Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2023; 14(3): 299-312
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.299
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.299
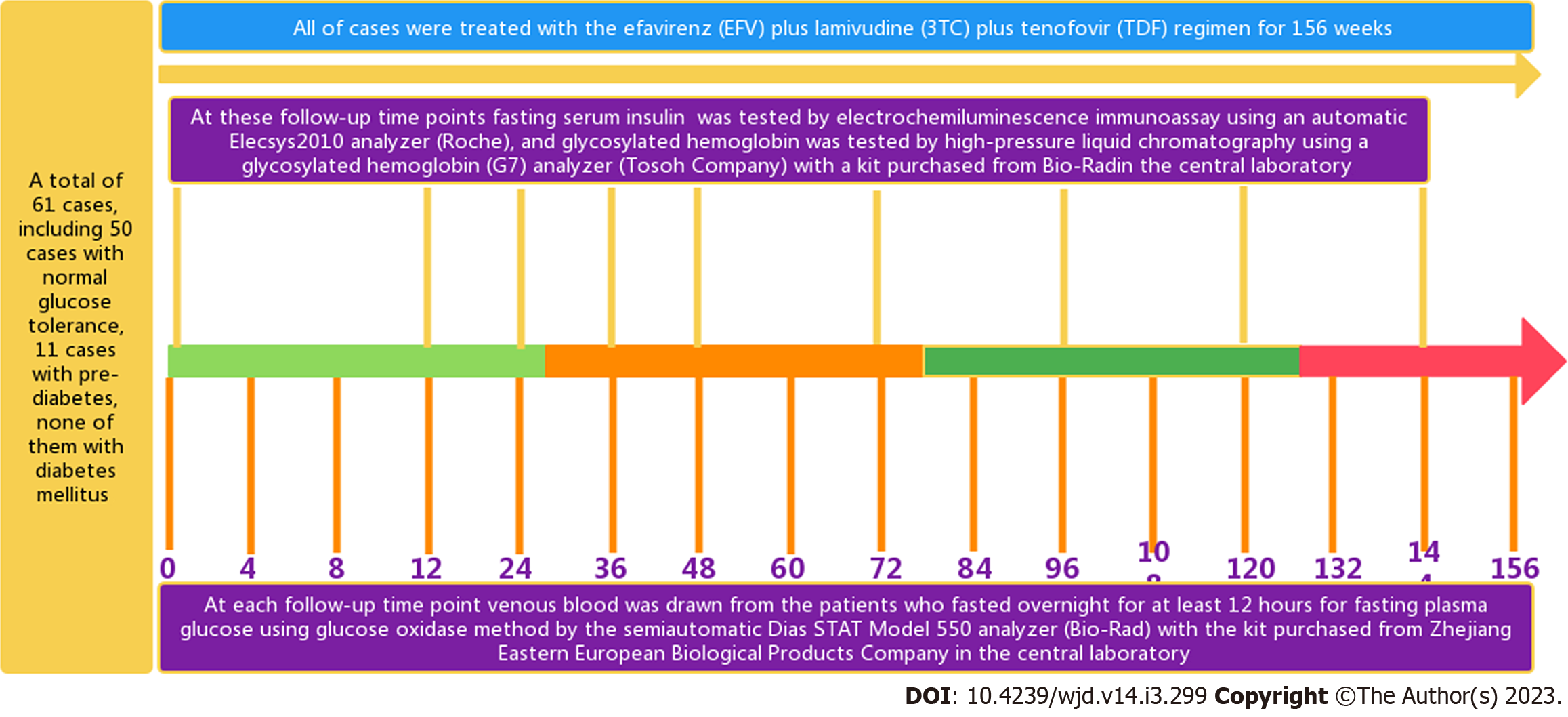
Figure 1 Schematic diagram.
A total of 61 cases were included, including 50 cases with normal glucose tolerance, 11 cases with prediabetes, and none of them with diabetes mellitus. All cases were treated with the efavirenz plus lamivudine plus tenofovir regimen for 156 wk. At 0, 4, 8, 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120, 132, 144, and 156 wk, venous blood was drawn from the patients who fasted overnight for at least 12 h for fasting plasma glucose using the glucose oxidase method by the semiautomatic Dias STAT Model 550 analyzer (Bio-Rad) with the kit purchased from Zhejiang Eastern European Biological Products Company; at 0, 12, 24, 36, 48, 72, 96, 120, and 144 wk for fasting serum insulin using electrochemiluminescence immunoassay by automatic Elecsys2010 analyzer (Roche); and for glycosylated hemoglobin using high-pressure liquid chromatography by glycosylated hemoglobin (G7) analyzer (Tosoh Company) with a kit purchased from Bio-Rad in the central laboratory.
