Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2023; 14(2): 62-75
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.62
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.62
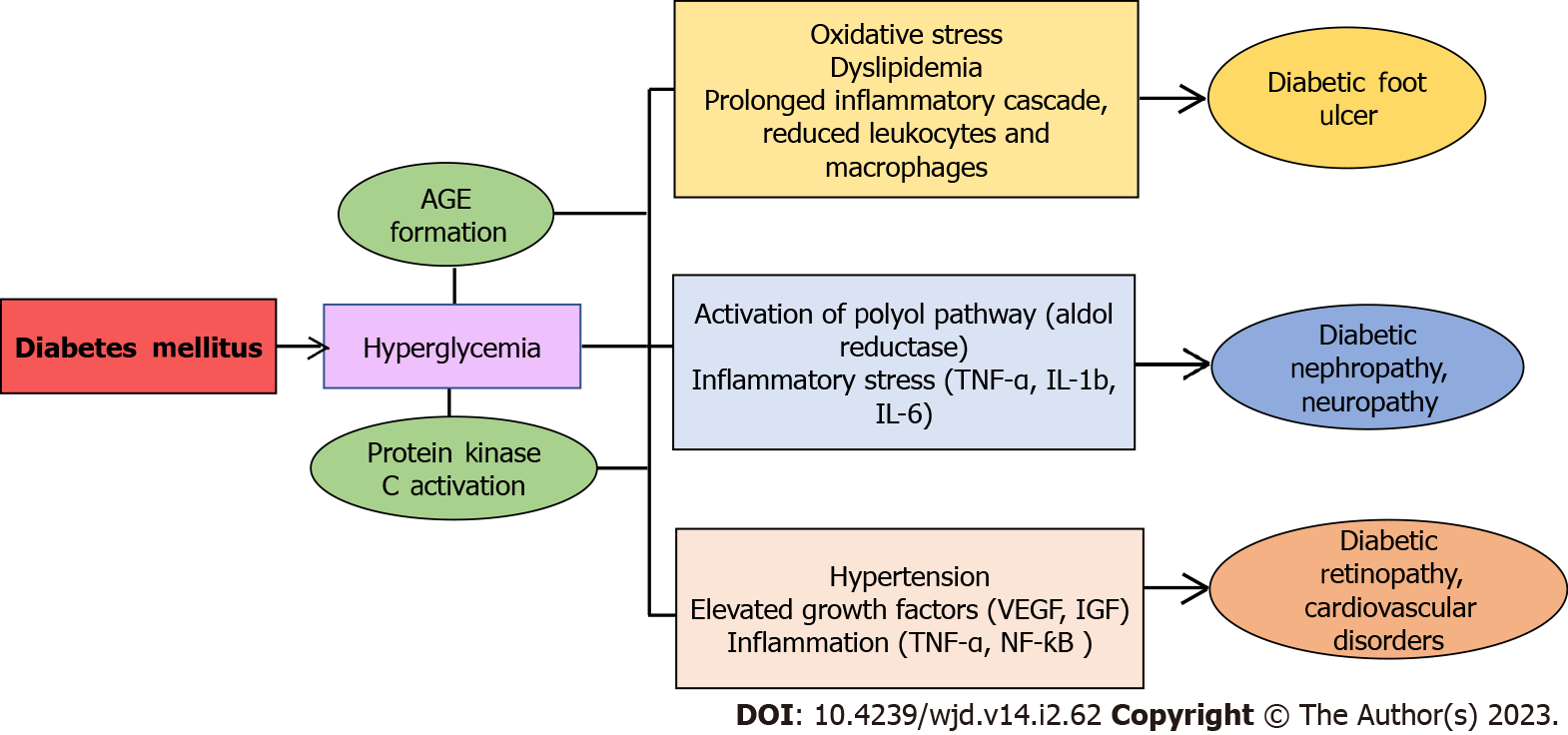
Figure 1 Multiple factors responsible for the onset and progression of diabetes mellitus and associated complications including diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disorders.
Hyperglycemia leads to the formation of advanced glycation end products and activation of protein kinase C. This further results in oxidative stress-mediated dyslipidemia, hypertension, activation of polyol pathway, and inflammatory stress. AGE: Advanced glycation end products; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: Interleukin; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; IGF: Insulin-like growth factors; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB.
