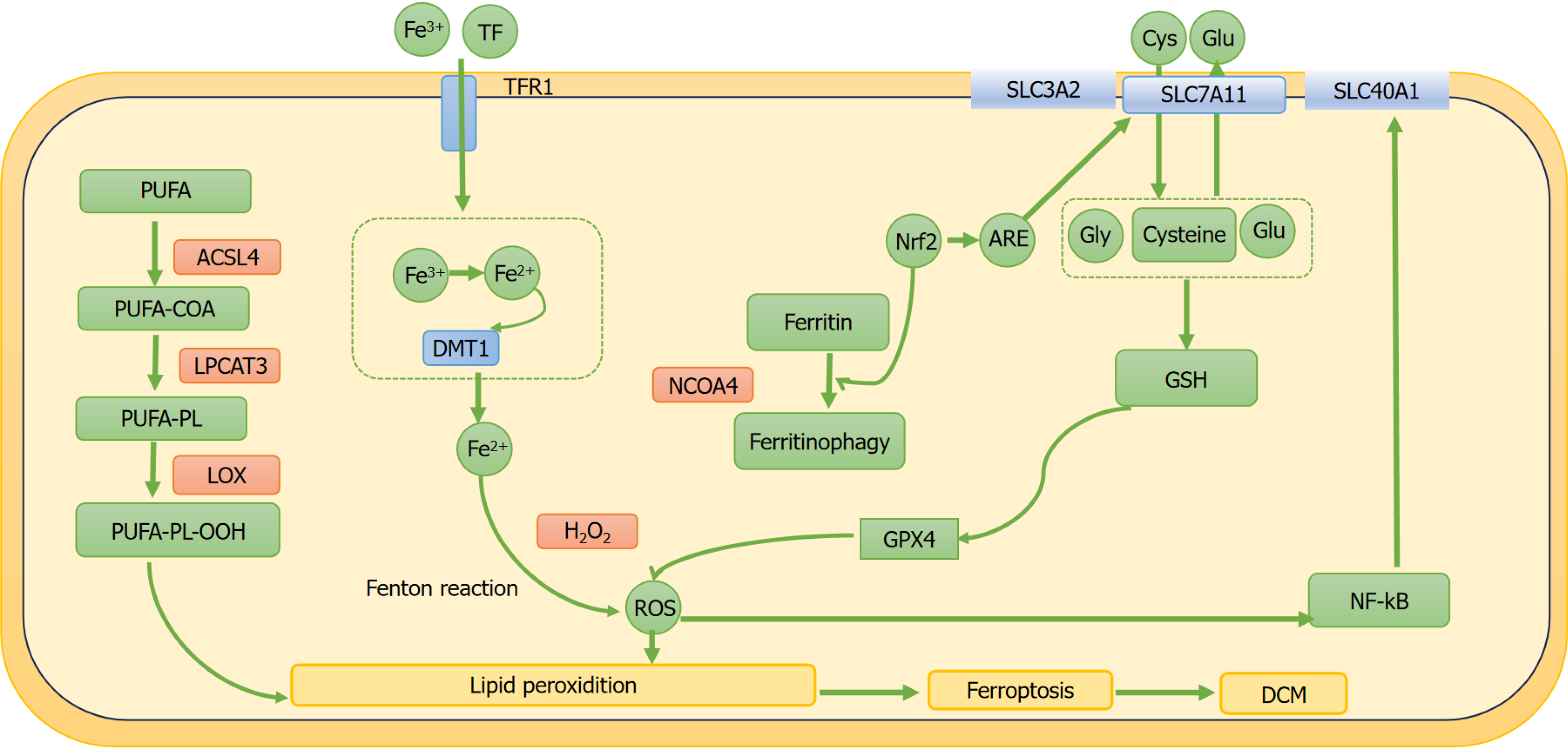
Figure 3 The regulatory role of ferroptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; SLC40A1: Solute carrier family 40 member 1; NCOA4: Nuclear receptor coactivator 4; TF: Transferrin; TFR1: Transferrin receptor1; DMT1: Divalent 311 metal transporter 1; ACSL4: Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; LPCAT3: Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; LOX: Lipoxygenase; SLC3A2: Solute carrier family 3 member 2; SLC7A11: Solute carrier family 7 member 11; GCL: Glutamate cysteine ligase; GSS: Glutathione synthase; Cys: Cystine; Glu: Glutamate; Gly: Glycine; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; PUFA: Polyunsaturated fatty acid; PUFA-PL: Polyunsaturated fatty acid-phospholipid; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase; GSH: Glutathione; ARE: Antioxidant response elements.
- Citation: Li GZ, Liu JY, Zhou H. Ferroptosis: A novel therapeutic target for diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(6): 104665
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i6/104665.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.104665