Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2022; 13(11): 986-1000
Published online Nov 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.986
Published online Nov 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.986
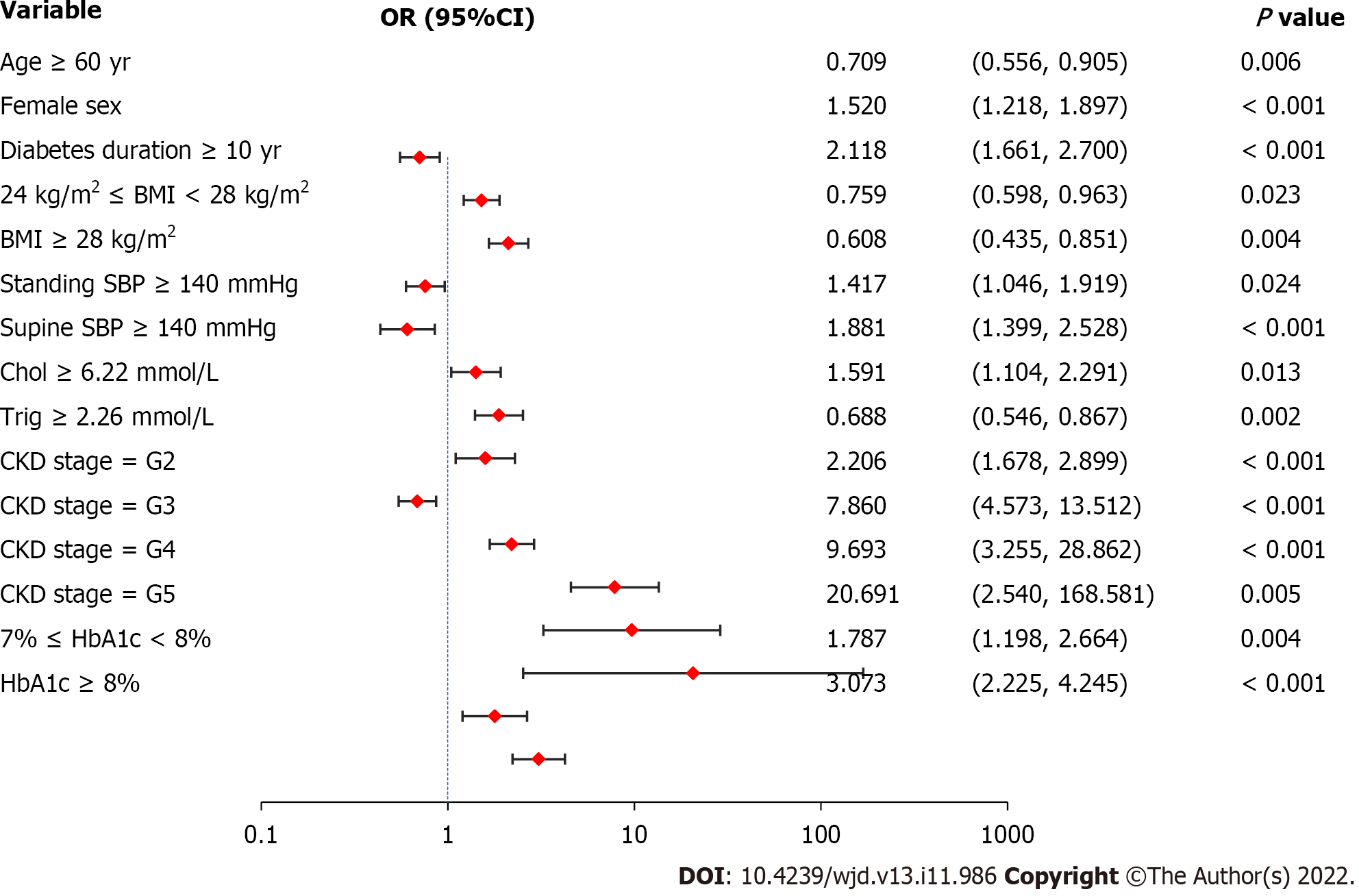
Figure 1 Logistic regression analysis of diabetic retinopathy-related risk factors.