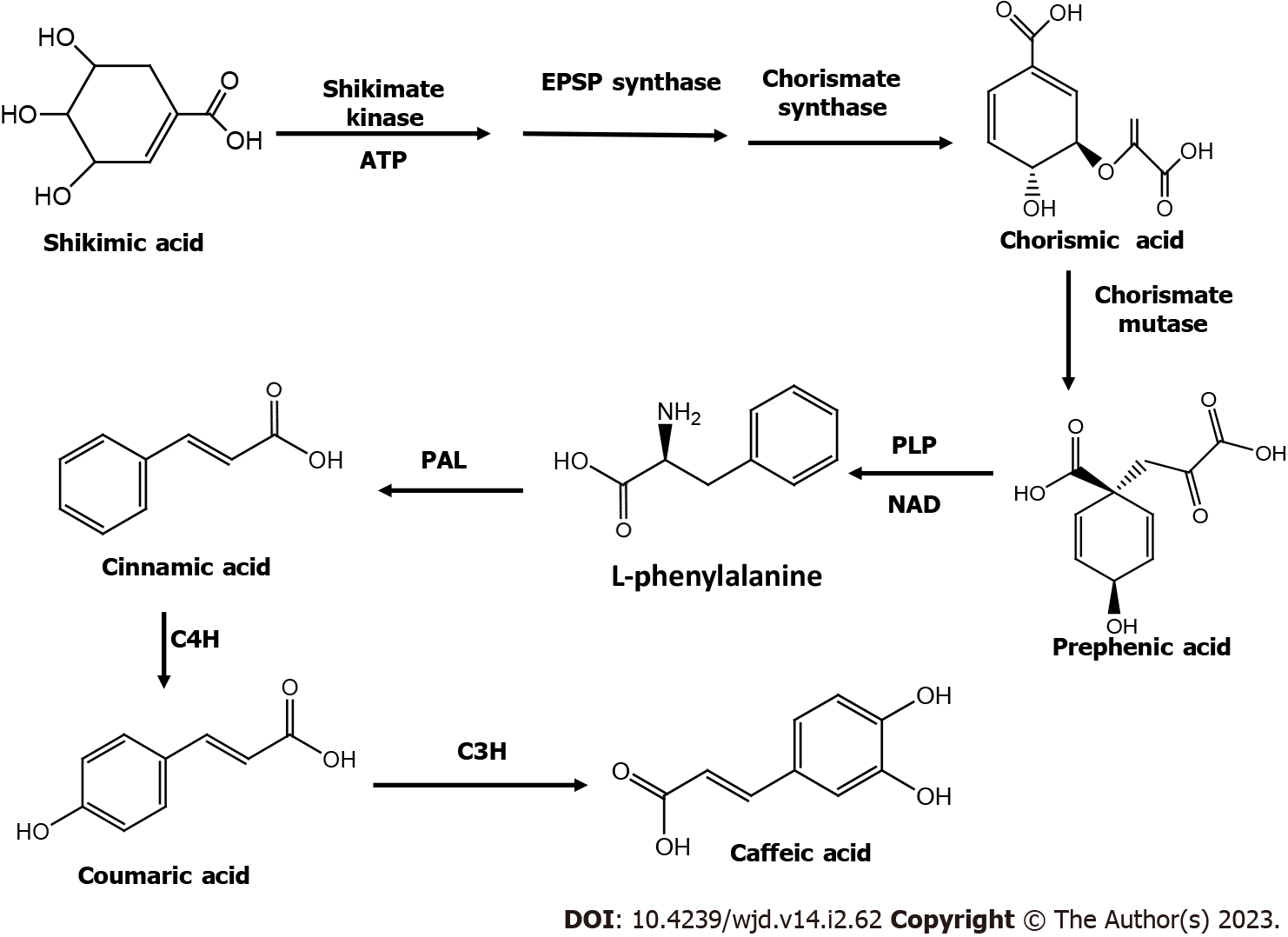
Figure 2 Biosynthesis of caffeic acid via the shikimic acid pathway.
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; EPSP: 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate; PLP: Pyridoxal phosphate; NAD: Nicotine adenine dinucleotide; PAL: Phenylalanine ammonia lyase; C4H: Cinnamate-4-hydroxylase; C3H: Coumarate 3-hydroxylase.
