Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2025; 16(4): 102390
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.102390
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.102390
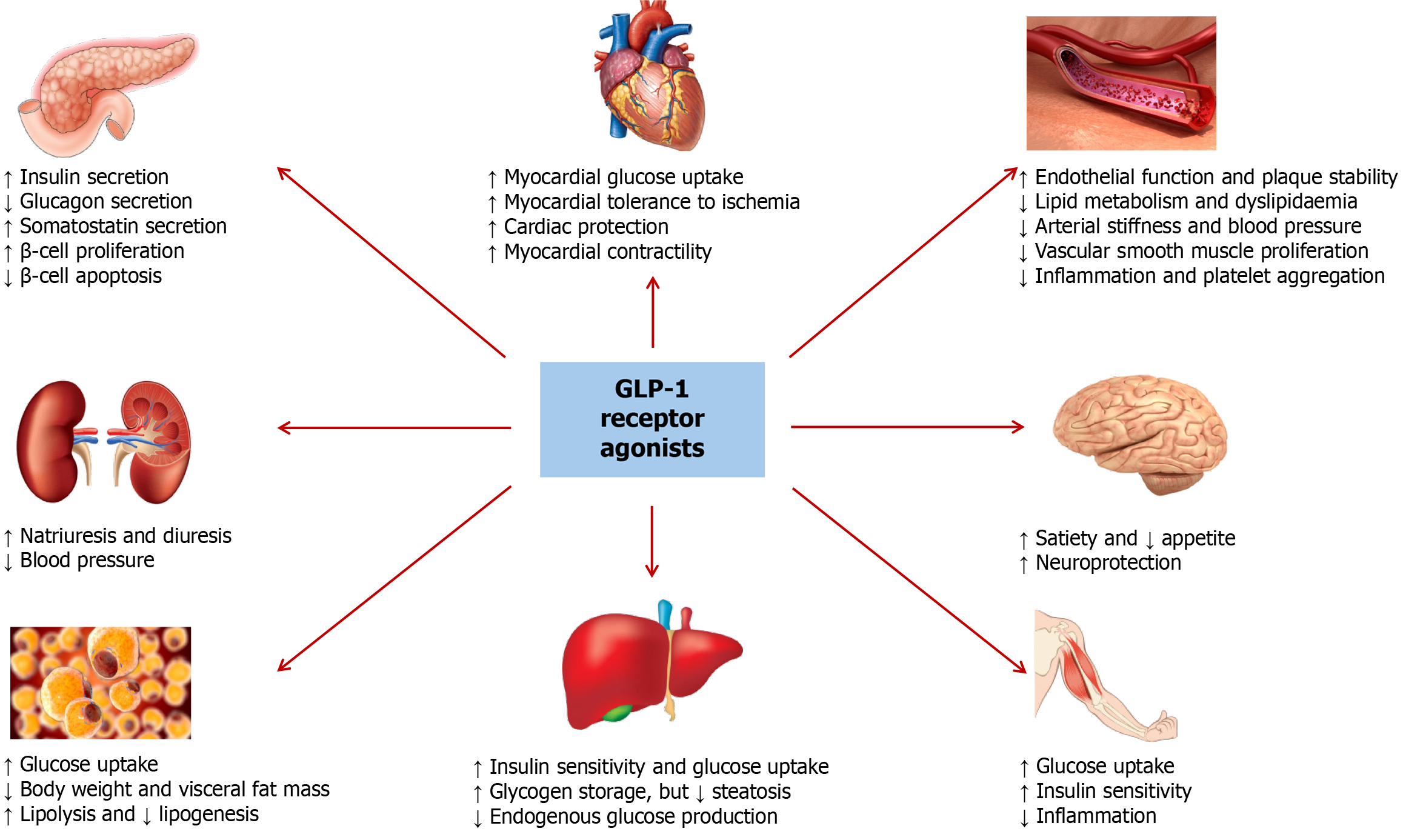
Figure 1 The putative mechanisms for cardiovascular protection associated with the use of glucagon-like insulinotropic peptide-1 receptor agonists.
GLP-1: Glucagon-like insulinotropic peptide-1.