Female sex, diabetes duration ≥ 10 years, standing systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mmHg, supine SBP ≥ 140 mmHg, cholesterol ≥ 6.22 mmol/L, greater severity of chronic kidney disease, and worse control of hemoglobin A 1c are associated with a higher risk of diabetic retinopathy. Values are shown using a base 10, logarithmic scale. DR: Diabetic retinopathy; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval; BMI: Body mass index; SBP: Systolic blood pressure; Chol: Cholesterol; Trig: Triglyceride; CKD: Chronic kidney disease; HbA1c: Glycated hemoglobin A1c.
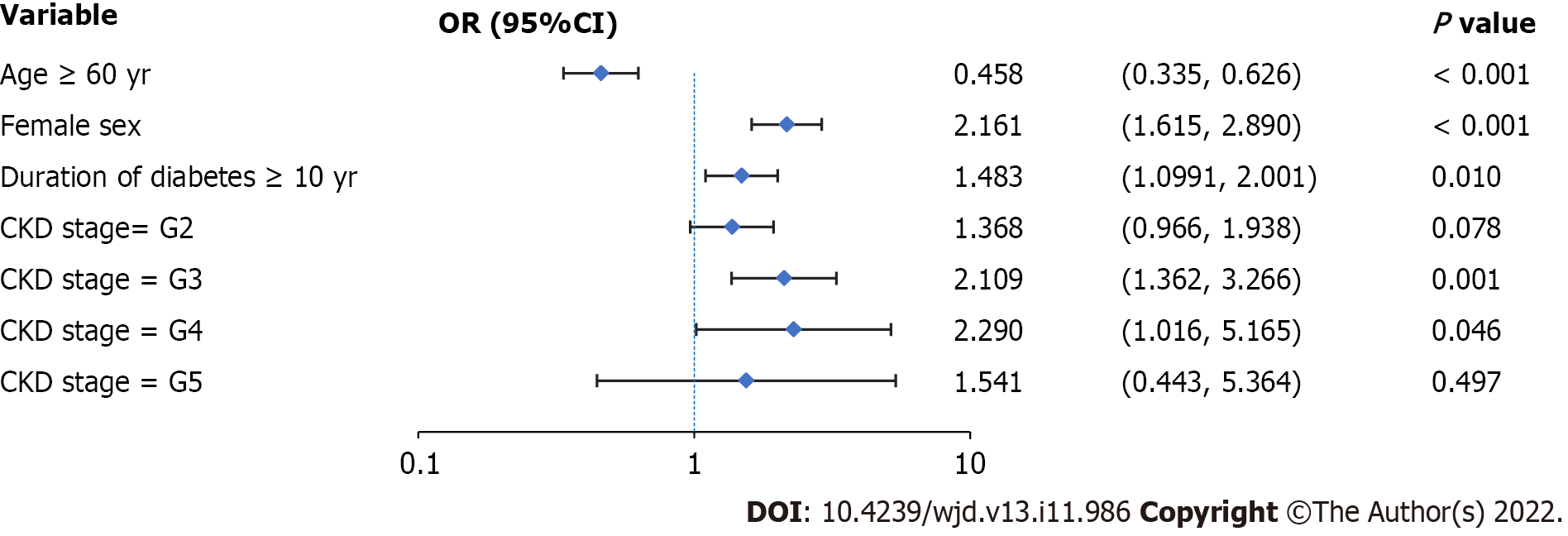
Figure 2 Logistic regression analysis of proliferative diabetic retinopathy-related risk factors.
Female sex, diabetes duration ≥ 10 years, and chronic kidney disease stage G3 or G4 are risk factors for the progression to proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Values are shown using a base 10, logarithmic scale. Abbreviations: PDR: Proliferative diabetic retinopathy; NPDR: Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval; CKD: Chronic kidney disease.