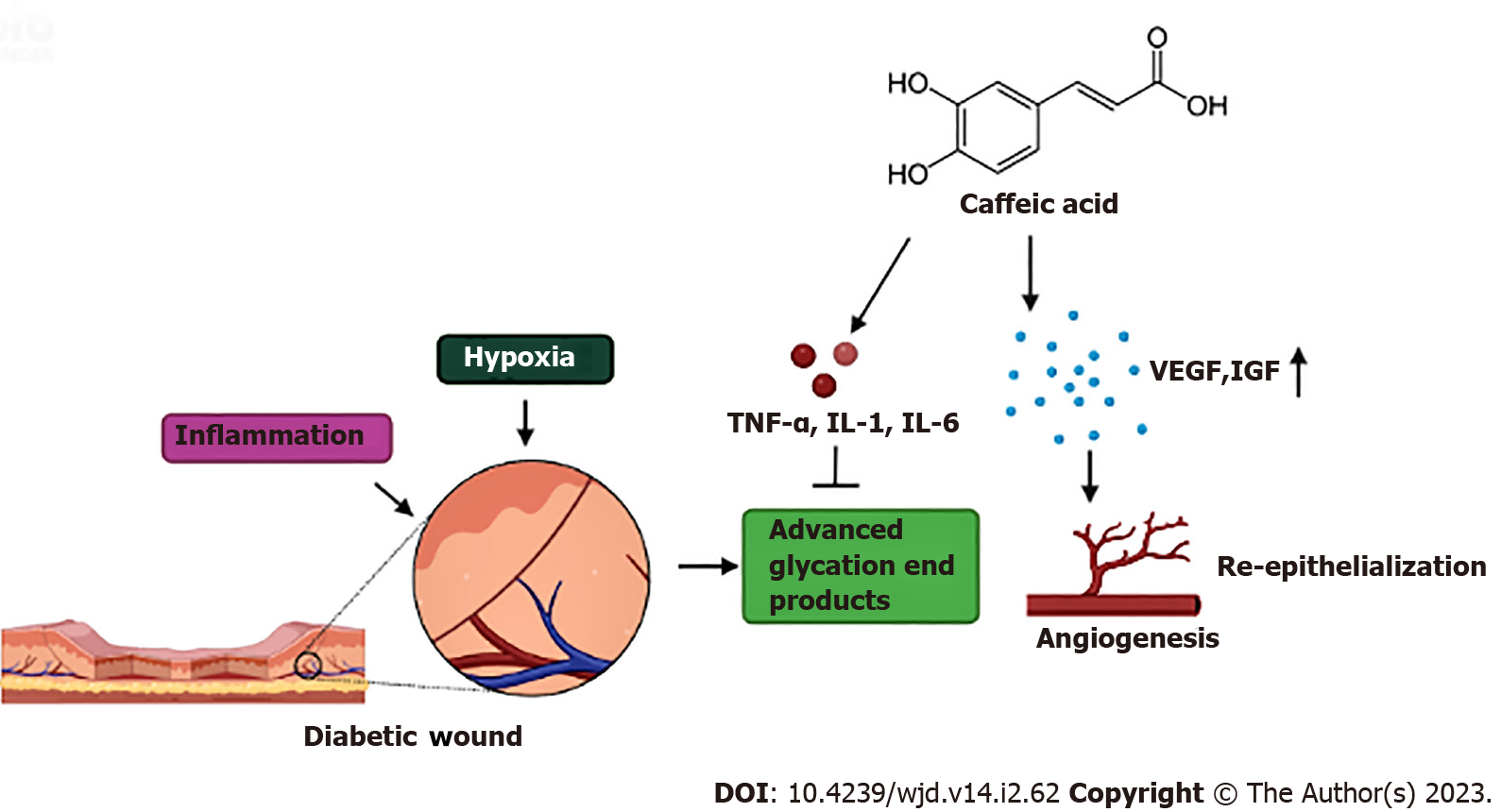
Figure 3 Mechanism of diabetic wound healing mediated by caffeic acid.
Hyperglycemia leads to formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), hypoxia, and inflammation at the site of injury. Caffeic acid stimulates the inflammatory cascade which inhibits the formation of AGEs and elevates the levels of vascular endothelial growth factorand insulin-like growth factors. This results in vascular angiogenesis and re-epithelialization at the site of injury. VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; IGFs: Insulin-like growth factors; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: Interleukin.