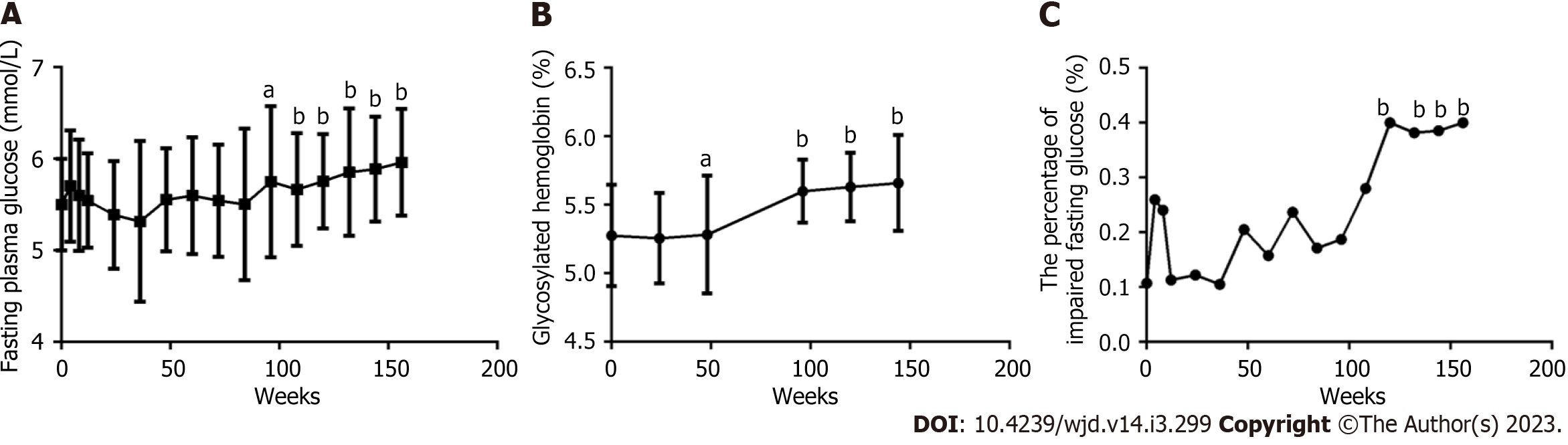
Figure 2 Long-term dynamic changes in fasting plasma glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c and impaired fasting plasma glucose within 156 wk after the initiation of antiretroviral therapy with tenofovir plus lamivudine plus efavirenz in male patients living with human immunodeficiency virus (including normal glucose tolerance and prediabetes) (n = 61).
A: Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level; B: Glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level; C: Impaired fasting plasma glucose rate. ANOVA was used to compare FPG and HbA1c from baseline to 156 wk (A, B, all P<0.0001). A paired t test was used to compare FPG and HbA1c between baseline and specific follow-up time points, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. The chi-square test was used to compare the percentage of IFG from baseline to 156 wk (C, P < 0.0001) and between baseline and specific follow-up time points, bP < 0.01.
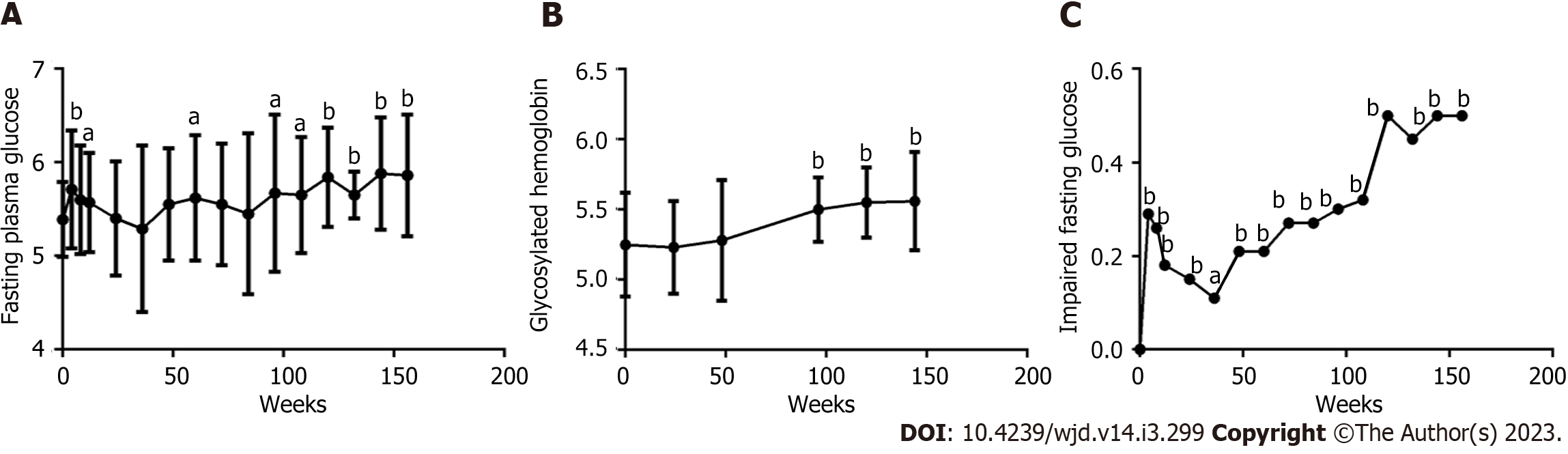
Figure 3 Long-term dynamic changes in fasting plasma glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c and impaired fasting plasma glucose within 156 wk after the initiation of antiretroviral therapy with tenofovir plus lamivudine plus efavirenz in male patients living with human immunodeficiency virus and with normal glucose tolerance (except 11 cases with prediabetes) (n = 50).
