Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Jul 15, 2021; 12(7): 997-1009
Published online Jul 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i7.997
Published online Jul 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i7.997
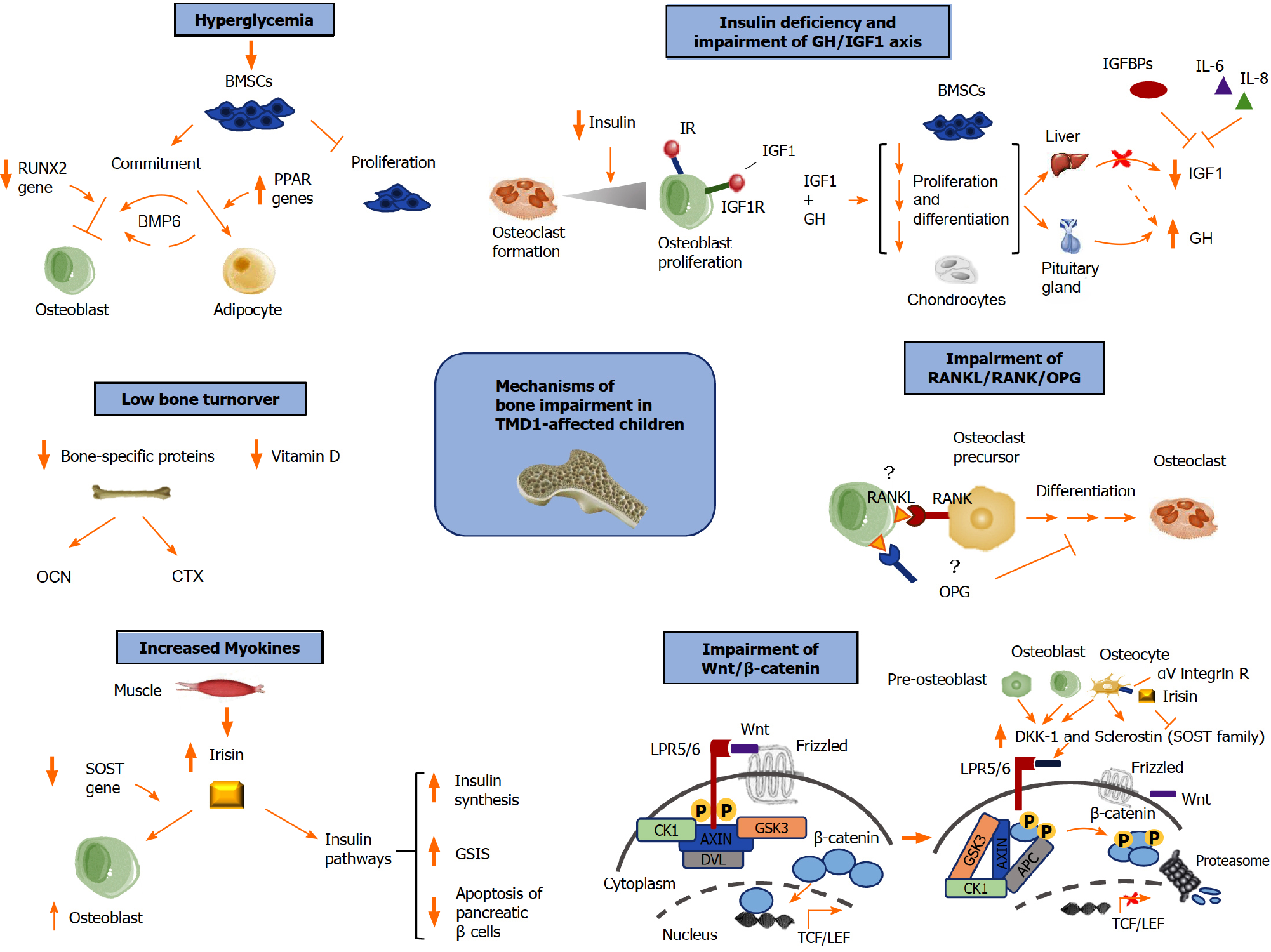
Figure 1 Mechanisms underlying altered bone remodeling in type-1-diabetes.
APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; BMP6: Bone morphogenetic protein-6; BMSCs: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; CK1: Casein kinase I; CTX: C-terminal cross-link of collagen; DKK-1: Dickkopf-1; DVL: Disheveled; GH: Growth hormone; GSIS: Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion; GSK3: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; IR: Insulin receptor; IGF1: Insulin-like growth factor-1; IGF1R: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; IGFBPs: IGF-1 binding proteins; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-8: Interleukin-8; LPR5/6: LDL receptor related protein 5; OCN: Osteocalcin; OPG: Osteoprotegerin; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; RANK: Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B; RANKL: Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand; RUNX2: Related transcription factor 2; SOST: Sclerostin; TCF/LEF: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor.
- Citation: Brunetti G, D'Amato G, De Santis S, Grano M, Faienza MF. Mechanisms of altered bone remodeling in children with type 1 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(7): 997-1009
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i7/997.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i7.997