Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2022; 13(12): 1001-1013
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1001
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1001
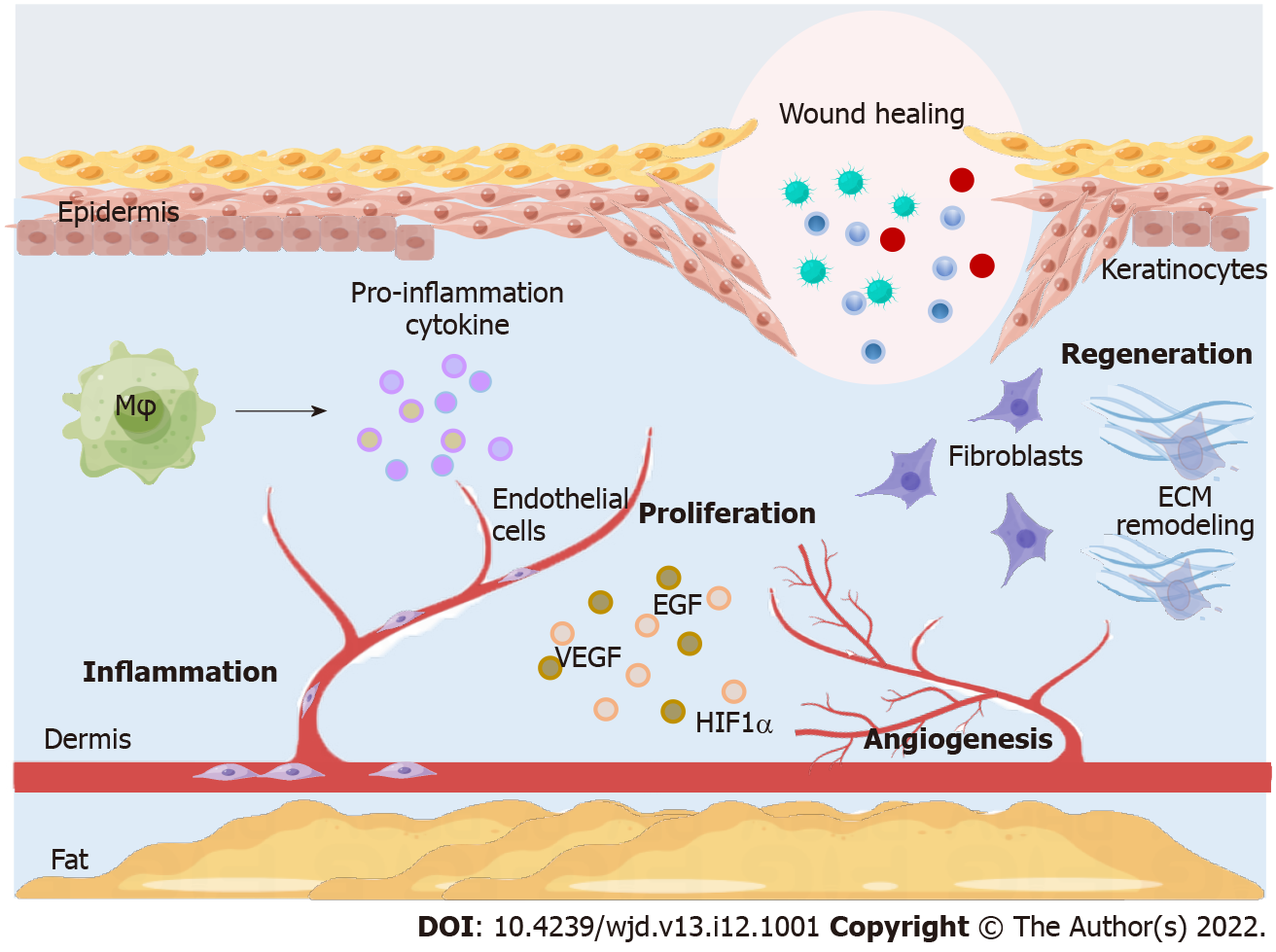
Figure 1 A diagram of the diabetic foot wound healing process.
In the inflammation phase, macrophages produce pro-inflammatory cytokines. In the proliferation phase, angiogenic growth factors promote angiogenesis by stimulating endothelial cell proliferation and migration. In the regeneration phase, fibroblasts proliferate and secrete extracellular matrix components to provide supportive structures for cell proliferation and migration to restore skin tissue function. Mφ: Macrophages; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α; ECM: Extracellular matrix.
- Citation: Tang YB, Uwimana MMP, Zhu SQ, Zhang LX, Wu Q, Liang ZX. Non-coding RNAs: Role in diabetic foot and wound healing. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(12): 1001-1013
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i12/1001.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1001