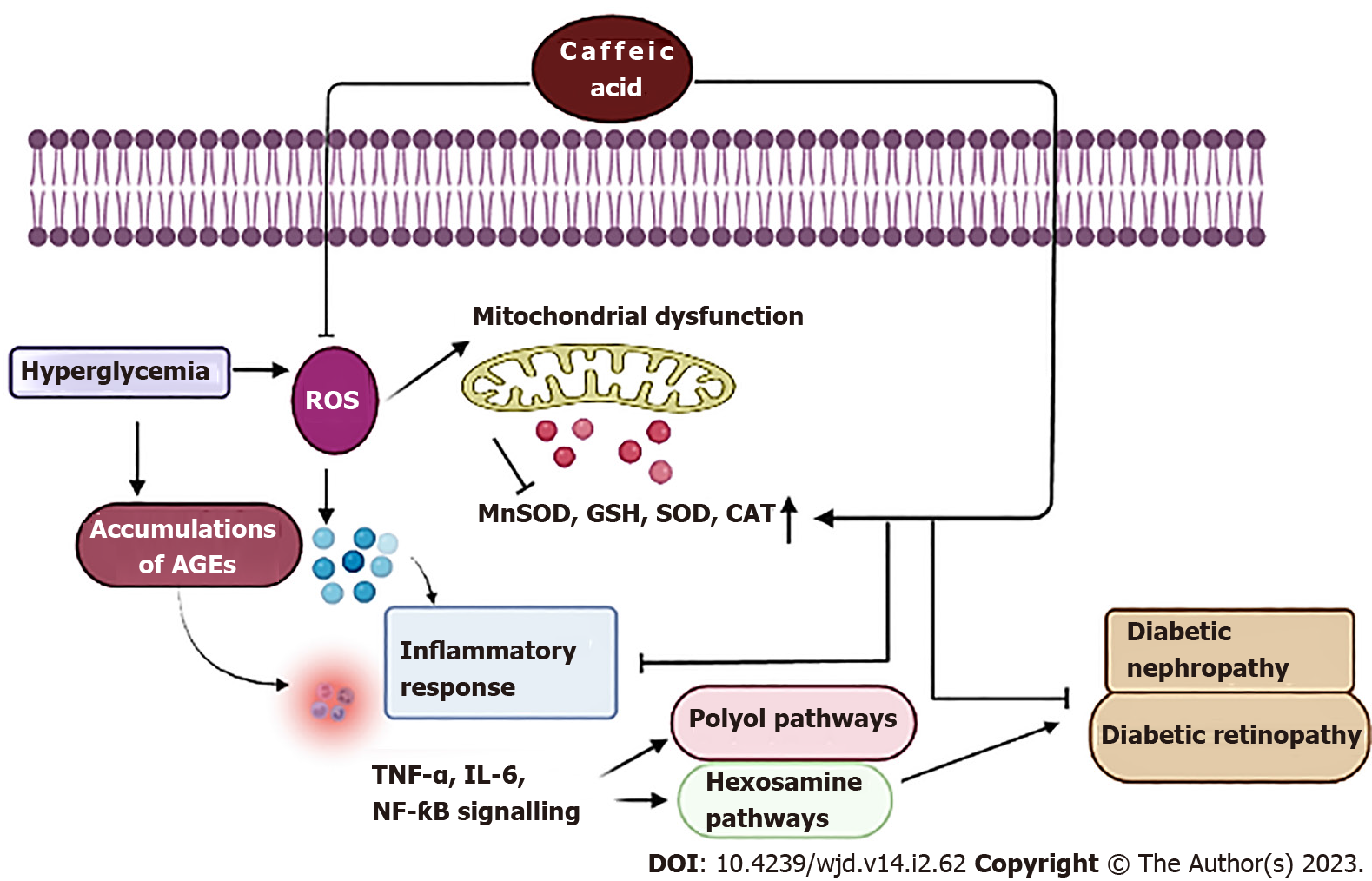
Figure 4 echanism of protective action of caffeic acid in diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy.
Hyperglycemia induces formation of advanced glycation end products and reactive oxygen species in renal and retinal tissues, which in turn causes mitochondrial dysfunction by inhibiting antioxidant enzymes such as manganese superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and activates the production of inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, nuclear factor-κB, polyol, and hexosamine signaling pathways. Caffeic acid increases the levels of antioxidant enzymes and suppresses inflammatory response, thus protecting the tissues from diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy. AGEs: Advanced glycation end products; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; Mn-SOD: Manganese superoxide dismutase; CAT: Catalase; SOD:Superoxide dismutase; GSH: Glutathione; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Ganguly R, Singh SV, Jaiswal K, Kumar R, Pandey AK. Modulatory effect of caffeic acid in alleviating diabetes and associated complications. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(2): 62-75
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i2/62.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.62