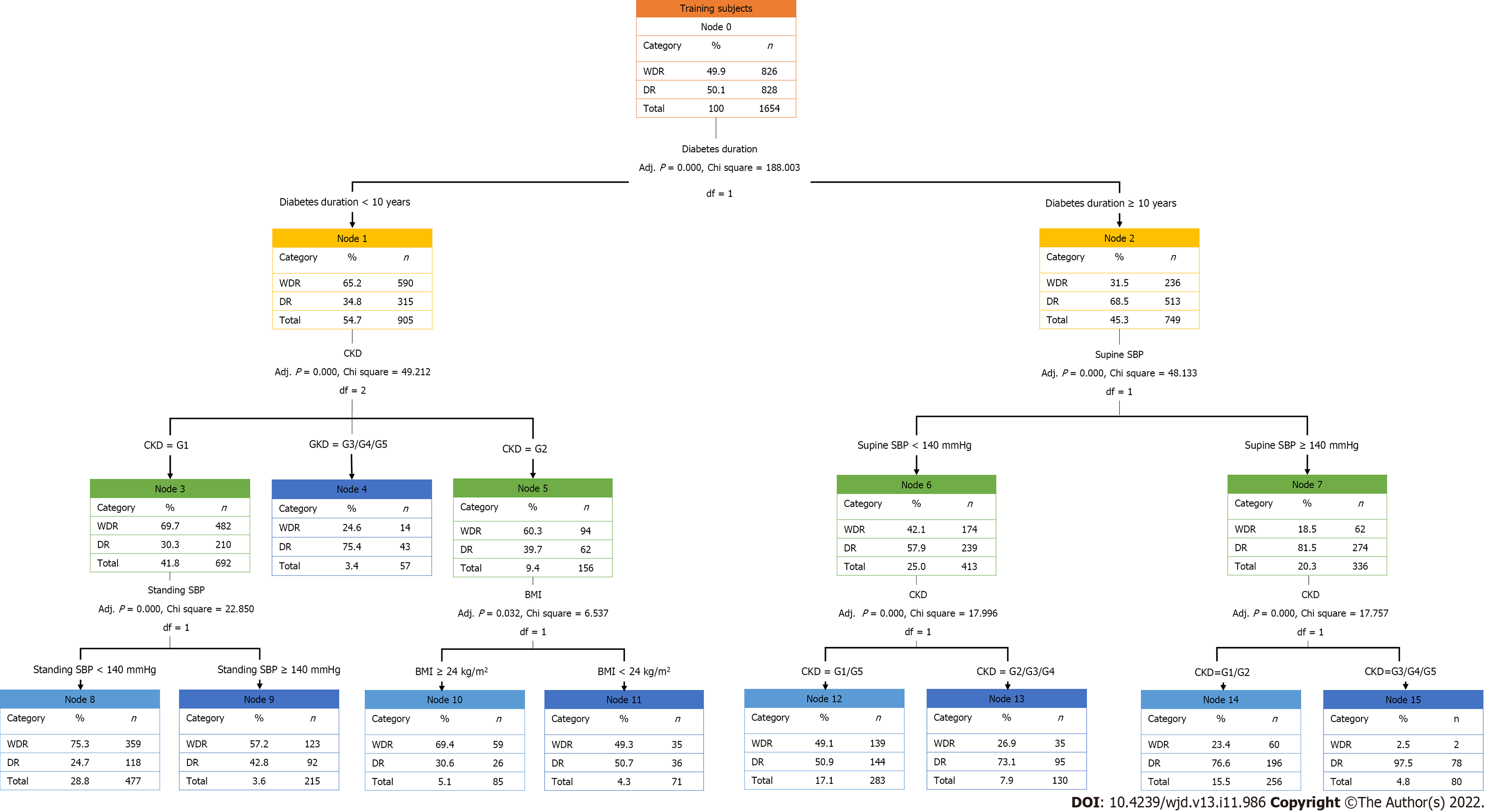
Figure 3 Training dataset of decision tree model for diabetic retinopathy.
Based on the decision tree model constructed in this study, the diabetic retinopathy classification outcomes are obtained by evaluating standing systolic blood pressure (SBP) or body mass index according to the chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage for patients with a diabetes duration < 10 years and the evaluation of CKD stage according to the supine SBP for patients with a diabetes duration ≥ 10 years. WDR: Without diabetic retinopathy; DR: Diabetic retinopathy; CKD: Chronic kidney disease; SBP: Systolic blood pressure; BMI: Body mass index.
- Citation: Zhou YY, Zhou TC, Chen N, Zhou GZ, Zhou HJ, Li XD, Wang JR, Bai CF, Long R, Xiong YX, Yang Y. Risk factor analysis and clinical decision tree model construction for diabetic retinopathy in Western China. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(11): 986-1000
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i11/986.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.986