Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2022; 13(12): 1035-1048
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1035
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1035
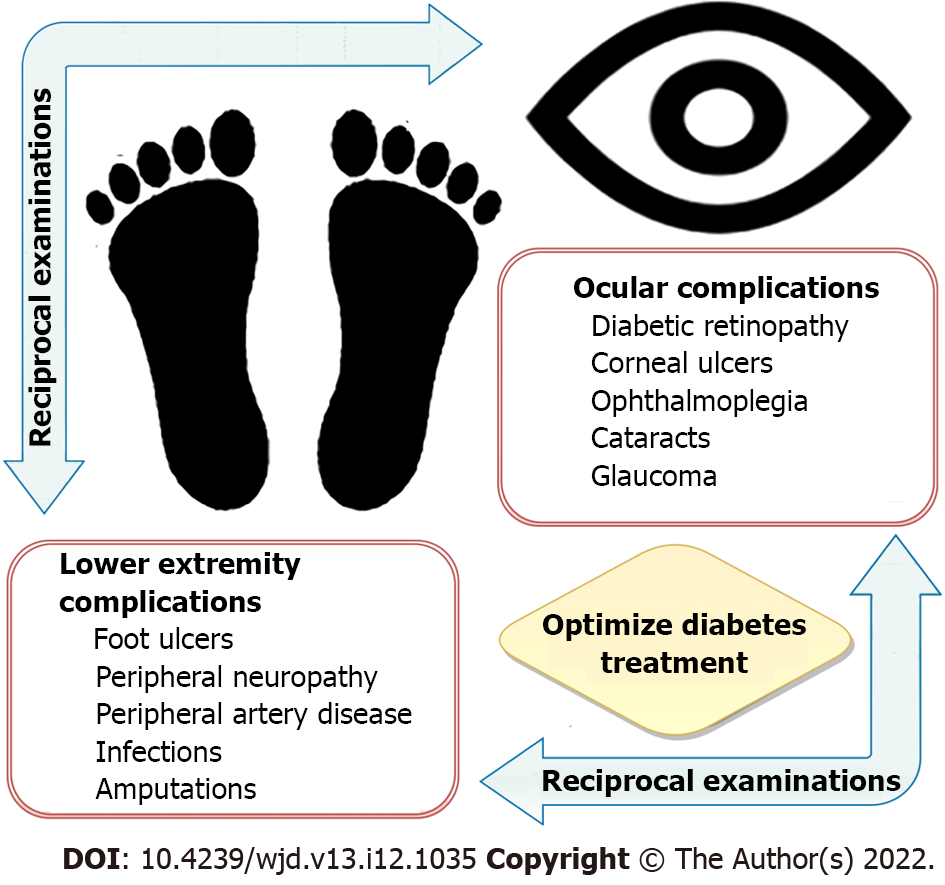
Figure 1 Upon identification of one or more of problems involving the lower extremity or the eye, reciprocal examinations are recommended to reduce the risk of further complications.
Preventing diabetic foot and eye problems is best achieved through regular examinations, diabetes education, and optimal management of underlying diabetes mellitus and its associated metabolic consequences.