A: Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level; B: Glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level; C: Impaired fasting plasma glucose rate. ANOVA was used to compare FPG and HbA1c from baseline to 156 wk (A, B, all P < 0.0001). A paired t test was used to compare FPG and HbA1c between baseline and specific follow-up time points, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. The chi-square test was used to compare the percentage of IFG from baseline to 156 wk (C, P < 0.0001) and between baseline and specific follow-up time points, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
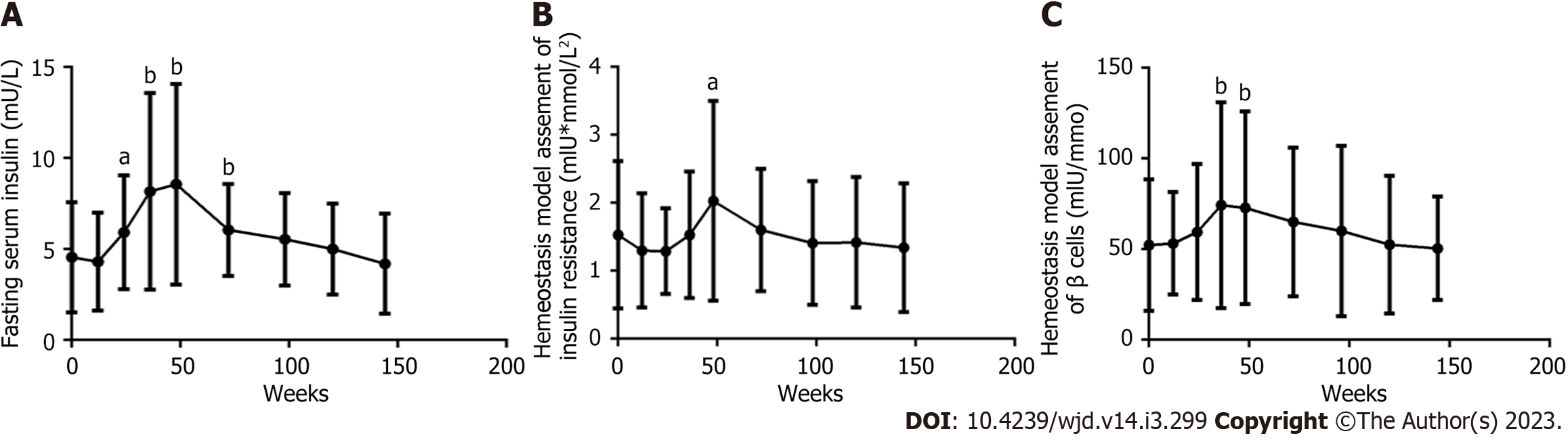
Figure 4 Long-term dynamic changes in other glucose metabolism parameters within 144 wk after the initiation of antiretroviral therapy with tenofovir plus lamivudine plus efavirenz in male patients living with human immunodeficiency virus (n = 61).