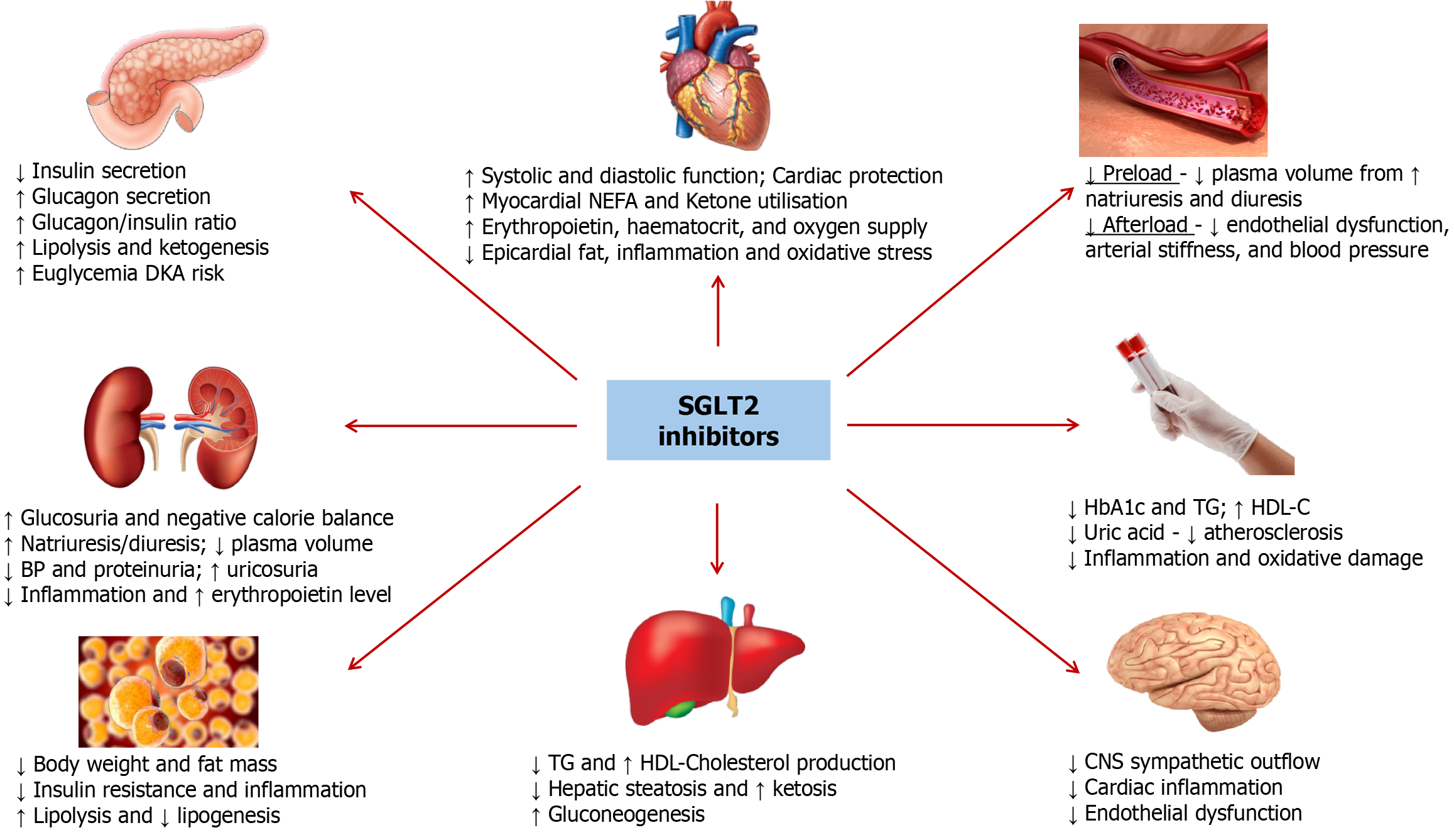
Figure 2 The putative mechanisms for cardiovascular protection associated with the use of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors.
DKA: Diabetes ketoacidosis; BP: Blood pressure; NEFA: Non-esterified fatty acids; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; TG: Triglycerides; CNS: Central nervous system; HbA1c: Glycated hemoglobin.