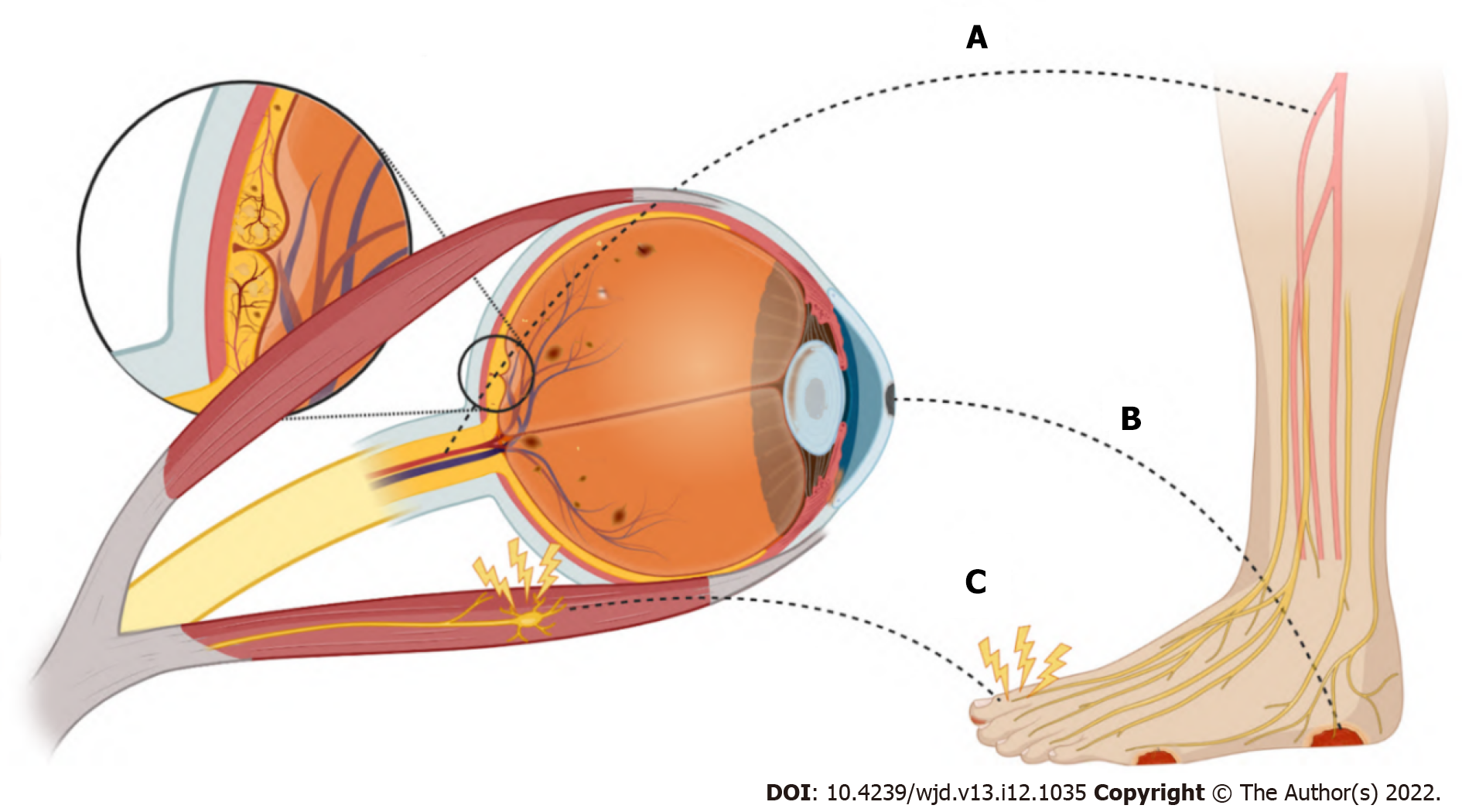
Figure 2 The connection between diabetic eye disease and diabetic foot and wound healing.
A: Diabetic micro- and macrovascular complications; B: Diabetic ulcers; C: Diabetic neuropathy. Each of these diabetic complications has multifactorial etiologies. Figure 2 was made in ©BioRender-biorender.com.
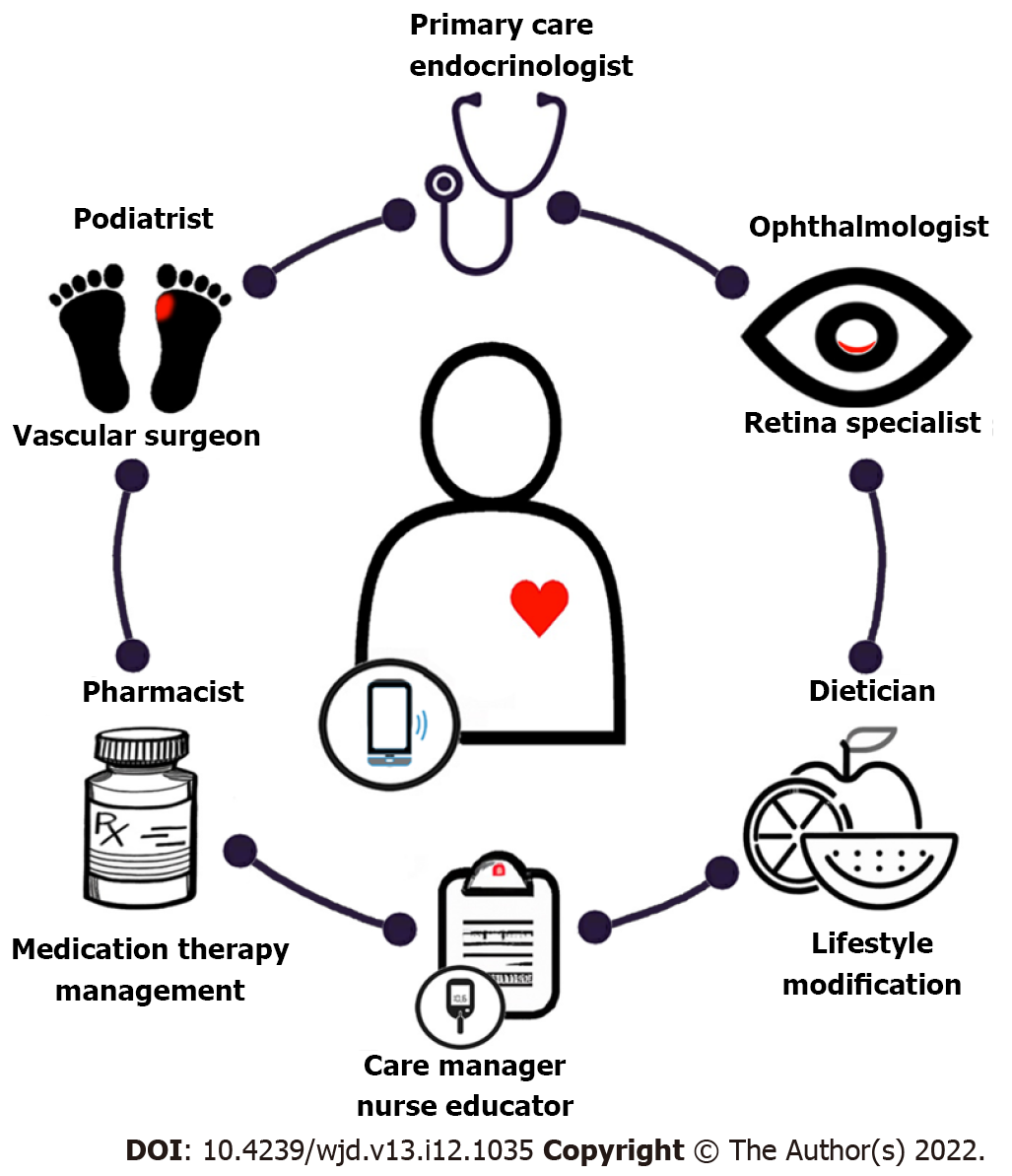
Figure 3 Diabetic care team process.
Primary care and endocrinology physicians are central to comprehensive diabetes mellitus (DM) evaluation including assessment of the level of glycemic control, prescription of medications, determining level of treatment adherence, and identification of gaps in care and risk of complications. The frequent concurrence of diabetic eye and foot problems mandate that patients affected by either condition should undergo reciprocal comprehensive eye and foot evaluations, in addition to optimizing diabetic control. Specialists are often required to manage diabetic foot problems, including referral to podiatry, lower extremity wound care specialists, or vascular surgery, each engaging treatment algorithms according to their expertise. Eye care is typically provided by ophthalmologists or optometrists, but often requires the expertise of a retinal specialist capable of providing the medical and surgical management of diabetic eye disease. Pharmacists provide medication therapy management and are an important sources of diabetes education. Dietitians, lifestyle coaches, and psychologists offer counseling that works toward improving or maintaining glycemic targets through nutrition, achieving weight management and physical activity goals, and implementing behavior changes. Diabetic care managers and nurse educators help individuals with DM establish long-term commitments. They provide instruction on foot and skin care; the use of medications, including the administration of insulin; the monitoring of blood glucose levels; and maintenance of proper diet and exercise. They develop an overall management strategy aimed at reducing risk factors linked to diabetes-associated complications. The integration of smartphone technology and telehealth may streamline the care coordination and communication between the patient and each component of the diabetic care team[106]. Figure 3 was made in ©BioRender-biorender.com. The authors generated parts of the digital images used in Figure 3 by using the Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3) autoregressive language model that employs deep learning to generate digital images from natural language descriptions (DALL·E, OpenAI, San Francisco, CA, labs.openai.com). The authors reviewed, edited, and revised these images and take ultimate responsibility for the content included in this publication.
- Citation: Ramsey DJ, Kwan JT, Sharma A. Keeping an eye on the diabetic foot: The connection between diabetic eye disease and wound healing in the lower extremity. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(12): 1035-1048
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i12/1035.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1035