A: Fasting serum insulin level; B: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance value; C: Homeostasis model assessment of β cell function value. ANOVA was used to compare glucose metabolism parameters from baseline to 144 wk (A, P < 0.0001; B, C, all P < 0.01). A paired t test was used to compare glucose metabolism parameters between baseline and specific follow-up time points, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
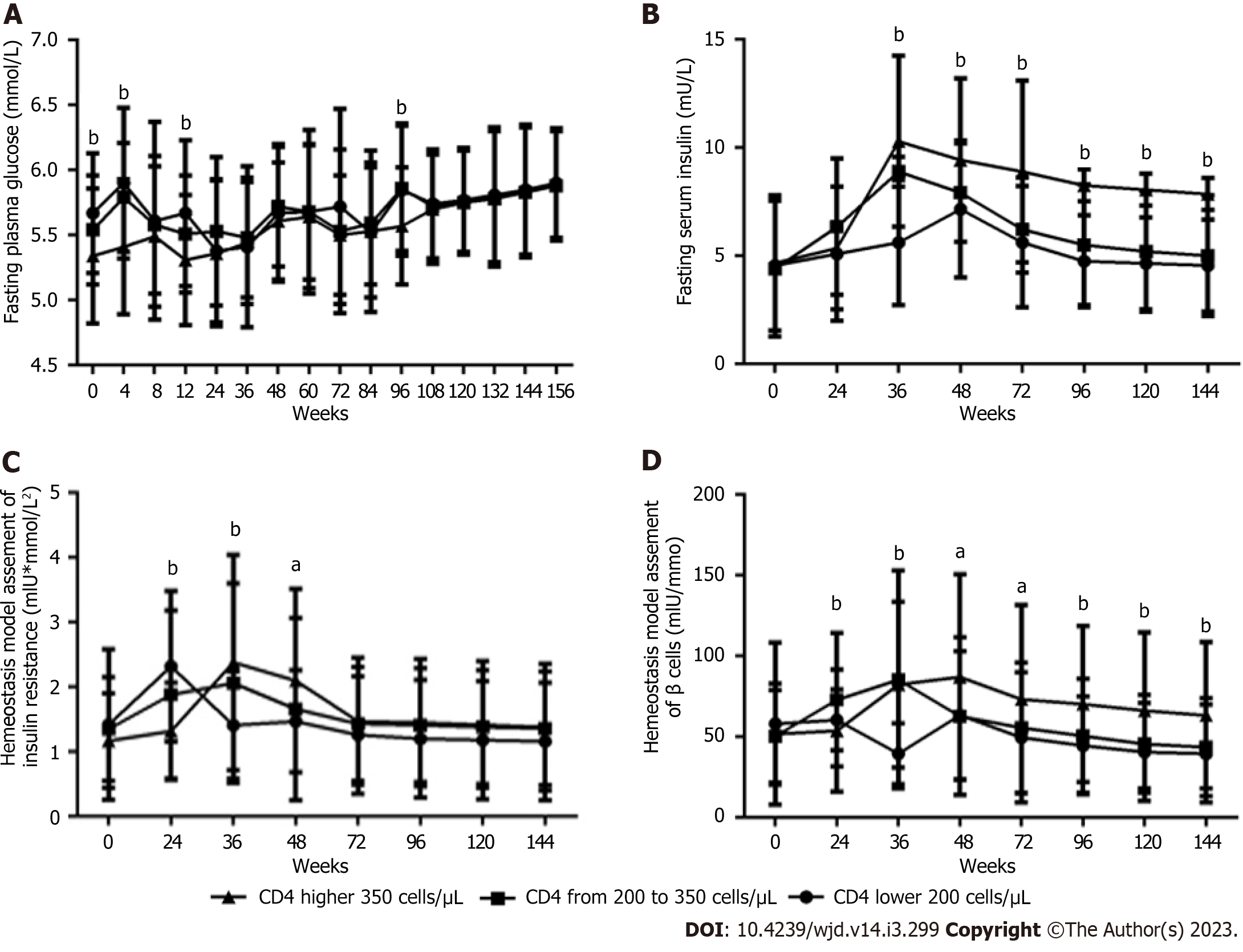
Figure 5 Long-term effects of baseline CD4+ T-cell count on glucose metabolism parameters within 156 wk after antiretroviral therapy with tenofovir plus lamivudine plus efavirenz in male patients living with human immunodeficiency virus (n = 61; 26, 12, and 23 patients in the < 200, 200 to 350, and > 350 groups, respectively).
A: Fasting plasma glucose level; B: Fasting serum insulin level; C: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance value; D: Homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function value. Two-way ANOVA was used to compare glucose metabolism parameters among the three groups from baseline to 156 wk (interaction, A, P < 0.01; B, C, D, all P < 0.0001. Row factor, A, B, C, D, all P < 0.0001. Column factor, A, B, D, all P < 0.0001; B, P < 0.05). One-way ANOVA was used to compare glucose metabolism parameters among the three groups at the same time point, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Liu DF, Zhang XY, Zhou RF, Cai L, Yan DM, Lan LJ, He SH, Tang H. Glucose metabolism continuous deteriorating in male patients with human immunodeficiency virus accepted antiretroviral therapy for 156 weeks. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(3): 299-312
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i3/299.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.299