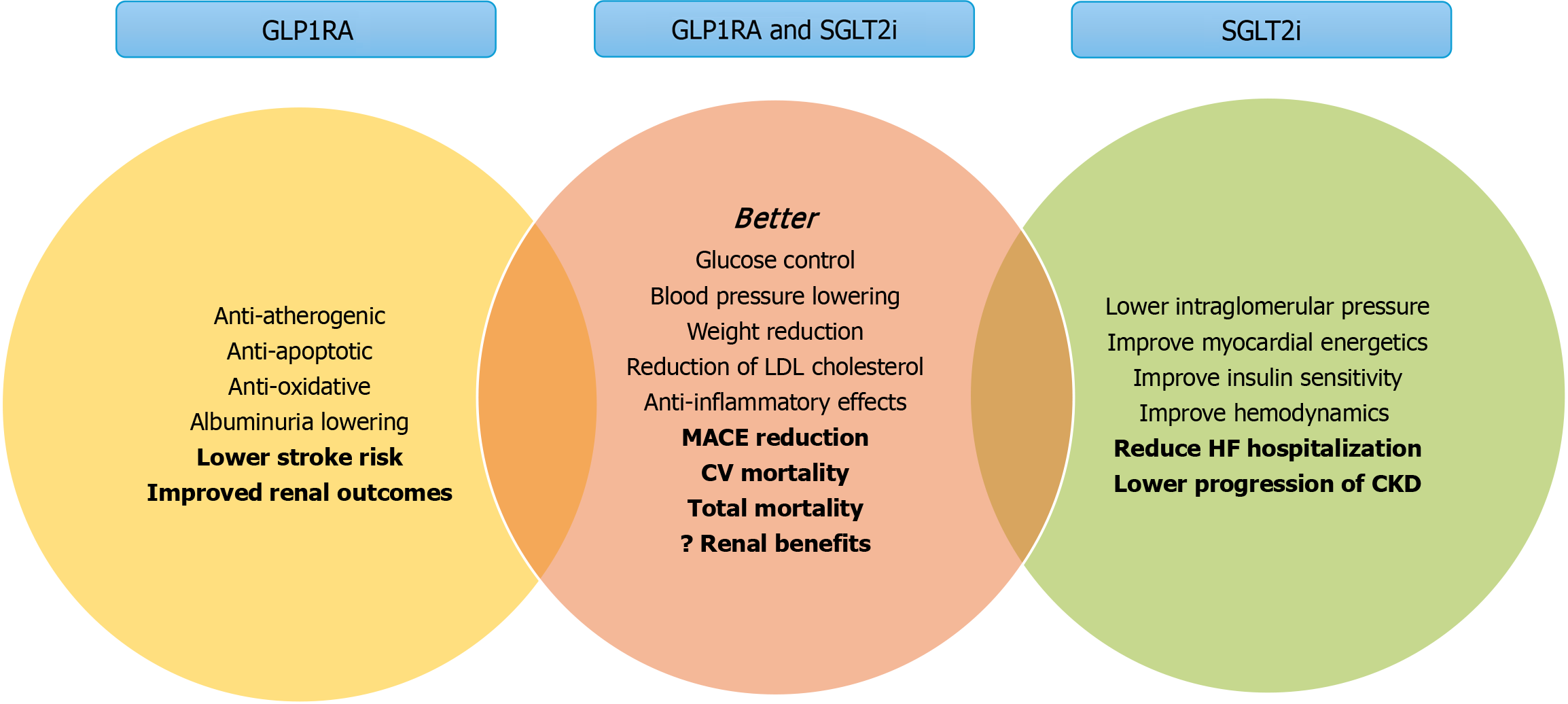
Figure 3 Shows the mechanisms of cardiorenal therapeutic benefits of glucagon-like insulinotropic peptide-1 receptor agonists, sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors, and their combination.
LDL: Low density lipoprotein cholesterol; CV: Cardiovascular; MACE: Major adverse cardiac event; HF: Heart failure; CKD: Chronic kidney disease; GLP1RA: Glucagon-like insulinotropic peptide-1 receptor agonists; SGLT2i: Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor.
- Citation: Ganakumar V, Fernandez CJ, Pappachan JM. Antidiabetic combination therapy and cardiovascular outcomes: An evidence-based approach. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(4): 102390
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i4/102390.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.102390